Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T-TESS_Rubric-Working_Copy
T-TESS_Rubric-Working_Copy
Uploaded by
Chris PriceCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T-TESS_Rubric-Working_Copy
T-TESS_Rubric-Working_Copy
Uploaded by
Chris PriceCopyright:
Available Formats
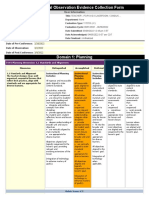
Texas Teacher Evaluation and Support System (T-TESS) Rubric
PLANNING
Standards and Alignment (Dimension 1.1)
Dimension 1.1 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Standards and
• All rigorous and measurable goals • All measurable goals aligned • All goals • Most goals aligned to • Few goals aligned to
Alignment: to state content standards. aligned to state state content state content
aligned to state content standards.
The teacher designs content standards. standards.
• All activities, materials and • All activities, materials
clear, well- standards.
assessments that: and assessments that: • Most activities, • Few activities,
organized, • All activities, materials and materials and
o are logically sequenced o are sequenced
sequential o are relevant to students’ prior o are relevant to materials and assessments that: assessments that:
lessons that reflect understanding and real-world students’ prior assessments that: o are sequenced o are sequenced
best practice, align applications understanding o are sequenced o sometimes provide o rarely provide time for
with standards o integrate and reinforce o integrate other disciplines o are relevant to appropriate time for lesson and lesson
and are appropriate concepts from other o provide appropriate time students lesson and lesson closure
for diverse learners. disciplines for student work, lesson o provide appropriate closure • Lessons where few
o provide appropriate time for and lesson closure time for lesson and • Lessons where most objectives are aligned
student work, student reflection, o reinforce broader unit lesson closure objectives are aligned and sequenced to the
Standards Basis: lesson and lesson closure and course objectives o fit into the broader and sequenced to the lesson’s goal.
1A, 1B, 3A, 3B, 3C o deepen understanding of o are vertically aligned unit and course lesson’s goal.
broader unit and course to state standards objectives
objectives o are appropriate for o are appropriate
Potential Sources of o are vertically aligned to state diverse learners for diverse
Evidence: standards • All objectives aligned learners.
Conferences and o are appropriate for diverse and logically sequenced • All objectives
conversations with the learners to the lesson‘s goal. aligned to the
teacher; formal • Objectives aligned and logically • Integration of technology lesson’s goal.
observations and sequenced to the lesson’s goal, to enhance mastery of • Integration of
walkthroughs; providing relevant and enriching goal(s). technology when
classroom artifacts; extensions of the lesson applicable.
student growth • Integration of technology to
processes enhance mastery of goal(s).
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© Texas Education Agency 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 1
PLANNING
Data and Assessment (Dimension 1.2)
Dimension 1.2 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Data and
Assessment: • Formal and informal assessments • Formal and informal • Formal and • Formal and • Few formal and
The teacher uses to monitor progress of all assessments to monitor informal informal informal
formal and informal students, shares appropriate progress of all students and assessments to assessments to assessments to
diagnostic, formative and incorporate appropriate monitor progress monitor progress monitor student
methods
summative assessment data with diagnostic, formative and of all students. of most students. progress.
to measure student
students to engage them in self- summative assessments • Consistent • Timely • Few opportunities
progress, then assessment, build awareness of data into lesson plans. feedback to feedback to for timely feedback
manages and their own strengths and • Substantive, specific and students, families students and to students or
analyzes student data weaknesses and track their own timely feedback to and other school families. families.
to inform instruction. progress. students, families and personnel while • Utilization of • Utilization of few
• Substantive, specific and timely other school personnel on maintaining multiple sources of student
Standards Basis: feedback to students, families and the growth of students in confidentiality. sources of data.
1B, 1F, 2B, 2C, 5A, 5B, school personnel on the growth of relation to classroom and • Analysis of student student data.
5C, 5D students in relation to classroom campus goals, while data connected to
and campus goals and engages maintaining student specific
with colleagues to adapt school- confidentiality. instructional
Potential Sources of wide instructional strategies and • Analysis of student data strategies.
Evidence: Conferences goals to meet student needs while connected to specific
and conversations with maintaining confidentially. instructional strategies and
the teacher; formal
• Analysis of student data connected use of results to reflect on
observations and to specific instructional strategies his or her teaching and to
walkthroughs; and use of results to reflect on his monitor teaching strategies
classroom artifacts; or her teaching and to monitor and behaviors in relation to
student growth teaching strategies and behaviors in student success.
processes; analysis of relation to student success.
student data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 2
PLANNING
Knowledge of Students (Dimension 1.3)
Dimension 1.3 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Knowledge of
Students: • All lessons that connect to • All lessons that connect • All lessons that • Most lessons that • Few lessons that
Through knowledge of students’ prior knowledge, to students’ prior connect to students’ connect to connect to students’
students and proven experiences, interests and knowledge, experiences prior knowledge and students’ prior prior knowledge and
future learning expectations and future learning experiences. knowledge and experiences.
practices, the teacher
across content areas. expectations. • Adjustments to address experiences. • Adjustments to
ensures high levels of
• Guidance for students to • Guidance for students to strengths and gaps in • Adjustments to address strengths and
learning, social- apply their strengths, apply their strengths, background knowledge, address strengths gaps in background
emotional background knowledge, life background knowledge, life experiences and and gaps in knowledge, life
development and experiences and skills to life experiences and skills skills of all students. background experiences and skills
achievement for all enhance each other’s to enhance their own knowledge, life of few students.
students. learning. learning. experiences and
• Opportunities for students • Opportunities for skills of most
Standards Basis: to utilize their individual students to utilize their students.
1A, 1B, 1C, 2A, 2B, learning patterns, habits individual learning
and needs to achieve high patterns, habits and
2C
levels of academic and needs.
social-emotional success.
Potential Sources of
Evidence: Conferences
and conversations with
the teacher; formal
observations and
walkthroughs;
classroom artifacts;
student growth
processes; analysis of
student data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 3
PLANNING
Activities (Dimension 1.4)
Dimension 1.4 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Activities: • Opportunities for students to • Questions that encourage • Questions that • Questions that • Encourages
The teacher plans generate questions that lead all students to engage in encourage all promote limited, little to no
engaging, flexible to further inquiry and complex, higher-order students to predictable or rote complex,
lessons that promote complex, higher- thinking and problem engage in responses and higher-order
encourage higher- order thinking, problem solving. complex, higher- encourage some thinking.
order thinking, solving and real-world • Instructional groups based order thinking. complex, higher- • Instructional
persistence and application on the needs of all students • Instructional order thinking. groups based on
achievement. • Instructional groups based on and maintains both group groups based on • Instructional groups the needs of a few
the needs of all students, and and individual accountability. the needs of all based on the needs of students.
allows for students to take • All students understanding students. most students. • Lack of student
Standards Basis: ownership of group and their individual roles within • All students • Most students understanding
1B, 1C, 1D, 1E individual accountability. instructional groups and understanding understanding of their
Potential Sources of • The ability for all students to facilitates opportunities for their individual their individual individual roles
Evidence: Conferences set goals, reflect on, evaluate student input on goals and roles within roles within within
and conversations with and hold each other outcomes of activities. instructional instructional instructional
the teacher; formal accountable within • Activities, resources, groups. groups. groups.
observations and instructional groups. technology and instructional • Activities, • Activities, resources, • Activities,
walkthroughs; • Activities, resources, materials that are all aligned resources, technology and/or resources,
classroom artifacts; technology and instructional to instructional purposes, technology and instructional materials technology and/or
student growth materials that are all aligned to are varied and appropriate instructional that are mostly instructional
processes; analysis of instructional purposes, are to ability levels of students. materials that are aligned to materials
student data varied and appropriate to all aligned to instructional purposes. misaligned to
ability levels of students and instructional instructional
actively engage them in purposes. purposes.
ownership of their learning.
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 4
INSTRUCTION
Achieving Expectations (Dimension 2.1)
Dimension 2.1 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Achieving • Provides opportunities for • Provides opportunities • Sets academic • Sets academic • Sets expectations
Expectations: students to establish high for students to establish expectations that expectations that that challenge few
The teacher academic and social- high academic and challenge all students. challenge most students.
supports all learners in emotional expectations social- emotional • Persists with the lesson students. • Concludes the lesson
their pursuit of high for themselves. expectations for until there is evidence • Persists with the even though there is
levels of academic and • Persists with the lesson themselves. that most students lesson until there is evidence that few
social- emotional until there is evidence • Persists with the lesson demonstrate mastery evidence that some students demonstrate
success. that all students until there is evidence of the objective. students mastery of the
demonstrate mastery of that most students • Addresses student demonstrate mastery objective.
the objective. demonstrate mastery of mistakes and follows of the objective. • Allows student
Standards Basis: the objective.
• Provides opportunities through to ensure • Sometimes mistakes to go
1B, 1D, 1E, 2A, 2C, for students to self- • Anticipates student student mastery. addresses unaddressed or
3B, 4A, 4D, 5B monitor and self-correct mistakes and encourages • Provides student confronts student
mistakes. students to avoid students mistakes. errors in a way that
Potential Sources of • Systematically enables common learning pitfalls. opportunities to • Sometimes discourages further
Evidence: Conferences students to set goals for • Establishes systems take initiative of provides effort.
and conversations with themselves and monitor where students take their own opportunities for • Rarely provides
the teacher; formal their progress over initiative of their own learning. students to take opportunities for
observations and time. learning and self- initiative of their students to take
walkthroughs; student monitor. own learning. initiative of their own
growth processes; learning.
analysis of student data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 5
INSTRUCTION
Content Knowledge and Expertise (Dimension 2.2)
Dimension 2.2 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Content Knowledge • Displays extensive content • Conveys a depth of • Conveys accurate • Conveys accurate content • Conveys inaccurate
and Expertise: knowledge of all the subjects content knowledge that content knowledge knowledge. content knowledge
The teacher uses she or he teaches and closely allows for differentiated in multiple contexts. • Sometimes integrates that leads to
content and related subjects. explanations. • Integrates learning objectives with student confusion.
pedagogical • Integrates learning • Integrates learning learning other disciplines. • Rarely integrates
expertise to design objectives with other objectives with other objectives with • Sometimes anticipates learning
and execute lessons disciplines, content areas disciplines and real- other possible student objectives with
aligned with state and real-world experience. world experiences. disciplines. misunderstandings. other disciplines.
standards, related • Consistently anticipates • Anticipates possible • Anticipates possible • Sometimes provides • Does not anticipate
possible student student student opportunities for students possible student
content and student
misunderstandings and misunderstandings and misunderstandings. to use different types of misunderstandings.
needs. proactively develops
proactively develops • Provides thinking (e.g., analytical, • Provides few
teaching techniques to teaching techniques to opportunities for practical, creative and opportunities for
Standards Basis: 1A, mitigate concerns. mitigate concerns. students to use research-based). students to use
1C, 1E, 1F, 2C, 3A, • Consistently provides • Regularly provides different types of different types of
3B, 3C opportunities for students opportunities for thinking (e.g., thinking (e.g.,
to use different types of students to use analytical, practical, analytical, practical,
thinking (e.g., analytical, different types of creative and creative and
Potential Sources of
practical, creative and thinking (e.g., analytical, research- based). research- based).
Evidence:
research-based). practical, creative and • Accurately reflects
Conferences and
• Sequences instruction that research-based). how the lesson fits
conversations with
allows students to • Sequences instruction within the structure
the teacher; formal
understand how the lesson that allows students to of the discipline and
observations and
fits within the structure of understand how the the state standards.
walkthroughs; student
the discipline, the state lesson fits within the
growth processes;
standards, related content structure of the discipline
analysis of student
and within real-world and the state standards.
data
scenarios.
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 6
INSTRUCTION
Communication (Dimension 2.3)
Dimension 2.3 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Communication: • Establishes classroom • Establishes classroom • Establishes classroom • Leads lessons with • Directs lessons with
The teacher clearly practices that encourage all practices that encourage practices that provide some opportunity for little opportunity for
and accurately students to communicate all students to opportunities for dialogue, clarification dialogue, clarification
communicates to safely and effectively using a communicate effectively, most students to or elaboration. or elaboration.
variety of tools and methods including the use of visual communicate • Recognizes student • Is sometimes unaware
support persistence,
with the teacher and their tools and technology, with effectively with the misunderstandings of or unresponsive to
deeper learning and
peers. the teacher and their teacher and their but has a limited student
effective effort. • Uses possible student peers. peers. ability to respond. misunderstandings.
misunderstandings at strategic • Anticipates possible • Recognizes student • Uses verbal and • Uses verbal
Standards Basis: points in lessons to highlight student misunderstandings written communication that is
1D, 1E, 2A, 3A, 4D misconceptions and inspire misunderstandings and and responds with communication that characterized by
exploration and discovery. proactively develops an array of teaching is generally clear inaccurate grammar;
Potential Sources of • Provides explanations that are techniques to address techniques to with minor errors of written communication
Evidence: clear and coherent and uses obstacles to learning. clarify concepts. grammar. that has inaccurate
Conferences and verbal and written • Provides explanations that • Provides explanations • Asks remember and spelling, grammar,
conversations with communication that is clear are clear and coherent that are clear and understand level punctuation or
the teacher; formal and correct. and uses verbal and uses verbal and questions that focus structure.
observations and • Asks questions at the creative, written communication written on the objective of • Rarely asks questions,
walkthroughs; student evaluative and/or analysis that is clear and correct. communication that is the lesson but do or asks questions that
growth processes; levels that require a deeper • Asks questions at the clear and correct. little to amplify do not amplify
analysis of student learning and broader creative, evaluative • Asks remember, discussion. discussion or align to
data understanding of the and/or analysis levels that understand and apply the objective of the
objective of the lesson. focus on the objective of level questions that lesson.
• Skillfully balances wait time, the lesson and provoke focus on the
questioning techniques and thought and discussion. objective of the
integration of student • Skillfully uses lesson and provoke
responses to support student- probing questions discussion.
directed learning. to clarify, elaborate • Uses probing
• Skillfully provokes and guides and extend learning. questions to clarify
discussion to pique curiosity • Provides wait time when and elaborate
and inspire student-led questioning students. learning.
learning of meaningful and
challenging content.
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 7
INSTRUCTION
Differentiation (Dimension 2.4)
Dimension 2.4 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Differentiation:
• Adapts lessons with a wide • Adapts lessons to • Adapts lessons to • Adapts lessons to • Provides one-size-fits-
The teacher
variety of instructional address individual needs address individual address some all lessons without
differentiates
strategies to address of all students. needs of all students. student needs. meaningful
instruction, aligning
individual needs of all • Regularly monitors • Regularly monitors • Sometimes differentiation.
methods and
students. the quality of student the quality of monitors the quality • Rarely monitors the
techniques to
• Consistently monitors the participation and student of student quality of student
diverse student participation and
quality of student performance. participation and participation and
needs. performance.
participation and • Regularly provides performance. performance.
performance. differentiated instructional • Provides differentiated • Sometimes provides • Rarely provides
Standards Basis: • Always provides methods and content to instructional methods differentiated differentiated
1C, 1F, 2A, 2B, 2C, differentiated instructional ensure students have the and content to ensure instructional methods instructional
3C, 4A, 5A, 5C, methods and content to opportunity to master students have the and content. methods and
5D ensure students have the what is being taught. opportunity to master • Sometimes recognizes content.
opportunity to master what • Proactively minimizes what is being taught. when students become • Does not recognize
is being taught. student confusion or • Recognizes when confused or disengaged when students
Potential Sources of • Consistently prevents disengagement by students become and minimally responds become confused or
Evidence: student confusion or addressing learning confused or disengaged to student learning or disengaged, or does
Conferences and disengagement by and/or social/emotional and responds to student social/emotional needs. not respond
conversations with addressing learning and/or needs of all students. learning or appropriately to
the teacher; formal social/emotional needs of social/emotional needs. student learning or
observations and all students. social/ emotional
walkthroughs; needs.
classroom artifacts;
student growth
processes; analysis of
student data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 8
INSTRUCTION
Monitor and Adjust (Dimension 2.5)
Dimension 2.5 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Monitor and Adjust:
• Systematically gathers • Utilizes input from • Consistently invites • Sometimes utilizes • Rarely utilizes input
The teacher formally
input from students in students in order to input from students in input from students in from students in order
and informally
order to monitor and monitor and adjust order to monitor and order to monitor and to monitor and adjust
collects, analyzes adjust instruction, instruction, activities and adjust instruction and adjust instruction and instruction and
and uses student activities or pacing to pacing to respond to activities. activities. activities.
progress data and respond to differences differences in student • Adjusts instruction • Adjusts some • Persists with instruction
makes needed in student needs. needs. and activities to instruction within a or activities that do not
lesson adjustments. • Adjusts instruction • Adjusts instruction maintain student limited range. engage students.
and activities to and activities to engagement. • Sees student behavior • Generally does not
Standards Basis: maintain student maintain student • Monitors student but misses some signs link student behavior
engagement. engagement. behavior and responses of disengagement. and responses with
1D, 1F, 2B, 2C, 3B,
• Uses discreet and • Continually checks for for engagement and • Is aware of most student student engagement
4D, 5C, 5D explicit checks for understanding through understanding. responses but misses and understanding.
understanding purposeful questioning some clues of • Makes no attempts
Potential Sources of through questioning and academic feedback. misunderstanding. to engage students
Evidence: and academic who appear
Conferences and feedback. disengaged or
conversations with disinterested.
the teacher; formal
observations and
walkthroughs;
classroom artifacts;
student growth
processes; analysis of
student data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 9
LEARNING ENVIRONMENT
Classroom Environment, Routines and Procedures (Dimension 3.1)
Dimension 3.1 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Classroom
Environment, • Establishes and uses • Establishes and uses • All procedures, • Most procedures, • Few procedures and
effective routines, effective routines, routines and routines and transitions routines guide student
Routines and
transitions and transitions and transitions are clear provide clear direction behavior and maximize
Procedures: procedures that procedures that she or and efficient. but others are unclear learning. Transitions are
The teacher primarily rely on he implements • Students actively and inefficient. characterized by
organizes a safe, student leadership effortlessly. participate in groups, • Students depend on the confusion and
accessible and and responsibility. • Students take some manage supplies and teacher to direct them in inefficiency.
efficient classroom. • Students take primary responsibility for equipment with very managing student • Students often do
leadership and managing student limited teacher groups, supplies and/or not understand
Standards Basis: responsibility for groups, supplies and/or direction. equipment. what is expected of
managing student equipment. • The classroom is safe and • The classroom is safe and them.
1D, 4A, 4B, 4C, 4D
groups, supplies, • The classroom is safe, organized to support accessible to most • The classroom is
and/or equipment. inviting and organized to learning objectives and is students, but is unsafe, disorganized
Potential Sources of
• The classroom is safe support learning accessible to most disorganized and and uncomfortable.
Evidence:
and thoughtfully objectives and is students. cluttered. • Some students are not
Conferences and
designed to engage, accessible to all able to access materials.
conversations with challenge and inspire students.
the teacher; formal students to
observations and participate in high-
walkthroughs; level learning beyond
classroom artifacts; the learning
analysis of student objectives.
data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 10
LEARNING ENVIRONMENT
Managing Student Behavior (Dimension 3.2)
Dimension 3.2 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Managing Student
Behavior: • Consistently monitors • Consistently • Consistently implements • Inconsistently • Rarely or unfairly
behavior subtly, encourages and the campus and/or implements the campus enforces campus or
The teacher
reinforces positive monitors student classroom behavior and/or classroom classroom behavior
establishes, behaviors behavior subtly and system proficiently. behavior system. standards.
communicates and appropriately and responds to • Most students • Student failure to • Student behavior
maintains clear intercepts misbehavior swiftly. meet expected meet expected impedes learning in the
expectations for misbehavior fluidly. • Most students know, classroom classroom behavior classroom.
student behavior. • Students and the understand and behavior standards interrupts
teacher create, adopt respect classroom standards. learning.
Standards Basis: and maintain behavior standards.
classroom behavior
4A, 4B, 4C, 4D
standards.
Potential Sources of
Evidence:
Conferences and
conversations with
the teacher; formal
observations and
walkthroughs;
classroom artifacts;
analysis of student
data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 11
LEARNING ENVIRONMENT
Classroom Culture (Dimension 3.3)
Dimension 3.3 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Classroom Culture:
The teacher leads a • Consistently engages • Engages all students • Engages all students • Establishes a learning • Establishes a learning
all students with with relevant, in relevant, environment where most environment where few
mutually respectful
relevant, meaningful meaningful learning, meaningful students are engaged in students are engaged in
and collaborative learning based on their sometimes adjusting learning. the curriculum. the curriculum.
class of actively interests and abilities lessons based on • Students work • Students are sometimes • Students are
engaged learners. to create a positive student interests and respectfully individually disrespectful of each disrespectful of each
rapport amongst abilities. and in groups. other. other and of the
Standards Basis: students. • Students collaborate teacher.
1E, 1F, 3B, 4C, 4D, • Students collaborate positively with each
positively and other and the teacher.
5A, 5B, 5D
encourage each
other’s efforts and
Potential Sources of achievements.
Evidence:
Conferences and
conversations with
the teacher; formal
observations and
walkthroughs;
classroom artifacts;
analysis of student
data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 12
PROFESSIONAL PRACTICES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
Professional Demeanor and Ethics (Dimension 4.1)
Dimension 4.1 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Professional • Behaves in accordance • Behaves in accordance • Behaves in accordance • Behaves in accordance • Fails to meet the Code
Demeanor and with the Code of Ethics with the Code of Ethics with the Code of Ethics with the Code of Ethics of Ethics and Standard
Ethics: and Standard Practices and Standard Practices and Standard Practices and Standard Practices Practices for Texas
The teacher meets for Texas Educators. for Texas Educators. for Texas Educators. for Texas Educators. Educators.
district expectations • Models all professional • Models all professional • Meets all professional • Meets most professional • Meets few professional
for attendance, standards (e.g., standards (e.g., standards (e.g., standards (e.g., standards (e.g.,
professional attendance, attendance, professional attendance, professional attendance, professional attendance, professional
appearance, professional appearance and appearance and appearance and appearance and
decorum, appearance and behaviors) within the behaviors). behaviors). behaviors) or violates
behaviors) across the classroom. • Advocates for the needs legal requirements.
procedural, ethical,
campus and district for • Advocates for the needs of students in the
legal and statutory educators and students. classroom.
of all students in the
responsibilities. • Advocates for the classroom.
needs of all students in
Standards Basis: the classroom and
6B, 6C, 6D campus.
Potential Sources of
Evidence:
Conferences and
conversations with
the teacher; formal
observations and
walkthroughs;
classroom artifacts;
analysis of student
data; daily
interaction with
others
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 13
PROFESSIONAL PRACTICES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
Goal Setting (Dimension 4.2)
Dimension 4.2 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Goal Setting:
The teacher • Consistently sets, • Sets some short- and • Sets short- and long-term • Sets short-term goals • Sets low or ambiguous
modifies and meets long- term professional professional goals based based on self-assessment. goals unrelated to
reflects on
short- and long- goals based on self- on self-assessment, • Meets most professional student needs or self-
his/her practice. term professional assessment, reflection, reflection and supervisor assessment.
goals resulting in some
goals based on self- peer and supervisor feedback. visible changes in • Meets few professional
Standards Basis: assessment, feedback, contemporary • Meets all professional practice. goals and persists in
5D, 6A, 6B reflection, peer and research and analysis of goals resulting in instructional practices
supervisor feedback, student learning. improvement in practice that remain substantially
Potential Sources of contemporary • Meets all professional and student performance. unimproved over time.
Evidence: Goal- research and goals resulting in
analysis of student improvement in practice
setting and
learning. and student performance.
professional
• Implements
development plan substantial
(GSPD); conferences changes in
and conversations practice resulting
with the teacher, in significant
including the end-of- improvement in
year conference; student
analysis of student performance.
data
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 14
PROFESSIONAL PRACTICES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
Professional Development (Dimension 4.3)
Dimension 4.3 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
Professional • Leads colleagues • Leads colleagues • Collaboratively practices • Engages in most • Engages in few
Development: collaboratively in and collaboratively on in all scheduled scheduled professional professional
The teacher beyond the school to campus to identify professional development activities, development activities,
enhances the identify professional professional development activities, professional learning professional learning
professional development needs development needs campus professional communities, committee, communities or
community. through detailed data through self- learning communities, grade- or subject-level committees to improve
analysis and self- reflection. grade- or subject-level team meetings as professional practice.
reflection. • Fosters faculty team membership, directed.
Standards Basis:
• Seeks resources and knowledge and skills in committee membership
3A, 6A, 6B, 6C collaboratively support of the school or other opportunities.
fosters faculty improvement plan
Potential Sources of knowledge and skills. through professional
Evidence: Goal- • Develops and fulfills the learning communities,
setting and school and district grade- or subject-level
professional improvement plans team leadership,
development plan through professional committee
(GSPD); conferences learning communities, membership or other
and conversations grade- or subject- level opportunities beyond
team leadership, the campus.
with the teacher,
committee leadership or
including the end-of-
other opportunities
year conference; beyond the campus.
analysis of student
data; daily
interaction with
others
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 15
PROFESSIONAL PRACTICES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
School Community Involvement (Dimension 4.4)
Dimension 4.4 DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
School Community
Involvement: • Systematically • Systematically contacts • Contacts • Contacts • Contacts parents
contacts parents/ parents/guardians parents/guardians parents/guardians in generally about
The teacher
guardians regarding regarding students’ regularly regarding accordance with campus disciplinary matters.
demonstrates students’ academic academic and students’ academic and policy. • Attends few required
leadership with and social/emotional social/emotional social/emotional growth. • Attends most required school outreach
students, colleagues, growth through growth through various • Actively participates in school outreach activities.
and community various methods. methods. all school outreach activities.
members in the • Initiates • Joins colleagues in activities • Communicates school
school, district and collaborative collaborative efforts • Communicates the goals to students,
community through efforts that that enhance student mission, vision and goals parents and families.
effective enhance student learning and welfare. of the school to
communication and learning and • Clearly communicates students, colleagues,
growth. the mission, vision and parents and families.
outreach.
• Leads students, goals of the school to
colleagues, families students, colleagues,
Standards Basis: and community parents and families,
2A, 2B, 4A, 4D, 5B, members toward and other community
6B, 6C, 6D reaching the mission, members.
vision and goals of the
school.
Potential Sources of
Evidence:
Conferences and
conversations with
the teacher,
including the end-of-
year conference;
classroom artifacts;
student data; daily
interaction with
others
STUDENT-CENTERED ACTIONS TEACHER-CENTERED ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 16
RUBRIC WORD BANK
(with examples of qualifiers that are interchangeably used)
DIMENSION EXAMPLE: DISTINGUISHED ACCOMPLISHED PROFICIENT DEVELOPING IMPROVEMENT NEEDED
LEARNING ENVIRONMENT:
ALL ALL ALL MOST FEW
CLASSROOM CULTURE
LEARNING ENVIRONMENT:
MANAGING STUDENT CONSISTENTLY CONSISTENTLY CONSISTENTLY INCONSISTENTLY RARELY
BEHAVIOR
INSTRUCTION:
ACHIEVING EXPECTATIONS ALL MOST MOST SOME FEW
INSTRUCTION:
CONTENT KNOWLEDGE AND
CONSISTENTLY REGULARLY DOES (ACTION) SOMETIMES FEW
EXPERTISE
INSTRUCTION:
ALWAYS REGULARLY DOES (ACTION) SOMETIMES DOES NOT (ACTION)
DIFFERENTIATION
FOCUSES ON FOCUSES ON FOCUSES ON
MOVES TO MOVES TO
MOSTLY TEACHER- TEACHER-
STUDENTCENTERED STUDENTCENTERED
TEACHER- CENTERED CENTERED
ACTIONS ACTIONS
CENTERED ACTIONS ACTIONS
ACTIONS
© TEA 2/10/2022 T-TESS Rubric-Working Copy 17
You might also like
- VSP - Multi Cloud Solutions - AssessmentDocument2 pagesVSP - Multi Cloud Solutions - AssessmentrkkkNo ratings yet
- Betcher Alexander Edfd548 Assignment 1-3Document3 pagesBetcher Alexander Edfd548 Assignment 1-3api-433580241No ratings yet
- Snu 4BDocument233 pagesSnu 4BJS Lee100% (1)
- Formal EvaluationDocument14 pagesFormal Evaluationapi-605133868No ratings yet
- What Are The Principles of PlanningDocument7 pagesWhat Are The Principles of Planningisabel oliveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Assessment of Student's Learning in The Philippine SettingDocument20 pagesChapter 1: Assessment of Student's Learning in The Philippine SettingHaezil MioleNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis: Utilising Data To Inform The Instruction Process January 2020Document36 pagesData Analysis: Utilising Data To Inform The Instruction Process January 2020Althaf MubinNo ratings yet
- ERA Curriculum Farzana 16-12-14Document48 pagesERA Curriculum Farzana 16-12-14Yongho LouisNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan RubricDocument1 pageLesson Plan RubricKen Neth Ray Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- Project Based Teaching dr3 PDFDocument4 pagesProject Based Teaching dr3 PDFandreiasalgueiro1923No ratings yet
- Summer Institute Guide To Facilitation Math.2018Document30 pagesSummer Institute Guide To Facilitation Math.2018David WalkeNo ratings yet
- T-TESS Virtual Instruction RubricDocument17 pagesT-TESS Virtual Instruction RubricKimberly BubenikNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Lesson PlansDocument29 pagesSession 2 - Lesson PlansHussein AlwaseefNo ratings yet
- StdsplanningunlockingDocument80 pagesStdsplanningunlockingapi-649376507No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Instructional DesignDocument21 pagesTopic 2 - Instructional DesignHamizah ZuhairahNo ratings yet
- EllisonDocument32 pagesEllisonapi-434245139No ratings yet
- Language Assessment Module MINED - InATECDocument23 pagesLanguage Assessment Module MINED - InATECGerardoNo ratings yet
- Planning For Learning and AssessmentDocument3 pagesPlanning For Learning and AssessmentTami WeissNo ratings yet
- CH 4 SlidesDocument16 pagesCH 4 SlidesCameron BezuidenhoutNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment For The K-12 Basic Education ProgramDocument43 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment For The K-12 Basic Education Programanon_601516922No ratings yet
- Visual Literacy Lesson Plan Assignment 2023Document4 pagesVisual Literacy Lesson Plan Assignment 2023api-742522303No ratings yet
- Name of Pre-Service Teacher: Subject Area: Date:: Lesson Plan RubricDocument3 pagesName of Pre-Service Teacher: Subject Area: Date:: Lesson Plan Rubricjustin may tuyorNo ratings yet
- FPAW in Person Participant Packet October 21 2022Document84 pagesFPAW in Person Participant Packet October 21 2022stem schoolNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Preliminary Concepts and Recent Trends: Assessment in Learning 1Document35 pagesUnit 1: Preliminary Concepts and Recent Trends: Assessment in Learning 1ronatabbu100% (1)
- Levels of Practice #6 - Curriculum, Instruction and AssessmentDocument2 pagesLevels of Practice #6 - Curriculum, Instruction and AssessmentLanguages CoordinationNo ratings yet
- TAPS - Reference - Sheet 6-5-14 PDFDocument2 pagesTAPS - Reference - Sheet 6-5-14 PDFjenNo ratings yet
- National Teachers StandardsDocument17 pagesNational Teachers Standardstahiru jaraaNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan & Teaching DemoDocument2 pagesInstructional Plan & Teaching DemoJOSEPH GABRIEL EDUCADONo ratings yet
- Relation To Learning Standards and in TheDocument17 pagesRelation To Learning Standards and in TheLea Lian Aquino AbejeroNo ratings yet
- 1ab - Basics of Language TestingDocument4 pages1ab - Basics of Language TestingAbas HadizadehNo ratings yet
- Parts of Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesParts of Lesson PlanedmyrnNo ratings yet
- Domain 1 Artifacts 4 Column - TeachersDocument4 pagesDomain 1 Artifacts 4 Column - Teachersapi-384069095No ratings yet
- Criteria in Evaluating A Training ProgramDocument2 pagesCriteria in Evaluating A Training ProgramMuslim SeekerNo ratings yet
- Assessment of LearningDocument3 pagesAssessment of LearningfloresstephaniejoycNo ratings yet
- Visual Literacy Lesson Plan AssignmentDocument3 pagesVisual Literacy Lesson Plan Assignmentapi-547119633No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Evaluation Rubric InstructionsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Evaluation Rubric InstructionsDNo ratings yet
- Performance-Based TaskDocument4 pagesPerformance-Based TaskMarivic OsmanNo ratings yet
- Logical Framework Matrix and WorkplanDocument7 pagesLogical Framework Matrix and WorkplanEmmigidius EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Training For Master Teacher On The Philippine Professional Standards For TeachersDocument48 pagesTraining For Master Teacher On The Philippine Professional Standards For TeachersAngelica Fojas RañolaNo ratings yet
- Process Oriented AssessmentDocument20 pagesProcess Oriented AssessmentMary Ann DalaguitNo ratings yet
- Compiled & Presented by Michele Walden-PinnockDocument37 pagesCompiled & Presented by Michele Walden-PinnockNOXIOUSNo ratings yet
- Professional Learning Portfolio ConstructionDocument32 pagesProfessional Learning Portfolio ConstructionRaghu ChintuNo ratings yet
- 9 Che Ix 202324Document21 pages9 Che Ix 202324shivam9087jijNo ratings yet
- Frwk17 Case Study 2 Monitoring and TrackingDocument10 pagesFrwk17 Case Study 2 Monitoring and TrackingTogrul NesibliNo ratings yet
- Marzano Teacher Evaluation Model All 8 QuestionsDocument26 pagesMarzano Teacher Evaluation Model All 8 Questionskeila mercedes schoolNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Curriculum AssessmentDocument30 pagesCriteria For Curriculum AssessmentMissia H. Sabtal67% (3)
- Student Assessment Appendix B: Rating Adjectival Rating Range PercentageDocument6 pagesStudent Assessment Appendix B: Rating Adjectival Rating Range PercentageMARCELO, FRANCIS MICHAEL S.No ratings yet
- Direct Assessment of Learning OutcomesDocument27 pagesDirect Assessment of Learning OutcomesAhmed ElkomyNo ratings yet
- Instructional Materials Evaluation Criteria - MathematicsDocument5 pagesInstructional Materials Evaluation Criteria - MathematicsVillanueva Ameera MaeNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3218698095482873397Document36 pagesInbound 3218698095482873397Rodel Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- EDUC612 Lesson Plan RubricDocument3 pagesEDUC612 Lesson Plan RubricMay IinhNo ratings yet
- Ncte Conference Class Hamre PDFDocument47 pagesNcte Conference Class Hamre PDFLeslie SolayaoNo ratings yet
- PBLWorks Project Based Teaching Rubric v2019 PDFDocument4 pagesPBLWorks Project Based Teaching Rubric v2019 PDFLaura RojasNo ratings yet
- TOS Samples 1Document11 pagesTOS Samples 1Dominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Edtp 4302 A&eDocument6 pagesEdtp 4302 A&eAshley HernandezNo ratings yet
- Rubric Feasibility StudyDocument1 pageRubric Feasibility Studyafvillodres7471No ratings yet
- Educ206 - Module 1Document8 pagesEduc206 - Module 1Genevieve Viesca FuyonanNo ratings yet
- The 2010 Secondary Education CurriculumDocument35 pagesThe 2010 Secondary Education CurriculumMarvin ValienteNo ratings yet
- Taule BachainDocument38 pagesTaule BachainJeah mae TauleNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2Document26 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2Andrea Nicole BalaresNo ratings yet
- 3-Day Professional Development PlanDocument3 pages3-Day Professional Development PlanCarolina Del RioNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis & Probability - Task & Drill Sheets Gr. 6-8From EverandData Analysis & Probability - Task & Drill Sheets Gr. 6-8No ratings yet
- Prof Ed: 50 Questions W/ Answers Part 2Document28 pagesProf Ed: 50 Questions W/ Answers Part 2Jane Uranza CadagueNo ratings yet
- Tallinna Inglise Kolledži RaamatukoguDocument5 pagesTallinna Inglise Kolledži RaamatukoguLiina LelovNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 1 Module 2Document12 pagesProf. Ed. 1 Module 2Alyssa May Tabinas OxinaNo ratings yet
- Em 314Document32 pagesEm 314Aristotle GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter 2023 - 2024 Exam TOS Practical ResearchDocument1 page1st Quarter 2023 - 2024 Exam TOS Practical ResearchJefferson Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- CBC Elect Install and Maint NC II 2017Document63 pagesCBC Elect Install and Maint NC II 2017ralphNo ratings yet
- 3 Levin LongDocument113 pages3 Levin LongSisma rellyNo ratings yet
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument10 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersMohammad Shahidullah ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- RW 1st Summative TestDocument2 pagesRW 1st Summative TestLejeb TCNo ratings yet
- Teacher Development: An International Journal of Teachers' Professional DevelopmentDocument4 pagesTeacher Development: An International Journal of Teachers' Professional DevelopmentShipra Sudeshna Rohini MinzNo ratings yet
- Resume For MB HydroDocument2 pagesResume For MB Hydroapi-608285654No ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics SBA Ideas and Topics - CSEC Math TutorDocument1 pageCSEC Mathematics SBA Ideas and Topics - CSEC Math TutorJaviene JamesNo ratings yet
- McCormack & Slaght 2012Document157 pagesMcCormack & Slaght 2012Ánh Lê QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Elec 301, Unit 2 - Lesson 1Document6 pagesElec 301, Unit 2 - Lesson 1Justine Obo100% (1)
- Adv Eng Induction 2024 (BPS 1-15)Document6 pagesAdv Eng Induction 2024 (BPS 1-15)adeelsoomro012345No ratings yet
- WEEKLY LEARNING PLAN 2021 2022 WK 7Document6 pagesWEEKLY LEARNING PLAN 2021 2022 WK 7Ida May LaboreraNo ratings yet
- Aqa Igcse English Literature Coursework ExemplarsDocument4 pagesAqa Igcse English Literature Coursework Exemplarsafjwoamzdxwmct100% (1)
- MODULE NO. 2 Homework Template - Verb BE - SaulFrancoDocument4 pagesMODULE NO. 2 Homework Template - Verb BE - SaulFrancoAlejandra PinedaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 ValuesDocument15 pagesGrade 4 Valuescollen corminalNo ratings yet
- Improving The Vocabulary Mastery Using Inquiry-Based LEARNING (A Classroom Action Research in The Fifth Grade of SDNDocument9 pagesImproving The Vocabulary Mastery Using Inquiry-Based LEARNING (A Classroom Action Research in The Fifth Grade of SDNDjo HNo ratings yet
- CA1 Productive People: Looking Back: Pre-TasksDocument4 pagesCA1 Productive People: Looking Back: Pre-TasksJuan Pablo BlanchNo ratings yet
- Certification of Assumption To Duty: Department of Education Schools Division of SiargaoDocument1 pageCertification of Assumption To Duty: Department of Education Schools Division of SiargaoricksNo ratings yet
- Regarding Japanese Language Class at Terakoya AcademiaDocument2 pagesRegarding Japanese Language Class at Terakoya Academiasaroj khanalNo ratings yet
- Cot Q4 Week4Document9 pagesCot Q4 Week4cattleyaJoy TaparNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document9 pagesHomeroom Guidance: Quarter 1 - Module 3Raphael MananganNo ratings yet
- Difference Between C.V & ResumeDocument3 pagesDifference Between C.V & ResumePradeepYadavNo ratings yet
- Attestation Process Checklist: First Name Middle Name Surname Extension NameDocument17 pagesAttestation Process Checklist: First Name Middle Name Surname Extension NameJhude Ravilas100% (1)
- Grade 1 Math Q2 PTDocument5 pagesGrade 1 Math Q2 PTchristine lozantaNo ratings yet