Professional Documents
Culture Documents
06 Science Ch10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
06 Science Ch10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
Uploaded by
gosim28126Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Iso 2178 - 2016 - PDFDocument1 pageIso 2178 - 2016 - PDFbala0% (1)
- Hydrogels and Biodegradable Polymers For Bioapplications by Raphael M. Ottenbrite, Samuel J. Huang, and Kinam Park (Eds.)Document271 pagesHydrogels and Biodegradable Polymers For Bioapplications by Raphael M. Ottenbrite, Samuel J. Huang, and Kinam Park (Eds.)LA100% (1)
- 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances NotesDocument2 pages10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Notesprem wakodeNo ratings yet
- Motion and Measurement of DistancesDocument3 pagesMotion and Measurement of DistancescharliecharliestoryNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Measurement & Motion - NotesDocument4 pagesCh-11 Measurement & Motion - NoteskanzahshafeerNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 3Document3 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 3GHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- L-10 - Motion and Measurement of Distances - Part 2Document11 pagesL-10 - Motion and Measurement of Distances - Part 2Chaitra KamuriNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document27 pagesCH 1Bhavik NerkarNo ratings yet
- kinematics 3Document4 pageskinematics 3chaitanya.palutlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 Motion and Time: He Action or Process of Moving or Being MovedDocument1 pageChapter - 13 Motion and Time: He Action or Process of Moving or Being MovedPrabhakar BharatamNo ratings yet
- 7TH HOMEWORKNotes.1702534342Document2 pages7TH HOMEWORKNotes.1702534342hetal.patil7511No ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line and Motion PrudeDocument83 pagesMotion in A Straight Line and Motion PrudeTanujNo ratings yet
- CH 10 MotionDocument4 pagesCH 10 MotionWAZ CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Motion and Measurement of Distances-Notebook WorkDocument7 pagesMotion and Measurement of Distances-Notebook WorkShreya GuptaNo ratings yet
- FSC115 KinematicsDocument68 pagesFSC115 KinematicsOluwagbotemi AmosunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances (CBSE Class 6 Science) notesDocument2 pagesChapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances (CBSE Class 6 Science) notesDivayam SharmaNo ratings yet
- 6 ThmathsDocument3 pages6 Thmathslearn4chatgptNo ratings yet
- Future Classes Is A Part of Iqra Coaching Institute (ICI)Document5 pagesFuture Classes Is A Part of Iqra Coaching Institute (ICI)Mustafa ImranNo ratings yet
- Motion and Types of MotionDocument12 pagesMotion and Types of MotionRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- MotionsDocument4 pagesMotionschandanchiranthcr12No ratings yet
- Motion in Straight Line-Neet-Short-Notes - pdf-50Document8 pagesMotion in Straight Line-Neet-Short-Notes - pdf-50Sanaur Talukdar100% (1)
- MotionDocument19 pagesMotionRacine CariahNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument13 pagesClass NotesAbhit Rao RaiNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument8 pagesMotion and TimeALLURI DEDEEPYA LAKSHYANo ratings yet
- Complete General Science Notes by Anuj JindalDocument141 pagesComplete General Science Notes by Anuj JindalDigvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Motion Chapter NotesDocument45 pagesMotion Chapter Notess.anoura07No ratings yet
- IX PHY Motion NotesDocument10 pagesIX PHY Motion NotesFaraz khanNo ratings yet
- IX PHY Motion NotesDocument10 pagesIX PHY Motion NotesFaraz khanNo ratings yet
- Class-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THDocument11 pagesClass-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THBhav GrewalNo ratings yet
- Motion and Measurement of DistancesDocument38 pagesMotion and Measurement of DistancesShiney KoshyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document7 pagesChapter 13Pta PNo ratings yet
- Motion and Measurement of DistancesDocument7 pagesMotion and Measurement of DistancesGovind ChhawsariaNo ratings yet
- VI-10-Motion and Measurement of DistancesDocument13 pagesVI-10-Motion and Measurement of DistancesAnnAmmusNo ratings yet
- Experimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesStephanie AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet#2 - Science - Class 9Document5 pagesWorksheet#2 - Science - Class 9MugdhaNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument5 pagesDynamicsAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument1 pageMotionyogesh joshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document9 pagesChapter 10Abhinaba PaulNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument4 pagesMotionMadona FahemNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 MYP4 Phy U1 Resource Part II On M&M-02 MayDocument34 pages2023-24 MYP4 Phy U1 Resource Part II On M&M-02 Maytushant.avudurthiNo ratings yet
- Motion Notes Part 1Document2 pagesMotion Notes Part 1Perajothi PalanirajaNo ratings yet
- MOTIONDocument36 pagesMOTIONRajendra RathNo ratings yet
- Types of Motion 2Document4 pagesTypes of Motion 2reduandcNo ratings yet
- 422 Topper 21 110 6 4 57 Motion Up201506181308 1434613126 8189Document13 pages422 Topper 21 110 6 4 57 Motion Up201506181308 1434613126 8189Rupali Nikhare100% (1)
- Motion In A Straight Line Notes CLASS 11Document6 pagesMotion In A Straight Line Notes CLASS 11sussyacc123frNo ratings yet
- MOTIONDocument1 pageMOTIONSantoshPathakNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 emDocument47 pagesUnit 4 embhaskarraj1714No ratings yet
- Definitions XI StandardDocument22 pagesDefinitions XI StandardFredrickNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 7 Note (2) - 1Document2 pagesPhysics Grade 7 Note (2) - 1Melkamu YigzawNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Lecture 1Document18 pagesKinematics Lecture 1aryanNo ratings yet
- Motion (Final TTB) 1-42Document42 pagesMotion (Final TTB) 1-42Anisha PanditNo ratings yet
- Measurement and MotionDocument6 pagesMeasurement and MotionbittuchintuNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion and Torque3Document34 pagesRotational Motion and Torque3Odtülü FizikçiNo ratings yet
- Types of MotionDocument4 pagesTypes of MotionCeasar Epsilonian MundalaNo ratings yet
- Aees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 MotionDocument5 pagesAees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 Motionseenu nadarajanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Second Quarter LecturesDocument10 pagesPhysical Science Second Quarter LecturesJohn Patrick De CastroNo ratings yet
- Motion.IX.NotesDocument10 pagesMotion.IX.NotesParveen NagiNo ratings yet
- Mech 2 Module 1 Unit 2 (Motion of A Particle)Document10 pagesMech 2 Module 1 Unit 2 (Motion of A Particle)Zamantha DomingoNo ratings yet
- Motion - Short NotesDocument2 pagesMotion - Short Notesalok.coding123No ratings yet
- Group 5 Control EngineeringDocument62 pagesGroup 5 Control Engineeringlittlesilver0810No ratings yet
- The Future of the Impossible: The Physics and Ethics of Time TravelFrom EverandThe Future of the Impossible: The Physics and Ethics of Time TravelNo ratings yet
- Tips Writing Exam Good SaqDocument1 pageTips Writing Exam Good SaqGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- REG ETA-IMG-038 Assessing A SIMGs Comparability To An ANZ Trained Surgical Specialist PDFDocument14 pagesREG ETA-IMG-038 Assessing A SIMGs Comparability To An ANZ Trained Surgical Specialist PDFGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Math Mastery Online Series: Group C Lesson 1 - Answer KeyDocument1 pageMath Mastery Online Series: Group C Lesson 1 - Answer KeyGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Plastic Surgery ResultDocument10 pagesPlastic Surgery ResultGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- National and Official Symbols of IndiaDocument4 pagesNational and Official Symbols of IndiaGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Office-Holders in Government of India PDFDocument6 pagesOffice-Holders in Government of India PDFGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Swine Flu: Bala Vinoth, D Suresh KumarDocument4 pagesSwine Flu: Bala Vinoth, D Suresh KumarGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- List of Salonag and History of Famus Freedom Fighters-1Document11 pagesList of Salonag and History of Famus Freedom Fighters-1GHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- List of God Vehicles & ObjectsDocument15 pagesList of God Vehicles & ObjectsGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Flu Vaccine For ColdDocument3 pagesFlu Vaccine For ColdGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- 5422160319Document308 pages5422160319MadhaviNo ratings yet
- Thesis Budaya OrganisasiDocument5 pagesThesis Budaya Organisasigbrgvvfr100% (2)
- PW15PHDocument4 pagesPW15PHShivenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29: Curl, Divergence and FluxDocument2 pagesLecture 29: Curl, Divergence and FluxKen LimoNo ratings yet
- Design Basis Report NewDocument29 pagesDesign Basis Report Newrpdharshan04No ratings yet
- Essay Questions Lesson 3: AnswerDocument2 pagesEssay Questions Lesson 3: AnswerDanny ClintonNo ratings yet
- 5 Sem Lab BSC Programs - C++Document19 pages5 Sem Lab BSC Programs - C++LohithokNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers PROBDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers PROBSivagami Saminathan100% (1)
- SC ST Fund InformationDocument6 pagesSC ST Fund InformationDevunoor GpNo ratings yet
- DRAWING WITH LIGHT THE PENCIL OF NATURET - Thesis PDFDocument233 pagesDRAWING WITH LIGHT THE PENCIL OF NATURET - Thesis PDFVinit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sectorial Planning VS Integrated PlanningDocument3 pagesSectorial Planning VS Integrated PlanningMuhammad IDREES KHANNo ratings yet
- How To Audit Fmeas Using Quality ObjectivesDocument41 pagesHow To Audit Fmeas Using Quality ObjectivesAmir KhakzadNo ratings yet
- Eelectron Solutions and MarketsDocument36 pagesEelectron Solutions and MarketsEngineer AccasNo ratings yet
- Study Guide:: Ricks P. Ortiz Principles of Soil Science - DedeDocument4 pagesStudy Guide:: Ricks P. Ortiz Principles of Soil Science - DedeRicks P. OrtizNo ratings yet
- San Pedro CollegeDocument3 pagesSan Pedro CollegeMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- CALL For FDP Proposals 2019-20Document12 pagesCALL For FDP Proposals 2019-20SHIVAM TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Anish Bhandari.22015997.FE5056, Problem Solving Methods and AnalysisDocument20 pagesAnish Bhandari.22015997.FE5056, Problem Solving Methods and AnalysisAnish bhandariNo ratings yet
- Ilford Pan 100 y 400 FilmDocument9 pagesIlford Pan 100 y 400 FilmJohann Walter Carpio AcurioNo ratings yet
- MulugetaDocument13 pagesMulugetaMilkias MenaNo ratings yet
- V2k (Voice To Skull: Download Free PDFDocument43 pagesV2k (Voice To Skull: Download Free PDFLazlo Secret0% (1)
- Manufacturing and Process Optimization of Porous Rice Straw BoardDocument10 pagesManufacturing and Process Optimization of Porous Rice Straw BoardAmit Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Conceptual Framework of Mathematics From K 3Document34 pagesLesson 1 Conceptual Framework of Mathematics From K 3Godwin Jerome Reyes100% (2)
- Mesl Set 1Document8 pagesMesl Set 1RENE JOSHUA PECASONo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument14 pages4 PDFMANo ratings yet
- New Hello 3rd Year Unit 1 - 2022Document50 pagesNew Hello 3rd Year Unit 1 - 2022essamwahbaNo ratings yet
- Self-Awareness and Self - Management: Dare To Dream, Dare To Be!Document7 pagesSelf-Awareness and Self - Management: Dare To Dream, Dare To Be!nan nan100% (3)
- IB 2 Mechanics MSDocument18 pagesIB 2 Mechanics MSleesha.sahaNo ratings yet
- Overlight - Extra #2 - The Leviathan Grand (February 2020)Document2 pagesOverlight - Extra #2 - The Leviathan Grand (February 2020)DeeAnaNo ratings yet
06 Science Ch10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
06 Science Ch10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
Uploaded by
gosim28126Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
06 Science Ch10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
06 Science Ch10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
Uploaded by
gosim28126Copyright:
Available Formats
www.ncrtsolutions.
in NCR
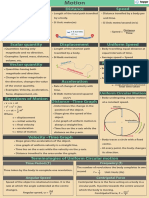
CHAPTER – 10
MOTION AND MEASUREMENT OF DISTANCES
• Different modes of transport are used to go from one place to another.
• In ancient times, people used length of a foot, the width of a finger, the distance of a step
as units of measurement. This caused confusion and a need to develop a uniform system
of measurement arose.
• Now, we use International System of Unit ( SI unit). This is accepted all over the world.
• Metre is the unit of length in SI unit.
• Motion in a straight line is called rectilinear motion.
• In circular motion an object moves such that its distance from a fixed point remains the
same.
• Motion that repeats itself after some period of time, is called periodic motion.
• Measurement: The comparison of an unkown quantity with some known quantity of the
same kind. Measurement of an object consists of :
The unit of measurement.
The number of units the object measures.
• Conventional Methods of Measurement: Conventsinal measurements have only been
approximate measurement. Differ from person to person. Lack precision.
(i) Handspan: Length between the tip of thumb and little finger.
(ii) Cubit: Length between the tip of middle finger and elbo.
(iii) Arm length: Length from shoulder to the tip of middle finger.
(iv) Footstep: It is the distance covered by a step.
• Standard units of Measurement: It is a unit to measure any quantity completely and
uniformly. Standard units for measuring, length-metre, mass-kilogram, time-second.
• Motion: When the position of a body does not change with the passage of time, the body
is said to be at rest. When the position of a body changes with the passage of time, the
body is said to be in motion.
Types of motion:
(a) Linear motion: Linear motion are further classified into two:
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Material Downloaded From http://www.ncrtsolutions.in
www.ncrtsolutions.in NCR
(i) Rectilinear Motion: Object moves from one position to another along a
straight line. Example: group of ants moving in a line.
(ii) Curvilinear Motion: Object moving alogn a curved lines. Example: a car
moving along a curved road.
(b) Random Motion: When object moves from one position to another and changes
direction in an irregular manner. Example: butterfly, flies randomly in garden.
(c) Circular Motion: Object moves in a circular manner in relation to its own axis or
around a fixed centre. Object remains at the same distance from a fixed point which is
the centre of the path of the motion. Two types of circular motion:
(i) Revolution: Object moves as a whole around a fixed centre. Example: earth
revolving around the sun in a definite orbit.
(ii) Rotation: Object moves in a circular path in relation to its own fixed axis.
Example: blades of a moving fan, windmill, etc.
(d) Vibratory Motion: Object moves to and fro very fast. Example: strings of a guitar
when plucked.
(e) Periodic Motion: Object oscillates to and fro along the same path again and again and
with the same speed. Time taken by an object to complete one oscillation is same, no
matter how many oscillations the object takes. Example: heartbeat, pendulum of a
clock.
(f) Non-periodic Motion: Object do not repeat motion at regular intervals of time.
(g) Uniform Motion: When the body covers equal distance in equal time interval.
(h) Non-uniform Motion: Motion in which the body covers unequal distance in equal
inter of time
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Material Downloaded From http://www.ncrtsolutions.in
You might also like
- Iso 2178 - 2016 - PDFDocument1 pageIso 2178 - 2016 - PDFbala0% (1)
- Hydrogels and Biodegradable Polymers For Bioapplications by Raphael M. Ottenbrite, Samuel J. Huang, and Kinam Park (Eds.)Document271 pagesHydrogels and Biodegradable Polymers For Bioapplications by Raphael M. Ottenbrite, Samuel J. Huang, and Kinam Park (Eds.)LA100% (1)
- 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances NotesDocument2 pages10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Notesprem wakodeNo ratings yet
- Motion and Measurement of DistancesDocument3 pagesMotion and Measurement of DistancescharliecharliestoryNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Measurement & Motion - NotesDocument4 pagesCh-11 Measurement & Motion - NoteskanzahshafeerNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 3Document3 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 3GHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- L-10 - Motion and Measurement of Distances - Part 2Document11 pagesL-10 - Motion and Measurement of Distances - Part 2Chaitra KamuriNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document27 pagesCH 1Bhavik NerkarNo ratings yet
- kinematics 3Document4 pageskinematics 3chaitanya.palutlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 Motion and Time: He Action or Process of Moving or Being MovedDocument1 pageChapter - 13 Motion and Time: He Action or Process of Moving or Being MovedPrabhakar BharatamNo ratings yet
- 7TH HOMEWORKNotes.1702534342Document2 pages7TH HOMEWORKNotes.1702534342hetal.patil7511No ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line and Motion PrudeDocument83 pagesMotion in A Straight Line and Motion PrudeTanujNo ratings yet
- CH 10 MotionDocument4 pagesCH 10 MotionWAZ CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Motion and Measurement of Distances-Notebook WorkDocument7 pagesMotion and Measurement of Distances-Notebook WorkShreya GuptaNo ratings yet
- FSC115 KinematicsDocument68 pagesFSC115 KinematicsOluwagbotemi AmosunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances (CBSE Class 6 Science) notesDocument2 pagesChapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances (CBSE Class 6 Science) notesDivayam SharmaNo ratings yet
- 6 ThmathsDocument3 pages6 Thmathslearn4chatgptNo ratings yet
- Future Classes Is A Part of Iqra Coaching Institute (ICI)Document5 pagesFuture Classes Is A Part of Iqra Coaching Institute (ICI)Mustafa ImranNo ratings yet
- Motion and Types of MotionDocument12 pagesMotion and Types of MotionRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- MotionsDocument4 pagesMotionschandanchiranthcr12No ratings yet
- Motion in Straight Line-Neet-Short-Notes - pdf-50Document8 pagesMotion in Straight Line-Neet-Short-Notes - pdf-50Sanaur Talukdar100% (1)
- MotionDocument19 pagesMotionRacine CariahNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument13 pagesClass NotesAbhit Rao RaiNo ratings yet
- Motion and TimeDocument8 pagesMotion and TimeALLURI DEDEEPYA LAKSHYANo ratings yet
- Complete General Science Notes by Anuj JindalDocument141 pagesComplete General Science Notes by Anuj JindalDigvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Motion Chapter NotesDocument45 pagesMotion Chapter Notess.anoura07No ratings yet
- IX PHY Motion NotesDocument10 pagesIX PHY Motion NotesFaraz khanNo ratings yet
- IX PHY Motion NotesDocument10 pagesIX PHY Motion NotesFaraz khanNo ratings yet
- Class-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THDocument11 pagesClass-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THBhav GrewalNo ratings yet
- Motion and Measurement of DistancesDocument38 pagesMotion and Measurement of DistancesShiney KoshyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document7 pagesChapter 13Pta PNo ratings yet
- Motion and Measurement of DistancesDocument7 pagesMotion and Measurement of DistancesGovind ChhawsariaNo ratings yet
- VI-10-Motion and Measurement of DistancesDocument13 pagesVI-10-Motion and Measurement of DistancesAnnAmmusNo ratings yet
- Experimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperimentno.4 Uniform Motion I. ObjectivesStephanie AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet#2 - Science - Class 9Document5 pagesWorksheet#2 - Science - Class 9MugdhaNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument5 pagesDynamicsAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument1 pageMotionyogesh joshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document9 pagesChapter 10Abhinaba PaulNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument4 pagesMotionMadona FahemNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 MYP4 Phy U1 Resource Part II On M&M-02 MayDocument34 pages2023-24 MYP4 Phy U1 Resource Part II On M&M-02 Maytushant.avudurthiNo ratings yet
- Motion Notes Part 1Document2 pagesMotion Notes Part 1Perajothi PalanirajaNo ratings yet
- MOTIONDocument36 pagesMOTIONRajendra RathNo ratings yet
- Types of Motion 2Document4 pagesTypes of Motion 2reduandcNo ratings yet
- 422 Topper 21 110 6 4 57 Motion Up201506181308 1434613126 8189Document13 pages422 Topper 21 110 6 4 57 Motion Up201506181308 1434613126 8189Rupali Nikhare100% (1)
- Motion In A Straight Line Notes CLASS 11Document6 pagesMotion In A Straight Line Notes CLASS 11sussyacc123frNo ratings yet
- MOTIONDocument1 pageMOTIONSantoshPathakNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 emDocument47 pagesUnit 4 embhaskarraj1714No ratings yet
- Definitions XI StandardDocument22 pagesDefinitions XI StandardFredrickNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 7 Note (2) - 1Document2 pagesPhysics Grade 7 Note (2) - 1Melkamu YigzawNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Lecture 1Document18 pagesKinematics Lecture 1aryanNo ratings yet
- Motion (Final TTB) 1-42Document42 pagesMotion (Final TTB) 1-42Anisha PanditNo ratings yet
- Measurement and MotionDocument6 pagesMeasurement and MotionbittuchintuNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion and Torque3Document34 pagesRotational Motion and Torque3Odtülü FizikçiNo ratings yet
- Types of MotionDocument4 pagesTypes of MotionCeasar Epsilonian MundalaNo ratings yet
- Aees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 MotionDocument5 pagesAees-Distant Learning Programme Class Ix - Physics Chapter - 8 Motionseenu nadarajanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Second Quarter LecturesDocument10 pagesPhysical Science Second Quarter LecturesJohn Patrick De CastroNo ratings yet
- Motion.IX.NotesDocument10 pagesMotion.IX.NotesParveen NagiNo ratings yet
- Mech 2 Module 1 Unit 2 (Motion of A Particle)Document10 pagesMech 2 Module 1 Unit 2 (Motion of A Particle)Zamantha DomingoNo ratings yet
- Motion - Short NotesDocument2 pagesMotion - Short Notesalok.coding123No ratings yet
- Group 5 Control EngineeringDocument62 pagesGroup 5 Control Engineeringlittlesilver0810No ratings yet
- The Future of the Impossible: The Physics and Ethics of Time TravelFrom EverandThe Future of the Impossible: The Physics and Ethics of Time TravelNo ratings yet
- Tips Writing Exam Good SaqDocument1 pageTips Writing Exam Good SaqGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- REG ETA-IMG-038 Assessing A SIMGs Comparability To An ANZ Trained Surgical Specialist PDFDocument14 pagesREG ETA-IMG-038 Assessing A SIMGs Comparability To An ANZ Trained Surgical Specialist PDFGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Math Mastery Online Series: Group C Lesson 1 - Answer KeyDocument1 pageMath Mastery Online Series: Group C Lesson 1 - Answer KeyGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Plastic Surgery ResultDocument10 pagesPlastic Surgery ResultGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- National and Official Symbols of IndiaDocument4 pagesNational and Official Symbols of IndiaGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Office-Holders in Government of India PDFDocument6 pagesOffice-Holders in Government of India PDFGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Swine Flu: Bala Vinoth, D Suresh KumarDocument4 pagesSwine Flu: Bala Vinoth, D Suresh KumarGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- List of Salonag and History of Famus Freedom Fighters-1Document11 pagesList of Salonag and History of Famus Freedom Fighters-1GHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- List of God Vehicles & ObjectsDocument15 pagesList of God Vehicles & ObjectsGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Flu Vaccine For ColdDocument3 pagesFlu Vaccine For ColdGHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- 5422160319Document308 pages5422160319MadhaviNo ratings yet
- Thesis Budaya OrganisasiDocument5 pagesThesis Budaya Organisasigbrgvvfr100% (2)
- PW15PHDocument4 pagesPW15PHShivenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29: Curl, Divergence and FluxDocument2 pagesLecture 29: Curl, Divergence and FluxKen LimoNo ratings yet
- Design Basis Report NewDocument29 pagesDesign Basis Report Newrpdharshan04No ratings yet
- Essay Questions Lesson 3: AnswerDocument2 pagesEssay Questions Lesson 3: AnswerDanny ClintonNo ratings yet
- 5 Sem Lab BSC Programs - C++Document19 pages5 Sem Lab BSC Programs - C++LohithokNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers PROBDocument3 pagesComplex Numbers PROBSivagami Saminathan100% (1)
- SC ST Fund InformationDocument6 pagesSC ST Fund InformationDevunoor GpNo ratings yet
- DRAWING WITH LIGHT THE PENCIL OF NATURET - Thesis PDFDocument233 pagesDRAWING WITH LIGHT THE PENCIL OF NATURET - Thesis PDFVinit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sectorial Planning VS Integrated PlanningDocument3 pagesSectorial Planning VS Integrated PlanningMuhammad IDREES KHANNo ratings yet
- How To Audit Fmeas Using Quality ObjectivesDocument41 pagesHow To Audit Fmeas Using Quality ObjectivesAmir KhakzadNo ratings yet
- Eelectron Solutions and MarketsDocument36 pagesEelectron Solutions and MarketsEngineer AccasNo ratings yet
- Study Guide:: Ricks P. Ortiz Principles of Soil Science - DedeDocument4 pagesStudy Guide:: Ricks P. Ortiz Principles of Soil Science - DedeRicks P. OrtizNo ratings yet
- San Pedro CollegeDocument3 pagesSan Pedro CollegeMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- CALL For FDP Proposals 2019-20Document12 pagesCALL For FDP Proposals 2019-20SHIVAM TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Anish Bhandari.22015997.FE5056, Problem Solving Methods and AnalysisDocument20 pagesAnish Bhandari.22015997.FE5056, Problem Solving Methods and AnalysisAnish bhandariNo ratings yet
- Ilford Pan 100 y 400 FilmDocument9 pagesIlford Pan 100 y 400 FilmJohann Walter Carpio AcurioNo ratings yet
- MulugetaDocument13 pagesMulugetaMilkias MenaNo ratings yet
- V2k (Voice To Skull: Download Free PDFDocument43 pagesV2k (Voice To Skull: Download Free PDFLazlo Secret0% (1)
- Manufacturing and Process Optimization of Porous Rice Straw BoardDocument10 pagesManufacturing and Process Optimization of Porous Rice Straw BoardAmit Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Conceptual Framework of Mathematics From K 3Document34 pagesLesson 1 Conceptual Framework of Mathematics From K 3Godwin Jerome Reyes100% (2)
- Mesl Set 1Document8 pagesMesl Set 1RENE JOSHUA PECASONo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument14 pages4 PDFMANo ratings yet
- New Hello 3rd Year Unit 1 - 2022Document50 pagesNew Hello 3rd Year Unit 1 - 2022essamwahbaNo ratings yet
- Self-Awareness and Self - Management: Dare To Dream, Dare To Be!Document7 pagesSelf-Awareness and Self - Management: Dare To Dream, Dare To Be!nan nan100% (3)
- IB 2 Mechanics MSDocument18 pagesIB 2 Mechanics MSleesha.sahaNo ratings yet
- Overlight - Extra #2 - The Leviathan Grand (February 2020)Document2 pagesOverlight - Extra #2 - The Leviathan Grand (February 2020)DeeAnaNo ratings yet