Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q1. What Do You Understand by Information Processes Data? Ans
Q1. What Do You Understand by Information Processes Data? Ans
Uploaded by
prafullmathurOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q1. What Do You Understand by Information Processes Data? Ans
Q1. What Do You Understand by Information Processes Data? Ans
Uploaded by
prafullmathurCopyright:
Available Formats
Q1. What do you understand by Information processes data?
Ans:- Data are generally considered to be raw facts that have undefined uses and application; information is considered to be
processed data that influences choices, that is, data that have somehow been formatted, filtered, and summarized; and knowledge is considered to be an understanding derived from information distinctions among data, information, and knowledge may be derived from scientific terminology. The researcher collects data to test hypotheses; thus, data refer to unprocessed and unanalyzed numbers. When the data are analyzed, scientists talk about the information contained in the data and the knowledge acquired from their analyses. The confusion often extends to the information systems context, and the three terms maybe used interchangeably.
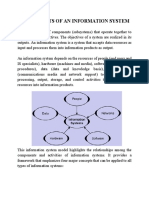
Q.2 Discuss the Components of an Organizational Information System
Ans :Software
Information technology includes computer software, hardware, database management systems, and data communication systems. How does the computer system at Department Store know how to process sales information? What tells the computer system at Federal Express how to record the arrival or departure of aircraft?
Computer software provides the instructions, in the form of computer code and its accompanying documentation, for processing data electronically. Systems software directs the functioning of the computer machinery. Applications software assists in the acquisition, processing, storage, retrieval, and communication of information. Software development tools such as computer languages and screen generators facilitate creating or modifying software to respond to an organizations information needs. Individuals and organizations can purchase an array of software products. Off-the-shelf software is mass-produced software made for a variety of generic uses such as word processing. Sometimes managers and other organizational members require experts to write customized software because they have a unique need that no off-the-shelf software adequately meets. In some circumstances these same employees may develop their own software that they modify over time to meet their changing work or personal needs. Hardware Computer hardware refers to the equipment used in electronic information processing. Significant strides have occurred in the development of hardware in the last decade. While processing power has increased, the size of the hardware has decreased considerably. Today desktop and portable computers costs are continuously reducing and can outperform the room-sized, million-dollar computers of ten years ago. Input hardware captures raw data and information from interactive uses. Processing hardware converts or transforms data. Storage hardware includes removable and fixed media that allow rapid access to information. Output hardware provides copies of data on paper, microform, and video screens; it offers varying quality for graphics, print, voice, or other effects. Database Management Systems Database management system offers a vehicle for storing and supporting the processing of large quantities of non- scientific information, such as data on employees, products, customers, and suppliers. This technology allows managers to easily access, sort, and analyse databases of information along a variety of dimensions. Data communication technology Data communication technology has dramatically improved the communication of information across short and long distances. Managers and other employees can easily send data from one plant location to another or access data located halfway around the world using dialin options, computer networks, video conferences, and other electronic media. Advances in communication technology occur frequently, reducing the cost and increasing the accuracy and speed of data transmission.
You might also like
- Man B&W l23-30h ManualDocument358 pagesMan B&W l23-30h Manual陈浩祥73% (11)
- A Complete MDMA Synthesis For The First Time Chemist: Compilation and Editorial by Bright StarDocument14 pagesA Complete MDMA Synthesis For The First Time Chemist: Compilation and Editorial by Bright StarAdrien G. S. Wald100% (3)
- Introdution To Information TechnologyDocument81 pagesIntrodution To Information TechnologyPratibha Jha100% (1)
- Role of Data For Emerging TechnologiesDocument12 pagesRole of Data For Emerging TechnologiesGosa Guta86% (14)
- To Ict Practical Hardware Software Liveware Firmware StorageDocument10 pagesTo Ict Practical Hardware Software Liveware Firmware StorageiroshiniwijesinheNo ratings yet
- (Networks) and Stored Data (Data Resources) - Although Today's Information Systems Are Typically Thought of AsDocument5 pages(Networks) and Stored Data (Data Resources) - Although Today's Information Systems Are Typically Thought of AsAbu BasharNo ratings yet
- 5014 Technology Policy and AdministrationDocument7 pages5014 Technology Policy and AdministrationKanwal umerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics LEARNING OUTCOMES After Completing This Chapter, YouDocument22 pagesNursing Informatics LEARNING OUTCOMES After Completing This Chapter, Youtwy113100% (1)
- Final Project: Introduction To Computing: Information SystemDocument24 pagesFinal Project: Introduction To Computing: Information SystemVanielle BilunoNo ratings yet
- CAB - Data Processing File &recordsDocument19 pagesCAB - Data Processing File &recordsRohit MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument6 pagesInformation TechnologyWenice CampbellNo ratings yet
- 3 - Edms-2Document4 pages3 - Edms-2spnatuNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems: Definition - What Does Decision Support System (DSS) Mean?Document4 pagesExpert Systems: Definition - What Does Decision Support System (DSS) Mean?Angel LawsonNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument6 pagesInformation TechnologyAyu Pratika sariNo ratings yet
- MIS AssignmentDocument29 pagesMIS AssignmentBijay MishraNo ratings yet
- 76 (Repaired)Document6 pages76 (Repaired)Rabi SinghNo ratings yet
- Is NotesDocument24 pagesIs NotesTinu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Components of An Information SystemDocument9 pagesComponents of An Information SystemKhoa Anh BùiNo ratings yet
- MIS TermsDocument6 pagesMIS TermssamiNo ratings yet
- BA ComputerDocument3 pagesBA ComputerMary Cris MostacisaNo ratings yet
- Information Technology (IT) : IT Software and HardwareDocument4 pagesInformation Technology (IT) : IT Software and Hardwareblueboy100% (1)
- DCIT21 LectureWeek2to3StudentsDocument7 pagesDCIT21 LectureWeek2to3StudentsmendoladeeNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument3 pagesResearchrobertbillatteNo ratings yet
- Components of Information SystemDocument4 pagesComponents of Information SystemSanjay YadavNo ratings yet
- Seminar Of: Foundation of Enterprise Information SystemDocument15 pagesSeminar Of: Foundation of Enterprise Information Systemabdool_21No ratings yet
- CONCEPTS OF IT and ICTDocument43 pagesCONCEPTS OF IT and ICTMoon IightNo ratings yet
- Computer For Hi (Autorecovered)Document36 pagesComputer For Hi (Autorecovered)MULUKENNo ratings yet
- Computer Technology and Business ResearchDocument19 pagesComputer Technology and Business Researchnugroho saputroNo ratings yet
- MIS TermsDocument8 pagesMIS TermssamiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 The Computer Environment and Controls in An IT Environment HODocument11 pagesCHAPTER 2 The Computer Environment and Controls in An IT Environment HOtjasonkiddNo ratings yet
- 3457Document3 pages3457Mahamodul Hasan ShohanNo ratings yet
- in PeoplewareDocument40 pagesin PeoplewareGlenda C. Flores0% (1)
- Information System in Our LifeDocument3 pagesInformation System in Our LifeMaleeha SabirNo ratings yet
- Csis 151 Lecture 1aDocument33 pagesCsis 151 Lecture 1alinuxsilva32No ratings yet
- Eapp Concept PaperDocument4 pagesEapp Concept PapertrishagabbyrodriguezNo ratings yet
- Operations Support SystemDocument5 pagesOperations Support SystemAishu SathyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Paperless OfficeDocument4 pagesLecture 1 - Paperless OfficeMakinwa RehobothNo ratings yet
- THE IMPORTANCE OF IT TOOL (Research)Document4 pagesTHE IMPORTANCE OF IT TOOL (Research)Annaya LuzNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 5Document4 pagesLecture Note 5johnsamba15No ratings yet
- Huliganga, John Paul V. BSTM A32Am What Is Management Information Systems (MIS) ?Document3 pagesHuliganga, John Paul V. BSTM A32Am What Is Management Information Systems (MIS) ?John Paul Vejiga HuligangaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Application: Chapter OneDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Computer Application: Chapter OneMaldini NyachNo ratings yet
- Data Processing SystemDocument5 pagesData Processing SystemsameerghouriNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument8 pagesInformation TechnologyAnkur MahteNo ratings yet
- Business Application Software Module 1Document9 pagesBusiness Application Software Module 1Hannah Fae BarcebalNo ratings yet
- PCA20S01L - IT Infrastructure ManagementDocument25 pagesPCA20S01L - IT Infrastructure ManagementMOHAMED FIRNAS (RA1931005020191)No ratings yet
- NURSING INFORMATICS Review NotesDocument4 pagesNURSING INFORMATICS Review Notespoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Lec. 3Document31 pagesLec. 3eseemNo ratings yet
- Review Questions For Chapter 5 Business Information SystemsDocument3 pagesReview Questions For Chapter 5 Business Information Systemsrobj20076404No ratings yet
- What Is Software Hardware and People 1.PptmDocument55 pagesWhat Is Software Hardware and People 1.Pptmrci.angelorendainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1behailuNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Using ICTs in BusinessDocument7 pagesThe Benefits of Using ICTs in BusinessRicardo B. ViganNo ratings yet
- IT TrainingDocument12 pagesIT TrainingShital SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Intro To IT-1Document36 pagesIntro To IT-1ahmad mujtabaNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document16 pagesCH 2Dessu AshagrieNo ratings yet
- Graphical User InterfaceDocument59 pagesGraphical User InterfaceeseemNo ratings yet
- ICT Chapter 1Document7 pagesICT Chapter 1Birhanu AtnafuNo ratings yet
- Information Technology - A DefinitionDocument11 pagesInformation Technology - A DefinitionArvind ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- MIS Unit-4Document19 pagesMIS Unit-4Kunal KambleNo ratings yet
- IS ComponentsDocument28 pagesIS ComponentsSTEPHENNo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Lecture: FIVE Chapter: THREEDocument11 pagesInformation Systems: Lecture: FIVE Chapter: THREEMd. Saiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Dry CleaningDocument7 pagesDry Cleaningziniya rahmanNo ratings yet
- Airseal 2 - ENDocument1 pageAirseal 2 - ENАндрей МошкинNo ratings yet
- House Plan Sample Plan SignedDocument23 pagesHouse Plan Sample Plan SignedSolidr ArchitectsNo ratings yet
- Rp6s - Master For Idc - 8-Oct-2021 Printed PDFDocument25 pagesRp6s - Master For Idc - 8-Oct-2021 Printed PDFItz GyyyNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Distillation of ALcoholic BeveragesDocument12 pagesFormal Report Distillation of ALcoholic Beveragespatricia_moran_4No ratings yet
- 2013 1357 Wang 02 WDocument15 pages2013 1357 Wang 02 WReinaldo Side JuniorNo ratings yet
- Interhane 990 MSDSDocument8 pagesInterhane 990 MSDSSyawaluddin Fitri AwangNo ratings yet
- Foreva - Maintenance of Stay CableDocument12 pagesForeva - Maintenance of Stay CableHuy Nguyen VanNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Paraplast X-TRA®Document7 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Paraplast X-TRA®meganingtyasNo ratings yet
- Southern Cross - Iso Pump - Installation and Operating InstructionDocument4 pagesSouthern Cross - Iso Pump - Installation and Operating InstructionFerryNo ratings yet
- HDCE-30C User ManualDocument54 pagesHDCE-30C User ManualmazolasboNo ratings yet
- English Medium Lec. Physics-2 2020-Ok PDFDocument23 pagesEnglish Medium Lec. Physics-2 2020-Ok PDFSakib KhanNo ratings yet
- Minfc21814 Astm A29 Grade 1065 PDFDocument3 pagesMinfc21814 Astm A29 Grade 1065 PDFDaniel HerreraNo ratings yet
- Ista 3BDocument12 pagesIsta 3Bduygu9merve100% (1)
- S12R-Y1PTA-2 Mitsubishi Diesel Generator EngineDocument3 pagesS12R-Y1PTA-2 Mitsubishi Diesel Generator EnginealstomNo ratings yet
- The Dark Side of Winsock - Lecture NotesDocument23 pagesThe Dark Side of Winsock - Lecture NotesragorillaNo ratings yet
- Metal Inelasticity in ABAQUS - L3 - Direct Cyclic Procedure PDFDocument7 pagesMetal Inelasticity in ABAQUS - L3 - Direct Cyclic Procedure PDFFahrgerusteNo ratings yet
- g10 Fr4 DatasheetDocument1 pageg10 Fr4 DatasheetrajendaranNo ratings yet
- Apollo Pro SpecificaitonDocument4 pagesApollo Pro SpecificaitonpedropcNo ratings yet
- Calax ItpbDocument1 pageCalax ItpbCharlon MayoNo ratings yet
- 1.intro Electrical SafetyMicrosoft PowerPoint - PPT 1 Introduction To Electrical Safety 1 OshaDocument22 pages1.intro Electrical SafetyMicrosoft PowerPoint - PPT 1 Introduction To Electrical Safety 1 OshaMohd MuzaniNo ratings yet
- Capacities and Specifications: MaintenanceDocument22 pagesCapacities and Specifications: MaintenanceAlexander the greatNo ratings yet
- Fiat MultiAir System - Operation Diagnosis & ServiceDocument72 pagesFiat MultiAir System - Operation Diagnosis & Servicetonny1996No ratings yet
- Fieldwork Exercise No. 5 Differential Leveling: STA BA HI FS Elevation RemarksDocument3 pagesFieldwork Exercise No. 5 Differential Leveling: STA BA HI FS Elevation RemarksBeaumont Serene Del ReigoNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Data QualityDocument16 pagesEnsuring Data QualityAlsayed AlgergawyNo ratings yet
- Fire Control Frontrest Instructions PDFDocument4 pagesFire Control Frontrest Instructions PDFNoemiJusticiaNo ratings yet
- CAED Project PDFDocument5 pagesCAED Project PDFUsama AameerNo ratings yet
- W - 8-10ab Mole-Mass Problems Wkst-Key and QDocument4 pagesW - 8-10ab Mole-Mass Problems Wkst-Key and QR RenegadeNo ratings yet