Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sequence and Series
Sequence and Series
Uploaded by
meghasinghgahloth0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesSequence and Series
Sequence and Series
Uploaded by
meghasinghgahlothCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1
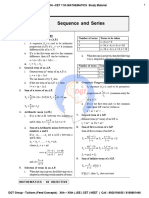
Sequence and Series
1. AP: Arithmetic progression 2. GP: Geometric progression 3. HP: Harmonic progression
4. AGP: Arithmetic geometric progression 5. Method of difference
Arithmetic progression: Common difference between the numbers in a sequence.
M= total number of terms L= last term Sn= Sum of n terms
Nth term of AP: a+ (n-1) d | nth term from last: [m –n+1] Th term from start
Sn = n/2 [2a+ (n-1) d] or Sn= n/2 (a+l)
Properties: If a, b and c are in AP then;
Kb, kc, ka AP k+a, k+b, k+c AP k-a, k-b, k-c AP a/k, b/k, c/k AP
2b = a+c
3 number in AP = a-d, a, a+d c.d= d
4 numbers in AP = a-3d, a-d, a+d, a+3d c.d= 2d
5 numbers in AP = a-2d, a-d a, a+d a+2d c.d= d
Tn= Sn – Sn-1
Tn= An+B then c.d= A and a= A+B
If in an AP Sn=An2 + Bn then c.d= 2A and a=A+B
If Sp= q & Sq= p then Sp+q= -(p+q)
If Sp=Sq then Sp+q=0
If in an AP, the ratio Sm:Sn = m2: n2 then Tm: Tn = (2m-1) : (2n-1)
If the ratio of sum of n terms of 2 different APs is f(n): g(n) then the ratio of their n th term is f(2n-1): g(2n-1)
If pth term of an AP is q and qth term is p, then it’s (p+q)th term is equal to 0 and it’s nth term= p+q–n
If in AP Tmth term = 1/n and Tnth term = 1/m then 1. a=d=1/mn
2. T rTh term = r/mn 3. Tmn = 1
4. Smn = ½ (mn+1)
Arithmetic Mean = Sum of observations/ number of observations
If we insert n A.M’s between a&b then 1. d= b-a/n+1 2. A 1= an+b/n+1 3. An= a+nb/n+1
Sum of n arithmetic mean added= n(a+b)/2
2
GEOMETRIC PROGRESSION: The ratio between the numbers in a series is same.
M= total number of terms L= last term Sn= Sum of n terms
Nth term of GP: arn-1
Sn = a (rn-1)/r-1 [r>1] or Sn= a (1-rn)/1-r [r<1]
Sum of infinite terms in GP= a/1-r, |r|<1 i.e. -1<r<1
Properties:
Kb, kc, ka GP a/k, b/k, c/k GP k/a, k/b, k/c GP
The reciprocal of the no.s in GP are in GP.
If all the terms in Gp are raised to the same power then also the resulting progression will remain in GP
b2 = ac
3 terms in GP a/r, a , ar
4 terms in GP a/r3, a/r, ar , ar3
5 terms in GP a/r2, a/r, a, ar, ar2
If a1, a2, a3………..an are in GP then loga1, loga2, loga3,…………logan are in AP
If xa, xb, xc are in GP then a, b, c are in AP
Geometric mean: product of the numbers raised to the power 1/ number of terms.
GM: (abc) 1/3
If n GM are inserted between a&b then common ratio= (b/a)1/n+1 G 1= a(b/a)1/n+1 Gn= a(b/a)n/n+1
Sum of n geometric mean added= (ab)n/2
Relation b/w AM & GM: If the ratio of AM and GM of a, b is m:n then a/b = m+ √m2 – n2 / m - √m2 – n2
Harmonic progression: If a, b, c AP then 1/a, 1/b, 1/c HP and vice versa
General condition: b= 2ac/a+c
Nth term of HP: 1/ a+ (n-1) d
Sum of n terms of HP is not defined
Harmonic mean: n/1/a1+1/a2+……..+1/an
If n HM’s are inserted between a&b then H1= (n+1)ab/ a+nb or (n+1)ab/ an+b
RELATIONSHIP B/W AM, GM AND HM:
If AM=GM=HM, then no.s are equal
If 3 no.s are in AP, GP& HP then no.s are in equal
AM(greater or equal) GM(greater or equal) HM
AM, GM&HM are always in GP i.e. (GM)2=AM.HM or GM/AM = HM
3
∑1 =n
Arithmetico Geometric progression: a, (a+d)r, (a+2d)r , …………….., (a+(n-1)d)r
2 n-1
∑k= nk
Common difference = d Common ratio= r ∑n= n (n+1)/2
Nth term = (a+(n-1)d)r n-1 2
∑n = n (n+1) (2n+1)/6
Sum of n terms: a/1-r + dr(1-rn-1)/(1-r)2 – (a+(n-1)d)rn/(1-r) ∑n3= n2 (n+1)2/4
Sum of infinite AGP: a/1-r + dr/(1-r)2 r<1 2+4+6+……. +2n= n (n+1)
1+3+5+………. +2n-1= n2
Method of difference:
You might also like
- Sequence and SeriesDocument5 pagesSequence and SeriesS. LakshanyaNo ratings yet
- SNSDocument4 pagesSNShchawla421No ratings yet
- Sequence Finite Sequence Infinite Sequence Series: For ExampleDocument2 pagesSequence Finite Sequence Infinite Sequence Series: For ExampleNaresh bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic ProgressionDocument6 pagesArithmetic ProgressionLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Series Best ApproachDocument55 pagesSequence and Series Best Approachnamangoyal1024No ratings yet
- Best Approach: Sequence & SeriesDocument46 pagesBest Approach: Sequence & SeriesIshhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 - Sequence - SeriesDocument3 pagesChapter 04 - Sequence - SeriesaccesshanifNo ratings yet
- Important Concepts and Formulas Number SeriesDocument6 pagesImportant Concepts and Formulas Number SeriesangjoelaNo ratings yet
- Important Concepts and Formulas - Sequence and SeriesDocument11 pagesImportant Concepts and Formulas - Sequence and SeriesWizuri SiblahNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Key ConceptsDocument3 pagesDefinition:: Key Conceptsvirat gandhiNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression, AP: ElementsDocument6 pagesArithmetic Progression, AP: ElementsJohnray CastroNo ratings yet
- Number Systems: Mathematical FormulasDocument23 pagesNumber Systems: Mathematical FormulasRishi Sawant100% (1)
- CHAP # 6 Sequence and SeriesDocument8 pagesCHAP # 6 Sequence and SeriesNME KALEEMNo ratings yet
- Sequence & Series126Document22 pagesSequence & Series126Sanagavarapu SubrahmanyamNo ratings yet
- ALGEBRA 1 - Wide Screen PDFDocument13 pagesALGEBRA 1 - Wide Screen PDFKrisha Jean MacalinoNo ratings yet
- M A T H S: KautilyaDocument31 pagesM A T H S: KautilyaUtsav AnalNo ratings yet
- Geometric ProgressionDocument8 pagesGeometric ProgressionKaushaljm PatelNo ratings yet
- Topics To Be Covered: Sequences Series Arithmetic Progression Geometric ProgressionDocument22 pagesTopics To Be Covered: Sequences Series Arithmetic Progression Geometric ProgressionJavian CampbellNo ratings yet
- Series: Arithmetic Series Geometric Series Method of DifferenceDocument20 pagesSeries: Arithmetic Series Geometric Series Method of DifferenceCYNo ratings yet
- Gradeup_Short_Notes on Sequence and Series.pdf-47Document6 pagesGradeup_Short_Notes on Sequence and Series.pdf-47poonam8448dNo ratings yet
- Gradeup_Short_Notes on Sequence and Series.pdf-47Document6 pagesGradeup_Short_Notes on Sequence and Series.pdf-47poonam8448dNo ratings yet
- APGPDocument51 pagesAPGPMuskaan AvasthiNo ratings yet
- Sequence 12Document36 pagesSequence 12shivam bhartiNo ratings yet
- SequenceDocument4 pagesSequenceJak RichardNo ratings yet
- Jee Mainsample Chapter Maths 11 Sequences and Series PDFDocument44 pagesJee Mainsample Chapter Maths 11 Sequences and Series PDFAditya JadhavNo ratings yet
- ProgressionsDocument8 pagesProgressionsAayush DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Day 2-Class X-Maths - CHP 5,6,7-Final RevisionDocument42 pagesDay 2-Class X-Maths - CHP 5,6,7-Final Revisionaaryajavia13No ratings yet
- PSDocument156 pagesPSRamakrishnan KannanNo ratings yet
- Classnote 5604e12da1f93Document11 pagesClassnote 5604e12da1f93HarshitShuklaNo ratings yet
- Sequence and SeriesDocument2 pagesSequence and SeriesRININo ratings yet
- Sequence & Series All in OneDocument345 pagesSequence & Series All in Onedivyanshishan3008No ratings yet
- Arithmetic ProgressionDocument3 pagesArithmetic Progressionmudulijagannath1999No ratings yet
- JEE+Crash+course+ +Phase+I+ +Sequence+and+Series+ +vmathDocument121 pagesJEE+Crash+course+ +Phase+I+ +Sequence+and+Series+ +vmathananshi 10c2020No ratings yet
- Seque Ces Series LectureDocument10 pagesSeque Ces Series LectureDhananjayNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: G A (B/a)Document1 pageSequences and Series: G A (B/a)vidyakumari808940No ratings yet
- Sequence and Series - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Document1 pageSequence and Series - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024dushyantsiwach3263No ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression - ImportantDocument2 pagesArithmetic Progression - ImportantMeenaka RajenderanNo ratings yet
- 10seqence&seriesMAT 111 2021-2022 Lecture 10Document29 pages10seqence&seriesMAT 111 2021-2022 Lecture 10tobelgift447No ratings yet
- Arithmetic Progression - Short NotesDocument2 pagesArithmetic Progression - Short Noteschanmol12024No ratings yet
- 11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument7 pages11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrShivek SinghalNo ratings yet
- 7 Sequence & Series Part 2 of 2Document6 pages7 Sequence & Series Part 2 of 2sabhari_ramNo ratings yet
- AP GP FormulaDocument2 pagesAP GP Formulasilvergod.agNo ratings yet
- Sequence & SeriesDocument5 pagesSequence & SeriesgladiatortorqueNo ratings yet
- Unit - 7 Sequence and Series: Important PointsDocument51 pagesUnit - 7 Sequence and Series: Important PointsAteeb TaseerNo ratings yet
- Article On GP Using LatexDocument3 pagesArticle On GP Using LatexPreyanshMitharwalNo ratings yet
- 3 - Maths Bridge Course Material - 23-24 (16 04 23)Document33 pages3 - Maths Bridge Course Material - 23-24 (16 04 23)Sasi SasiNo ratings yet
- QuantsDocument12 pagesQuantsumang goelNo ratings yet
- ProgressionDocument5 pagesProgressionManju SreeNo ratings yet
- Sequence and SeriesDocument31 pagesSequence and SeriesSiddhanth VengaliNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formulas CompleteDocument28 pagesMathematics Formulas CompleteMark Lester LindoNo ratings yet
- Progressions Classnotes-1Document9 pagesProgressions Classnotes-1shhhs6831No ratings yet
- DGT Sequence and SeriesDocument60 pagesDGT Sequence and SeriesRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 0278 MathematicsDocument30 pages0278 MathematicsZarex BorjaNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Geometry: Tests For Special QuadrilateralsDocument5 pagesCo-Ordinate Geometry: Tests For Special QuadrilateralsJane Koay100% (1)
- 11 Progressions Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages11 Progressions Formula Sheets Quizrrshivam tirmanwarNo ratings yet
- Formulae Book PDFDocument8 pagesFormulae Book PDFShaily NainNo ratings yet
- AP GP FinalDocument53 pagesAP GP FinalPratul PrakharNo ratings yet
- SequencesDocument2 pagesSequencesashanidasguptaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Power SeriesDocument2 pagesPower SeriesAbhi DebNo ratings yet
- Sequence & Series Engineering Mathematics.Document38 pagesSequence & Series Engineering Mathematics.Muhammad Aqeel DarNo ratings yet
- 8-Convergence TestDocument16 pages8-Convergence TestAlfez tintoiyaNo ratings yet
- A B C D E F G H I J K L M: Geometric Sequences CodebreakerDocument2 pagesA B C D E F G H I J K L M: Geometric Sequences CodebreakerJohn Angelo Ryan CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Math Revision Notes by STUDY RATEDocument99 pagesMath Revision Notes by STUDY RATEAditya Singh Rathaur100% (1)
- AP Calculus Notes and Homework For Chapter 9: Mr. Surowski)Document35 pagesAP Calculus Notes and Homework For Chapter 9: Mr. Surowski)Reekh TNo ratings yet
- Maths 1Document61 pagesMaths 1Patricia JosephNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Convergence Tests For SeriesDocument2 pagesLecture 14 Convergence Tests For SeriesShresth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Series Summary CompleteDocument3 pagesSeries Summary CompleteFrantz ClermontNo ratings yet
- PP 18Document3 pagesPP 18monu991No ratings yet
- 9 1doneDocument2 pages9 1doneeperlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MAT455 PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 1 MAT455 PDFaleeyakamalNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Sequences: TH TH TH THDocument2 pagesArithmetic Sequences: TH TH TH THAndrei MarcelisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1b - Math148Document17 pagesLesson 1b - Math148Raynard YuNo ratings yet
- Calculus Unit 4Document4 pagesCalculus Unit 4OmegaUserNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter7 PDFtala kholeNo ratings yet
- SumpartDocument1 pageSumpartDario RuysNo ratings yet
- 4.1.power Series PDFDocument8 pages4.1.power Series PDFManasaNo ratings yet
- Power Series: By: Engr. Ferdinand L. MarcosDocument35 pagesPower Series: By: Engr. Ferdinand L. MarcosVince Joseph FabayNo ratings yet
- Infinite Series - Cauchy's Root TestDocument7 pagesInfinite Series - Cauchy's Root TestSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- One Million Digits of Pi On One Page! - (Plus Guides and Information) - Pi DayDocument151 pagesOne Million Digits of Pi On One Page! - (Plus Guides and Information) - Pi DayThomas Desjardins-VachonNo ratings yet
- 16 2 Infinite SeriesDocument13 pages16 2 Infinite SeriesEbookcrazeNo ratings yet
- Math 1432 Notes - Week 12 Some Review From Last WeekDocument11 pagesMath 1432 Notes - Week 12 Some Review From Last WeekKyle BroflovskiNo ratings yet
- Infinite Series Session 23-24: Course: MATH6031 - Calculus I Year: 2015Document42 pagesInfinite Series Session 23-24: Course: MATH6031 - Calculus I Year: 2015bryan chandra100% (1)
- Power Series Representations: David R. JacksonDocument32 pagesPower Series Representations: David R. JacksonSweqZNo ratings yet
- Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesDocument38 pagesTaylor and Maclaurin SeriesAhmad ZaidNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Series Chapter 7 (Text Book) : ECC3001 Dr. Suryani Binti KamarudinDocument37 pagesSequence and Series Chapter 7 (Text Book) : ECC3001 Dr. Suryani Binti Kamarudinnur hashimahNo ratings yet
- 1 Deret BoasDocument40 pages1 Deret BoaskorrynilyaniNo ratings yet
- Calc2 Study Guide (Section 2)Document26 pagesCalc2 Study Guide (Section 2)Gabriela FrederickNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 NotesDocument6 pagesUnit 10 NotesyilmazalyaduruNo ratings yet