Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2017 Unit 1 Chemistry KTT 2 - Metals and ionic bonding Solutions Book
2017 Unit 1 Chemistry KTT 2 - Metals and ionic bonding Solutions Book
Uploaded by
Yue WeiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2017 Unit 1 Chemistry KTT 2 - Metals and ionic bonding Solutions Book
2017 Unit 1 Chemistry KTT 2 - Metals and ionic bonding Solutions Book
Uploaded by
Yue WeiCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMISTRY 2017
Unit 1
Key Topic Test 2 – Metals and Ionic Bonding
Recommended writing time*: 45 minutes
Total number of marks available: 50 marks
SOLUTIONS
TSSM 2017 Page 1 of 8
2017 CHEMISTRY KEY TOPIC TEST
SECTION A: Multiple-choice questions (1 mark each)
Question Response
1 A
2 C
3 D
4 E
5 C
6 E
7 C
8 A
9 B
10 D
11 B
12 C
13 E
14 D
15 B
Question 1
Answer: A
Explanation:
All metals are malleable, good conductors of electricity and many have high tensile strength
Question 2
Answer: C
Explanation:
Metals are conductors of electricity in the solid state due to the presence of delocalised electrons,
ionic solids are non-conductors in the solid state as the ions are not free to move.
TSSM 2017 Page 2 of 8
2017 CHEMISTRY KEY TOPIC TEST
Question 3
Answer: D
Explanation:
Metals have delocalised electrons that are free to move forming non-direction bonds which in
turn hold the lattice intact regardless of the direction of the force.
The delocalised electrons are able to move through the lattice structure.
Question 4
Answer: E
Explanation:
From least reactive to most reactive.
Question 5
Answer: C
Explanation:
The smaller carbon atoms fit between the iron atoms and stop layers from sliding past one
another they therefore act as braces.
Question 6
Answer: E
Explanation:
CO acts as a reducing agent which reacts with iron oxide to form iron.
Question 7
Answer: C
Explanation:
The compound formed between X and Y would be XY2, as X forms 2+ cations and Y would
form 1- anions.
TSSM 2017 Page 3 of 8
2017 CHEMISTRY KEY TOPIC TEST
Question 8
Answer: A
Explanation:
Repulsions that occur when like charges align when the lattice is disrupted due to applied force.
Question 9
Answer: B
Explanation:
The charged particles (ions) are fixed in place in the lattice structure and therefore cannot conduct
a current.
Question 10
Answer: D
Explanation:
Al2(SO4)3 forms from Al3+and SO42-
Question 11
Answer: B
Explanation:
Quenching, a metal is heated then cooled quickly.
Question 12
Answer: C
Explanation:
Alloys are generally harder but less malleable.
TSSM 2017 Page 4 of 8
2017 CHEMISTRY KEY TOPIC TEST
Question 13
Answer: E
Explanation:
Ionic solids have a regular three dimensional lattice of alternating Na+ and Cl- ions
Question 14
Answer: D
Explanation:
Transition metals are harder and can lose electrons from either the d or s subshells therefore they
have a greater number of oxidation states and many have catalytic properties
Question 15
Answer: B
Explanation:
Nano-metals have numerous useful properties including excellent electrical conductivity, very
high tensile strength and catalytic behaviour
SECTION B: Short-answer questions
Question 1
a. i. Molten ionic compounds have mobile ions which are able to conduct an electric current but
do not have any mobile charges in the solid state thus they cannot conduct an electric current
in the solid state.
1 mark
ii. MgCl2, is relatively hard, due to strong ionic bonds and stable 3d ionic lattice structure
but will shatter easily when struck with a hammer as the like charges repel when they
align when a force is applied disrupting the lattice.
2 marks
TSSM 2017 Page 5 of 8
2017 CHEMISTRY KEY TOPIC TEST
iii. Al 3+2 O2- 3 = Al2O3
1 mark
b.
i. KCl CaO
4 marks
ii. In KCl the ionic charges are 1+ and 1- respectively whereas in CaO they are 2+
and 2- resulting in a much greater attractive force between the ions in CaO thus
requiring more energy to break the bonds.
1 mark
Total 9 marks
Question 2
a. i. A metal is a pure element with no other element mixed with it whereas an alloy is a
mixture of two or more elements, one of which is a metal,
1mark
ii. The alloy generally is harder, less malleable and a lower melting point and lower
electrical conductivity than the pure metals from which it was made.
b.
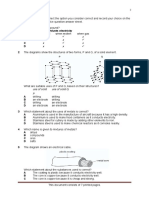
i. The two main types of alloys are substitutional and interstitial.
lead Tin
TSSM 2017 Page 6 of 8
2017 CHEMISTRY KEY TOPIC TEST
iii.
Interstitial- e.g. steel Substitutional-e.g. solder
iv. Interstitial alloys have a metal element which is much larger than the added
element.
The metal element has a much higher percentage than the other element.
Substitutional alloys have atoms which are about the same size and percentage.
2 marks
Total 8 marks
Question 3
i. Cu(I)NO3: copper (I) nitrate
ii. BaSO4: barium sulfate
iii. PbCO3: lead (II) carbonate
iv. Al(OH)3 : aluminium hydroxide
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4 marks
a. Write the chemical formulae for each of the following compounds:
i. Calcium orthophosphate: Ca3(PO4)2
ii. Potassium permanganate: KMnO4
iii. Aluminium sulfate: Al2(SO4)3
iv. Ammonium dichromate: (NH4)2 Cr2O7
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4 marks
TSSM 2017 Page 7 of 8
2017 CHEMISTRY KEY TOPIC TEST
b. State one use of each of the following ionic compounds:
i. NaOH - making soap and alcohols
ii. CaCO3 - building material, glass
iii. Al2O3 - making aluminium
iv. NH4NO3 – fertiliser, explosives
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4 marks
Total 12 marks
Question 4
a. C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
b. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
c. C(s) + CO2(g) → 2CO(g)
d. 3CO(g) + Fe2O3(s) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
e. CaO(s) + SiO2(s) → CaSiO3(s)
1+1+1+2+1=6
Total 6 marks
TSSM 2017 Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- Grade - 10 Term - I - Metals and Non-Metals Questionnaire - 2021-22Document5 pagesGrade - 10 Term - I - Metals and Non-Metals Questionnaire - 2021-22AnilNo ratings yet
- GZB Xii Ws-9 Chemistry D & F Block Elements October Sarita KhokharDocument4 pagesGZB Xii Ws-9 Chemistry D & F Block Elements October Sarita KhokharSaman PanwarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 3 (10)Document6 pagesWorksheet Chapter 3 (10)Satyam DeoraNo ratings yet
- First Term Exam Chemistry Answer KeyDocument9 pagesFirst Term Exam Chemistry Answer KeyRutujaNo ratings yet
- Uppp2 Sem 2 2017Document5 pagesUppp2 Sem 2 2017Loh Wai YeeNo ratings yet
- Quiz (Structures and Properties of Substances) Section A: Multiple-ChoiceDocument3 pagesQuiz (Structures and Properties of Substances) Section A: Multiple-Choice袁愉棋No ratings yet
- chemistry_practice_packet_7_-_units_breakdownDocument10 pageschemistry_practice_packet_7_-_units_breakdownShamit SharifNo ratings yet
- 10chemistry General Trial Test AnsDocument6 pages10chemistry General Trial Test AnsMNo ratings yet
- Exam Chew 1Document7 pagesExam Chew 1ThilagaNo ratings yet
- Etoos S Block PDFDocument12 pagesEtoos S Block PDFvivek kumar0% (1)
- IB Chemistry HL Periodicity Review 1.: (Total 1 Mark)Document5 pagesIB Chemistry HL Periodicity Review 1.: (Total 1 Mark)y. k.No ratings yet
- Important Questions: Exam PracticeDocument3 pagesImportant Questions: Exam PracticeSachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Minjun & Dongha Lesson SheetDocument68 pagesMinjun & Dongha Lesson SheetRicky SaputraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2Document5 pagesChapter 1 & 2Naqash RasheedNo ratings yet
- Wings of Chemistry 2 3 Marks OnlyDocument12 pagesWings of Chemistry 2 3 Marks OnlypearlynNo ratings yet
- D and F Block PYQ FOR 2024 CLASS 12 EXAMS BY Gtctuition For YtDocument34 pagesD and F Block PYQ FOR 2024 CLASS 12 EXAMS BY Gtctuition For YtDr SaabNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Chemistry Notes 2024 CH 8Document35 pages9th Class Chemistry Notes 2024 CH 8Kashi MoaviaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3叶震森No ratings yet
- 2017 Unit 1 Chemistry KTT 2 - Metals and ionic bonding Question BookDocument12 pages2017 Unit 1 Chemistry KTT 2 - Metals and ionic bonding Question BookYue WeiNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry Answers S3Document14 pagesIb Chemistry Answers S3Carlos JesúsNo ratings yet
- PART II: Metals: Unit 3: The Chemistry of Engineening MaterialsDocument72 pagesPART II: Metals: Unit 3: The Chemistry of Engineening MaterialsGlecie RasNo ratings yet
- Cordova Class 8 Solution-12-15Document4 pagesCordova Class 8 Solution-12-15Rashmi MuhalNo ratings yet
- Cbjescco 03Document9 pagesCbjescco 03Krishan LohanNo ratings yet
- 12 - TPP - Transition ElementsDocument3 pages12 - TPP - Transition ElementsSaadia AsgharNo ratings yet
- 9th 8th CHPDocument2 pages9th 8th CHPMuhammad Qadir RafiqueNo ratings yet
- ChemistryXII Metals&NonMetalsDocument16 pagesChemistryXII Metals&NonMetalsCorneliaNo ratings yet
- D-Block ElementDocument15 pagesD-Block ElementFedex WalterNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Element TestDocument2 pagesD and F Block Element TestasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CorrosionDocument2 pagesTutorial CorrosionSana chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet S Block ElementsDocument6 pagesWork Sheet S Block ElementsxxxxNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 Practice WSDocument3 pagesCh-3 Practice WSJuwariyah NafeesNo ratings yet
- Revision III Metals&CurrentDocument4 pagesRevision III Metals&Currentgoodshifa1No ratings yet
- 10 Science Ncert ch3Document10 pages10 Science Ncert ch3Rakshitha SNo ratings yet
- Handouts FilledDocument31 pagesHandouts FilledMeherwaan SayyedNo ratings yet
- Property of Metals 2 MCQ - QsDocument7 pagesProperty of Metals 2 MCQ - QsdawsontangxyNo ratings yet
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonNo ratings yet
- D and F Block ElementsDocument23 pagesD and F Block Elementsvkn2417No ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet Periodic Classification of Elements - 2022-23Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet Periodic Classification of Elements - 2022-23Malolan SriramNo ratings yet
- Sblock NotesDocument22 pagesSblock NotesLaukikNo ratings yet
- CLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 4. Metals and Non-MetalsDocument7 pagesCLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 4. Metals and Non-MetalsSurbhi NayarNo ratings yet
- ch3 1Document14 pagesch3 1stanotbtsNo ratings yet
- Case Study Class 10 Science Metals Non MetalsDocument7 pagesCase Study Class 10 Science Metals Non Metalsaarna4858No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions: ClassDocument11 pagesNcert Solutions: ClassAlok RanjanNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemistry Series Test # 4: Q. 1: Choose The Correct Option.Document3 pages9 Chemistry Series Test # 4: Q. 1: Choose The Correct Option.CosmeriesNo ratings yet
- Klks 9 Test-LatihanDocument6 pagesKlks 9 Test-LatihankrisnuNo ratings yet
- Revision Paper Chem-12, Unit-Viii, 2022-23Document2 pagesRevision Paper Chem-12, Unit-Viii, 2022-23ANUPAM S PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 4Document6 pagesChapter 3 - 4Sureshkumar DevanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQDocument2 pagesChemistry MCQUswa ChNo ratings yet
- Binary Ionic CompoundsDocument26 pagesBinary Ionic CompoundsMaxine de la Torre100% (1)
- X STB Sci1 Chapt8 Part1Document3 pagesX STB Sci1 Chapt8 Part1Dharmesh DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Elements Class XIIDocument6 pagesD and F Block Elements Class XIIShyrestha BarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledSpark HiresNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Pyq-Ans-4. D and F Block ElementsDocument8 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Pyq-Ans-4. D and F Block ElementskrishnaswamyharikaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Bonding SL AnswersDocument48 pagesTopic 4 Bonding SL AnswersŁØNo ratings yet
- E0725a72 Cc6c 4079 9162 8638715cba3b - Metals Non Metals ExerciseDocument10 pagesE0725a72 Cc6c 4079 9162 8638715cba3b - Metals Non Metals Exercisehz4t5mv597No ratings yet
- Your Mistakes Are Proof That You Are TryingDocument10 pagesYour Mistakes Are Proof That You Are TryingAtta ur rafayNo ratings yet
- Freelancers - G10 - Chem - Metals and Non-Metals PDFDocument13 pagesFreelancers - G10 - Chem - Metals and Non-Metals PDFKodati Durga Prasad KodatiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Handout 4 REF #: 004: Structure and BondingDocument4 pagesChemistry Handout 4 REF #: 004: Structure and BondingNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (LDA) NMDocument19 pagesChemical Bonding (LDA) NMkaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Transition and Inner-Transition MetalsFrom EverandInorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Transition and Inner-Transition MetalsA. P. HagenNo ratings yet
- Pt. MMF 15 Juli 2022Document249 pagesPt. MMF 15 Juli 2022Agus Sudiana NurmansyahNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Double Pipe Heat Exchangers PDFDocument16 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Double Pipe Heat Exchangers PDFTrần Công MinhNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Epoxy Primer EP-R-30Document2 pagesTechnical Data Epoxy Primer EP-R-30Sheikh Shoaib100% (1)
- Alkaline Surfactant Polymer in AlbertaDocument35 pagesAlkaline Surfactant Polymer in AlbertaRasesh Saraiya100% (1)
- Igenetics A Mendelian Approach 1St Edition Russell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesIgenetics A Mendelian Approach 1St Edition Russell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFMichaelFletcheroiqr100% (11)
- Azulene and NaphthaleneDocument5 pagesAzulene and NaphthaleneDanNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual: 3G MetricDocument20 pagesTechnical Manual: 3G MetricJosé FerrerNo ratings yet
- A Size Bobbin Cell: Technical DatasheetDocument2 pagesA Size Bobbin Cell: Technical DatasheetdbmNo ratings yet
- AWRI ResearchDocument16 pagesAWRI ResearchChris MidtunNo ratings yet
- Correct Procedure For Flange BoltingDocument7 pagesCorrect Procedure For Flange BoltingAkshay KalraNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Chematur WheaterlyDocument4 pagesNitric Acid Chematur WheaterlyAnonymous 1XHScfCI100% (1)
- Nitrogen CycleDocument12 pagesNitrogen Cycleasa bspcpkNo ratings yet
- Metal-Insulator-Metal CapacitorsDocument16 pagesMetal-Insulator-Metal Capacitorspilotvivek1087No ratings yet
- DIY Etched Bullet Necklaces 5467Document14 pagesDIY Etched Bullet Necklaces 5467Santiago GdsNo ratings yet
- Chem Chapter05 LECDocument112 pagesChem Chapter05 LECsaxman011No ratings yet
- Cu Al Fe PDFDocument4 pagesCu Al Fe PDFreyhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SSC-I (3rd Set)Document5 pagesChemistry SSC-I (3rd Set)Amaan KareemNo ratings yet
- 3 - Biological Molecules - Cie Ial Biology QPDocument16 pages3 - Biological Molecules - Cie Ial Biology QPBoney StephenNo ratings yet
- Kertas 1 Pat 2023Document15 pagesKertas 1 Pat 2023Nazirah binti HarunNo ratings yet
- PIR Catalogue - POLYISOCYANURATEDocument12 pagesPIR Catalogue - POLYISOCYANURATESachin Bansode100% (1)
- 7 Gas Turbine Plant: G. Boxer, Applications of Engineering Thermodynamics © G. Boxer 1979Document2 pages7 Gas Turbine Plant: G. Boxer, Applications of Engineering Thermodynamics © G. Boxer 1979WestNo ratings yet
- G Friends Forensic Toxi SpecialDocument51 pagesG Friends Forensic Toxi SpecialAdam ZaaadNo ratings yet
- Wartsila Tribo PackDocument7 pagesWartsila Tribo Packsuper_seeker100% (1)
- Cambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/02Document20 pagesCambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/02Syed Ashar50% (2)
- Laboratory Chemical ProcedureDocument20 pagesLaboratory Chemical ProcedureRimil GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Solberg: Multistage Liquid/Particulate SeparatorDocument4 pagesSolberg: Multistage Liquid/Particulate SeparatorRUN GONo ratings yet
- Eng Standard F&G SystemsDocument16 pagesEng Standard F&G Systemsytd7524No ratings yet
- IEC 60708 SummaryDocument6 pagesIEC 60708 SummaryAdnan Khan0% (1)
- Commission ChecklistDocument1 pageCommission ChecklistmasreenuNo ratings yet
- REDOX EQUATIONS Under Alkaline Conditions: Chemguide - QuestionsDocument1 pageREDOX EQUATIONS Under Alkaline Conditions: Chemguide - QuestionsmacgyverNo ratings yet