Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SEBI
SEBI
Uploaded by
Akash ShrivastavaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SEBI
SEBI
Uploaded by
Akash ShrivastavaCopyright:
Available Formats
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
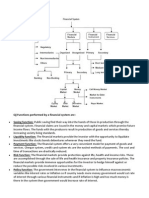
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was first established in the year 1988 as a non-statutory body for regulating the securities market. SEBI is the regulator for the securities market in India. It became an autonomous body in 1992 and more powers were given through an ordinance. Since then it regulates the market through its independent powers. It was chaired by C B Bhave, SEBI is headquartered in the popular business district of Bandra-Kurla complex in Mumbai, and has Northern, Eastern, Southern and Western regional offices in New Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai and Ahmedabad. Objectives of SEBI: As an important entity in the market it works with following objectives: 1. It tries to develop the securities market. 2. Promotes Investors Interest. 3. Makes rules and regulations for the securities market. Functions of SEBI: Find below SEBI's important functions: 1. Regulates Capital Market 2. Checks Trading of securities. 3. Checks the malpractices in securities market. 4. It enhances investor's knowledge on market by providing education. 5. It regulates the stockbrokers and sub-brokers. Functions and responsibilities: SEBI has to be responsive to the needs of three groups, which constitute the market:
the issuers of securities the investors the market intermediaries.
SEBI has three functions rolled into one body quasi-legislative, quasi-judicial and quasiexecutive. It drafts regulations in its legislative capacity, it conducts investigation and enforcement action in its executive function and it passes rulings and orders in its judicial capacity. Though this makes it very powerful, there is an appeals process to create accountability. There is a Securities Appellate Tribunal which is a three-member tribunal and is presently headed by a former Chief Justice of a High court - Mr. Justice NK Sodhi. A second appeal lies directly to the Supreme Court. SEBI has enjoyed success as a regulator by pushing systemic reforms aggressively and successively (e.g. the quick movement towards making the markets electronic and paperless rolling settlement on T+2 basis). SEBI has been active in setting up the regulations as required under law. SEBI has also been instrumental in taking quick and effective steps in light of the global meltdown and the Satyam fiasco.[citation needed] It had[when?] increased the extent and quantity of disclosures to be made by Indian corporate promoters. More recently, in light of the global meltdown,it liberalised the takeover code to facilitate investments by removing regulatory strictures.
You might also like
- Launch an "ICO" & Token Crowdsale: The Complete Guide to Prepare Your Startup for Launching Successful Initial Coin Offering, Raising Venture & Cryptocurrency CapitalFrom EverandLaunch an "ICO" & Token Crowdsale: The Complete Guide to Prepare Your Startup for Launching Successful Initial Coin Offering, Raising Venture & Cryptocurrency CapitalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Should There Be Limits To Free Speech ViewpointsDocument95 pagesShould There Be Limits To Free Speech ViewpointszeeNo ratings yet
- Project On SebiDocument15 pagesProject On SebiVrushti Parmar88% (17)
- Philippine Politics and Governance: Quarter 2-Module 9Document21 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance: Quarter 2-Module 9Fenando Sabado100% (14)
- SEBIDocument1 pageSEBIApurva DipnaikNo ratings yet
- Introductio 1Document2 pagesIntroductio 1Anil ShelarNo ratings yet
- Sebi Power and FunctionDocument13 pagesSebi Power and Functionaman kadriNo ratings yet
- Investment and Securities AssignmentDocument16 pagesInvestment and Securities Assignmentkhusboo kharbandaNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument48 pagesINTRODUCTIONtanisq10100% (2)
- Role of SEBI in Capital MarketDocument6 pagesRole of SEBI in Capital MarketShashank HatleNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument21 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of IndiaDeepa A PoojaryNo ratings yet
- Functional Report of SEBIDocument9 pagesFunctional Report of SEBIAMIT K SINGH100% (1)
- Capital Market and SEBIDocument4 pagesCapital Market and SEBINishant GoyalNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesCorporate Social Responsibilityperumbhuduru manoharNo ratings yet
- Index: S. No. Title No. Remark SDocument17 pagesIndex: S. No. Title No. Remark SSiddhi PatwaNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of India: Regulator Securities SEBI Act, 1992Document6 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of India: Regulator Securities SEBI Act, 1992Pawan LohanaNo ratings yet
- C C CM: MMMMMMDocument4 pagesC C CM: MMMMMMGaurav RauthanNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument5 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of IndiaKanna RajeshNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument73 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of IndiaSurya ParkashNo ratings yet
- Name-Meyechila Luho Reg. No. - 19019100017 Bba 5 Sem Investment Management (U18BBA52)Document6 pagesName-Meyechila Luho Reg. No. - 19019100017 Bba 5 Sem Investment Management (U18BBA52)MechiluhoNo ratings yet
- National Law Institute University Bhopal: Project - Administrative Law SebiDocument20 pagesNational Law Institute University Bhopal: Project - Administrative Law SebiSurbhi LaddhaNo ratings yet
- SEBIDocument3 pagesSEBIsruthi karthiNo ratings yet
- Internal Backlog Company Law Role of Sebi in Stock ExchangeDocument9 pagesInternal Backlog Company Law Role of Sebi in Stock ExchangeApoorv SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Topic: Sebi As A Regulatory Authority On Companies: Company LawDocument21 pagesTopic: Sebi As A Regulatory Authority On Companies: Company LawsrivarshiniNo ratings yet
- History: Government of India Indian Parliament Bandra Kurla Complex Mumbai New Delhi Kolkata Chennai AhmedabadDocument2 pagesHistory: Government of India Indian Parliament Bandra Kurla Complex Mumbai New Delhi Kolkata Chennai AhmedabadVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Group10 LABDocument15 pagesGroup10 LABRADHIKA MUKATINo ratings yet
- Sebi Functional ReportDocument7 pagesSebi Functional ReportRohan Pawar61% (18)
- Upendra Kumar Sinha C. B. Bhave: Was Appointed Chairman On 18 February 2011 Replacing - TH e Board ComprisesDocument4 pagesUpendra Kumar Sinha C. B. Bhave: Was Appointed Chairman On 18 February 2011 Replacing - TH e Board ComprisesAbhishek ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of India: SEBI - A Brief IntroductionDocument37 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of India: SEBI - A Brief IntroductionBhushan KharatNo ratings yet
- Sebi'S Background: Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument15 pagesSebi'S Background: Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaAnjaliNo ratings yet
- Investment Law PresentationDocument11 pagesInvestment Law PresentationNanda SurajNo ratings yet
- Sebi Upsc Notes 45Document4 pagesSebi Upsc Notes 45tipuchouhan3No ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument11 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of IndiaRanesh Raveendran RNo ratings yet
- Project On Investment Law Sebi SecuritieDocument14 pagesProject On Investment Law Sebi Securitielalit 08No ratings yet
- Project: Sebi (Securities and Exchange Board of India) Role, Powers and Functions Submitted ToDocument14 pagesProject: Sebi (Securities and Exchange Board of India) Role, Powers and Functions Submitted ToDHANANJAY MIRLEKARNo ratings yet
- Ifm AssignmentDocument15 pagesIfm AssignmentRockstar KshitijNo ratings yet
- Co Law IiDocument15 pagesCo Law IiRitik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Business Environment GroupDocument11 pagesBusiness Environment Grouphazrak133No ratings yet
- SEBIDocument12 pagesSEBIdeeptiNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of India PDFDocument18 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of India PDFShifa RasheedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On SebiDocument17 pagesAssignment On SebiSUFIYAN SIDDIQUINo ratings yet
- FMR AssignmentDocument8 pagesFMR AssignmentABHISHEK MARORIANo ratings yet
- Debt Market SEBIDocument7 pagesDebt Market SEBIvidhipatadia3013No ratings yet
- Labour Law AssignmentDocument8 pagesLabour Law AssignmentTanya SinghNo ratings yet
- Establishment of SEBI: The Securities And: BanksDocument6 pagesEstablishment of SEBI: The Securities And: BanksAkku GuptaNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument13 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of Indiasonal jainNo ratings yet
- SebiDocument26 pagesSebikhilchiadilNo ratings yet
- SP ProjectDocument14 pagesSP ProjectVyankatesh KarnewarNo ratings yet
- SEBI's Role in Capital MarketDocument57 pagesSEBI's Role in Capital MarketSagar Agarwal100% (9)
- Mfsi Unit 4 FinalDocument15 pagesMfsi Unit 4 Finalsauravnagpal309No ratings yet
- SEBI - The Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument35 pagesSEBI - The Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaRohan FodnaikNo ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument14 pagesFinancial ServicesChaitanya NandaNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument10 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of IndiajaseelekaNo ratings yet
- Regulators-Sebi: Courses Offered: Rbi Grade B Sebi Grade A Nabard Grade A and B Ugc Net Paper 1 and 2Document12 pagesRegulators-Sebi: Courses Offered: Rbi Grade B Sebi Grade A Nabard Grade A and B Ugc Net Paper 1 and 2ramanNo ratings yet
- Role of SebiDocument3 pagesRole of SebiAnkush PoojaryNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument32 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of IndiaMohan kashyapNo ratings yet
- Investment LawDocument31 pagesInvestment LawKhushi SalujaNo ratings yet
- The Purpose, Objective and Functions of SEBIDocument9 pagesThe Purpose, Objective and Functions of SEBIAlexander McfarlandNo ratings yet
- Role of SEBI in Primary MarketDocument19 pagesRole of SEBI in Primary MarketTwinkle RajpalNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaDocument6 pagesSecurities and Exchange Board of IndiaSiddhi PatwaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Stefan Loesch's A Guide to Financial Regulation for Fintech EntrepreneursFrom EverandSummary of Stefan Loesch's A Guide to Financial Regulation for Fintech EntrepreneursNo ratings yet
- Conflict of LawsDocument15 pagesConflict of LawsAkash Shrivastava100% (3)
- Types of EvidencesDocument13 pagesTypes of EvidencesAkash Shrivastava100% (2)
- Role of Press in IndiaDocument13 pagesRole of Press in IndiaAkash Shrivastava100% (4)
- Mining Laws in IndiaDocument30 pagesMining Laws in IndiaAkash Shrivastava100% (1)
- Judicial ReviewDocument16 pagesJudicial ReviewAkash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Arrest Without WarrantDocument35 pagesArrest Without WarrantAkash Shrivastava100% (1)
- Arrest Without WarrantDocument35 pagesArrest Without WarrantAkash Shrivastava100% (1)
- Arrest Without WarrantDocument35 pagesArrest Without WarrantAkash Shrivastava100% (1)
- Family Law ProjectDocument14 pagesFamily Law ProjectAkash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Do We Need Law To Curb The Black Money: Submitted by - Akash Shrivastava B.A.L.L.B. S.S.L.G (JNU, Jaipur)Document9 pagesDo We Need Law To Curb The Black Money: Submitted by - Akash Shrivastava B.A.L.L.B. S.S.L.G (JNU, Jaipur)Akash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Jaipur National University: Project On "Brain Drain in India"Document8 pagesJaipur National University: Project On "Brain Drain in India"Akash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PIL IHL Part 1Document5 pagesPIL IHL Part 1Pierre AlvizoNo ratings yet
- Air - Manila - Inc. - v. - Court - of - Industrial Relations - GR No L-39742Document12 pagesAir - Manila - Inc. - v. - Court - of - Industrial Relations - GR No L-39742Timmy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 2022-07-21 Letter To Kate LeFurgyDocument3 pages2022-07-21 Letter To Kate LeFurgyAdam HarringtonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document9 pagesChapter 12api-294763222No ratings yet
- Cases and Definitions in LawDocument53 pagesCases and Definitions in LawJoseReneRomanoCruelNo ratings yet
- A Resolution UbasDocument3 pagesA Resolution UbasKristine Lara Virata Espiritu100% (3)
- NEA vs. GonzagaDocument3 pagesNEA vs. GonzagaJeushl Wensh Tiu IINo ratings yet
- Baudl Poverty Reps KDocument86 pagesBaudl Poverty Reps KJohnBoalsNo ratings yet
- C4C Requests Investigation of MSPB Vice-Chairman Anne WagnerDocument2 pagesC4C Requests Investigation of MSPB Vice-Chairman Anne WagnerC4CNo ratings yet
- Bito-Onon V FernandezDocument1 pageBito-Onon V FernandezYieMaghirangNo ratings yet
- Polirev Syllabus Case DigestDocument120 pagesPolirev Syllabus Case DigestGladys Bustria OrlinoNo ratings yet
- Office of The Court Administrator v. GinesDocument14 pagesOffice of The Court Administrator v. Ginesida_chua8023No ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument1 pageCommunity Health NursingNeenu RajputNo ratings yet
- Ra 6713Document5 pagesRa 6713attywithnocaseyet100% (1)
- Whether or Not The Accused Should Be Held Liable As A Co-Principal For The Crime of RapeDocument2 pagesWhether or Not The Accused Should Be Held Liable As A Co-Principal For The Crime of Rapevincent nifasNo ratings yet
- Petitioners Vs Vs Respondent Romulo, Mabanta, Buenaventura, Sayoc & Delos Angeles Castillo Laman Tan Pantaleon & San JoseDocument10 pagesPetitioners Vs Vs Respondent Romulo, Mabanta, Buenaventura, Sayoc & Delos Angeles Castillo Laman Tan Pantaleon & San JoseGael MoralesNo ratings yet
- Congress Receives Irrefutable Evidence of IRS Harassment of Pro-Life OrganizationsDocument151 pagesCongress Receives Irrefutable Evidence of IRS Harassment of Pro-Life OrganizationsTom CiesielkaNo ratings yet
- Data Protection Law in IndiaDocument3 pagesData Protection Law in IndiaNaveen SihareNo ratings yet
- Comparative Legal System and ProcessDocument57 pagesComparative Legal System and ProcessRolito OroscoNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Health, Safety, and SecurityDocument25 pagesHuman Resource Management: Health, Safety, and SecurityJoko DewotoNo ratings yet
- Crim Case Digests - Compiled (13 March 2019) PDFDocument294 pagesCrim Case Digests - Compiled (13 March 2019) PDFAnnyleneMauricioNo ratings yet
- ANIKET SINGH THAKUR Enroll. No. R19515031004Document59 pagesANIKET SINGH THAKUR Enroll. No. R19515031004OMSAINATH MPONLINENo ratings yet
- Csi Res Reentry Services BrochureDocument2 pagesCsi Res Reentry Services Brochureapi-243106884No ratings yet
- Republic vs. SerenoDocument3 pagesRepublic vs. SerenoChristine LaguraNo ratings yet
- Van Luspo Vs People of The PhilippinesDocument23 pagesVan Luspo Vs People of The PhilippinesJennifer Berg0% (1)
- 'Crime Situation in Bangladesh During ''Covid-19 Lockdown'''Document4 pages'Crime Situation in Bangladesh During ''Covid-19 Lockdown'''Tauky YasirNo ratings yet
- European Union Law Compliance: Case ScenarioDocument20 pagesEuropean Union Law Compliance: Case ScenarioKipng'etichRonoNo ratings yet
- Conversion Vs ReclassificationDocument7 pagesConversion Vs ReclassificationCharonel Lague GalendezNo ratings yet