Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standard For Steel Roof Deck: CSSBI 10M - 08 October 2008
Standard For Steel Roof Deck: CSSBI 10M - 08 October 2008
Uploaded by
Anonymous P73cUg73LCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Joist LH DLH SeriesDocument13 pagesJoist LH DLH SeriescadsultanNo ratings yet
- Steel Joists - MST PDFDocument7 pagesSteel Joists - MST PDFwafikmh4No ratings yet
- AISI S214-07 Standard and Commentary (1st Printing) PDFDocument54 pagesAISI S214-07 Standard and Commentary (1st Printing) PDFthjozsefNo ratings yet
- Icbo Es Report-Er2078pDocument65 pagesIcbo Es Report-Er2078peltorro-tNo ratings yet
- Element of Space Making PDFDocument99 pagesElement of Space Making PDFsrishti bhowal100% (1)
- Hotel Centre PointDocument18 pagesHotel Centre PointTanvir AliNo ratings yet
- Kahlil Gibran-Love LettersDocument4 pagesKahlil Gibran-Love Lettersapi-3737310100% (2)
- Stability of SpeedCore Walls Under Fire Loading Summary of Numerical AnalysesDocument13 pagesStability of SpeedCore Walls Under Fire Loading Summary of Numerical Analysesjackcan501No ratings yet
- The Development of A New Design Procedure For Conventional Single-Plate Shear ConnectionsDocument12 pagesThe Development of A New Design Procedure For Conventional Single-Plate Shear ConnectionsMiguelNo ratings yet
- OPSS 906 - Nov12Document20 pagesOPSS 906 - Nov12umerfr2No ratings yet
- Algoma Steel Sheet PDFDocument10 pagesAlgoma Steel Sheet PDFSH1961No ratings yet
- Washers, Steel, Plain (Flat), Unhardened For General UseDocument4 pagesWashers, Steel, Plain (Flat), Unhardened For General UsekrutikNo ratings yet
- Design Guide Spec and Manual ReferencesDocument2 pagesDesign Guide Spec and Manual ReferencesRiza SuwondoNo ratings yet
- Geometric Properties of Hot-Rolled Steel Angles Including The Effects of Toe Radii and FilletDocument10 pagesGeometric Properties of Hot-Rolled Steel Angles Including The Effects of Toe Radii and FilletDianna Lambert100% (1)
- Aisi S907-13Document34 pagesAisi S907-13Edison BecerraNo ratings yet
- Aisc - StudentDocument148 pagesAisc - StudentRamiro Flores MoraNo ratings yet
- Mil C 39012CDocument57 pagesMil C 39012CMITHUN.V POWARNo ratings yet
- Astm A36 1977Document6 pagesAstm A36 1977Ben Yie Min100% (1)
- Astm C955-09Document4 pagesAstm C955-09rodrigoNo ratings yet
- Schedule 40 Pipe, Galvanized: ASTM F1043 Group I-A, Federal Specification RR-F-191 Type 1, Grade A, AASHTO M-181 Grade 1Document2 pagesSchedule 40 Pipe, Galvanized: ASTM F1043 Group I-A, Federal Specification RR-F-191 Type 1, Grade A, AASHTO M-181 Grade 1Caolboy ButchNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Screws Through Gypsum Board Wall Sheathing: RecentlyDocument4 pagesSheet Metal Screws Through Gypsum Board Wall Sheathing: Recentlytigani brigdarNo ratings yet
- Size RangeDocument15 pagesSize RangelucidbaseNo ratings yet
- Astm D2729 PDFDocument2 pagesAstm D2729 PDFShan Adrias100% (1)
- AISI Manual Cold-Formed Steel Design 2002 EditionDocument462 pagesAISI Manual Cold-Formed Steel Design 2002 EditionVatova JarrandNo ratings yet
- 05.40.00 Cold-Formed Metal Framing Specification Updated June 2015Document26 pages05.40.00 Cold-Formed Metal Framing Specification Updated June 2015mishikhanNo ratings yet
- Astm A325 PernosDocument14 pagesAstm A325 PernosDiego Lever TorresNo ratings yet
- AISIS240 15 (1stprinting)Document204 pagesAISIS240 15 (1stprinting)Roberto Pérez LeónNo ratings yet
- Pren 14509 51 - e - STF PDFDocument147 pagesPren 14509 51 - e - STF PDFBoris Dikov100% (2)
- Astm A1063A1063MDocument11 pagesAstm A1063A1063Mارفع راسك فوق انت يمنيNo ratings yet
- ANSI RD1.0 - 2006 - Standard For Steel Roof DeckDocument5 pagesANSI RD1.0 - 2006 - Standard For Steel Roof DeckDaniel PereiraNo ratings yet
- A 586Document4 pagesA 586Gustavo SuarezNo ratings yet
- Night School 23 Session 2Document41 pagesNight School 23 Session 2Luis CortesNo ratings yet
- AISI S211-07 (Raffirmed 2012) - E1Document2 pagesAISI S211-07 (Raffirmed 2012) - E1Jon JacobsNo ratings yet
- 3090 Slope Build Up NH PDFDocument2 pages3090 Slope Build Up NH PDFTodd St. GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Problem 1-015 PDFDocument3 pagesProblem 1-015 PDFOscar SanchezNo ratings yet
- b905 SBDH Chapter05Document35 pagesb905 SBDH Chapter05qgfytzvqabzqrxyilmNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Manual - Google SearchDocument3 pagesSeismic Design Manual - Google Searchchondroc110% (1)
- Specification For Structural Quality Steels: SA/CSA-G40.21Document7 pagesSpecification For Structural Quality Steels: SA/CSA-G40.21Meyer Antonio LozanoNo ratings yet
- High-Strength Steel Bolts, Classes 10.9 and 10.9.3, For Structural Steel Joints (Metric)Document6 pagesHigh-Strength Steel Bolts, Classes 10.9 and 10.9.3, For Structural Steel Joints (Metric)Ngoc BuiNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Design Manual: FOURTH EDITION - First PrintingDocument1 pageDiaphragm Design Manual: FOURTH EDITION - First Printingaandueza_1No ratings yet
- Section - 05520 - Handrails and RailingsDocument3 pagesSection - 05520 - Handrails and RailingsNana DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Stud Welding: State-Of-The-Art PaperDocument13 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Stud Welding: State-Of-The-Art Paperalbert limantonoNo ratings yet
- AISI S230-12-E1Document2 pagesAISI S230-12-E1Jon JacobsNo ratings yet
- Astm C90 16Document5 pagesAstm C90 16Arquiva SA de CVNo ratings yet
- Design of Pallet Rack Upright Frames Subject To CompressionDocument107 pagesDesign of Pallet Rack Upright Frames Subject To CompressionssierroNo ratings yet
- Ansi c80-6 2005Document22 pagesAnsi c80-6 2005supervisor.electricistaNo ratings yet
- CJP & PJPDocument3 pagesCJP & PJPRobertBostanNo ratings yet
- Astm - E1996-09Document13 pagesAstm - E1996-09Raju KCNo ratings yet
- Don't Put Welds in BendingDocument2 pagesDon't Put Welds in BendingRune OveraasNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Strength of Fillet Welded Connections Loaded in PlaneDocument13 pagesUltimate Strength of Fillet Welded Connections Loaded in PlanePatrick PolujanNo ratings yet
- Sherman - Extended Shear TabsDocument148 pagesSherman - Extended Shear TabsRohan KarandeNo ratings yet
- Astm F 568MDocument9 pagesAstm F 568MZahoor Ahmed MohsanNo ratings yet
- NBC 2010 - Commentaries - Section IDocument24 pagesNBC 2010 - Commentaries - Section IRick HenbidNo ratings yet
- Mixing Weld and Bolt Part2Document4 pagesMixing Weld and Bolt Part2ihpeterNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification For Cast-in-Place Nonreinforced Concrete Pipe (ACI 346-90) (Reapproved 1997)Document7 pagesStandard Specification For Cast-in-Place Nonreinforced Concrete Pipe (ACI 346-90) (Reapproved 1997)nathanNo ratings yet
- AISI DSM Design Guide Schafer VersionDocument180 pagesAISI DSM Design Guide Schafer VersionOmar Eduardo Alvarado Valle100% (1)
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Plates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and AnalysisFrom EverandPlates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CSSBI-12M-13 - Standard For Composite Steel DeckDocument9 pagesCSSBI-12M-13 - Standard For Composite Steel DeckjulianobiancoNo ratings yet
- CSSBI 12M-2015:: Standard For Composite Steel DeckDocument7 pagesCSSBI 12M-2015:: Standard For Composite Steel DeckPhablo GustavoNo ratings yet
- Hwachong - Oxbridge Admissions For Singaporean ApplicantsDocument14 pagesHwachong - Oxbridge Admissions For Singaporean ApplicantsAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Stair RailDocument1 pageStair RailAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- HSBC Investments Investdirect Hsbc-Hidc-Brochure - enDocument2 pagesHSBC Investments Investdirect Hsbc-Hidc-Brochure - enAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- SECTION 13 05 41 Seismic Restraint Requirements For Non-Structural Components Part 1 - General 1.1 DescriptionDocument6 pagesSECTION 13 05 41 Seismic Restraint Requirements For Non-Structural Components Part 1 - General 1.1 DescriptionAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- HSBC HSBC Holdings PLC: (New York Stock Exchange)Document12 pagesHSBC HSBC Holdings PLC: (New York Stock Exchange)Anonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Puxy - MCD PDFDocument4 pagesMathcad - Puxy - MCD PDFAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- 2240 001 PDFDocument1 page2240 001 PDFAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- HSBC Holdings PLC ADR: HSBC Is Undervalued at A 23% DiscountDocument4 pagesHSBC Holdings PLC ADR: HSBC Is Undervalued at A 23% DiscountAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Ronstan Structural Rod CatalogueDocument44 pagesRonstan Structural Rod CatalogueAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group Inc MUFG (XNYS) : MUFG Also Reports Modest Uptick in Credit Costs in 3Q We Prefer SMFGDocument14 pagesMitsubishi UFJ Financial Group Inc MUFG (XNYS) : MUFG Also Reports Modest Uptick in Credit Costs in 3Q We Prefer SMFGAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- CP35Document1 pageCP35Anonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- SECTION 13 05 41 Seismic Restraint Requirements For Non-Structural ComponentsDocument9 pagesSECTION 13 05 41 Seismic Restraint Requirements For Non-Structural ComponentsAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- HSBC Holdings PLCDocument9 pagesHSBC Holdings PLCAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- VFV Vs VSPDocument2 pagesVFV Vs VSPAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- ViewdocDocument12 pagesViewdocAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- FVR 2018 JulyDocument15 pagesFVR 2018 JulyAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Alibaba Group Holding Limited: Strong BuyDocument9 pagesAlibaba Group Holding Limited: Strong BuyAnonymous P73cUg73L100% (1)
- Appendix CDocument3 pagesAppendix CAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Pile Spacing: Table 5-6: P-Y Curve Multipliers For Group Effects Pile Row Row Spacing 3D4D5D6DDocument1 pagePile Spacing: Table 5-6: P-Y Curve Multipliers For Group Effects Pile Row Row Spacing 3D4D5D6DAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Ladder Training ProgramDocument31 pagesLadder Training ProgramAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Huntsman of ZeusDocument10 pagesHuntsman of ZeushdsjkahsdakNo ratings yet
- Wiki Sicilian LanguageDocument20 pagesWiki Sicilian LanguageSalvatore BellaviaNo ratings yet
- Typographic Posters 1900 - 2007: Introduction To Graphic Design July 21, 2008Document38 pagesTypographic Posters 1900 - 2007: Introduction To Graphic Design July 21, 2008Patricia DamascenoNo ratings yet
- Excerpt of "Allegiant" by Veronica RothDocument7 pagesExcerpt of "Allegiant" by Veronica RothHere & NowNo ratings yet
- Sweet Charity, He Worked With Some of The Biggest Names in Theatre During His Incredibly ExpansiveDocument5 pagesSweet Charity, He Worked With Some of The Biggest Names in Theatre During His Incredibly ExpansiveWill ArundellNo ratings yet
- 3.5 To Pathfinder Conversion - TsocharDocument1 page3.5 To Pathfinder Conversion - TsocharDana HelmanNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself Instant Italian (With Audio) (PDFDrive)Document129 pagesTeach Yourself Instant Italian (With Audio) (PDFDrive)Sonya Kashperova100% (1)
- Norse FolkloreDocument3 pagesNorse FolkloreJr MadredinosNo ratings yet
- (Paralyzed On One) Sideman: Disability Studies Meets Jazz, Through The Hands of Horace ParlanDocument8 pages(Paralyzed On One) Sideman: Disability Studies Meets Jazz, Through The Hands of Horace ParlanSoad KhanNo ratings yet
- Aalto University School of Arts Design and Architecture Presentation April2012Document40 pagesAalto University School of Arts Design and Architecture Presentation April2012José FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Sample Convocation Programme & ScriptDocument2 pagesSample Convocation Programme & ScriptMayen Lopez Elvinia-Templo100% (4)
- Software Life Cycle Process Models: Pradeep TomarDocument31 pagesSoftware Life Cycle Process Models: Pradeep Tomartushar umraoNo ratings yet
- Slightly Differently, The Law Cannot Tell Us What To Pursue, Only What To Avoid. Would We BeDocument4 pagesSlightly Differently, The Law Cannot Tell Us What To Pursue, Only What To Avoid. Would We BeCJ IbaleNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Edward Albees The Zoo StoryDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Edward Albees The Zoo StoryGabriela Macarei100% (1)
- OdDocument22 pagesOdwenkNo ratings yet
- Cinderellla GirlDocument3 pagesCinderellla GirlReen T. AliNo ratings yet
- Adventure of Living W Jesus 161216Document65 pagesAdventure of Living W Jesus 161216D100% (1)
- Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2: EditionDocument87 pagesDigital Design and Computer Architecture, 2: EditionСергей КапустаNo ratings yet
- Genesis - Allan KardecDocument227 pagesGenesis - Allan KardecSpiritism USA100% (5)
- Andrea Michelon - DIT:Data WranglerDocument1 pageAndrea Michelon - DIT:Data WranglerAndrea MichelonNo ratings yet
- I. Choose The Right Answer and Cross The Letter!Document4 pagesI. Choose The Right Answer and Cross The Letter!yusufNo ratings yet
- Tunga Pushkara EnglishDocument4 pagesTunga Pushkara EnglisharunagirinatharNo ratings yet
- Motokawa-Sushi Science and Hamburger ScienceDocument13 pagesMotokawa-Sushi Science and Hamburger Scienceluky8aNo ratings yet
- Cultures & Races MERP - To Rolemaster (RMSS-RMFRP)Document187 pagesCultures & Races MERP - To Rolemaster (RMSS-RMFRP)Loricia100% (4)
- MA English 2008 PatternDocument69 pagesMA English 2008 PatternKuNdAn DeOrENo ratings yet
- SWR 2005 CatalogDocument18 pagesSWR 2005 CatalogMultiarsNo ratings yet
- Capitalization: Lesson SummaryDocument7 pagesCapitalization: Lesson Summarydina mawarNo ratings yet
Standard For Steel Roof Deck: CSSBI 10M - 08 October 2008
Standard For Steel Roof Deck: CSSBI 10M - 08 October 2008
Uploaded by
Anonymous P73cUg73LOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard For Steel Roof Deck: CSSBI 10M - 08 October 2008
Standard For Steel Roof Deck: CSSBI 10M - 08 October 2008
Uploaded by
Anonymous P73cUg73LCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard for Steel Roof Deck
CSSBI 10M 08 October 2008
CANADIAN SHEET STEEL BUILDING INSTITUTE
Standard for Steel Roof Deck
PREFACE
One of the objectives of the Canadian Sheet Steel Building Institute is the development of product standards to promote safety and sound construction practices. This Standard is intended to assist specifiers, designers, buyers, manufacturers and erectors of steel roof deck by providing information which can be adopted by reference where desired. This Standard replaces the previous edition dated September 2006. Steel roof deck is a basic component of the overall roof system which normally would also include the roof framing, the various roofing materials, and other items necessary to provide a complete assembly. A compatible relationship between the various roof system components is an important consideration when job plans and specifications are being developed. It is intended that this Standard for Steel Roof Deck will provide useful guidance to designers and specifiers, as well as to suppliers and trades involved in roof construction. The requirements contained herein are in accordance with sound engineering principles, augmented by experience. They include recommended minimum requirements for grade of steel, base steel design thickness, metallic coating designation, loads, resistances and deflections, as well as design, fabrication and erection in general. While the material is believed to be technically correct and in accordance with recognized practice at the time of publication, it does not obviate the need to determine its suitability for a given situation. Neither the Canadian Sheet Steel Building Institute nor its Members warrant or assume any liability for the suitability of the material for any general or particular purpose.
REFERENCE PUBLICATIONS
This Standard makes reference to the following: American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) A653/A653M Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) or Zinc-Iron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed) by the Hot-Dip Process A792/A792M Steel Sheet, 55% Aluminum-Zinc Alloy-Coated by the Hot-Dip Process Canadian Standards Association (CSA) CAN/CSA-S136 North American Specification for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members W47.1 Certification of Companies for Fusion Welding of Steel
Copyright October 2008 by CANADIAN SHEET STEEL BUILDING INSTITUTE All rights reserved. This publication, nor any part thereof, may be reproduced in any form without the written permission of the publisher. ISBN 978-1-895534-64-8
CANADIAN SHEET STEEL BUILDING INSTITUTE
Standard for Steel Roof Deck
1. SCOPE
1.1 This Standard covers the design, fabrication and erection of steel roof deck intended for use with appropriate roofing materials installed on top of the deck. 1.2 This Standard applies to roof deck sections formed from metallic coated steel sheet which have: (a) a nominal depth not greater than 77 mm; (b) a nominal flute spacing not greater than 200 mm; (c) a flute width not greater than 75 mm; (d) a flat top width between flutes not less than 75 mm; and (e) side laps to interconnect adjacent parallel units. 1.3 This Standard is not intended to apply to prefinished or factory post-painted steel roof deck without appropriate modifications in respect of fabrication, handling, transportation, storage, erection, and method of attachment to the supporting structure.
diaphragm action to resist in-plane shear forces, composite slab roofs, and roofs that will be subjected to heavy moving loads.
3. DEFINITIONS
3.1 Buyer means the person, firm or company contracting with the Manufacturer or Erector for the supply and installation of steel roof deck. 3.2 Erector means an erector of steel roof deck. 3.3 Manufacturer means a manufacturer of steel roof deck. 3.4 Roofing Materials include vapour retarder, insulation, felts, sheathing, gravel, concrete, gypsum thermal barrier, and other materials placed on top of the steel roof deck as roofing, including related adhesives and mechanical fasteners. 3.5 Span of steel roof deck means the lesser of: (a) the centre to centre distance of structural supports; or (b) the clear distance between edges of structural supports plus the depth of the deck. 3.6 Design Thickness of sheet steel used for steel roof deck means the base steel thickness, exclusive of any coatings used to establish section properties of the deck. The Minimum Thickness shall not be less than 95% of the Design Thickness as permitted by CAN/CSAS136.
2. GENERAL
2.1 This Standard is to govern in those cases where the provisions of building codes, architects' and engineers plans and specifications are not specific. In the event of any conflict between this Standard and any legal regulations, such regulations shall apply and this Standard shall only supplement as applicable. 2.2 Where reference is made to another publication, such reference shall be considered to refer to the latest revision or edition approved by the organization issuing that publication, unless otherwise noted. 2.3 When details of design, fabrication or erection are not clearly specified in the plans and specifications furnished by the Buyer, the Manufacturer shall furnish all materials required in accordance with the current specifications and standards of the Canadian Sheet Steel Building Institute (CSSBI). 2.4 Supplementary rules or requirements may be necessary for specific applications such as insulated roof membrane assemblies, 3
4. SHEET STEEL REQUIREMENTS
4.1 Materials Sheet steel used for steel roof deck shall conform to one of the following material specifications: (a) ASTM A653/A653M Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) or Zinc- Iron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed) by the Hot-Dip Process; or (b) ASTM A792/A792M Steel Sheet, 55% Aluminum-Zinc Alloy-Coated by the Hot-Dip Process. 4.2 Design Thickness Limitation The design thickness of sheet steel used for roof deck shall not be less than 0.76 mm. 4.3 Minimum Base Steel Thickness The minimum base steel thickness (excluding any metallic coatings) of sheet used for roof
CANADIAN SHEET STEEL BUILDING INSTITUTE
deck shall not be less than 95% of the specified design steel thickness as permitted by CAN/CSA-S136. 4.4 Metallic Coatings 4.4.1 The minimum metallic coating designations for steel roof deck not exposed in service to the weather are ZF75 (zinc-iron alloy coating) or Z180 (zinc coating) for ASTM A653/A653M material, and AZM150 (55% aluminumzinc alloy coating) for ASTM A792/A792M material, 4.4.2 The minimum metallic coating designations for steel roof deck exposed in service to the weather are Z275 (zinc coating) for ASTM A653/A653M material and AZM150 (55% aluminum-zinc alloy coating) for ASTM A792/A792M material.
normal occupancy conditions. Additional insulation, beyond this minimum requirement, is usually desirable for thermal efficiency. Insulation shall be properly installed. 6.4 Sheet Metal Work All sheet metal work, such as flashings, shall be detailed and furnished by others unless otherwise specified. 6.5 Field Painting Any field painting is the responsibility of the Buyer who should check with the paint supplier for the proper paint type and application procedures. Primer that may be required to cover wet staining discolouration is not the responsibility of the deck supplier.
7. SAFETY DURING ERECTION
7.1 Minimum safety requirements for steel roof deck erection are outlined in 7.2 to 7.8 inclusive. In the event of any conflict between these requirements and any legal regulations, such regulations shall apply and these requirements shall only supplement as applicable . 7.2 All steel roof deck being hoisted to the working level shall be adequately banded and carefully slung employing steel wire rope and a choker type sling or multi-lift beams. 7.3 All bundles shall be tag lined during the ascent of the hoisting operation. Bundles shall be placed so as to avoid overloading the supporting structure. 7.4 All steel roof deck sheets, after being laid and aligned, shall be properly secured in place prior to leaving the jobsite at the end of each working day. 7.5 All loose bundles of steel roof deck sheets shall be secured at the completion of each working day. 7.6 All steel roof deck cuttings, strapping, packaging material, and other debris pertaining to steel roof deck shall be removed from the roof area each working day and disposed of in a suitable manner. 7.7 Perimeter safety lines, safety lines at discontinued or incomplete construction and barricading of openings shall be the responsibility of the General Contractor. 4
5. FABRICATION
5.1 General Steel roof deck shall be fabricated in accordance with the applicable requirements of CAN/CSAS136. 5.2 Tolerances 5.2.1 Upon completion of fabrication, the depth of steel roof deck shall not be more than 1 mm under the design depth. 5.2.2 Upon completion of fabrication, the actual cover width of steel roof deck shall not exceed the design cover width by more than 10 mm per metre of width.
6. COLLATERAL MATERIALS
6.1 General Collateral materials are items such as vapour retarder, thermal barrier, insulation, waterproofing membrane, and related sheet metal work normally supplied by parties other than the Manufacturer and/or Erector. This Standard is not intended to encroach upon the standard practices of suppliers of collateral materials and related trades, but is intended only to supplement and amplify such practices. 6.2 Vapour Retarder A vapour retarder is required for the majority of applications. 6.3 Insulation Steel roof deck shall be insulated with a suitable insulating material of sufficient thermal resistance to prevent condensation under
CANADIAN SHEET STEEL BUILDING INSTITUTE
7.8 Steel roof deck is designed primarily to support uniformly distributed load. Care shall be taken to avoid excessive concentration of loads during the temporary storage of materials for subtrades.
8. GUIDE SPECIFICATION FOR STEEL ROOF DECK
8.1 General Conditions The General Conditions shall be and are hereby made a part of this division. 8.2 Work Included 8.2.1 Furnish all labour, materials and equipment necessary to fabricate and, where shown or called for by the tender documents, hoist into position and erect the steel roof deck. 8.2.2 Supply and install accessories where shown or called for by the tender documents (e.g. cell closures). 8.2.3 Cut and reinforce holes and openings up to 450 mm across the flutes. Cut only, holes and openings larger than 450 mm across the flutes, where shown or called for by the tender documents. 8.3 Work Not Included 8.3.1 Reinforcing or structural framing of openings larger than 450 mm across the flutes. 8.3.2 Field painting including touch-up to the underside of top chords or flanges of supporting steel members where discolouration due to welding has occurred. 8.3.3 Mechanical clips, nails, adhesives or other fasteners for securing insulation, thermal barrier, or vapour retarder to steel roof deck. 8.3.4 Cutting and drilling of holes for the attachment of suspended ceiling hangers, or for the attachment of any work of other trades. 8.3.5 Bearing plates, shelf angles, diagonal supports and other structural steel required to support the steel roof deck. 8.3.6 Wood nailers, cants, vapour retarder, insulation, thermal barrier, waterproofing membrane, and ballast. 8.3.7 Architectural trim. 8.4 Materials 8.4.1 Steel roof deck shall be formed of metallic coated sheet steel conforming to 5
one of the following specifications: (a) ASTM A653/A653M Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) or ZincIron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed) by the Hot-Dip Process, minimum Grade 230 with a base steel design thickness or 0.76 mm or greater and a minimum zinc-iron alloy coating designation of ZF75; or, (b) ASTM A792/A792M Steel Sheet, 55% Aluminum-Zinc Alloy-Coated by the Hot-Dip Process, minimum Grade 230 with a base steel design thickness or 0.76 mm or greater and a minimum 55% aluminumzinc alloy coating designation of AZM150. Note: Specification writer may specify a heavier base steel design thickness and/or a heavier metallic coating to satisfy any special requirements. 8.5 Drawings 8.5.1 The Buyer shall provide complete architectural and structural plans, specifications, and approved structural support spacings, correctly dimensioned. 8.5.2 The steel roof deck Erector shall submit ... copies of erection drawings for review. The Buyer shall return one copy with his approval, or with such corrections as he may deem necessary. 8.5.3 Erection drawings shall show clearly the location of various sheet lengths, sheet quantities, thicknesses, and metallic coating designations. 8.5.4 When changes are made by the Buyer, the cost of such changes shall be the basis for re-negotiating the contract. 8.6 Design 8.6.1 In the absence of laws, regulations, ordinances and specifications to the contrary, structural design of the steel roof deck shall be in accordance with 8.6.2 to 8.6.9 inclusive. 8.6.2 Structural properties and member resistances shall be calculated in accordance with CAN/CSA-S136. 8.6.3 Wherever structural framing permits, and subject to reasonable limitations for handling, steel roof deck shall be fabricated to span continuously over at least four structural supports (three spans).
CANADIAN SHEET STEEL BUILDING INSTITUTE
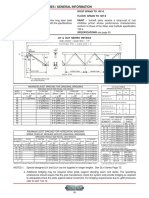
8.6.4 Steel roof deck shall be fastened to the supporting structural steel by mechanical fastening or arc spot welding. Notes: (1) When arc spot welding is used, the thickness and width of the supporting steel element to which the deck is to be attached is a factor in producing satisfactory arc spot welds. A minimum thickness of 2.5 mm and a minimum width of 38 mm is recommended. (2) Where deck is required to be fastened to structural supports by mechanical fasteners such as screws, pneumatic or powderactuated pins or other fasteners, the Specification Writer should state the fastening requirements clearly.. 8.6.5 Steel roof deck shall have at least the minimum strength and stiffness appropriate for the applica-tion and performance of conventional built-up roof-ing. Unless otherwise specified, the minimum uni-form total factored load for the design of steel roof deck shall be 3.5 kPa. Deflection shall not exceed L/240 of the span under a minimum uniform service load of 1.9 kPa. Note: The load and deflection requirements of Clause 8 are intended to provide the minimum deck strength and stiffness, which combined with a sufficiently sturdy framing system, are considered to be appro-priate for the application and performance of con-ventional types of built-up roofing. The loads spe-cified in 8.6.5 are not those due to wind, snow or other forces, which for a particular locality, may be higher or lower. Where other criteria are to apply, the Specification Writer should state the requirements clearly. 8.6.6 Loads due to wind, snow or other forces, including related loading distributions and building Importance Category, shall be as prescribed by the structural plans and specifications. 8.6.7 Deck deflection due to service load, uniformly distributed, shall be calculated as follows:
For a single span: 5 w L4 = ______ 384EI For two equal spans: = 0.42 times single span value For three or more equal spans: = 0.53 times single span value Where, = calculated live load deflection, mm w = maximum uniform service load, kPa L = span, mm E = modulus of elasticity of steel, (203 000 MPa) I = moment of inertia of the steel roof deck at midspan, when supporting the service load, w, with top flange of the deck in compression, mm4/m of width 8.6.8 Steel roof deck shall have a factored moment resistance capable of resisting the effects of the uniformly distributed factored loads determined as follows: For a single span: Mr 0.125(w)L2 For two equal spans: Mr 0.070(w)L2 Mr' 0.125((w)L2, at the interior support For three or more equal spans: Mr 0.080(w)L2 Mr' 0.100(w)L2, at the interior supports Where, Mr = factored moment resistance at midspan with the top flange of the deck in compression, kNm/m width Mr' = factored moment resistance at an interior support with the bottom flange of the deck in compression, kNm/m width For the definition of the other symbols see 8.6.9
CANADIAN SHEET STEEL BUILDING INSTITUTE
8.6.9 Steel roof deck shall have a factored web crippling resistance capable of resisting the effects of the factored uniform loads determined as follows: For a single span: Pr 0.50(w)L For two equal spans: Pr 1.25(w)L, at the interior support Pr 0.375(w)L, at the end supports For three or more equal spans: Pr 1.10(w)L, at the interior supports Pr 0.40(w)L, at the end supports Where Pr = factored web crippling resistance, kN/m width w= Effect of load combinations given in Table D = Dead load: a permanent load, including the weight of steelwork and all materials of construction, partitions, stationary equipment, and the additional weight of concrete and finishes resulting from deflections of supporting members, kPa E = Earthquake load and effects, kPa L = Live load: a variable load due to intended use and occupancy, kPa S = Variable load due to snow, including ice and associated rain or rain alone, kPa W = Wind load: a variable load due to wind, kPa
Case 1 2 3 4 5 Load Combination Principal Loads Companion Loads 1.4D (1.25D or 0.9D) + 1.5L 0.5S or 0.4W (1.25D or 0.9D) + 1.5S 0.5L or 0.4W (1.25D or 0.9D) + 1.4W 0.5L or 0.5S 1.0D + 1.0E 0.5L + 0.25S
8.7.2
8.7.3
8.7.4 8.7.5
8.7.6
8.7.7
Note: The length of bearing of steel roof deck on structural supports should be equal to the depth of the deck section, where practicable. 8.7 Erection 8.7.1 All erection work, including field welding, shall be the responsibility of the Erector and such erection work shall be carried 7
8.7.8
8.7.9
out by trained erection crews, all in accordance with the Manufacturers and these specifications. When arc spot welding is used, Erectors shall be qualified in accor-dance with CSA Standard W47.1 Certification of Companies for Fusion Welding of Steel, and weld-ers shall be qualified for deck welding by the Cana-dian Welding Bureau. Steel roof deck units shall be placed and adjusted to final position on the supporting structure before being permanently fastened thereto. If structural supports are not in proper alignment, the problem shall be reported to the General Contractor in order that the necessary corrections can be made before proceeding with the work. Steel roof deck units shall be adequately fastened to structural supports. The maximum spacing of fastenings along bearing supports shall be 400 mm or 2 flute spacings, whichever is the lesser. Where arc spot welds are used they shall have a 20 mm nominal top diameter. End laps shall be not less than 50 mm and shall be formed over supports. Side laps of adjacent units shall be fastened at intervals not exceeding 900 mm on centre. Closer spacing may be required for diaphragm action, as determined by design. For thicknesses 0.91 mm and greater, side laps may be welded using 25 mm long seam welds. For openings up to 150 mm across the flutes, no reinforcement is necessary provided that not more than two vertical webs are removed. For openings over 150 mm to 300 mm across the flutes, provide not less than a 50 x 50 x 6 mm angle reinforcement to frame across each side of the opening in a direction perpendicular to the flutes. The angles shall be fastened to at least two flutes on each side of the opening. Alternatively, reinforcing shall be provided based on a structural analysis of the loads involved. For openings over 300 mm to 450 mm across the flutes, provide suitable reinforcement based on a structural analysis of the loads involved. If additional openings not shown or called for by the tender documents are
CANADIAN SHEET STEEL BUILDING INSTITUTE
required, such openings shall be cut and reinforced by the Erector, but the cost of such extra work shall be charged to the Buyer. 8.7.10 Where steel roof deck is welded in place, the steel deck surface shall be immediately inspected, and all topside areas where the metallic coating has been burned by welding shall be covered by a suitable primer, applied according to the primer manufacturer's instructions. 8.8 Limitations 8.8.1 Any damage or alterations by others to the steel roof deck, including that due to construction loads applied at any time, shall not be the responsibility of the Erector or the Manufacturer. 8.9 Access 8.9.1 Access for unloading bundles of deck onto the structure shall be provided by the General Contractor. 8.10 Storage of Materials on Site 8.10.1 Steel roof deck shall normally be delivered to the jobsite as required for erection, but if site storage becomes necessary, the following requirements shall be observed: (1) tilt bundles for drainage; (2) block bundles off ground for effective drainage and ventilation; (3) block long bundles to prevent sagging; and (4) store away from chemically corrosive substances (e.g. salt, cement, fertilizer), away from materials that could contaminate the surface (e.g. diesel oil, paint, grease), and away from site traffic. If the bundles are to be covered, avoid impermeable material such as plastic and ensure that adequate ventilation is provided to prevent condensation. 8.10.2 Moisture can cause wet staining of deck material and usually occurs in one of three ways: (1) condensation from high humidity and/or temperature cycling; (2) wet shipping conditions; or (3) wind-driven rain penetration (outdoor storage). 8
The usual progression is from visible water staining to unsightly white staining (dark grey to dull black on 55% aluminum-zinc alloy coated sheet) to red rust. On material where wet staining has occurred, it should be noted that a minor amount of staining is not detrimental to the functioning of the product and is considered acceptable. 8.10.3 Areas for storage shall be provided by the General Contractor as close to the building as is practicable. 8.10.4 Protection against damage shall be provided by the General Contractor. 8.11 Cleanup 8.11.1 Remove all debris of this trade and leave work ready for other trades. 8.12 Field Painting 8.12.1 Metallic coated steel deck material is normally given a passivation treatment at the steel mill in order to inhibit the formation of wet storage stain. Material so treated is often difficult to paint satisfactorily unless the passivating treatment is removed by mechanical or chemical means.
You might also like
- Joist LH DLH SeriesDocument13 pagesJoist LH DLH SeriescadsultanNo ratings yet
- Steel Joists - MST PDFDocument7 pagesSteel Joists - MST PDFwafikmh4No ratings yet
- AISI S214-07 Standard and Commentary (1st Printing) PDFDocument54 pagesAISI S214-07 Standard and Commentary (1st Printing) PDFthjozsefNo ratings yet
- Icbo Es Report-Er2078pDocument65 pagesIcbo Es Report-Er2078peltorro-tNo ratings yet
- Element of Space Making PDFDocument99 pagesElement of Space Making PDFsrishti bhowal100% (1)
- Hotel Centre PointDocument18 pagesHotel Centre PointTanvir AliNo ratings yet
- Kahlil Gibran-Love LettersDocument4 pagesKahlil Gibran-Love Lettersapi-3737310100% (2)
- Stability of SpeedCore Walls Under Fire Loading Summary of Numerical AnalysesDocument13 pagesStability of SpeedCore Walls Under Fire Loading Summary of Numerical Analysesjackcan501No ratings yet
- The Development of A New Design Procedure For Conventional Single-Plate Shear ConnectionsDocument12 pagesThe Development of A New Design Procedure For Conventional Single-Plate Shear ConnectionsMiguelNo ratings yet
- OPSS 906 - Nov12Document20 pagesOPSS 906 - Nov12umerfr2No ratings yet
- Algoma Steel Sheet PDFDocument10 pagesAlgoma Steel Sheet PDFSH1961No ratings yet
- Washers, Steel, Plain (Flat), Unhardened For General UseDocument4 pagesWashers, Steel, Plain (Flat), Unhardened For General UsekrutikNo ratings yet
- Design Guide Spec and Manual ReferencesDocument2 pagesDesign Guide Spec and Manual ReferencesRiza SuwondoNo ratings yet
- Geometric Properties of Hot-Rolled Steel Angles Including The Effects of Toe Radii and FilletDocument10 pagesGeometric Properties of Hot-Rolled Steel Angles Including The Effects of Toe Radii and FilletDianna Lambert100% (1)
- Aisi S907-13Document34 pagesAisi S907-13Edison BecerraNo ratings yet
- Aisc - StudentDocument148 pagesAisc - StudentRamiro Flores MoraNo ratings yet
- Mil C 39012CDocument57 pagesMil C 39012CMITHUN.V POWARNo ratings yet
- Astm A36 1977Document6 pagesAstm A36 1977Ben Yie Min100% (1)
- Astm C955-09Document4 pagesAstm C955-09rodrigoNo ratings yet
- Schedule 40 Pipe, Galvanized: ASTM F1043 Group I-A, Federal Specification RR-F-191 Type 1, Grade A, AASHTO M-181 Grade 1Document2 pagesSchedule 40 Pipe, Galvanized: ASTM F1043 Group I-A, Federal Specification RR-F-191 Type 1, Grade A, AASHTO M-181 Grade 1Caolboy ButchNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Screws Through Gypsum Board Wall Sheathing: RecentlyDocument4 pagesSheet Metal Screws Through Gypsum Board Wall Sheathing: Recentlytigani brigdarNo ratings yet
- Size RangeDocument15 pagesSize RangelucidbaseNo ratings yet
- Astm D2729 PDFDocument2 pagesAstm D2729 PDFShan Adrias100% (1)
- AISI Manual Cold-Formed Steel Design 2002 EditionDocument462 pagesAISI Manual Cold-Formed Steel Design 2002 EditionVatova JarrandNo ratings yet
- 05.40.00 Cold-Formed Metal Framing Specification Updated June 2015Document26 pages05.40.00 Cold-Formed Metal Framing Specification Updated June 2015mishikhanNo ratings yet
- Astm A325 PernosDocument14 pagesAstm A325 PernosDiego Lever TorresNo ratings yet
- AISIS240 15 (1stprinting)Document204 pagesAISIS240 15 (1stprinting)Roberto Pérez LeónNo ratings yet
- Pren 14509 51 - e - STF PDFDocument147 pagesPren 14509 51 - e - STF PDFBoris Dikov100% (2)
- Astm A1063A1063MDocument11 pagesAstm A1063A1063Mارفع راسك فوق انت يمنيNo ratings yet
- ANSI RD1.0 - 2006 - Standard For Steel Roof DeckDocument5 pagesANSI RD1.0 - 2006 - Standard For Steel Roof DeckDaniel PereiraNo ratings yet
- A 586Document4 pagesA 586Gustavo SuarezNo ratings yet
- Night School 23 Session 2Document41 pagesNight School 23 Session 2Luis CortesNo ratings yet
- AISI S211-07 (Raffirmed 2012) - E1Document2 pagesAISI S211-07 (Raffirmed 2012) - E1Jon JacobsNo ratings yet
- 3090 Slope Build Up NH PDFDocument2 pages3090 Slope Build Up NH PDFTodd St. GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Problem 1-015 PDFDocument3 pagesProblem 1-015 PDFOscar SanchezNo ratings yet
- b905 SBDH Chapter05Document35 pagesb905 SBDH Chapter05qgfytzvqabzqrxyilmNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Manual - Google SearchDocument3 pagesSeismic Design Manual - Google Searchchondroc110% (1)
- Specification For Structural Quality Steels: SA/CSA-G40.21Document7 pagesSpecification For Structural Quality Steels: SA/CSA-G40.21Meyer Antonio LozanoNo ratings yet
- High-Strength Steel Bolts, Classes 10.9 and 10.9.3, For Structural Steel Joints (Metric)Document6 pagesHigh-Strength Steel Bolts, Classes 10.9 and 10.9.3, For Structural Steel Joints (Metric)Ngoc BuiNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Design Manual: FOURTH EDITION - First PrintingDocument1 pageDiaphragm Design Manual: FOURTH EDITION - First Printingaandueza_1No ratings yet
- Section - 05520 - Handrails and RailingsDocument3 pagesSection - 05520 - Handrails and RailingsNana DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Stud Welding: State-Of-The-Art PaperDocument13 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Stud Welding: State-Of-The-Art Paperalbert limantonoNo ratings yet
- AISI S230-12-E1Document2 pagesAISI S230-12-E1Jon JacobsNo ratings yet
- Astm C90 16Document5 pagesAstm C90 16Arquiva SA de CVNo ratings yet
- Design of Pallet Rack Upright Frames Subject To CompressionDocument107 pagesDesign of Pallet Rack Upright Frames Subject To CompressionssierroNo ratings yet
- Ansi c80-6 2005Document22 pagesAnsi c80-6 2005supervisor.electricistaNo ratings yet
- CJP & PJPDocument3 pagesCJP & PJPRobertBostanNo ratings yet
- Astm - E1996-09Document13 pagesAstm - E1996-09Raju KCNo ratings yet
- Don't Put Welds in BendingDocument2 pagesDon't Put Welds in BendingRune OveraasNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Strength of Fillet Welded Connections Loaded in PlaneDocument13 pagesUltimate Strength of Fillet Welded Connections Loaded in PlanePatrick PolujanNo ratings yet
- Sherman - Extended Shear TabsDocument148 pagesSherman - Extended Shear TabsRohan KarandeNo ratings yet
- Astm F 568MDocument9 pagesAstm F 568MZahoor Ahmed MohsanNo ratings yet
- NBC 2010 - Commentaries - Section IDocument24 pagesNBC 2010 - Commentaries - Section IRick HenbidNo ratings yet
- Mixing Weld and Bolt Part2Document4 pagesMixing Weld and Bolt Part2ihpeterNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification For Cast-in-Place Nonreinforced Concrete Pipe (ACI 346-90) (Reapproved 1997)Document7 pagesStandard Specification For Cast-in-Place Nonreinforced Concrete Pipe (ACI 346-90) (Reapproved 1997)nathanNo ratings yet
- AISI DSM Design Guide Schafer VersionDocument180 pagesAISI DSM Design Guide Schafer VersionOmar Eduardo Alvarado Valle100% (1)
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Plates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and AnalysisFrom EverandPlates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CSSBI-12M-13 - Standard For Composite Steel DeckDocument9 pagesCSSBI-12M-13 - Standard For Composite Steel DeckjulianobiancoNo ratings yet
- CSSBI 12M-2015:: Standard For Composite Steel DeckDocument7 pagesCSSBI 12M-2015:: Standard For Composite Steel DeckPhablo GustavoNo ratings yet
- Hwachong - Oxbridge Admissions For Singaporean ApplicantsDocument14 pagesHwachong - Oxbridge Admissions For Singaporean ApplicantsAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Stair RailDocument1 pageStair RailAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- HSBC Investments Investdirect Hsbc-Hidc-Brochure - enDocument2 pagesHSBC Investments Investdirect Hsbc-Hidc-Brochure - enAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- SECTION 13 05 41 Seismic Restraint Requirements For Non-Structural Components Part 1 - General 1.1 DescriptionDocument6 pagesSECTION 13 05 41 Seismic Restraint Requirements For Non-Structural Components Part 1 - General 1.1 DescriptionAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- HSBC HSBC Holdings PLC: (New York Stock Exchange)Document12 pagesHSBC HSBC Holdings PLC: (New York Stock Exchange)Anonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Puxy - MCD PDFDocument4 pagesMathcad - Puxy - MCD PDFAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- 2240 001 PDFDocument1 page2240 001 PDFAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- HSBC Holdings PLC ADR: HSBC Is Undervalued at A 23% DiscountDocument4 pagesHSBC Holdings PLC ADR: HSBC Is Undervalued at A 23% DiscountAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Ronstan Structural Rod CatalogueDocument44 pagesRonstan Structural Rod CatalogueAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group Inc MUFG (XNYS) : MUFG Also Reports Modest Uptick in Credit Costs in 3Q We Prefer SMFGDocument14 pagesMitsubishi UFJ Financial Group Inc MUFG (XNYS) : MUFG Also Reports Modest Uptick in Credit Costs in 3Q We Prefer SMFGAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- CP35Document1 pageCP35Anonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- SECTION 13 05 41 Seismic Restraint Requirements For Non-Structural ComponentsDocument9 pagesSECTION 13 05 41 Seismic Restraint Requirements For Non-Structural ComponentsAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- HSBC Holdings PLCDocument9 pagesHSBC Holdings PLCAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- VFV Vs VSPDocument2 pagesVFV Vs VSPAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- ViewdocDocument12 pagesViewdocAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- FVR 2018 JulyDocument15 pagesFVR 2018 JulyAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Alibaba Group Holding Limited: Strong BuyDocument9 pagesAlibaba Group Holding Limited: Strong BuyAnonymous P73cUg73L100% (1)
- Appendix CDocument3 pagesAppendix CAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Pile Spacing: Table 5-6: P-Y Curve Multipliers For Group Effects Pile Row Row Spacing 3D4D5D6DDocument1 pagePile Spacing: Table 5-6: P-Y Curve Multipliers For Group Effects Pile Row Row Spacing 3D4D5D6DAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Ladder Training ProgramDocument31 pagesLadder Training ProgramAnonymous P73cUg73LNo ratings yet
- Huntsman of ZeusDocument10 pagesHuntsman of ZeushdsjkahsdakNo ratings yet
- Wiki Sicilian LanguageDocument20 pagesWiki Sicilian LanguageSalvatore BellaviaNo ratings yet
- Typographic Posters 1900 - 2007: Introduction To Graphic Design July 21, 2008Document38 pagesTypographic Posters 1900 - 2007: Introduction To Graphic Design July 21, 2008Patricia DamascenoNo ratings yet
- Excerpt of "Allegiant" by Veronica RothDocument7 pagesExcerpt of "Allegiant" by Veronica RothHere & NowNo ratings yet
- Sweet Charity, He Worked With Some of The Biggest Names in Theatre During His Incredibly ExpansiveDocument5 pagesSweet Charity, He Worked With Some of The Biggest Names in Theatre During His Incredibly ExpansiveWill ArundellNo ratings yet
- 3.5 To Pathfinder Conversion - TsocharDocument1 page3.5 To Pathfinder Conversion - TsocharDana HelmanNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself Instant Italian (With Audio) (PDFDrive)Document129 pagesTeach Yourself Instant Italian (With Audio) (PDFDrive)Sonya Kashperova100% (1)
- Norse FolkloreDocument3 pagesNorse FolkloreJr MadredinosNo ratings yet
- (Paralyzed On One) Sideman: Disability Studies Meets Jazz, Through The Hands of Horace ParlanDocument8 pages(Paralyzed On One) Sideman: Disability Studies Meets Jazz, Through The Hands of Horace ParlanSoad KhanNo ratings yet
- Aalto University School of Arts Design and Architecture Presentation April2012Document40 pagesAalto University School of Arts Design and Architecture Presentation April2012José FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Sample Convocation Programme & ScriptDocument2 pagesSample Convocation Programme & ScriptMayen Lopez Elvinia-Templo100% (4)
- Software Life Cycle Process Models: Pradeep TomarDocument31 pagesSoftware Life Cycle Process Models: Pradeep Tomartushar umraoNo ratings yet
- Slightly Differently, The Law Cannot Tell Us What To Pursue, Only What To Avoid. Would We BeDocument4 pagesSlightly Differently, The Law Cannot Tell Us What To Pursue, Only What To Avoid. Would We BeCJ IbaleNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Edward Albees The Zoo StoryDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Edward Albees The Zoo StoryGabriela Macarei100% (1)
- OdDocument22 pagesOdwenkNo ratings yet
- Cinderellla GirlDocument3 pagesCinderellla GirlReen T. AliNo ratings yet
- Adventure of Living W Jesus 161216Document65 pagesAdventure of Living W Jesus 161216D100% (1)
- Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2: EditionDocument87 pagesDigital Design and Computer Architecture, 2: EditionСергей КапустаNo ratings yet
- Genesis - Allan KardecDocument227 pagesGenesis - Allan KardecSpiritism USA100% (5)
- Andrea Michelon - DIT:Data WranglerDocument1 pageAndrea Michelon - DIT:Data WranglerAndrea MichelonNo ratings yet
- I. Choose The Right Answer and Cross The Letter!Document4 pagesI. Choose The Right Answer and Cross The Letter!yusufNo ratings yet
- Tunga Pushkara EnglishDocument4 pagesTunga Pushkara EnglisharunagirinatharNo ratings yet
- Motokawa-Sushi Science and Hamburger ScienceDocument13 pagesMotokawa-Sushi Science and Hamburger Scienceluky8aNo ratings yet
- Cultures & Races MERP - To Rolemaster (RMSS-RMFRP)Document187 pagesCultures & Races MERP - To Rolemaster (RMSS-RMFRP)Loricia100% (4)
- MA English 2008 PatternDocument69 pagesMA English 2008 PatternKuNdAn DeOrENo ratings yet
- SWR 2005 CatalogDocument18 pagesSWR 2005 CatalogMultiarsNo ratings yet
- Capitalization: Lesson SummaryDocument7 pagesCapitalization: Lesson Summarydina mawarNo ratings yet