Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kwv Education Financial Maths
Kwv Education Financial Maths
Uploaded by
Lerato bunnyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kwv Education Financial Maths
Kwv Education Financial Maths
Uploaded by
Lerato bunnyCopyright:
Available Formats
KWV MATHS 11 & 12
FINANCIAL MATHS
EMAIL : admin@kwv-education.co.za
FACEBOOK P. : KWV EDUCATION
TWITTER : @KWVEDUCATION
INSTAGRAM : KWVEDUCATION
WHATSAPP GROUP : 082 6727 928
WEBSITE : www.kwv-education.co.za
WHERE TO START IN MATHS AND SCIENCE
➢ FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS
✓ It deals with two types of interest rates:
➢ Simple interest
➢ Compound interest
➢ SIMPLE/LINEAR METHOD INTEREST
✓ Shape is very important to take note for both Appreciation and Depreciation.
✓ It is based only on the amount of money invested/borrowed and not on balanced basis.
✓ To check your understanding simple tries the example below without using the
➢ FORMULAE FOR SIMPLE INTEREST RATE
o Formula: [appreciation]
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 2
o Formula: [Depreciation]
➢ TAKE NOTE OF THE FOLLOWING
✓ If A > P : Appreciation
✓ If A < P : Depreciation
✓ A : Future/accumulated/investment amount (NB- will / to…)
✓ P : Present/principal /invested amount (NB-is / was, cost)
✓ n : Term loan (NB-stated in years)
✓ i : Interest (rate =100i)
✓ Equal instalment using simple interest rate :
✓ The future amount is given by
✓ The interest earned
✓ The percentage of the interest earned
➢ HIRE PURCHASE AGREEMENTS
✓ A hire purchase agreement (HP) is a short-term loan e.g. Furniture.
✓ Buyers sign an agreement with the seller to pay a specified amount per month.
✓ The interest paid on a hire purchase loan is simple interest.
✓ It is calculated on the full value of the loan over the repayment period.
✓ Normally a deposit is paid initially and the balance is paid over a short time period.
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 3
➢ TAKE NOTE OF THE FOLLOWING
✓ Loan
✓ Total amount paid off to the loan:
➢ COMPOUND INTEREST
✓ Shape is very important to take note for both Appreciation and Depreciation.
✓ Interest paid on the initial principal and previously earned interest.
✓ To check your understanding simple tries the example below without using the
➢ FORMULAE FOR COMPOUND INTEREST RATE
o Formula: [appreciation]
o Formula: [Depreciation]
➢ INFLATION
✓ Inflation is the steady compounded increase in prices over time throughout the
economy.
✓ The effect of inflation is to erode the buying power of money over time.
✓ It is calculated using COMPOUND INTEREST.
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 4
➢ EXCHANGE RATE
✓ There are different money systems in different countries.
✓ Currency is the term used to describe the particular money system of a country.
✓ Here are the currencies of a few countries.
Country Currency used Symbol for the currency
South Africa Rand R
United States of America US dollar $
United Kingdom British Pound £
Several European countries Euro €
✓ In every country, in order to purchase goods and services, you would need to use their
currency.
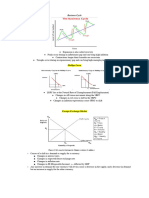
➢ THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TWO INTEREST RATES
❖ CONCLUSION
✓ Initially the simple interest growth will be greater than the compounded growth. but
later on will be equal,
✓ And as time goes on the compound interest will be greater than the simple interest
rate.
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 5
DBE PAST PAPERS
KWV Q 01
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 6
KWV M 01
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 7
KWV Q 02
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 8
KWV M 02
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 9
➢ DEPRECIATION
✓ Book value-is the value of equipment at a given time after depreciation has taken
place.
✓ Scrap value-is the book value of the equipment at the end of its useful life.
➢ SIMPLE INTEREST
✓ It depreciates based on the straight line method.
o
o
➢ COMPOUND INTEREST
✓ It depreciates based on the reducing balanced basis.
o o
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 10
➢ COMPOUNDING PERIODS
❖ EFFECTIVE INTEREST RATE:
✓ The rate where the stated period and the compounding periods are the same
❖ NOMINAL INTEREST RATE:
✓ The rate where the stated period and the compounding period are not the same KEY!
✓ Effect of compounding period:
Term loan and interest must be converted ✓
The units are very important.
✓ Compounding periods (m) KEY!!!
Annually :m=1 Semi-annually :m=2
Monthly : m = 12 After every three months :m=4
Half yearly :m=2 Quarterly :m=4
Weekly : m = 52 After every six months :m=2
Daily : m = 365
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 11
➢ CALCULATING THE INTEREST RATE
❖ If money:
✓ Double, or triple the initial :[ Appreciation]
✓ Quarter or became certain % of its original amount : [ Depreciation]
➢ THE TIME LINE
✓ The value of P or A must be multiplied by an increasing or decreasing factor.
✓ Calculating A : exponents must be positive (left to right)
✓ Calculating P : exponents must be negative (right to left)
➢ ADDITIONAL (DEPOSIT) AND WITHDRAWAL OF AMOUNT
✓ For deposit : positive sign must be used.
✓ For withdrawal : negative sign must be used.
✓ Note : Treat each amount separately and grow it up to the last period.
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 12
➢ NOMINAL AND ANNUAL EFFECTIVE RATES
➢ Conversion between annual effective and nominal interest rate:
Formula
✓ = effective rate (annual)
✓ = nominal rate
✓ n = number of compoundings per year
❖ Effective interest rate:
✓ The rate where the stated period and the compounding periods are the same
❖ Nominal interest rate:
✓ The rate where the stated period and the compounding period are not the same
KEY!
✓ Effect of compounding period:
✓ Term loan and interest must be converted
✓ If you have calculated the effective interest rate then there is no need of putting
the value of m(compounding period) in the formula
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 13
➢ DBE PAST PAPERS
KWV Q 01
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 14
KWV M 01
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 15
KWV Q 01
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 16
KWV M 01
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 17
➢ CALCULATING THE VALUE OF: n
Calculating number of periods (n) if:
✓ When calculating the time of the investment (n) in a compound formula you need to
make use of Logs
✓ The money double / triple the initial value : Appreciation
✓ The money becomes 20% /quarter of its original value : Depreciation
➢ ANNUITIES
✓ It deals with regular fixed payments
✓ There are two types of annuities
➢ ORDINARY ANNUITY
✓ Payments are made at the end of each period
➢ ANNUITY DUE
✓ Payments are made at the beginning of each period (immediately).
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 18
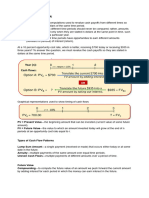
➢ FUTURE VALUE ANNUITY
✓ It work forward the end of the time line
❖ Ordinary annuity:
✓ The first payment is made at the end of the month and the last payment at the end of n
months
❖ Annuity due:
✓ The first payment is made immediately and last payment is made at the beginning of
the last period
o Formula
✓ F = total accumulated at the end of the time period
✓ x = monthly instalment
✓ i = interest rate per annum
✓ n = number of instalments /payments
KEY!
✓ Ordinary:
• Payments are made in one month’s time
• Starting at the end of the first month
o n+1
• Payments start immediately and end on the last day
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 19
✓ Annuity due:
• Last payment into account is due one month before the money becomes matured.
• Payment made immediately and ending one month before.
➢ COMPOUND AND FUTURE VALUE
✓ Once off deposit indicate the compound interest.
✓ Regular fixed payments indicate the future value annuity.
✓ Use addition sign to separate the two interest rates
✓ Remember to treat them separately.
➢ FURTHER ACCUMULATED AMOUNT
✓ If the payments stop for certain periods and the money then remain in the account to
accumulate for further period:
✓ Add the increasing factor
✓ Use the future value annuity formula and multiply it by the increasing factor.
➢ STARTING LATER AND ENDING EARLY TO PAY
✓ The amount must be forwarded up to the start of payments
✓ The amount will accumulate for the remaining periods
➢ INFLATION ON THE EQUAL PAYMENTS
✓ The amount will accumulate after the change of the interest rate.
➢ MISSING THE CERTAIN PAYMENT(S)
✓ The amount will accumulate for that period and treat them separately ( TIME LINE)
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 20
➢ SINKING FUND
✓ A sinking fund is an investment that is made to replace expensive equipment / items
in a few years’ time.
✓ It is used as a “savings account” that will accumulate funds over a period of time,
which will enable the investor to purchase expensive items.
➢ The steps:
✓ Calculate the replacement/expected/new cost (appreciation) o
Formula
o or
✓ Calculate the scrap value/trade-in/resale/decay value
(depreciation)
o Formula
o or
✓ Sinking( fv) = new cost – scrap value
✓ The monthly instalments in the sinking fund:
✓ Use the future value annuity formula.
✓ And check the payments period
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 21
➢ SERVICES TO BE MADE
✓ Talking some money for service of the equipment:
✓ The sinking fund will not only lose the future value, it will also lose the interest
earned on the future value at the end of that particular period.
✓ In order to calculate the future value of the amount, you first need to get the annual
effective rate and then use the future value annuity formula.
✓ Therefore new sinking fund = future value – future value of the withdrawals.
✓ Equal instalment must be increased so as sinking fund cannot be affected.
➢ PRESENT VALUE ANNUITY
✓ It works backwards the beginning of the time line.
✓ Key words: loans, bursary and repayments
✓ In a present value annuity, a sum of money is normally borrowed from a financial
institution and paid back with interest by means of regular payments at equal interval
over a time period.
✓ The loan is said to be amortised (paid off) when it together with interest charges paid
off.
✓ The interest is calculated on the reducing balance.
o Formula
✓ P = present value
✓ x = monthly instalment ✓ i = interest rate p.a.
✓ n = number of time periods to repay the loan
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 22
Note:
✓ The first payment is made at the end of the month and the last payment at the end of n
months, so this is an ordinary annuity.
✓ There is no need of using present value formula if we have the future value of the
loan.
✓ If we are given a deposit, this money is taken off from the value of the loan:
Loan
Total amount paid off to the loan:
➢ PERCENTAGE DEPOSITS
✓ Loan is the given by the cost minus deposit in cash or percentage.
✓ Loan= or
✓ Loan
➢ GAP PAYMENTS FOR LOANS
✓ Starting payment later, the amount of the loan will accumulate for that period.
✓ Use the compound interest formula to calculate the accumulate amount.
✓ And then that amount will for the loan.
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 23
➢ OUTSTANDING BALANCE ON A LOAN
❖ TWO METHODS
a. Balance on a loan = (loan + interest) - (instalments + interest)
We need to move the original amount of the loan forward with interest and also the regular
payment that were made
b. Present value formula
This method just focuses on the payments that still have to be made and work backwards on
the time line.
Note:
✓ Outstanding balance on any loan is always calculated directly after the last payment is
made.
➢ CALCULATING THE LAST PAYMENT LESS THAN
✓ Firstly calculate the outstanding balance after the last full payment of the instalment.
✓ And the use the compound formula to calculate the last payment for one month.
➢ INFLATION BASED ON THE OUTSTANDING BALANCE
✓ After calculating the outstanding balance on a loan for the certain period of time, if
then interest changes;
✓ Use the balance on the loan in order to calculate the monthly instalment after the
change.
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 24
➢ CALCULATING THE NUMBER OF PAYMENTS ON FUTURE VALUE
✓ Knowledge of logarithms must be also applied
✓ Algebra skill of simplification and making a variable be the subject of the formula.
➢ CALCULATING NUMBER OF PATMENT ON LOANS
✓ Knowledge of logarithms must be also applied.
✓ Algebra skill of simplification and making a variable be the subject of the formula.
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 25
➢ DBE PAST PAPERS
KWV Q 01
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 26
KWV M 01
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 27
KWV Q 02
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 28
KWV M 02
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 29
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 30
KWV Q 03
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 31
KWV M 03
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 32
KWV : QP: 04
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 33
KWV MEMO: 04
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 34
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 35
KWV QP: 05
MEMO : 05
WHERE TO START 082 6727 928 36
You might also like
- Powerpoint Slides © Luke M. Froeb, Vanderbilt 2014Document23 pagesPowerpoint Slides © Luke M. Froeb, Vanderbilt 2014Ihab yassinNo ratings yet
- Traditional Contracts and Legal Concepts: Al-Maktoum College of Higher EducationDocument33 pagesTraditional Contracts and Legal Concepts: Al-Maktoum College of Higher Educationdzikri hakamNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance: Anders BäckströmDocument16 pagesCorporate Finance: Anders BäckströmbollenNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument18 pagesTime Value of MoneyGabriella PrathapsonNo ratings yet
- FM2 Notes 3prefinalsDocument13 pagesFM2 Notes 3prefinalsLera KathNo ratings yet
- FM 5Document3 pagesFM 5gojo satoru100% (1)
- MODULE 6 Topic 1Document34 pagesMODULE 6 Topic 1Lowie Aldani SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. INTEREST RATES AND BOND VALUATIONDocument45 pagesChapter 7. INTEREST RATES AND BOND VALUATIONChloe JtrNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document29 pagesLec 5Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- S6&7 - EquitiesDocument31 pagesS6&7 - EquitiesGenesis mia Albornoz ochoaNo ratings yet
- Cost of CapitalDocument23 pagesCost of CapitalUdit DhawanNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics 2023 Short Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesMacro Economics 2023 Short Cheat Sheetnarane rampNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - DoneDocument22 pagesLecture 03 - DoneHady MagedNo ratings yet
- Fixed Rate Bond Valuation and Risk: FinpricingDocument10 pagesFixed Rate Bond Valuation and Risk: FinpricingTrader CatNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance - Summary FKDocument32 pagesCorporate Finance - Summary FKFrédéric KrögerNo ratings yet
- Discounted Cash FlowDocument7 pagesDiscounted Cash FlowMuzzamil Shamim Shamim MalikNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money (TVM)Document5 pagesTime Value of Money (TVM)Yesha Jade SaturiusNo ratings yet
- S2. Time Value of MoneyDocument17 pagesS2. Time Value of MoneyGenesis mia Albornoz ochoaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economic Lecture 6Document27 pagesEngineering Economic Lecture 6omar meroNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economic Lecture 2Document21 pagesEngineering Economic Lecture 2omar meroNo ratings yet
- 2024S FM Week6 Chapter7 v2Document52 pages2024S FM Week6 Chapter7 v222000492No ratings yet
- Acm 31 FM Lec 6N7Document49 pagesAcm 31 FM Lec 6N7Vishal AmbadNo ratings yet
- 3 Managing Bond PortfoliosDocument51 pages3 Managing Bond PortfoliosShazelNo ratings yet
- Part - 3 - Application1 - Equity ValuationDocument35 pagesPart - 3 - Application1 - Equity Valuationts wNo ratings yet
- Manning For Growth: Revised Salary Scales IntroductionDocument7 pagesManning For Growth: Revised Salary Scales IntroductionAlex BurcăNo ratings yet
- Genmath 6Document6 pagesGenmath 6JOYCE ENGARANNo ratings yet
- 03 How To Calculate Present Values-2Document23 pages03 How To Calculate Present Values-2melekkbass10No ratings yet
- Session 9Document9 pagesSession 9yaraNo ratings yet
- Q&ans Hw3aDocument9 pagesQ&ans Hw3aAbdulaziz FaisalNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Cost of Capital: Important PointsDocument11 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Cost of Capital: Important PointsAshutosh BarseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Bond and Stock ValuationDocument53 pagesChapter 5 - Bond and Stock ValuationQuang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Notes-11Document8 pagesBusiness Finance Notes-11Anonymus PershonNo ratings yet
- Intro 2Document16 pagesIntro 2Zack ZhangNo ratings yet
- 2023 Time Value of MoneyDocument81 pages2023 Time Value of Moneyk61.2212155031No ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument13 pagesTime Value of MoneyAulia EndiniNo ratings yet
- Eiteman, D.K., Stonehill, A.I. and Moffett, M.H. (2021), Multinational Business Finance, Global Edition, 15th EditionDocument11 pagesEiteman, D.K., Stonehill, A.I. and Moffett, M.H. (2021), Multinational Business Finance, Global Edition, 15th Editionerikssonalbin00No ratings yet
- Important Accounting PrinciplesDocument2 pagesImportant Accounting PrinciplesMarie Sol GalingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document34 pagesLecture 1duygualsan1No ratings yet
- 6 - Economics - BasicsDocument14 pages6 - Economics - BasicsIsmail ismailNo ratings yet
- Audit of Property, Plant, and Equipment, Wasting Assets, and Intangible AssetsDocument9 pagesAudit of Property, Plant, and Equipment, Wasting Assets, and Intangible AssetsyhygyugNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Part IIIDocument4 pagesTime Value of Money Part IIINailiah MacakilingNo ratings yet
- Notes - EE 3Document149 pagesNotes - EE 3Lloyd DionosaNo ratings yet
- Investments - 2: Fixed Income - BondsDocument36 pagesInvestments - 2: Fixed Income - BondsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Session 5 - Valuing Bonds and StocksDocument51 pagesSession 5 - Valuing Bonds and Stocksmaud balesNo ratings yet
- TVM - Unit 4Document32 pagesTVM - Unit 4gajakesari738No ratings yet
- FINS5513 Lecture NotesDocument47 pagesFINS5513 Lecture Notes萬之晨No ratings yet
- ch9 1Document33 pagesch9 1Sai Karthik BaggamNo ratings yet
- 2023 Time Value of MoneyDocument81 pages2023 Time Value of Moneylynthehunkyapple205No ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Valuing StocksDocument56 pagesLecture 4-Valuing StocksNguyên KhôiNo ratings yet
- Accounting: THE Language of BusinessDocument53 pagesAccounting: THE Language of BusinessBAM ZAHARDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6+7 (CKP SIR)Document26 pagesChapter 6+7 (CKP SIR)Jannatul FardusNo ratings yet
- Equities: Alexei Alvarez Drobush, CFA, FRMDocument12 pagesEquities: Alexei Alvarez Drobush, CFA, FRMRuyarmsNo ratings yet
- COst of Capital Edutap-Rbi SummaryDocument11 pagesCOst of Capital Edutap-Rbi SummaryashishNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Mathematics of FinanceDocument15 pagesLesson 1 Mathematics of FinanceEdnan DiazNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure TheoriesDocument10 pagesCapital Structure TheoriesBrahamdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- FM 4Document3 pagesFM 4gojo satoruNo ratings yet
- 5 - Capital Investment Appraisal (Part-1)Document29 pages5 - Capital Investment Appraisal (Part-1)Fahim HussainNo ratings yet
- Acst6003 Week3Document24 pagesAcst6003 Week3Andre OKcNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument2 pagesCapital Budgetingmengjun0987654311No ratings yet
- Fin 440 Chapter 9Document19 pagesFin 440 Chapter 9Mehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- KWV EDUCATION PROBABILITYDocument36 pagesKWV EDUCATION PROBABILITYLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 TrigonometryDocument14 pagesGrade 12 TrigonometryLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Kwv Electricity and Electrostatics SolutionsDocument62 pagesKwv Electricity and Electrostatics SolutionsLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Wts 12 Maths Winter BootcampDocument32 pagesWts 12 Maths Winter BootcampLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Kwv Education StatisticsDocument48 pagesKwv Education StatisticsLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Maths NW Sep 2022 p1 Memo EngDocument17 pagesGR 12 Maths NW Sep 2022 p1 Memo EngLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Maths Gr12 Session 16-19 Ssip TNDocument86 pagesMaths Gr12 Session 16-19 Ssip TNLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Fell in Love With My Brother-1-1Document976 pagesFell in Love With My Brother-1-1Lerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Gem P DisclaimerDocument4 pagesGem P DisclaimerLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- 2015 Sept Maths QP MemoDocument12 pages2015 Sept Maths QP MemoLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Gauteng Dept of Health Bursary Application FormDocument4 pagesGauteng Dept of Health Bursary Application FormLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Sci Bono Mathematics Module 4 5 FinalDocument85 pagesSci Bono Mathematics Module 4 5 FinalLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 Finance Growth and Decay Grade 11 MathematicsDocument3 pagesWorksheet 9 Finance Growth and Decay Grade 11 MathematicsLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument16 pagesAcids and BasesLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document19 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12Lerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument7 pagesChemical EquilibriumLerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- National Power Corporation vs. The Court of AppealsDocument17 pagesNational Power Corporation vs. The Court of AppealsSam AndresNo ratings yet
- Reyna Rousseau Recognized As A Professional of The Year For 2021 by Strathmore's Who's Who Worldwide PublicationDocument3 pagesReyna Rousseau Recognized As A Professional of The Year For 2021 by Strathmore's Who's Who Worldwide PublicationPR.comNo ratings yet
- Registration NoteDocument14 pagesRegistration Notearola ifeoluwaNo ratings yet
- Etc Lease BG - SBLC 22Document32 pagesEtc Lease BG - SBLC 22Tonio EdevNo ratings yet
- Loan ReceivableDocument3 pagesLoan ReceivableJenelyn AliordeNo ratings yet
- Most Important Terms and Conditions: Sbi-Scholar Loan SchemeDocument2 pagesMost Important Terms and Conditions: Sbi-Scholar Loan SchemeAkhil RajNo ratings yet
- CHAP 2 Lending To Business and Pricing Business LoansDocument72 pagesCHAP 2 Lending To Business and Pricing Business LoansDương Thuỳ TrangNo ratings yet
- VSD 609Document1 pageVSD 609Alexander DaltonNo ratings yet
- Debt Collection Research PaperDocument5 pagesDebt Collection Research Paperrsbptyplg100% (3)
- Assignment 2 Property TaxDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 Property TaxAHMAD ALINo ratings yet
- The Collapse of Lehman Brothers (2008) : A Case StudyDocument14 pagesThe Collapse of Lehman Brothers (2008) : A Case StudyKimberly Joy DimaanoNo ratings yet
- ARMANDO GEAGONIA v. COURT OF APPEALS Et Al.Document3 pagesARMANDO GEAGONIA v. COURT OF APPEALS Et Al.Karl CabarlesNo ratings yet
- P14 SFM (2nd Paper)Document9 pagesP14 SFM (2nd Paper)Shivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ahmad AyubDocument16 pagesAhmad Ayubfresh juiceNo ratings yet
- Financial System in BD 08.10.2020 - UpdateDocument39 pagesFinancial System in BD 08.10.2020 - UpdateShamim IqbalNo ratings yet
- Colliers Manila Q3 2022 Residential v2Document4 pagesColliers Manila Q3 2022 Residential v2bhandari_raviNo ratings yet
- Insurance Midterms ReviewerDocument28 pagesInsurance Midterms ReviewerMichaela SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Igse Accounting: by Ms Tara EsaDocument89 pagesIgse Accounting: by Ms Tara EsaDIllaNo ratings yet
- Short-Term FinancingDocument4 pagesShort-Term FinancingJavi Hannah Jewel Del CampoNo ratings yet
- Draft Guidelines On Interest Rate Risk in Banking Book Interest Rate RiskDocument28 pagesDraft Guidelines On Interest Rate Risk in Banking Book Interest Rate RiskPrasad MohanNo ratings yet
- Fortune's Global 500 Companies of The WorldDocument4 pagesFortune's Global 500 Companies of The Worldsujeet kumarNo ratings yet
- Partnership FormationDocument3 pagesPartnership FormationJules AguilarNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Constructive Notice & Indoor ManagementDocument11 pagesDoctrine of Constructive Notice & Indoor ManagementEkta ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Promisory Note With Chattel MortgateDocument5 pagesPromisory Note With Chattel MortgateluckyNo ratings yet
- Financial SystemDocument15 pagesFinancial SystemRTushar BeeshmNo ratings yet
- AAOIFI FAS 25 - Quiz (MBL To BIBF)Document3 pagesAAOIFI FAS 25 - Quiz (MBL To BIBF)AL-HAMD GROUPNo ratings yet
- FM 03 Financial IntermediationDocument8 pagesFM 03 Financial IntermediationIvy ObligadoNo ratings yet
- History of LoansDocument2 pagesHistory of LoansHimmanshu SabharwalNo ratings yet