Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Matter and composition
Matter and composition
Uploaded by
meghasinghgahlothCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Matter and composition
Matter and composition
Uploaded by
meghasinghgahlothCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Matter and composition
Matter: Anything that occupies space and has mass.
Properties: 1. they are made up of small particles. 2. They have space between them 3. Particles are continuously moving 4. Particles
attract each other
Energy: Capacity to supply heat or to do work
Physical classification:
SOLID LIQUID GAS
Same shape and volume Takes shape of the container but volume is No definite shape and
same volume
Force is strong Force is weak Very weak force
Can’t be compressed Can be compressed Highly compressible
Solids can’t flow Can flow Can flow
High density, BP & MP Low density, BP & MP Very low
KE is min. KE is more than solid Very high KE
Thermal energy is very low Higher than solid Very high thermal energy
Particles vibrate in its fixed Particles slide over one another Particles move freely
position
Crystallin Amorpho
e solid us
Regular Not having
arrangeme regular
nts of arrangeme
particles nts of
particles
True solids Super
cooled
Solid to liquid: meltingsolids
MP is MP
Liq to solid: freezing
sharp depends
Gas to liq: condensation on range of
Liq to gas: vaporization temp.
Anisotropi
Solid to gas: sublimationIsotropic
c in nature
Gas to solid: deposition in nature
PLASMA: Super excited and energetic particles. Occurs when heated at high temp. Produce magnetic and
electric field.
BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDESATION STATE: discovered in 1920. Formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density. Atoms join together
and form super atom. Very low KE and high force and attraction.
BOLING POINT: VAPOUR PRESSURE= ATM PRESSURE MELTING POINT: TEMP. AT WHICH SOLID CHANGES INTO A
LIQUID.
KELVIN SCALE: DEGREE +273 FAHRENHEIT: 9/5*DEGREE+32
NOTE: -40 is the temp. Same at both degree and Fahrenheit. Lowest possible temperature: -273.1 C
ROOM TEMP: 25-27 C NORMAL BODY TEMP. = 37C DENSITY OF ICE IS MORE THAN WATER
LATENT HEAT: Energy absorbed or released by a substance during change in physical state without change in its temp.
L= QUANTITY OF HEAT [Q]/ MASS OF SUBSTANCE [S]
DIFFUSION: Movement of any substance from high conc. To lower conc. Region. It occurs in all directions.
PURE SUBSTANCE: Contains single type of particles. Same in their chemical nature. Matter cannot be separated by any physical process.
TYPES OF PURE SUBSTANCE:
ELEMENT: Simple and basic form of pure substance which cannot be broken into simpler substances by any physical or chemical
method. Made up of only one kind of atom.
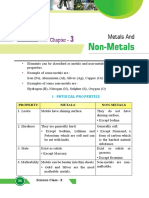
METALS NON METALS
Which have 1,2,3 electron in outermost shell Have 4,5,6,7 electron in outermost shell
Malleable and ductile [gold and silver most ductile] Non malleable and non ductile
Generally solid and hard in nature [except Na, K, Zn, Hg, Na, K, Cs & Ga] Exist in all 3 states
Have luster [except lead] Do not have luster[except Iodine, diamond and graphite]
High MP& BP [except Ga, Hg, Li, Na, K &Cs] Low MP&BP [except diamond and graphite]
2
Sonorous Non-sonorous
Good conductors of heat and electricity [best: silver & poor: lead] Poor conductors of heat and electricity [ except graphite]
Produce basic oxide when dissolved in water Produce acidic oxide when dissolved in water
Form cation and are good reducing agent Form anion and are good oxidizing agent
Have high density [except Na&K] Low density [except diamond]
Non brittle [except Zn] Brittle [except gases]
In vapour state are monoatomic Polyatomic in vapour state
METTALOID: Materials which posses both metal and non metals. Ex: boron, germanium, silicon antimony, arsenic, tellurium and
pollanium.
AMPHOTERIC: Oxides which shows both acidic and basic behaviors to produce salt and water. Ex: ZnO, PbO, Cr2O3, Fe2O3 etc.
Reaction of Metal with Oxygen
Metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides
Whenever sodium or potassium is exposed to air it catches fire. Hence, they are kept in kerosene.
Reaction of Metal with Water
Some metals react with water to form metal hydroxide whereas some of them do not react. Reactivity with water differs from metal to
metal.
Metals like sodium and potassium are highly reactive. They react with water to form alkalis such as sodium hydroxide and potassium
hydroxide. Calcium also reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen. Whereas, magnesium and zinc do not react with
cold water. They form their respective oxides when reacted with hot water. Iron reacts with steam to form magnetic oxides.
Reaction with Dilute Acids
Metals like sodium, potassium, lithium and calcium react vigorously with dilute HCl and H 2SO4 to form their metal salt and hydrogen.
While magnesium, zinc, irons, tin and lead do not react vigorously with acids.
Reaction of Metal with Other Metal
Metals that are more reactive will readily with less reactive metals. More reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its oxides,
chlorides or sulphides.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Reaction of Non Metal with Oxygen Reaction of Non metals with bases
Non metals + O2 Non metallic oxide / Acidic oxide Form salts when reacted with bases
Reaction of Non Metal with Water
Do not react with water to produce h2 gas because they cannot reduce hydrogen ions of water to h2 gas. Except highly reactive non
metals.
Reaction with Dilute Acids
Do not react with dil. acids because they act as electron acceptor and can’t supply to H+ ions of acid to reduce them to hydrogen acid. But
on heating form oxides or salt with conc. Acids.
Reactivity of Non metal
3
As we go down the reactivity of non metal decreases due to the increase on the number of shells and tendency to lose electrons. Also the
nuclear force of attraction decreases.
IONIC BONDS: Are formed due to the transfer of electrons from metals to non-metals. Ions with opposite charges attract each other to
form ionic bonds.
Properties: 1. Solid compounds due to strong force of attraction. 2. Compounds are brittle 3. Compounds have high MP&BP
4. Compounds dissolve in water 5. Insoluble in organic solvents 6. Do not conduct electricity in solid state
ORE: Impurities from which metal is extracted.
CALCINATION: Carbonate ores heated in absence of oxygen. CO2 gas will be released.
ROASTING: Sulphide ores heated in presence of oxygen. SO2 gas will be released
ALLOYS: uniform mixture of 2 or more metals and non-metals.
TYPES OF ALLOYS:
1. FERROUS ALLOYES: Alloys in which ion is present as one of its constituents.
Example: Manganese steel [Fe- 86%, Mn- 13% & C- 1%]
Nickel steel [Fe- 96-97% & Ni- 3-4%] Stainless steel- Iron + Nickel + Chromium
2. NON-FERROS ALLOYES: Alloys which doesn’t contain iron.
Example: Brass [Cu- 80% and Zn- 20%] Bronze [Cu-88% and Sn-12%] Solder [Pb- 50% and Sn-50%]
3. AMALGAM: Contains mercury as one of its constituents.
Example: Zn amalgam [Zn (Hg)], Sodium amalgam [Na (Hg)]
CORROSION: Metals het corroded when exposed o moist air for long period of time
RUSTING: 4Fe + 3O2 + 6H2O Fe2O3 + 2Fe (OH) 3
FORMULA OF RUSTING: Fe2O3. XH2O
COMPOUMDS: Pure substances that are composed of 2 or more different elements in fixed proportion by mass.
Organic: which are obtained from living sources? Inorganic: obtained from non-living sources.
Properties: Compounds are homogenous in nature.
Compounds are formed by the chemical reaction between 2 elements. Constituents cannot be separated by physical or mechanical
means.
They have fixed MP&BP.
MIXTURE: Combination of more than one kind of pure substances in any ratio. Constituents can be separated by physical methods.
HOMOGENOUS HETEROGENOUS
Uniform composition Non-uniform composition
Single phase and no physical separation 2 or more phases and physical separation is possible.
Size of particle is small Size of particle is very large and can be visible by naked eye
SOLUTION COLLOIDS SUSPENSION
Homogenous Heterogeneous Heterogeneous
Has a solute and solvent Has solute and dispersed medium[solution] Has suspended particles and medium
Very small in size Particle size is 10^-9 m to 10^-7m Large in size
Particles can be separated by filtration Cannot be separated Cannot be separated
Transparent Translucent Opaque
Ex: sugar solution in water Ex: milk, muddy water Ex: sane water, milk of manganese
Tyndall effect can be observed when a fine beam of light enters a room through a small hole. This happens due to scattering of light by
the particles of dust and smoke in the air.
CONCENTATION OF A SOLUTION:
MASS BY MASS PERCENT: Mass of solute / mass of solvent * 100
MASS BY VOLUME PERCENT: Mass of solute / volume of solution * 100
You might also like
- Grade Ten: Science Exam NotesDocument10 pagesGrade Ten: Science Exam NotesLuna90% (21)
- Chapter - 3 Metals - and - Non - Metals NewDocument14 pagesChapter - 3 Metals - and - Non - Metals NewRahul IngleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Preliminary Exam NotesDocument25 pagesChemistry: Preliminary Exam NotesHussainMohammedNo ratings yet
- Uydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4Document6 pagesUydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4varshatagade126No ratings yet
- 3 Metals and Non-Metals 1Document20 pages3 Metals and Non-Metals 1Shivam TiwariNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document32 pagesCH 3Prachi RaniNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument22 pagesThe Periodic Table21605No ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument28 pagesMetals and Non MetalsALEENANo ratings yet
- Element Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesElement Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsInsha Hasan 10DNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument29 pagesMetals and Non Metalsayushmallick07No ratings yet
- Science: (Chemistry)Document22 pagesScience: (Chemistry)Isaiah JohnsonNo ratings yet
- CLASS IX - CHEMISTRY CH2. NOTESDocument27 pagesCLASS IX - CHEMISTRY CH2. NOTESkhandelwalraghav9002No ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument72 pagesMetals and Non MetalssimoneNo ratings yet
- Ch3 MetalsDocument6 pagesCh3 MetalsVibha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals N 1Document8 pagesMetals and Non Metals N 1rincyNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument17 pagesClassification of MatterAshmyra ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes-Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesChemistry Notes-Metals and Non MetalsKISHORE ADITYA DHINESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23Document37 pagesMetals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406100% (1)
- Chapter 16 - Periodic TableDocument3 pagesChapter 16 - Periodic TableKayla WNo ratings yet
- Chem PrintsDocument18 pagesChem Printsanayaa agarwalNo ratings yet
- Bonding & Structure of Matter. Note 3Document19 pagesBonding & Structure of Matter. Note 3shadowsenpai98No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument9 pagesPeriodic TableXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Science Chapter 6Document10 pagesForm 1 Science Chapter 6Koo SengleeNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Metal & Non-Metals Lecture SlidesDocument25 pagesPadhle 10th - Metal & Non-Metals Lecture SlidesBitan DasNo ratings yet
- Che 513 Introduction To Polymer EngineeringDocument19 pagesChe 513 Introduction To Polymer EngineeringHappyNo ratings yet
- GCSE ChemistryDocument22 pagesGCSE ChemistryAmeerul HazeeqNo ratings yet
- C3 Elements and CompoundsDocument81 pagesC3 Elements and CompoundskarenelizabethjamiNo ratings yet
- Materials Metals and Non-MetalsDocument5 pagesMaterials Metals and Non-Metalssidhantm823No ratings yet
- S Block (Landscape)Document8 pagesS Block (Landscape)Drastic Pranksters Inc.No ratings yet
- Classifying MatterDocument53 pagesClassifying MatterTanya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Revision of Matter and MaterialsDocument29 pagesRevision of Matter and Materialsrapolailesego3No ratings yet
- Period IcDocument72 pagesPeriod Icmasterupsi2014No ratings yet
- Comparison of Physical and Chemical Properties of Metals and Non - MetalsDocument3 pagesComparison of Physical and Chemical Properties of Metals and Non - MetalsSWATINo ratings yet
- Solid State - PLPN MhtCetDocument42 pagesSolid State - PLPN MhtCetsiddheshmundlik6No ratings yet
- Metalic Elements and PropertiesDocument5 pagesMetalic Elements and PropertiesM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- Matter and SubstancesDocument32 pagesMatter and SubstancesnorazlanwahabNo ratings yet
- M&NM-TABLE - Phy and Chem PropDocument3 pagesM&NM-TABLE - Phy and Chem PropanjanaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and PeriodicityDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and PeriodicityYash BhattNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument49 pagesMATTERHakdog100% (1)
- MATTERDocument49 pagesMATTERHakdogNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Metals NonmetalsDocument7 pages9 Science Metals NonmetalsAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument12 pagesElements Compounds and MixturesMarie LopesNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure?Document6 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure?kanusoni0835No ratings yet
- Metal, Non-metal and MetalloidDocument32 pagesMetal, Non-metal and Metalloidinter16rungradaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument51 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsSubir BiswasNo ratings yet
- Notes - Metals Ad Non-Metals - C-XDocument8 pagesNotes - Metals Ad Non-Metals - C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Topic: Elements, Compounds and MixturesDocument2 pagesChemistry Topic: Elements, Compounds and MixturesamandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 140108061342 Phpapp01Document32 pagesChapter4 140108061342 Phpapp01Nitya DewiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- 3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals ChemDocument40 pages3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals Chemgourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument8 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesMohita RastogiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals Revision NotesDocument22 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals Revision Notesrohan thakurNo ratings yet
- 8 Science Metals and Non Metals Notes VLDocument11 pages8 Science Metals and Non Metals Notes VLShravani BogarNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Earth: Chemistry NotesDocument14 pagesThe Chemical Earth: Chemistry NotesClayton FengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document58 pagesChapter 12maysunNo ratings yet
- Matter and EnergyDocument16 pagesMatter and EnergyBiancaQuitasolNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Chemistry Week 4 5 HandoutDocument4 pagesEnhanced Chemistry Week 4 5 HandoutMelissa Jean BayobayNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals Notes Provided by TeacherDocument7 pagesMetals and Non-Metals Notes Provided by TeacherAdeeba Raheel QureshiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsDocument15 pagesChemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsBhavesh BhaveshNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Thermodynamic and Heat TransferDocument26 pagesThermodynamic and Heat Transfernhanhuynhhiv2003No ratings yet
- LaserssemDocument24 pagesLaserssemks7580713No ratings yet
- Cengel의 기본 열역학 솔루션 3장Document74 pagesCengel의 기본 열역학 솔루션 3장here80002No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition - Bergman, Lavine, Incropera, DeWitt (1) - p0009Document1 pageFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition - Bergman, Lavine, Incropera, DeWitt (1) - p0009CladyNo ratings yet
- UNIT2 Interference DiffractionDocument57 pagesUNIT2 Interference Diffractionfunkpatel123No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer For Fins (Or Extended Surfaces) Handout Table 3.4 Fin Temperature Distribution, Table 3.5 Fin EfficiencyDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer For Fins (Or Extended Surfaces) Handout Table 3.4 Fin Temperature Distribution, Table 3.5 Fin Efficiencypratik patelNo ratings yet
- L2-Heat Conduction Equation in Rectangular-Cylinderical & Spherical CoordinatesDocument19 pagesL2-Heat Conduction Equation in Rectangular-Cylinderical & Spherical CoordinatesskNo ratings yet
- Atmoic Structure 11thDocument33 pagesAtmoic Structure 11thiitianwasimNo ratings yet
- Intregration PT 2Document4 pagesIntregration PT 2Augustin LouisNo ratings yet
- Gas Law HomeworkDocument6 pagesGas Law Homeworkneo cultureNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Pt. 2Document22 pagesKinematics Pt. 2Eloisa Ann FilladoNo ratings yet
- Dissertation TenzerDocument139 pagesDissertation TenzerfabioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 6th Edition Tro Test BankDocument14 pagesChemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 6th Edition Tro Test Bankbeyradicantdays100% (36)
- W - ! ObjectivesDocument1 pageW - ! ObjectivesmenksterNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 3Document70 pagesLecture Notes 3joshuaNo ratings yet
- Jsu Fizik Trial SPM Form 5Document12 pagesJsu Fizik Trial SPM Form 5Ika EikocarolNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International AS Physics: Interference & Stationary WavesDocument30 pagesEdexcel International AS Physics: Interference & Stationary WavesAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Calculated MovesDocument75 pagesChapter 7 Calculated MovesChryscha Jhae Nulud NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- TEG Regeneration PackageDocument1 pageTEG Regeneration Packageyadav yadavNo ratings yet
- Waves Mcq's Set IIDocument4 pagesWaves Mcq's Set IIFida Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Alcorcon Engineering Review Center: I. Machine FoundationDocument5 pagesAlcorcon Engineering Review Center: I. Machine FoundationReinzo GallegoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (Part 1.1) - WEEK 1Document20 pagesCHAPTER 1 (Part 1.1) - WEEK 1Aliaa AkbarNo ratings yet
- Fiziks: Second Law of Thermodynamics and EntropyDocument34 pagesFiziks: Second Law of Thermodynamics and EntropySURAJ PRATAP SINGHNo ratings yet
- List of FormulasDocument1 pageList of FormulasKevin ElevenNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Phenomena in Concentrating Solar Power SystemsDocument191 pagesHeat Transfer Phenomena in Concentrating Solar Power SystemsOmosekeji TimilehinNo ratings yet
- Heavy-Ion Beam-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species and Redox ReactionsDocument12 pagesHeavy-Ion Beam-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species and Redox ReactionseNo ratings yet
- Quantum ChemistryDocument71 pagesQuantum Chemistrybinseung skzNo ratings yet
- Problems in Heat ExchangersDocument4 pagesProblems in Heat ExchangersNkoshiEpaphrasShoopalaNo ratings yet
- Nondestructive Examination (NDE) Technology and Codes Student Manual Introduction To Ultrasonic ExaminationDocument78 pagesNondestructive Examination (NDE) Technology and Codes Student Manual Introduction To Ultrasonic ExaminationRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Experimental Verification of Einstein'S Photoelectric EquationDocument11 pagesExperimental Verification of Einstein'S Photoelectric EquationNayana MDNo ratings yet