Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effective Communication Handout
Effective Communication Handout
Uploaded by
drakosroroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- TEFL Lesson Plan For AdultsDocument7 pagesTEFL Lesson Plan For AdultsNikki Goss100% (2)
- Understanding Humor Throu CommunicationDocument146 pagesUnderstanding Humor Throu CommunicationpeperetruNo ratings yet
- WorkingWithYouisKilling MeDocument12 pagesWorkingWithYouisKilling MeClover1897100% (1)
- Swot AnalysisDocument31 pagesSwot Analysisapi-531473888No ratings yet
- Using The MBTI To Enhance Workplace Communication PDFDocument4 pagesUsing The MBTI To Enhance Workplace Communication PDFVijay Chandra SekarNo ratings yet
- Student Action Items PrintDocument3 pagesStudent Action Items Printapi-373239722No ratings yet
- Flexing Your Social StyleDocument20 pagesFlexing Your Social StyleM A MandalNo ratings yet
- # 0 Soft Skills ListDocument12 pages# 0 Soft Skills ListAde Reni SavitriNo ratings yet
- Process Consultation Revisited - My SummaryDocument32 pagesProcess Consultation Revisited - My Summaryapi-254207666No ratings yet
- What Is Executive Presence - Booklet 2018Document4 pagesWhat Is Executive Presence - Booklet 2018Efl Idiomas100% (1)
- Summary 2 TCH Story PitchDocument2 pagesSummary 2 TCH Story PitchVasanth RajaNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Team Leadership ModelDocument33 pagesTopic 10 Team Leadership ModelNayama Nayama100% (1)
- Building Rapport - : Process & Principle An Article by Ken Buist 1Document4 pagesBuilding Rapport - : Process & Principle An Article by Ken Buist 1tanwiNo ratings yet
- ACAS How To Manage Change Booklet Ver Jan 2010Document44 pagesACAS How To Manage Change Booklet Ver Jan 2010anhngocNo ratings yet
- Book Creating Learning CultureDocument20 pagesBook Creating Learning CultureIwan SyahNo ratings yet
- Setting Goals in Career ManagementDocument10 pagesSetting Goals in Career ManagementhernanrjNo ratings yet
- Leading Through Transitions Participant Workbook One-Day WorkshopFrom EverandLeading Through Transitions Participant Workbook One-Day WorkshopNo ratings yet
- Building and Sustaining A Winning CultureDocument19 pagesBuilding and Sustaining A Winning CultureNoah RaecekNo ratings yet
- My CliftonStrengths - Student Action ItemsDocument9 pagesMy CliftonStrengths - Student Action ItemsCorbin FowlerNo ratings yet
- Interview Skills Workshop: What Attributes Are The College Looking For ? (Selection Criteria)Document7 pagesInterview Skills Workshop: What Attributes Are The College Looking For ? (Selection Criteria)Samia Naz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Leadership Challenge 2019 PPT-SHA Edit-2Document32 pagesLeadership Challenge 2019 PPT-SHA Edit-2Hessam SobhaniNo ratings yet
- Leading From The Heart PresentationDocument11 pagesLeading From The Heart Presentationapi-204108071No ratings yet
- Transactional Analysis in MarketingDocument15 pagesTransactional Analysis in Marketingबिक्रम नेपालीNo ratings yet
- What's Your Goal After Graduate: Prof. Susi Endrini, PH.D RectorDocument19 pagesWhat's Your Goal After Graduate: Prof. Susi Endrini, PH.D RectorSendriniNo ratings yet
- Meg Wheatley + Angela Blanchard - Leaders For The Storm, Aug 2011Document6 pagesMeg Wheatley + Angela Blanchard - Leaders For The Storm, Aug 2011David HoodNo ratings yet
- Liberatory Design CardsDocument52 pagesLiberatory Design CardsAnonymous 30uDEC1f5No ratings yet
- Diverseo Reducing Unconscious Bias A Highly Effective Toolbox and How To Avoid The Unconscious Bias PitfallsDocument12 pagesDiverseo Reducing Unconscious Bias A Highly Effective Toolbox and How To Avoid The Unconscious Bias PitfallsWebmaster DiverseoNo ratings yet
- July Unconscious BiasDocument4 pagesJuly Unconscious BiasEmily Ross100% (2)
- Retreat Made EasyDocument6 pagesRetreat Made EasyMarianaNo ratings yet
- Crisis Communication TheoryDocument16 pagesCrisis Communication TheoryFrank MartinNo ratings yet
- 7 Strategies To Build A More Resilient TeamDocument5 pages7 Strategies To Build A More Resilient TeamJuan CastelNo ratings yet
- SBL PDF For Legacy PrivilegeDocument82 pagesSBL PDF For Legacy PrivilegeClaytonNo ratings yet
- Organizational Innovation & Problem SolvingDocument33 pagesOrganizational Innovation & Problem SolvingChinmoy KrNo ratings yet
- Picking The Right Transition StrategyDocument9 pagesPicking The Right Transition Strategybiertapper1990100% (1)
- Introduction To Planning and Facilitating Effective MeetingsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Planning and Facilitating Effective MeetingsSANAL R PNo ratings yet
- Chairing A Difficult MeetingDocument3 pagesChairing A Difficult MeetingBill TaylorNo ratings yet
- Effective Meetings and DelegatingDocument21 pagesEffective Meetings and DelegatingfarisNo ratings yet
- Mentoring & Community BuildingDocument700 pagesMentoring & Community BuildingAnimals of the FieldsNo ratings yet
- 09 Stages in Conducting A FacilitationDocument1 page09 Stages in Conducting A FacilitationleksanathsingaporeNo ratings yet
- NIPM Cochin Chapter - Oct 29, 2013Document44 pagesNIPM Cochin Chapter - Oct 29, 2013jayadevmNo ratings yet
- Convergent Excellence RevDocument11 pagesConvergent Excellence RevSundeep RohilaNo ratings yet
- Challenging Conversations and How To Manage ThemDocument24 pagesChallenging Conversations and How To Manage ThemFlorina C100% (1)
- Leading Facilitating Change PDFDocument25 pagesLeading Facilitating Change PDFdilanhjNo ratings yet
- Amazeing Organizational Teams: Navigating 7 Critical Attributes for Cohesion, Productivity and ResilienceFrom EverandAmazeing Organizational Teams: Navigating 7 Critical Attributes for Cohesion, Productivity and ResilienceNo ratings yet
- Professional Communication in Today's Digital, Social, Mobile WorldDocument35 pagesProfessional Communication in Today's Digital, Social, Mobile WorldAdjeiNo ratings yet
- Drivers Working Styles Questionairre and SummaryDocument5 pagesDrivers Working Styles Questionairre and SummaryCosmina LungeanuNo ratings yet
- Book Review: Ego Free LeadershipDocument17 pagesBook Review: Ego Free LeadershipNikhilNo ratings yet
- Building ResilienceDocument8 pagesBuilding ResilienceRamovic Elvir-BeliNo ratings yet
- Trailblazer Mentorship - Mentee Playbook Jan 2020 PDFDocument20 pagesTrailblazer Mentorship - Mentee Playbook Jan 2020 PDFtalk2azhar.m100% (1)
- Eq ModelDocument3 pagesEq Modelzogclub100% (1)
- Strengths PlanDocument4 pagesStrengths Planapi-373188637No ratings yet
- 5 Easy Steps To Fearless Public Speaking: A Practical Powerful GuideDocument15 pages5 Easy Steps To Fearless Public Speaking: A Practical Powerful Guidehieu2100No ratings yet
- 2013 How To Be Brilliant at Public SpeakingDocument225 pages2013 How To Be Brilliant at Public Speakingrafi ziaeeNo ratings yet
- The Remote Facilitator's Pocket Guide: How Local Businesses Are Beating the Global CompetitionFrom EverandThe Remote Facilitator's Pocket Guide: How Local Businesses Are Beating the Global CompetitionNo ratings yet
- Small Group Strengths ActivitiesDocument2 pagesSmall Group Strengths ActivitiesnureevruslanNo ratings yet
- Leadership and AccountabilityDocument49 pagesLeadership and AccountabilityChineduNo ratings yet
- Leading High Performing Teams WorkbookDocument13 pagesLeading High Performing Teams WorkbookJyro TriviñoNo ratings yet
- Becoming An Excellent Facilitator: by Adam Fletcher, President, Commonaction ConsultingDocument6 pagesBecoming An Excellent Facilitator: by Adam Fletcher, President, Commonaction ConsultingvaleriaNo ratings yet
- ROHEI Building A Culture of TrustDocument24 pagesROHEI Building A Culture of TrustmaklpNo ratings yet
- DDI - DEI Report 2023 PDFDocument14 pagesDDI - DEI Report 2023 PDFSHRUTI DHUPIANo ratings yet
- Developing Personal EffectivenessDocument55 pagesDeveloping Personal Effectivenesssaleembutt341100% (2)
- Stress - WstępDocument11 pagesStress - WstępbadooagaNo ratings yet
- Cantera InglesDocument3 pagesCantera InglesJuan Reales0% (1)
- English-3 3RD QUARTER ExamDocument2 pagesEnglish-3 3RD QUARTER ExamRodel Corpuz MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Geometry ExercisesDocument12 pagesGeometry Exercisesann millendezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Pain Management by Ayurveda: Vaidya Aniruddha Shreedhar KulkarniDocument6 pagesClinical Approach To Pain Management by Ayurveda: Vaidya Aniruddha Shreedhar KulkarniAniruddha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Christian Religious Studies Waec SyllabusDocument6 pagesChristian Religious Studies Waec SyllabusPersonal PirearmNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Math HL 2001Document6 pagesSyllabus - Math HL 2001Marek KossowskiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 5 Introduction To Euclids GeometryDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 5 Introduction To Euclids Geometryshwetadutta1977No ratings yet
- Priniples of Church GrowthDocument47 pagesPriniples of Church Growthfrecousminzee5No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: - Make Sentences Using Possessive Cases - Speak About Parts of The HouseDocument2 pagesLesson Plan: - Make Sentences Using Possessive Cases - Speak About Parts of The HouseEugeniaUngureanuNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno Ec Sample CodeDocument1 pageArduino Uno Ec Sample Codeພໍ່ ທ້າວ ທະນາກອນNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformsDocument19 pagesLaplace TransformsJoshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Rpcgen Tutorial (ONC+ Developer's Guide)Document1 pageRpcgen Tutorial (ONC+ Developer's Guide)THAKKAR NARAYAN JAISUKHLALNo ratings yet
- A Study of Subject-Verb AgreementDocument7 pagesA Study of Subject-Verb AgreementWannaBuy GohNo ratings yet
- English Paper - XDocument7 pagesEnglish Paper - XvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHERS THINKING LOGIC and ARGUMENTDocument495 pagesPHILOSOPHERS THINKING LOGIC and ARGUMENTuriNo ratings yet
- The Politics of Panem - Challenging GenresDocument227 pagesThe Politics of Panem - Challenging GenresВалерияNo ratings yet
- South Park S26E06 NTB English-WWW MY-SUBS CODocument36 pagesSouth Park S26E06 NTB English-WWW MY-SUBS COgreen.paxNo ratings yet
- Interchange 1 Lab GuideDocument138 pagesInterchange 1 Lab GuideEdy Lopez Donis100% (1)
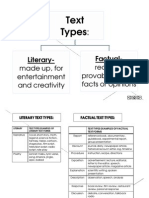
- Text TypesDocument24 pagesText Typesyosha16100% (2)
- 1 Hour Lesson PlanDocument2 pages1 Hour Lesson PlanKilah IlahNo ratings yet
- MA8353 PEC - by EasyEngineering - Net 02Document183 pagesMA8353 PEC - by EasyEngineering - Net 02SumanNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Titles in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesResearch Paper Titles in The Philippinesc9k7jjfk100% (1)
- Ext 2Document12 pagesExt 2swanandlawangareNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalsMaria Angel LopezNo ratings yet
- Word Formation SuffixesDocument3 pagesWord Formation SuffixesgarrotemacarenaNo ratings yet
- DCL SlideDocument6 pagesDCL SlideJyoti Bala WarwalNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter English 10 Assessment TestDocument6 pages4TH Quarter English 10 Assessment Testafbnjkcd100% (2)
- Lastexception 63847077330Document1 pageLastexception 63847077330lilll lopppzNo ratings yet
Effective Communication Handout
Effective Communication Handout
Uploaded by
drakosroroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effective Communication Handout
Effective Communication Handout
Uploaded by
drakosroroCopyright:
Available Formats
Effective communication Handout.
Definition: .......................................................................................................1 Communication model:......................................................................................1 Process or content focused ?..............................................................................2 Assertivness:...................................................................................................2 Instructing.......................................................................................................3 Types of Communication Barriers:......................................................................3 Overcoming communication barriers...................................................................4 Feedback......................................................................................................4 Receiving Feedback........................................................................................4 Active listening:.............................................................................................5 Further development:........................................................................................5
Definition:
The sharing of information between two or more individuals or groups We communicate always and are not able not to communicate
Communication model:
Sender
Message
Transmission
Encoding
Decoding Noise Medium
Feedback
Medium
Decoding
Encoding
Message
Receiver/Sender
Crucial point here to realize is that everybody becomes sender and also receiver, everybody decodes and encodes and everywhere we have threat of noise that can disrupt our message .
Process or content focused ?
Communication can be:
Process Friendship talk and chatting Pub talksneither process nor content Our goal high process and content Content Myth of perfect manager just content
Assertivness:
Assertive rights
It does not mean that:
You can do what do you want, regardless what you do to the others You never apologize or explain why you did particular thing.
I have right to judge my own behavior, thoughts, and feelings and take responsibility for them. I have right not to apologize or explain my behavior
I have right to consider if I am so That you will stop to help people. responsible for other peoples problems I have right to change my opinion. That you will change your mind according as you decide anytime, anyway. I have right to make mistakes and take That you will always prevaricate to right responsibility for them. to make mistakes anytime you ignore your duties. I have right to say: I do not know It will be your next excuse when you are lazy to think. I have right to be independent on other You will stop appreciate and manifest peoples will. love to people that help you and love you. I have right to make illogical decisions. That you can be mad and you do not take responsibility. I have right to say: I do not You stop trying to understand the others. Understand you. I have right to say: it is all the same to me. There You should become ignorant every time you do not want to listen to somebody.
are even more rights as follows: Express rights different from the others To be listened well and took serious Tell NO! if she/he really wants. Do not agree if he/she does not want to agree Right to other people treat him with respectfully Express anger when she/he is withheld with some right. Decide her/himself what is for her/him more important and what less.
To privacy if she/he wants to be alone Everybody has right to be or not to be assertive.
Instructing
Do you remember game with such a girl on a picture? This game was about how is it when we communicate using only one way. Then we transformed knowledge we gained during this game into guidelines for effective instructing: 1. Give a big picture when instructing. 2. Use as many channels as possible or optimum number 3. Work or message has to be meaningful. 4. Two way communication is necessary. 5. add your own
Types of Communication Barriers:
Filtering A senders manipulation of information so that it will be seen more favourably received by the receiver. The manipulation may be either conscious or sub-conscious and can drastically affect the message. Using feedback will determine to what extent the message has been filtered. ie: Tell someone something they want to hear. Selective Perception Receivers of communication selectively process a message based on their needs and attitudes. Once again, it may be onscious or sub-conscious. ie: Someone hears what they want to hear Language Language can be an imposing barrier to communicationimagine being an English-only speaker in Korea! Even assuming both parties are using the same language (eg. English), there are several levels of sophistication of language. Then you have the difficulty of dealing with specialist terms and jargon that may not be understood by the receiver. Giver Often there are personal characteristics of the communication giver that mean they will not be able to transfer the message as freely as possible. These can include: Afraid of being taken advantage of Makes us feel vulnerable Rejection by others Receiver By the same token, the receiver may have some personal characteristics that influence the way they accept communication.
They may be: Afraid No time Considered unimportant Resistant to change Lack of Communication skills
Overcoming communication barriers
Feedback
"Did you understand what I said?" Many inaccuracies occur because the feedback loop is not used. Asking questions is the most effective way to ensure effective communication. Feedback is a very simple concept to understand, and so the questions remains: why dont we do it more often? Below are some simple steps for giving feedback: Giving: 1. Make comments specific Feedback should relate to one incident that illustrates the point of your comment. This will make the person memorable to see where they acted in a way that was not acceptable. 2. At an appropriate time. If you approach someone while they are either busy or "not in the mood" they will not be in the mood of acceptance of your feedback, no matter how well you phrase it. 3. Behaviour must be in control of person. Only give feedback to someone if they have the ability to change the situation. If there is no control then you are not giving feedbackyou are whingeing! 4. Goal oriented Always explain in terms of the improvement that could occur and the benefits that would accrue to the individual if he/she were to take on the feedback and change their behaviour. Here are more tips:
Be sincere Talk on behalf of yourself Be descriptive not evaluative Be specific not general
Receiving Feedback
1. Ask open ended questions. "What do you mean by" 2. Listen actively with genuine interest.
Listening demands total concentration. The average person speaks at about 150 words per minute, whereas the capacity to listen is over 1,000 words per minute. This creates idle time for the brain to wander. Active listening helps the receiver to develop empathy with the sender, (putting yourself in the other persons position). Empathy helps you to understand the different attitudes of the sender, and to actually understand content of the message. 3. Establish rapport eye contact relaxed and receptive no interruptions 4. Respond and paraphrase "Do I understand you correctly?" - Simplify Language A sender should construct messages in manner that is easy to understand and process. Remember effective communication is achieved when a massage is received and understood. -Constrained Emotions It would be ludicrous to suggest that we always communicate in a clearly rational manner. Emotions can severely distort the transference of meaning. Ways to counter this include changing your message format, altering the time and location of your communication, or even filtering it in a positive way so that it is received better
Active listening:
The only thing that I advise You here is to listen for understanding. That is active listening all about. If your intent to understand is not genuine even showing your listening (do you remember training session?) like non-verbals etc. will unmasked.
Further development:
I recommend attending you also these training sessions: o Assertiveness o Effective email o Effective meetings o Presentation skills
You might also like
- TEFL Lesson Plan For AdultsDocument7 pagesTEFL Lesson Plan For AdultsNikki Goss100% (2)
- Understanding Humor Throu CommunicationDocument146 pagesUnderstanding Humor Throu CommunicationpeperetruNo ratings yet
- WorkingWithYouisKilling MeDocument12 pagesWorkingWithYouisKilling MeClover1897100% (1)
- Swot AnalysisDocument31 pagesSwot Analysisapi-531473888No ratings yet
- Using The MBTI To Enhance Workplace Communication PDFDocument4 pagesUsing The MBTI To Enhance Workplace Communication PDFVijay Chandra SekarNo ratings yet
- Student Action Items PrintDocument3 pagesStudent Action Items Printapi-373239722No ratings yet
- Flexing Your Social StyleDocument20 pagesFlexing Your Social StyleM A MandalNo ratings yet
- # 0 Soft Skills ListDocument12 pages# 0 Soft Skills ListAde Reni SavitriNo ratings yet
- Process Consultation Revisited - My SummaryDocument32 pagesProcess Consultation Revisited - My Summaryapi-254207666No ratings yet
- What Is Executive Presence - Booklet 2018Document4 pagesWhat Is Executive Presence - Booklet 2018Efl Idiomas100% (1)
- Summary 2 TCH Story PitchDocument2 pagesSummary 2 TCH Story PitchVasanth RajaNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Team Leadership ModelDocument33 pagesTopic 10 Team Leadership ModelNayama Nayama100% (1)
- Building Rapport - : Process & Principle An Article by Ken Buist 1Document4 pagesBuilding Rapport - : Process & Principle An Article by Ken Buist 1tanwiNo ratings yet
- ACAS How To Manage Change Booklet Ver Jan 2010Document44 pagesACAS How To Manage Change Booklet Ver Jan 2010anhngocNo ratings yet
- Book Creating Learning CultureDocument20 pagesBook Creating Learning CultureIwan SyahNo ratings yet
- Setting Goals in Career ManagementDocument10 pagesSetting Goals in Career ManagementhernanrjNo ratings yet
- Leading Through Transitions Participant Workbook One-Day WorkshopFrom EverandLeading Through Transitions Participant Workbook One-Day WorkshopNo ratings yet
- Building and Sustaining A Winning CultureDocument19 pagesBuilding and Sustaining A Winning CultureNoah RaecekNo ratings yet
- My CliftonStrengths - Student Action ItemsDocument9 pagesMy CliftonStrengths - Student Action ItemsCorbin FowlerNo ratings yet
- Interview Skills Workshop: What Attributes Are The College Looking For ? (Selection Criteria)Document7 pagesInterview Skills Workshop: What Attributes Are The College Looking For ? (Selection Criteria)Samia Naz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Leadership Challenge 2019 PPT-SHA Edit-2Document32 pagesLeadership Challenge 2019 PPT-SHA Edit-2Hessam SobhaniNo ratings yet
- Leading From The Heart PresentationDocument11 pagesLeading From The Heart Presentationapi-204108071No ratings yet
- Transactional Analysis in MarketingDocument15 pagesTransactional Analysis in Marketingबिक्रम नेपालीNo ratings yet
- What's Your Goal After Graduate: Prof. Susi Endrini, PH.D RectorDocument19 pagesWhat's Your Goal After Graduate: Prof. Susi Endrini, PH.D RectorSendriniNo ratings yet
- Meg Wheatley + Angela Blanchard - Leaders For The Storm, Aug 2011Document6 pagesMeg Wheatley + Angela Blanchard - Leaders For The Storm, Aug 2011David HoodNo ratings yet
- Liberatory Design CardsDocument52 pagesLiberatory Design CardsAnonymous 30uDEC1f5No ratings yet
- Diverseo Reducing Unconscious Bias A Highly Effective Toolbox and How To Avoid The Unconscious Bias PitfallsDocument12 pagesDiverseo Reducing Unconscious Bias A Highly Effective Toolbox and How To Avoid The Unconscious Bias PitfallsWebmaster DiverseoNo ratings yet
- July Unconscious BiasDocument4 pagesJuly Unconscious BiasEmily Ross100% (2)
- Retreat Made EasyDocument6 pagesRetreat Made EasyMarianaNo ratings yet
- Crisis Communication TheoryDocument16 pagesCrisis Communication TheoryFrank MartinNo ratings yet
- 7 Strategies To Build A More Resilient TeamDocument5 pages7 Strategies To Build A More Resilient TeamJuan CastelNo ratings yet
- SBL PDF For Legacy PrivilegeDocument82 pagesSBL PDF For Legacy PrivilegeClaytonNo ratings yet
- Organizational Innovation & Problem SolvingDocument33 pagesOrganizational Innovation & Problem SolvingChinmoy KrNo ratings yet
- Picking The Right Transition StrategyDocument9 pagesPicking The Right Transition Strategybiertapper1990100% (1)
- Introduction To Planning and Facilitating Effective MeetingsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Planning and Facilitating Effective MeetingsSANAL R PNo ratings yet
- Chairing A Difficult MeetingDocument3 pagesChairing A Difficult MeetingBill TaylorNo ratings yet
- Effective Meetings and DelegatingDocument21 pagesEffective Meetings and DelegatingfarisNo ratings yet
- Mentoring & Community BuildingDocument700 pagesMentoring & Community BuildingAnimals of the FieldsNo ratings yet
- 09 Stages in Conducting A FacilitationDocument1 page09 Stages in Conducting A FacilitationleksanathsingaporeNo ratings yet
- NIPM Cochin Chapter - Oct 29, 2013Document44 pagesNIPM Cochin Chapter - Oct 29, 2013jayadevmNo ratings yet
- Convergent Excellence RevDocument11 pagesConvergent Excellence RevSundeep RohilaNo ratings yet
- Challenging Conversations and How To Manage ThemDocument24 pagesChallenging Conversations and How To Manage ThemFlorina C100% (1)
- Leading Facilitating Change PDFDocument25 pagesLeading Facilitating Change PDFdilanhjNo ratings yet
- Amazeing Organizational Teams: Navigating 7 Critical Attributes for Cohesion, Productivity and ResilienceFrom EverandAmazeing Organizational Teams: Navigating 7 Critical Attributes for Cohesion, Productivity and ResilienceNo ratings yet
- Professional Communication in Today's Digital, Social, Mobile WorldDocument35 pagesProfessional Communication in Today's Digital, Social, Mobile WorldAdjeiNo ratings yet
- Drivers Working Styles Questionairre and SummaryDocument5 pagesDrivers Working Styles Questionairre and SummaryCosmina LungeanuNo ratings yet
- Book Review: Ego Free LeadershipDocument17 pagesBook Review: Ego Free LeadershipNikhilNo ratings yet
- Building ResilienceDocument8 pagesBuilding ResilienceRamovic Elvir-BeliNo ratings yet
- Trailblazer Mentorship - Mentee Playbook Jan 2020 PDFDocument20 pagesTrailblazer Mentorship - Mentee Playbook Jan 2020 PDFtalk2azhar.m100% (1)
- Eq ModelDocument3 pagesEq Modelzogclub100% (1)
- Strengths PlanDocument4 pagesStrengths Planapi-373188637No ratings yet
- 5 Easy Steps To Fearless Public Speaking: A Practical Powerful GuideDocument15 pages5 Easy Steps To Fearless Public Speaking: A Practical Powerful Guidehieu2100No ratings yet
- 2013 How To Be Brilliant at Public SpeakingDocument225 pages2013 How To Be Brilliant at Public Speakingrafi ziaeeNo ratings yet
- The Remote Facilitator's Pocket Guide: How Local Businesses Are Beating the Global CompetitionFrom EverandThe Remote Facilitator's Pocket Guide: How Local Businesses Are Beating the Global CompetitionNo ratings yet
- Small Group Strengths ActivitiesDocument2 pagesSmall Group Strengths ActivitiesnureevruslanNo ratings yet
- Leadership and AccountabilityDocument49 pagesLeadership and AccountabilityChineduNo ratings yet
- Leading High Performing Teams WorkbookDocument13 pagesLeading High Performing Teams WorkbookJyro TriviñoNo ratings yet
- Becoming An Excellent Facilitator: by Adam Fletcher, President, Commonaction ConsultingDocument6 pagesBecoming An Excellent Facilitator: by Adam Fletcher, President, Commonaction ConsultingvaleriaNo ratings yet
- ROHEI Building A Culture of TrustDocument24 pagesROHEI Building A Culture of TrustmaklpNo ratings yet
- DDI - DEI Report 2023 PDFDocument14 pagesDDI - DEI Report 2023 PDFSHRUTI DHUPIANo ratings yet
- Developing Personal EffectivenessDocument55 pagesDeveloping Personal Effectivenesssaleembutt341100% (2)
- Stress - WstępDocument11 pagesStress - WstępbadooagaNo ratings yet
- Cantera InglesDocument3 pagesCantera InglesJuan Reales0% (1)
- English-3 3RD QUARTER ExamDocument2 pagesEnglish-3 3RD QUARTER ExamRodel Corpuz MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Geometry ExercisesDocument12 pagesGeometry Exercisesann millendezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Pain Management by Ayurveda: Vaidya Aniruddha Shreedhar KulkarniDocument6 pagesClinical Approach To Pain Management by Ayurveda: Vaidya Aniruddha Shreedhar KulkarniAniruddha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Christian Religious Studies Waec SyllabusDocument6 pagesChristian Religious Studies Waec SyllabusPersonal PirearmNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Math HL 2001Document6 pagesSyllabus - Math HL 2001Marek KossowskiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 5 Introduction To Euclids GeometryDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 5 Introduction To Euclids Geometryshwetadutta1977No ratings yet
- Priniples of Church GrowthDocument47 pagesPriniples of Church Growthfrecousminzee5No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: - Make Sentences Using Possessive Cases - Speak About Parts of The HouseDocument2 pagesLesson Plan: - Make Sentences Using Possessive Cases - Speak About Parts of The HouseEugeniaUngureanuNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno Ec Sample CodeDocument1 pageArduino Uno Ec Sample Codeພໍ່ ທ້າວ ທະນາກອນNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformsDocument19 pagesLaplace TransformsJoshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Rpcgen Tutorial (ONC+ Developer's Guide)Document1 pageRpcgen Tutorial (ONC+ Developer's Guide)THAKKAR NARAYAN JAISUKHLALNo ratings yet
- A Study of Subject-Verb AgreementDocument7 pagesA Study of Subject-Verb AgreementWannaBuy GohNo ratings yet
- English Paper - XDocument7 pagesEnglish Paper - XvikramvsuNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHERS THINKING LOGIC and ARGUMENTDocument495 pagesPHILOSOPHERS THINKING LOGIC and ARGUMENTuriNo ratings yet
- The Politics of Panem - Challenging GenresDocument227 pagesThe Politics of Panem - Challenging GenresВалерияNo ratings yet
- South Park S26E06 NTB English-WWW MY-SUBS CODocument36 pagesSouth Park S26E06 NTB English-WWW MY-SUBS COgreen.paxNo ratings yet
- Interchange 1 Lab GuideDocument138 pagesInterchange 1 Lab GuideEdy Lopez Donis100% (1)
- Text TypesDocument24 pagesText Typesyosha16100% (2)
- 1 Hour Lesson PlanDocument2 pages1 Hour Lesson PlanKilah IlahNo ratings yet
- MA8353 PEC - by EasyEngineering - Net 02Document183 pagesMA8353 PEC - by EasyEngineering - Net 02SumanNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Titles in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesResearch Paper Titles in The Philippinesc9k7jjfk100% (1)
- Ext 2Document12 pagesExt 2swanandlawangareNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalsMaria Angel LopezNo ratings yet
- Word Formation SuffixesDocument3 pagesWord Formation SuffixesgarrotemacarenaNo ratings yet
- DCL SlideDocument6 pagesDCL SlideJyoti Bala WarwalNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter English 10 Assessment TestDocument6 pages4TH Quarter English 10 Assessment Testafbnjkcd100% (2)
- Lastexception 63847077330Document1 pageLastexception 63847077330lilll lopppzNo ratings yet