Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E2 6 Short Essay Eng
E2 6 Short Essay Eng
Uploaded by
qrincesschengCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E2 6 Short Essay Eng
E2 6 Short Essay Eng
Uploaded by
qrincesschengCopyright:
Available Formats
/*
SeriesID: 37
BookID: 239
TierOneID: 1010
TierTwoID: na
SubjectTypeID: 9
*/
Unit 1 Climate change in Hong Kong
Fundamental
1
[[geoge2se001a
Describe and explain the climatic characteristics of Hong Kong. (3)
@O
##
– Belongs to subtropical climate
– With four distinct seasons
– Affected by the monsoon system
– Onshore southwest and southeast winds in summer, offshore northeast winds in
winter
– Forming hot and humid summers and cool and dry winters in Hong Kong
@@
{{app,cld}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:3
]]
2
[[geoge2se002
Describe how the climate of Hong Kong has changed in recent decades. (4)
@O
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 1
##
– Has become warmer and wetter
– The annual mean temperature has been rising
– The rate of increase has become faster in the recent three decades
– More hot nights and very hot days
– Fewer cold days
– The annual rainfall and the annual number of heavy rain days have slightly
increased
– More extreme rainfall events have occurred
– The hourly rainfall record has been already broken several times
– The record has also been broken more frequently
@@
{{app}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
Advanced
3
[[geoge2se001b
Describe and explain the climatic characteristics of Hong Kong. (6)
@O
##
– Belongs to subtropical climate
– With four distinct seasons
– Affected by the monsoon system
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 2
– Monsoons are winds that change directions seasonally caused by the difference
in heating between the land and the sea
– In summer, the land absorbs heat faster than the sea. Hot air rises, forming a low-
pressure area
– Lower temperature of the sea causes air to sink, forming a high-pressure area
– Winds blow from the sea to the land, forming the onshore southeast and
southwest monsoons
– Bring a lot of rainfall
– In winter, the land loses heat faster than the sea. Cold air sinks, forming a high-
pressure area
– Higher temperature of the sea causes air to rise, forming a low-pressure area
– Winds blow from the land to the sea, forming the offshore northeast monsoons
– Unfavourable for the formation of rain
– Hong Kong is thus hot and humid in summer and cool and dry in winter
(Teachers may give additional marks based on the structure, elaboration, language
and fluency of the essay)
@@
{{app,cld}}
d:2;
t:sq;nil:6
]]
=============================================================
Unit 2 Global climate change
Fundamental
4
[[geoge2se004
Describe the distribution pattern of the global temperature and rainfall. (4)
@O
##
– Uneven distribution of temperature
– Temperature decreases with increasing latitude
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 3
– Temperature decreases from low-latitude regions to high-latitude regions
– Rainfall is unevenly distributed
– Regions along the Equator receive an abundant annual rainfall
– Deserts, inland areas and high-latitude regions are dry
– Rainfall is often seasonal in other parts of the world
@@
{{app}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
5
[[geoge2se005
How have the global climatic patterns changed in recent decades? (4)
@O
##
– The global mean temperature has kept increasing
– The rate of increase has begun to speed up
– Fewer cold days and cold nights but more hot days, hot nights and heat waves
– High-latitude regions in the Northern Hemisphere have experienced greater
temperature rises
– Global rainfall has increased
– Regional rainfall has become more extreme
– Some places have experienced more extreme rainfall events
– Some places have become drier, such as the Sahel in Africa
@@
{{app}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
=============================================================
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 4
Unit 3 Causes of climate change
Fundamental
6
[[geoge2se006
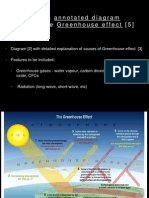
How is the natural greenhouse effect formed? (4)
@O
##
– Solar radiation travels through the atmosphere
– The Earth’s surface is heated and releases heat, warming the atmosphere
– Some of the heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases
– Such as water vapour, carbon dioxide and methane
– Keep the Earth warm for living things to survive
– Some of the heat escapes to space
@@
{{app}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
7
[[geoge2se007
Compare the similarities and differences between global warming and climate change.
(3)
@O
##
– Similarities:
Both are induced by increased concentrations of greenhouse gases
– Differences:
Global warming is the phenomenon of a rise in global temperature
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 5
Climate change refers to the significant long-term changes in climatic
patterns
Including weather elements such as temperature and rainfall
@@
{{app}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:3
]]
8
[[geoge2se008a
How do different human activities lead to global climate change? (4)
@O
##
– Use of fossil fuels for power generation and transport
– Carry out different farming activities, such as opening up farmland, pastoral
farming and using chemical fertilisers
– Carry out different industrial activities, such as producing cement, refrigerants
and aerosols
– Treat wastes by incineration and landfilling
– These activities produce large amounts of greenhouse gases and cause climate
change
@@
{{app,cld}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
9
[[geoge2se009
Why is the climate of Hong Kong changing? (4)
@O
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 6
##
– Increase in local emissions
Rapid urban development
Burning of coal and natural gas in power generation
Transport consumes huge amounts of energy
Produce a lot of greenhouse gases and absorb more heat
– Increase in regional emissions
Hong Kong is located at the mouth of Zhujiang
The Zhujiang Delta Region has undergone rapid urban and industrial
development
Increase in population and the number of factories, power plants and cars
has consumed a lot of fossil fuels
Resulting in significant increase in greenhouse gas emissions in the region
@@
{{app}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
Advanced
10
[[geoge2se008b
How do different human activities lead to global climate change? (8)
@O
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7
##
– Different human activities increase the concentration of greenhouse gases in the
atmosphere and trap more heat, causing climate change
– Use of fossil fuels for power generation and transport
– Including coal, oil and natural gas
– Produce large amounts of carbon dioxide during extraction and burning
– Carry out different farming activities, such as opening up farmland, pastoral
farming and using chemical fertilisers
– Deforestation to open up farmland reduces carbon sinks and the absorption of
carbon dioxide
– Burning vegetation to open up farmland and increase soil fertility releases huge
amounts of carbon dioxide
– Methane is produced when cattle digest food
– Decomposition of cattle manure releases methane and nitrous oxide
– Decomposition of chemical fertilisers releases nitrous oxide
– Carry out different industrial activities, such as producing cement, refrigerants
and aerosols
– The production of cement releases large amounts of carbon dioxide
– The production and use of industrial products such as refrigerants and aerosols
produce chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
– Treat wastes by incineration and landfilling
– Burning solid waste releases carbon dioxide
– Waste landfilling produces carbon dioxide and methane
(Teachers may give additional marks based on the structure, elaboration, language and
fluency of the essay)
@@
{{app,cld}}
d:2;
t:sq;nil:8
]]
=============================================================
Unit 4 Impacts of climate change
Fundamental
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 8
11
[[geoge2se011a
Account for the impacts of climate change on the natural environment and human
society. (4)
@O
##
– Impacts on the natural environment:
Melting of glaciers and sea ice
Sea level rise
More extreme weather events
Disruption to ecosystems
– Impacts on human society:
Water shortage
Reduction in long-term farming outputs
Loss of homes
Increase in health risks
Huge economic losses
Encouraging the exploitation of energy resources
@@
{{app,cld}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
Advanced
12
[[geoge2se011b
Account for the impacts of climate change on the natural environment and human
society. (8)
@O
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 9
##
– Impacts on the natural environment:
Melting of glaciers and sea ice
Reduced sunlight reflection and more soil exposes to the air allows the
Earth’s surface to absorbs more heat
Which accelerates temperature rise and glacier melting, forming a vicious
cycle
Sea level rise
Which will submerge large piece of coastal lowlands and island countries,
such as Maldives
More extreme weather events
Such as heat waves, rainstorms, flooding, droughts, tropical cyclones and
wildfires
Increase in their frequency, strength and duration
Disruption to ecosystems
Some species face extinction, such as polar bears
Warmer seawater causes coral bleaching
Decrease in biodiversity
The distribution of species is affected
Some species may move to high-latitude or high-altitude regions
– Impacts on human society:
Water shortage affect people’s daily lives and economic development
The dilution of river pollutants becomes more difficult and water pollution
becomes more serious
The long-term farming outputs decrease due to more extreme weather
events, a lack of irrigation water and higher pest risks
Many people lose their homes due to sea level rise and extreme weather
events, such as tropical cyclones
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 10
People are forced to leave their homelands and become climate refugees
Increase in health risks
A reduction in food production worsens malnutrition or triggers famine
The spread of some infectious diseases becomes easier, including dengue
fever and malaria
Heat waves and cold waves increases the risks of heat stroke and heart
disease, and may even cause deaths
Huge economic losses
Maintenance of all kinds of damaged infrastructure
Government expense increases as more capital and technology are invested
to cope with hazards
Encouraging the exploitation of energy resources
The melting and thinning of sea ice help open up new sea routes in the
Arctic Ocean
And make the extraction of energy resources easier
(Teachers may give additional marks based on the structure, elaboration, language
and fluency of the essay)
@@
{{app,cld}}
d:2;
t:sq;nil:8
]]
=============================================================
Unit 5 Measures against climate change
Fundamental
13
[[geoge2se013a
What measures have different countries taken to combat climate change? (4)
@O
##
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 11
– Mitigation strategies
Using alternative energy
Adopting better city design
Protecting existing ecosystems
Reducing and recycling waste
Capturing and storing carbon dioxide
– Adaptation strategies
Implementing land use planning
Building flood defences
Setting up warning systems and purchasing insurance
Adopting health protection measures
@@
{{app,cld}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
14
[[geoge2se014
What constraints does international cooperation encounter in coping with climate
change, leading to the slow progress of carbon reduction? (4)
@O
##
– Disagreement on emission reduction
– Emphasis on short-term interests
– Lack of capital and technology
– Lack of monitoring systems
@@
{{app}}
d:1;
t:sq;nil:4
]]
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 12
Advanced
15
[[geoge2se013b
What measures have different countries taken to combat climate change? (8)
@O
##
– Mitigation strategies
Using alternative energy
Such as renewable energy including wind power and solar energy
Which does not emit carbon dioxide during power generation and cannot be
used up
Adopting better city design
Developing mass transit systems to slow down the growth of cars and
reduce energy use
Building footpaths and cycling tracks to encourage people to walk or cycle
Carrying out large-scale greening to lower urban temperatures
Adopting green building designs to save energy and cut carbon emissions
Protecting existing ecosystems
Setting up nature reserves and national parks to prevent deforestation and
maintain carbon sinks
Reducing and recycling waste to reduce the carbon emissions from raw
materials extraction and waste treatment
Capturing and storing carbon dioxide to reduce the concentration of
greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
– Adaptation strategies
Implementing land use planning
For example, designating coastal lowlands as buffer zones / wetlands /
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 13
vacant land to prevent the loss of life and property
Building flood defences to lower the flood risks
For example, flood walls and flood gates were built after Hurricane Katrina
had caused widespread flooding in New Orleans, USA, so as to reduce
flood damage
Setting up warning systems to remind the public of taking precautionary
measures
Taking out insurance to cover the financial losses brought by the changing
climate
Adopting health protection measures
Developing vaccines to reduce health risks
Education to raise public hygiene awareness
Mosquito control to prevent the spread of diseases
(Teachers may give additional marks based on the structure, elaboration, language and
fluency of the essay)
@@
{{app,cld}}
d:2;
t:sq;nil:8
]]
© 2023 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 14
You might also like
- Climate Change - WikipediaDocument75 pagesClimate Change - WikipediaWajahat AliNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Air Travel On The EnvironmentDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Air Travel On The EnvironmentNastyaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument67 pagesClimate ChangeKarl GustavNo ratings yet
- Sahil Evs ProjectDocument27 pagesSahil Evs ProjectOmkar Rajmane0% (1)
- Physical Geog Climo Tutorial 12Document47 pagesPhysical Geog Climo Tutorial 12Sheryl UrieNo ratings yet
- 1 GlobalWarmingDocument44 pages1 GlobalWarmingArchana RamaniNo ratings yet
- Research About Global Warming - TaanDocument10 pagesResearch About Global Warming - TaanryanmartintaanNo ratings yet
- Ucsp-2 0Document5 pagesUcsp-2 0RejoyceNo ratings yet
- Discuss Climate Change in The Last 150 YearsDocument9 pagesDiscuss Climate Change in The Last 150 YearsLJWNo ratings yet
- CSTC NSTP Lesson 6 Environmental Awareness PDFDocument16 pagesCSTC NSTP Lesson 6 Environmental Awareness PDFRochelle Obdianela De CastroNo ratings yet
- 19030102-Lê Khánh Ngọc - Pre-11Document13 pages19030102-Lê Khánh Ngọc - Pre-11Ngọc Lê KhánhNo ratings yet
- Energy Engineering Chapter 7Document13 pagesEnergy Engineering Chapter 7Ajaya KarkiNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal WarmingKylliíanNo ratings yet
- Global Warming (33,34,35,36)Document14 pagesGlobal Warming (33,34,35,36)surajsinghNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument38 pagesGlobal WarmingManonmani PudhuezuthuNo ratings yet
- Dhananjayrao Gadgil College of Commerce, SataraDocument27 pagesDhananjayrao Gadgil College of Commerce, SataraRajesh RajmaneNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies (SSC202) Lesson 7Document41 pagesEnvironmental Studies (SSC202) Lesson 7Lawish KumarNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument16 pagesGlobal WarmingDhana SekarNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: Fisika Lingkungan 2007 Pfis-Fkip Untan LsDocument24 pagesClimate Change: Fisika Lingkungan 2007 Pfis-Fkip Untan LsBarageNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Climte Change Impacts, Sources and Solutions Dr. NizamiDocument33 pages10.1 Climte Change Impacts, Sources and Solutions Dr. NizamiSalman YousafNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23-Climate Change.2020Document94 pagesLecture 23-Climate Change.2020digestivegermNo ratings yet
- Student Name: Shiviti, N.G. Student Number: 200724527 Degree: BSC Env School:: Geog 351 Due Date: 10 - 08 - 2010Document6 pagesStudent Name: Shiviti, N.G. Student Number: 200724527 Degree: BSC Env School:: Geog 351 Due Date: 10 - 08 - 2010Sylvester Böhm MakhuveleNo ratings yet
- GreenhouseDocument20 pagesGreenhouseAbhilash Reddy PannalaNo ratings yet
- O Level Geography Elective PaperDocument6 pagesO Level Geography Elective PaperJiexin ZhangNo ratings yet
- TROPICAL DESIGN LectureDocument42 pagesTROPICAL DESIGN LectureLaNZ NesirioNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: 6.1 Causes and ImpactsDocument13 pagesClimate Change: 6.1 Causes and ImpactsBipin AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument15 pagesClimate ChangeManisha JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter Outlines:: 1 Lec 13 - RDGDocument22 pagesChapter Outlines:: 1 Lec 13 - RDGTanvir HossainNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument8 pagesClimate ChangeViolet PandaNo ratings yet
- Tropical Design: Module O1: IntroductionDocument15 pagesTropical Design: Module O1: Introductionxilen clevNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate Changeabiudonsare1No ratings yet
- STS Final Scope M. OlarteDocument7 pagesSTS Final Scope M. OlarteGlenn RadisNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Environmental EducationDocument61 pagesModule 5: Environmental EducationChristlly LamyananNo ratings yet
- Climate Change .Document22 pagesClimate Change .nugud siddigNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document10 pagesPresentation 3Kandagatla KamalNo ratings yet
- EGE 311 Module 3 Lesson 3 DiscussionDocument8 pagesEGE 311 Module 3 Lesson 3 DiscussionPeecha PaiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Causes: The Consequences of A Warming WorldDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming Causes: The Consequences of A Warming WorldDiana Liz Gamarra ZeñaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal WarmingDipika KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science in Building 2Document8 pagesEnvironmental Science in Building 2ch4nt333No ratings yet
- Research Paper About Climate Change in The Philippines PDFDocument8 pagesResearch Paper About Climate Change in The Philippines PDFaflbmmdddNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and It's Impact On Climate: Indra Gandhi Open UniversityDocument14 pagesGlobal Warming and It's Impact On Climate: Indra Gandhi Open UniversityMihir HareetNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Increase in TheDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Increase in TheVamsikrishna PanugantiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Refers To The RisingDocument4 pagesGlobal Warming Refers To The RisingShyam PraveenNo ratings yet
- Global Warming BsDocument21 pagesGlobal Warming BsShubhamNo ratings yet
- FsdfsfèdDocument2 pagesFsdfsfèdsonnb23No ratings yet
- SS Reviewer 1PTDocument4 pagesSS Reviewer 1PTjonNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument6 pagesGlobal Warming: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchJolly D.PuertosNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument6 pagesClimate ChangeKathyrine Herrera JavierNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Initial Causes of Temperature Changes (External Forcings)Document7 pagesGlobal Warming: Initial Causes of Temperature Changes (External Forcings)marvvinNo ratings yet
- New Kidus Problem StatmentsDocument16 pagesNew Kidus Problem StatmentsKidus FelekeNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Energy CrisisDocument9 pagesClimate Change and Energy CrisiscastrohelaenadaphnieNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document9 pagesAssignment 7OraNo ratings yet
- Observed Temperature Changes: Global Warming Refers To The RisingDocument11 pagesObserved Temperature Changes: Global Warming Refers To The RisingUmang MotaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Awareness ReviewerDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Awareness Reviewerуважать другихNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument410 pagesClimate ChangeJomel Paolo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Climate Change in India (UPSC Notes GS III)Document7 pagesClimate Change in India (UPSC Notes GS III)adarsh shahdeoNo ratings yet
- Building ClimatologyDocument3 pagesBuilding ClimatologyTobilobaNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument33 pagesFinal ReportSrishti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Increase in TheDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Increase in TheshailusolankiNo ratings yet
- Hist_QB_T3_5. NJECNDocument4 pagesHist_QB_T3_5. NJECNqrincesschengNo ratings yet
- E2 5 Data Response Eng-4Document26 pagesE2 5 Data Response Eng-4qrincesschengNo ratings yet
- Hist_QB_T1_3. NJETNDocument5 pagesHist_QB_T1_3. NJETNqrincesschengNo ratings yet
- Teacher E2 Ws U3-4.1Document12 pagesTeacher E2 Ws U3-4.1qrincesschengNo ratings yet
- 科学一年级上学期Document1 page科学一年级上学期qrincesschengNo ratings yet
- 科学一年级上学期 4Document1 page科学一年级上学期 4qrincesschengNo ratings yet
- Trends, Network and Critical Thinking in The 21st Century - PLANETARY NETWORKS - CLIMATE CHANGEDocument6 pagesTrends, Network and Critical Thinking in The 21st Century - PLANETARY NETWORKS - CLIMATE CHANGEJOHN BAYLON100% (2)
- Test Bank For Essentials of Meteorology An Invitation To The Atmosphere 6th Edition AhrensDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Meteorology An Invitation To The Atmosphere 6th Edition Ahrenscerasin.cocoon5pd1100% (54)
- STS Climate ChangeDocument6 pagesSTS Climate Changeambi100% (1)
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12Grace Marie TadeoNo ratings yet
- 02 Divine NatureDocument106 pages02 Divine NatureapuNo ratings yet
- Marti A., Luque A. (Eds.) Next Generation Photovoltaics (IOP, 2004) (ISBN 0750309059) (344s) - EEDocument344 pagesMarti A., Luque A. (Eds.) Next Generation Photovoltaics (IOP, 2004) (ISBN 0750309059) (344s) - EEsmile_with_sri1950No ratings yet
- The Real "Inconvenient Truth"Document94 pagesThe Real "Inconvenient Truth"David PristashNo ratings yet
- Ge10 Module 4Document9 pagesGe10 Module 4Autumn shieldNo ratings yet
- 06 Water and The HydrosphereDocument23 pages06 Water and The HydrosphereGeorgiana BălaşNo ratings yet
- Climate Changes: Climate Change Is A Change in The Statistical Distribution ofDocument16 pagesClimate Changes: Climate Change Is A Change in The Statistical Distribution ofSOHEL BANGINo ratings yet
- Meta 63Document16 pagesMeta 63Gülbin KiyiciNo ratings yet
- Hydrosphere & Atmosphere ExercisesDocument6 pagesHydrosphere & Atmosphere Exercisesa_trasNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Our FutureDocument25 pagesClimate Change and Our FutureNEHALL GOYALNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Atmosphere - K. Saha PDFDocument374 pagesThe Earth's Atmosphere - K. Saha PDFIvetteNo ratings yet
- 2020 Kimdas CH8Document34 pages2020 Kimdas CH8febrikaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadBrett Bunch100% (20)
- Cambridge IGCSE ™: Physics 0625/32Document13 pagesCambridge IGCSE ™: Physics 0625/32nexusdrops1No ratings yet
- 9.2 Carbon Dioxide & Methane As Greenhouse Gases MSDocument8 pages9.2 Carbon Dioxide & Methane As Greenhouse Gases MSRNo ratings yet
- Warming Power of CO2 and H2O: Correlations With Temperature ChangesDocument11 pagesWarming Power of CO2 and H2O: Correlations With Temperature ChangesthecynicaleconomistNo ratings yet
- Topic - 8.2Document4 pagesTopic - 8.2Niharika ChomalNo ratings yet
- Uwi Climate Change Comic Final Oct11Document28 pagesUwi Climate Change Comic Final Oct11FarazAhmedNo ratings yet
- DH18 10 LTT QN deDocument16 pagesDH18 10 LTT QN deMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Đề kiểm tra giữa HKII - 11Anh 211Document6 pagesĐề kiểm tra giữa HKII - 11Anh 211Ngô ThảoNo ratings yet
- UNIT II ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION Important QuestionDocument4 pagesUNIT II ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION Important Questionjowelantonio20No ratings yet
- Global Warming PointsDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming PointsRahulNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Bio-Geographical Aspects of Our Environment: Pro F04Document149 pagesUnit - I Bio-Geographical Aspects of Our Environment: Pro F04Ashraf Ali100% (1)
- Pref - 1 - Listening 3.1Document1 pagePref - 1 - Listening 3.1Elver HUERTAS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Effects of Consumption and Production Patterns To Climate ChangeDocument22 pagesEffects of Consumption and Production Patterns To Climate ChangeRomel Christian Zamoranos Miano100% (2)
- Environmental EthicsDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Ethicsbah-72-20No ratings yet