Professional Documents
Culture Documents
As Band45
As Band45
Uploaded by
Ramón Alfredo AmadoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 742 264Document4 pages742 264slymnNo ratings yet
- K72314 SeriesDocument1 pageK72314 SeriesrtparedesNo ratings yet
- VHPX4-71W Data SheetDocument3 pagesVHPX4-71W Data SheetjankorossNo ratings yet
- Andrew Antenas RFDocument123 pagesAndrew Antenas RFRoger Pereira Guerra0% (1)
- G KPI Monitoring and Improvement Guide 20081230 A 1 0 LibreDocument51 pagesG KPI Monitoring and Improvement Guide 20081230 A 1 0 LibreEunice IkaNo ratings yet
- DocDocument53 pagesDocBùi Quốc Lĩnh0% (1)
- 1 Datasheet Problemas Temas 1 A 4 V2016-1Document15 pages1 Datasheet Problemas Temas 1 A 4 V2016-1Estefania PachecoNo ratings yet
- BXV 80090 8CF Triples NextelDocument1 pageBXV 80090 8CF Triples NextelwhatiaasNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Antenne Kathrein 88-108 MHZDocument12 pagesCatalogo Antenne Kathrein 88-108 MHZTateszNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 2013Document16 pagesKathrein 2013PET6KAPOLTAVANo ratings yet
- 742 265Document4 pages742 265slymnNo ratings yet
- Dual-Polarized Panel Antennas - BXD SeriesDocument12 pagesDual-Polarized Panel Antennas - BXD SeriesJose Christian Mejia SantanderNo ratings yet
- Datong AD370 InstructionsDocument5 pagesDatong AD370 Instructionsdaniel21667No ratings yet
- Amphenol RWA 80015Document1 pageAmphenol RWA 80015Jonas AldaoNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument0 pagesPDFlu1agpNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 80010375Document2 pagesKathrein 80010375klamar5No ratings yet
- Kathrein BroadcastDocument152 pagesKathrein BroadcastEnzio BodoniNo ratings yet
- Vertex 13M CassegrainDocument2 pagesVertex 13M CassegrainSyarif LumintarjoNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFThi HuynhNo ratings yet
- Formato Antena KathreinDocument5 pagesFormato Antena KathreinJ Stiven Pachón GarciaNo ratings yet
- 742 265Document4 pages742 265alexteixeira1No ratings yet
- Andrew Omni02 - 4 - 800omniDocument28 pagesAndrew Omni02 - 4 - 800omnibowser0No ratings yet
- Peralatan PemancarDocument23 pagesPeralatan PemancarGhufranaka Aldrien NanangNo ratings yet
- 6812B CP Ring (Low Power)Document2 pages6812B CP Ring (Low Power)ensvNo ratings yet
- Vertically Polarized Panels - WPA-RWA-RWB SeriesDocument150 pagesVertically Polarized Panels - WPA-RWA-RWB SeriesHirak Jyoti MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Vertex Antenna 4.8m Cassegrain Ku BandDocument2 pagesDatasheet Vertex Antenna 4.8m Cassegrain Ku BandEng Simon Peter NsoziNo ratings yet
- An C240Document2 pagesAn C240kymk21No ratings yet
- AMP Tri SectorDocument5 pagesAMP Tri SectorGustavo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Antena Amphenol - Bsa-185065-10Document1 pageAntena Amphenol - Bsa-185065-10LuisChavezArmijoNo ratings yet
- Dualband X-Pol Tri-Sector Antenna With Integrated Combiners: 806-960 MHZ 1710-2170 MHZDocument2 pagesDualband X-Pol Tri-Sector Antenna With Integrated Combiners: 806-960 MHZ 1710-2170 MHZtqmquocNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 742270Document4 pagesKathrein 742270Anastasiya Burukhina100% (1)
- 7 6ESAdsDocument12 pages7 6ESAdsSandro Omar Lizano GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Antenna and Feeder SystemDocument9 pagesAntenna and Feeder SystemPlaban Pratim BhuyanNo ratings yet
- Catalog 27-512 Base Station AntennasDocument99 pagesCatalog 27-512 Base Station AntennasJocelyn DervainNo ratings yet
- 9 Cable Cascadable SwitcherDocument7 pages9 Cable Cascadable SwitcherTarek MatarNo ratings yet
- Antenne Eggbeater Engl Part1 FullDocument10 pagesAntenne Eggbeater Engl Part1 Full11090482No ratings yet
- 742222V01Document2 pages742222V01Tegar S DziqrianzNo ratings yet
- HPX12-70 Data SheetDocument3 pagesHPX12-70 Data SheetArniel RamirezNo ratings yet
- Vu 5146 WDocument2 pagesVu 5146 WSandaruwan DhananjayaNo ratings yet
- 3 SatLite Tech 1511peloris Flyaway 1.5mDocument2 pages3 SatLite Tech 1511peloris Flyaway 1.5mtux2testNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Andrew Antenna 9.3m C Band B Station ES93B 1Document14 pagesDatasheet Andrew Antenna 9.3m C Band B Station ES93B 1Eng Simon Peter NsoziNo ratings yet
- KATHREIN - 742 210 - 68° Panel Antenna 1710-2170 MHZDocument2 pagesKATHREIN - 742 210 - 68° Panel Antenna 1710-2170 MHZConstantin TucaNo ratings yet
- C Bxa 80065 8 MDocument1 pageC Bxa 80065 8 MManrique VasquezNo ratings yet
- 65° Panel Antenna: General SpecificationsDocument2 pages65° Panel Antenna: General Specificationsrukismen100% (2)
- Bxa 80090 8CF FPDocument1 pageBxa 80090 8CF FPalexteixeira1No ratings yet
- Cubic AA381M DF AntennaDocument2 pagesCubic AA381M DF AntennaanambroNo ratings yet
- 80010465Document1 page80010465Dzmitry HaidukNo ratings yet
- AVITEC - Axell Wireless CSFT Frequency Shifting RepeatersDocument4 pagesAVITEC - Axell Wireless CSFT Frequency Shifting Repeatersmajito546No ratings yet
- Eyring - ELPA 302A Operations Manual AppendixDocument32 pagesEyring - ELPA 302A Operations Manual AppendixAlexander J RokowetzNo ratings yet
- Skymasts Ground To Air Catalogue 2011Document63 pagesSkymasts Ground To Air Catalogue 2011cuonglom0% (1)
- 742210V01Document2 pages742210V01hakim_zadehNo ratings yet
- TIA329 B Sept 1999Document38 pagesTIA329 B Sept 1999colin370% (1)
- 1 - GHZ Avalanche Photo ReceiversDocument4 pages1 - GHZ Avalanche Photo ReceiversdarmokjaladNo ratings yet
- Bsa 1850120 12CFDocument1 pageBsa 1850120 12CFAndre RodNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 732 690Document2 pagesKathrein 732 690PavelKuzovkinNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- BW650 InstallDocument7 pagesBW650 InstallfreekenzoNo ratings yet
- 1-61339289563 G0060858057Document8 pages1-61339289563 G0060858057Shahaan ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesDocument3 pagesMobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesMugdha SinghNo ratings yet
- Relience CommunicationDocument27 pagesRelience CommunicationSagar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Smart SiteDocument6 pagesSmart Siteeng_meenaaNo ratings yet
- Trans CreationDocument6 pagesTrans CreationNikkan VillaNo ratings yet
- TWS Sec - ADocument86 pagesTWS Sec - AWilmer Huaman PasaperaNo ratings yet
- Pedal ManualDocument6 pagesPedal ManualLeo FernándezNo ratings yet
- (Microsoft Word - UVS-300 - 245 - 277 - 255 - 261Document2 pages(Microsoft Word - UVS-300 - 245 - 277 - 255 - 261edwtrimoNo ratings yet
- Wireless Rugged Remotes 868 MHZ Tyro PyxisDocument2 pagesWireless Rugged Remotes 868 MHZ Tyro PyxisVikram NagaNo ratings yet
- Politeknik Tuanku Sultanah Bahiyah: English For Technical PurposeDocument6 pagesPoliteknik Tuanku Sultanah Bahiyah: English For Technical PurposeLinggam KhanNo ratings yet
- Nokia Mediamaster: Owner's ManualDocument36 pagesNokia Mediamaster: Owner's ManualPankaj GargNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Bedienungsanleitung Használati UtasításDocument24 pagesInstruction Manual: Bedienungsanleitung Használati UtasításAdrienn DemeterNo ratings yet
- AD8307Document24 pagesAD8307Filip ZalioNo ratings yet
- Rich Communication Suite: Experience Enrichment For Business EnablementDocument12 pagesRich Communication Suite: Experience Enrichment For Business EnablementThato SebeshoNo ratings yet
- Low Loss Coaxial Cable For Radio Communications: CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesLow Loss Coaxial Cable For Radio Communications: CharacteristicsTateszNo ratings yet
- TRACE 1300 Series GC User GuideDocument384 pagesTRACE 1300 Series GC User GuideFabián B. Fernández ReyesNo ratings yet
- NSH 7 Element 2 Meter Beam AntennaDocument3 pagesNSH 7 Element 2 Meter Beam AntennaGeroldo 'Rollie' L. QuerijeroNo ratings yet
- Vpa Data 5k8,5k5,2k2Document5 pagesVpa Data 5k8,5k5,2k2sv6jhaNo ratings yet
- Telecom & Data InfraDocument6 pagesTelecom & Data InfraMohammad Ather SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- UHF-VHF Yagi ConstructionDocument8 pagesUHF-VHF Yagi Constructionmukhlison1989100% (1)
- UniFi Quick GuideDocument2 pagesUniFi Quick GuideAndhika TharunaNo ratings yet
- Pragati Maidan Exhibition DetailsDocument10 pagesPragati Maidan Exhibition DetailsDr-Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- RTL - SDR DIY KITs Installation InstructionsDocument22 pagesRTL - SDR DIY KITs Installation InstructionsSergio OlivieriNo ratings yet
- Navy Supplement To The DOD Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms, 2011Document405 pagesNavy Supplement To The DOD Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms, 2011bateljupko100% (1)
- CradlePoint COR IBR6x0 DataSheet 10.22.12Document8 pagesCradlePoint COR IBR6x0 DataSheet 10.22.12Buchi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Atif Jamil HuaweiDocument21 pagesMuhammad Atif Jamil Huaweifatemeh sameniNo ratings yet
- ImcDocument30 pagesImcMuhammad Qasim0% (1)
As Band45
As Band45
Uploaded by
Ramón Alfredo AmadoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
As Band45
As Band45
Uploaded by
Ramón Alfredo AmadoCopyright:
Available Formats
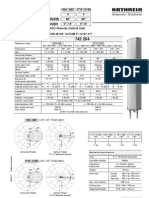
TV Transmitting Antenna with panels K 72 31 47 or K 73 31 47 470 860 MHz
Antenna systems consisting of dipole panels K 72 31 47 or K 73 31 47 for various radiation patterns. The feeder network is made up of coaxial power splitters and flexible connecting cables in accordance with the radiation patterns specification and the transmitting power.
Input Frequency range VSWR Impedance Polarization Internal connections Max. power Vertical radiation pattern Horizontal radiation pattern Half antenna splitting
Painting Structure
Grounding Max. wind velocity
No. of bays
Panels per bay
Gain* (at mid-band) dB times
Weight (without mounting hardware) kg 120 160 210 170 240 330 240 320 420 350 490 670 450 690 890
Antenna height H m
Windload / kN (v = 160 km/h) without with cylinder cylinder 1.6 m 5.2 6.4 6.2 7.8 9.6 9.3 10.4 12.8 12.4 15.6 19.2 18.6 20.8 25.6 24.8 6.2
2 3 4 2 3 4 2 3 4 2 3 4 2 3 4
15.2 13.6 12.3 17.0 15.4 14.1 18.2 16.6 15.3 20.0 18.4 17.1 21.2 19.6 18.3
33.1 22.9 17.0 50.1 34.7 25.7 66.1 45.7 33.9 100.0 69.2 51.3 131.8 91.2 67.6
4.45
6.75
9.5
9.05
12.7
12
13.65
19.2
16
18.25
25.7
* Referred to /2 dipole. Attenuation of the internal cabling and the gain-decrease in case of null fill in the vertical radiation pattern are not considered. Approximate values for gain decrease: cable attenuation: 0.2 0.5 dB null fill: 0.3 1.0 dB Gain figures are valid for the direction of maximum radiation. 38
Pressurization
Connectors according to IEC, EIA or DIN. 470 860 MHz < 1.05 in the operating channels after tuning. 50 Horizontal with dipole panels K 72 31 47 or vertical with dipole panels K 73 31 47 Connectors according to IEC, EIA or DIN are used throughout the system, allowing easy assembly and maintenance. According to customers requirements. Null fill and beam tilt upon request. Omnidirectional, directional or custom-designed. Upon request, the antenna can be divided into 2 halves (for measurement and maintenance). The 2 halves are connected by a 2-way power splitter or patch panel. Splitters and connecting cables can be supplied with dry air (please specify when ordering). If required, the antenna is painted in aviation warning colours. 2 versions are available: a) Panels mounted on hot-dip galvanized steel spine. b) Panels mounted inside self-supporting fiberglass cylinder (1.6 m ) Via mounting parts. 225 km/h
1150 mm
TV Transmitting Antenna with panels K 72 31 47 or K 73 31 47 470 860 MHz
Horizontal Radiation Patterns Examples of typical horizontal antenna arrays and their horizontal radiation patterns for minimal mast dimensions. Vertical Radiation Patterns Examples of typical vertical radiation patterns*) for several bays of identical, vertically stacked antenna arrays.
Equal power splitting
4 bays
100 E rel 50
10
8 bays
100 E rel 50
10 dB 10 dB
3 0
3 0
10
Equal power splitting
Different power splitting
12 bays
4/10 P
100 E rel
1/10 P
1/10 P
50
4/10 P
10
16 bays
100 E rel 50
10 dB 10 dB
3 0
3 0
0
*)
5
without null fill with null fill and beam tilt
10
39
TV Transmitting Antenna (Superturnstile Antenna) 470 860 MHz
Superturnstile antenna mounted in G.R.P. cylinder with 0.30 m diameter Type No. Input Frequency range VSWR Impedance Polarization Max. power Horizontal radiation pattern Half antenna splitting Superturnstile antenna in G.R.P. cylinder with 0.30 m diameter 1 5/8 EIA flange
Superturnstile antenna mounted in G.R.P. cylinder with 0.75 m diameter Superturnstile antenna in G.R.P. cylinder with 0.75 m diameter
Material Mounting Ice protection Grounding Max. wind velocity Internal connections
Connectors according to IEC, EIA or DIN. 470 860 MHz 1.1 broadband < 1.05 in the operating channels Optimization by tuning. after tuning. 50 Horizontal 5 kW (for Type No. 771 304) 5 kW per bay omnidirectional with minima of 3 dB Upon request, the antenna can be divided into 2 halves (for measurement and maintenance). The 2 halves are connected by a 2-way splitter or patch panel. Superturnstile antenna in a self supporting Superturnstile antenna in a self supporting G.R.P. cylinder with 0.30 m . G.R.P. cylinder with 0.75 m . Up to 6 bays may be stacked. Up to 8 bays may be stacked. On top of existing structure by means On top of existing structure by means of an adapter. of a flange. Fiberglass cylinder (= supporting structure) Via mounting parts. Via mounting parts resp. via 4 grounding ropes at the exterior cylinder surface. 225 km/h 225 km/h The radiating elements are fed with coaxial connecting cables and hybrid couplers. Connectors according to IEC, EIA or DIN are used throughout the system, allowing easy assembly and maintenance. Superturnstile antenna mounted in G.R.P. cylinder with 0.75 m diameter No. of bays 2 4 6 8 Gain* (at mid-band) dB times 7.0 10.0 11.8 13.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 Weight Antenna Windload height H (v = 160 km/h) kg m kN 200 350 550 850 2.25 4.50 6.75 9.00 2.2 3.6 5.2 6.6
Superturnstile antenna mounted in G.R.P. cylinder with 0.30 m diameter No. of bays 1 2 4 6 Type No. Gain* (at mid-band) dB times 5.0 8.0 11.0 12.8 3.15 6.3 12.6 18.9 Weight Antenna Windload height H (v = 160 km/h) kg m N 20 40 180 300 1.15 2.3 5.1 7.4 228 478 1370 1516
767 770 771 773
006 881 304 825
* Referred to /2 dipole. Attenuation of the internal cabling and the gain-decrease in case of null fill in the vertical radiation pattern are not considered. Approximate values for gain decrease: cable attenuation: 0.2 0.5 dB null fill: 0.3 1.0 dB Gain figures are valid for the direction of maximum radiation. 40
1125 mm
TV Transmitting Antenna (Superturnstile Antenna) 470 860 MHz
Typical Horizontal Radiation Pattern (at mid-band) Vertical Radiation Patterns Examples of typical vertical radiation patterns*) for several bays of identical, vertically stacked antenna arrays.
1 bay
100 E rel 50
10
3 0
10
20
dB
2 bays
100 E rel 50
10
20
4 bays
100 E rel 50
10
20
6 bays
100 E rel 50
0
*)
10
without null fill with null fill and beam tilt
20
41
TV Transmitting Antenna (Superturnstile Antenna) 470 860 MHz
q
Superturnstile antenna in a self-supporting fiberglass cylinder with 1.60 m diameter.
Vertical radiation pattern Horizontal radiation pattern Half antenna splitting
Internal connections
Structure Mounting Ice protection Grounding
No. of bays 2 4 8 12 16
Gain* (at mid-band) dB times 7.0 10.0 13.0 14.8 16.0 5.0 10.0 20.0 30.2 39.8
Weight (with cylinder) kg 400 800 1600 2600 3600
Antenna height H m 2.25 4.5 9.0 13.5 18.0
Windload (v = 160 km/h) kN 3.2 6.3 12.5 19.0 25.0
* Referred to /2 dipole. Attenuation of the internal cabling and the gain-decrease in case of null fill in the vertical radiation pattern are not considered. Approximate values for gain decrease: cable attenuation: 0.2 0.5 dB null fill: 0.3 1.0 dB Gain figures are valid for the direction of maximum radiation. 42
1125 mm
Input Frequency range VSWR Impedance Polarization Max. power
Connectors according to IEC, EIA or DIN. 470 860 MHz < 1.05 in operating channels 50 Horizontal According to customers requirements, 10 kW max. per bay. Null fill and beam tilt upon request. Omnidirectional Upon request, the antenna can be divided into 2 halves (for measurement and maintenance). The 2 halves are connected by a 2-way power splitter or patch panel. The radiating elements are fed with coaxial connecting cables and hybrid couplers. Connectors according to IEC, EIA or DIN are used throughout the system, allowing easy assembly and maintenance. Superturnstile antenna in self-supporting fiberglass-cylinder. Up to 16 bays may be stacked. On top of existing structure by means of a flange. Fiberglass-cylinder (= supporting structure) Via mounting parts resp. via 4 grounding ropes at the exterior cylinder-surface.
TV Transmitting Antenna (Superturnstile Antenna) 470 860 MHz
Typical Horizontal Radiation Pattern (at mid-band) Vertical Radiation Patterns Examples of typical vertical radiation patterns*) for several bays of identical, vertically stacked antenna arrays.
4 bays
100 E rel 50
10
3 0
dB
10
8 bays
100 E rel 50
10
12 bays
100 E rel 50
10
16 bays
100 E rel 50
0
*)
5
without null fill with null fill and beam tilt
10
43
TV Transmitting Antenna with panels K 72 31 47 or K 73 31 47 470 860 MHz
q
Typical antenna array with dipole panels K 72 31 47.
Input Frequency range VSWR Impedance Polarization Max. power Radiation pattern Half antenna splitting
Pressurization Painting Grounding Max. wind velocity
Connectors according to IEC, EIA or DIN. 470 860 MHz < 1.05 in the operating channel after tuning or < 1.1 in the whole frequency range 50 Horizontal or vertical 1 kW, higher power on request. The examples of radiation patterns are valid for horizontal polarization. At vertical polarization patterns vary slightly. Upon request, the antenna can be divided into 2 halves (for measurement and maintenance). The 2 halves are connected by a 2-way power splitter or patch panel. Splitters and connecting cables can be supplied with dry air (please specify when ordering). If required, the antenna is painted in aviation warning colours. Via mounting parts. 225 km/h
1150 mm
Top view
No. of bays 1
Panels per bay 2 3 4 2 3 4 2 3 4
Gain* (at mid-band) dB times 9.2 7.6 6.3 12.2 10.6 9.3 15.2 13.6 12.3 8.3 5.8 4.3 16.6 11.5 8.5 33.1 22.9 17.0
Weight (without mounting hardware) kg 31 45 59 59 86 116 116 172 228
Antenna height H m 1.15
Windload (v = 160 km/h) kN 1.3 1.4 1.2 2.6 2.8 2.4 5.2 5.6 4.8
2.15
10 dB
3 0
4.45
* Referred to /2 dipole. Attenuation of the internal cabling and the gain-decrease in case of null fill in the vertical radiation pattern are not considered. Approximate values for gain decrease: cable attenuation: 0.2 0.4 dB null fill: 0.2 0.5 dB Gain figures are valid for the direction of maximum radiation.
Horizontal Radiation Pattern of the antenna arrangement see above
44
TV Transmitting Antenna with panels K 72 31 47 or K 73 31 47 470 860 MHz
Horizontal Radiation Patterns Examples of typical horizontal antenna arrays and their horizontal radiation patterns for minimal mast dimensions. Vertical Radiation Patterns Examples of typical vertical radiation patterns for several bays of identical, vertically stacked antenna arrays.
Equal power splitting
1 bay
100 E rel 50
10
20
2 bays
100 E rel 50
10 dB 10 dB
3 0
3 0
10
20
Equal power splitting
Different power splitting
3 bays
1/6 P
100 E rel
4/6 P
50
1/6 P
10
20
4 bays
100 E rel 50
10 dB 10 dB
3 0
3 0
10
20
45
You might also like
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 742 264Document4 pages742 264slymnNo ratings yet
- K72314 SeriesDocument1 pageK72314 SeriesrtparedesNo ratings yet
- VHPX4-71W Data SheetDocument3 pagesVHPX4-71W Data SheetjankorossNo ratings yet
- Andrew Antenas RFDocument123 pagesAndrew Antenas RFRoger Pereira Guerra0% (1)
- G KPI Monitoring and Improvement Guide 20081230 A 1 0 LibreDocument51 pagesG KPI Monitoring and Improvement Guide 20081230 A 1 0 LibreEunice IkaNo ratings yet
- DocDocument53 pagesDocBùi Quốc Lĩnh0% (1)
- 1 Datasheet Problemas Temas 1 A 4 V2016-1Document15 pages1 Datasheet Problemas Temas 1 A 4 V2016-1Estefania PachecoNo ratings yet
- BXV 80090 8CF Triples NextelDocument1 pageBXV 80090 8CF Triples NextelwhatiaasNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Antenne Kathrein 88-108 MHZDocument12 pagesCatalogo Antenne Kathrein 88-108 MHZTateszNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 2013Document16 pagesKathrein 2013PET6KAPOLTAVANo ratings yet
- 742 265Document4 pages742 265slymnNo ratings yet
- Dual-Polarized Panel Antennas - BXD SeriesDocument12 pagesDual-Polarized Panel Antennas - BXD SeriesJose Christian Mejia SantanderNo ratings yet
- Datong AD370 InstructionsDocument5 pagesDatong AD370 Instructionsdaniel21667No ratings yet
- Amphenol RWA 80015Document1 pageAmphenol RWA 80015Jonas AldaoNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument0 pagesPDFlu1agpNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 80010375Document2 pagesKathrein 80010375klamar5No ratings yet
- Kathrein BroadcastDocument152 pagesKathrein BroadcastEnzio BodoniNo ratings yet
- Vertex 13M CassegrainDocument2 pagesVertex 13M CassegrainSyarif LumintarjoNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFThi HuynhNo ratings yet
- Formato Antena KathreinDocument5 pagesFormato Antena KathreinJ Stiven Pachón GarciaNo ratings yet
- 742 265Document4 pages742 265alexteixeira1No ratings yet
- Andrew Omni02 - 4 - 800omniDocument28 pagesAndrew Omni02 - 4 - 800omnibowser0No ratings yet
- Peralatan PemancarDocument23 pagesPeralatan PemancarGhufranaka Aldrien NanangNo ratings yet
- 6812B CP Ring (Low Power)Document2 pages6812B CP Ring (Low Power)ensvNo ratings yet
- Vertically Polarized Panels - WPA-RWA-RWB SeriesDocument150 pagesVertically Polarized Panels - WPA-RWA-RWB SeriesHirak Jyoti MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Vertex Antenna 4.8m Cassegrain Ku BandDocument2 pagesDatasheet Vertex Antenna 4.8m Cassegrain Ku BandEng Simon Peter NsoziNo ratings yet
- An C240Document2 pagesAn C240kymk21No ratings yet
- AMP Tri SectorDocument5 pagesAMP Tri SectorGustavo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Antena Amphenol - Bsa-185065-10Document1 pageAntena Amphenol - Bsa-185065-10LuisChavezArmijoNo ratings yet
- Dualband X-Pol Tri-Sector Antenna With Integrated Combiners: 806-960 MHZ 1710-2170 MHZDocument2 pagesDualband X-Pol Tri-Sector Antenna With Integrated Combiners: 806-960 MHZ 1710-2170 MHZtqmquocNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 742270Document4 pagesKathrein 742270Anastasiya Burukhina100% (1)
- 7 6ESAdsDocument12 pages7 6ESAdsSandro Omar Lizano GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Antenna and Feeder SystemDocument9 pagesAntenna and Feeder SystemPlaban Pratim BhuyanNo ratings yet
- Catalog 27-512 Base Station AntennasDocument99 pagesCatalog 27-512 Base Station AntennasJocelyn DervainNo ratings yet
- 9 Cable Cascadable SwitcherDocument7 pages9 Cable Cascadable SwitcherTarek MatarNo ratings yet
- Antenne Eggbeater Engl Part1 FullDocument10 pagesAntenne Eggbeater Engl Part1 Full11090482No ratings yet
- 742222V01Document2 pages742222V01Tegar S DziqrianzNo ratings yet
- HPX12-70 Data SheetDocument3 pagesHPX12-70 Data SheetArniel RamirezNo ratings yet
- Vu 5146 WDocument2 pagesVu 5146 WSandaruwan DhananjayaNo ratings yet
- 3 SatLite Tech 1511peloris Flyaway 1.5mDocument2 pages3 SatLite Tech 1511peloris Flyaway 1.5mtux2testNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Andrew Antenna 9.3m C Band B Station ES93B 1Document14 pagesDatasheet Andrew Antenna 9.3m C Band B Station ES93B 1Eng Simon Peter NsoziNo ratings yet
- KATHREIN - 742 210 - 68° Panel Antenna 1710-2170 MHZDocument2 pagesKATHREIN - 742 210 - 68° Panel Antenna 1710-2170 MHZConstantin TucaNo ratings yet
- C Bxa 80065 8 MDocument1 pageC Bxa 80065 8 MManrique VasquezNo ratings yet
- 65° Panel Antenna: General SpecificationsDocument2 pages65° Panel Antenna: General Specificationsrukismen100% (2)
- Bxa 80090 8CF FPDocument1 pageBxa 80090 8CF FPalexteixeira1No ratings yet
- Cubic AA381M DF AntennaDocument2 pagesCubic AA381M DF AntennaanambroNo ratings yet
- 80010465Document1 page80010465Dzmitry HaidukNo ratings yet
- AVITEC - Axell Wireless CSFT Frequency Shifting RepeatersDocument4 pagesAVITEC - Axell Wireless CSFT Frequency Shifting Repeatersmajito546No ratings yet
- Eyring - ELPA 302A Operations Manual AppendixDocument32 pagesEyring - ELPA 302A Operations Manual AppendixAlexander J RokowetzNo ratings yet
- Skymasts Ground To Air Catalogue 2011Document63 pagesSkymasts Ground To Air Catalogue 2011cuonglom0% (1)
- 742210V01Document2 pages742210V01hakim_zadehNo ratings yet
- TIA329 B Sept 1999Document38 pagesTIA329 B Sept 1999colin370% (1)
- 1 - GHZ Avalanche Photo ReceiversDocument4 pages1 - GHZ Avalanche Photo ReceiversdarmokjaladNo ratings yet
- Bsa 1850120 12CFDocument1 pageBsa 1850120 12CFAndre RodNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 732 690Document2 pagesKathrein 732 690PavelKuzovkinNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- BW650 InstallDocument7 pagesBW650 InstallfreekenzoNo ratings yet
- 1-61339289563 G0060858057Document8 pages1-61339289563 G0060858057Shahaan ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesDocument3 pagesMobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesMugdha SinghNo ratings yet
- Relience CommunicationDocument27 pagesRelience CommunicationSagar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Smart SiteDocument6 pagesSmart Siteeng_meenaaNo ratings yet
- Trans CreationDocument6 pagesTrans CreationNikkan VillaNo ratings yet
- TWS Sec - ADocument86 pagesTWS Sec - AWilmer Huaman PasaperaNo ratings yet
- Pedal ManualDocument6 pagesPedal ManualLeo FernándezNo ratings yet
- (Microsoft Word - UVS-300 - 245 - 277 - 255 - 261Document2 pages(Microsoft Word - UVS-300 - 245 - 277 - 255 - 261edwtrimoNo ratings yet
- Wireless Rugged Remotes 868 MHZ Tyro PyxisDocument2 pagesWireless Rugged Remotes 868 MHZ Tyro PyxisVikram NagaNo ratings yet
- Politeknik Tuanku Sultanah Bahiyah: English For Technical PurposeDocument6 pagesPoliteknik Tuanku Sultanah Bahiyah: English For Technical PurposeLinggam KhanNo ratings yet
- Nokia Mediamaster: Owner's ManualDocument36 pagesNokia Mediamaster: Owner's ManualPankaj GargNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Bedienungsanleitung Használati UtasításDocument24 pagesInstruction Manual: Bedienungsanleitung Használati UtasításAdrienn DemeterNo ratings yet
- AD8307Document24 pagesAD8307Filip ZalioNo ratings yet
- Rich Communication Suite: Experience Enrichment For Business EnablementDocument12 pagesRich Communication Suite: Experience Enrichment For Business EnablementThato SebeshoNo ratings yet
- Low Loss Coaxial Cable For Radio Communications: CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesLow Loss Coaxial Cable For Radio Communications: CharacteristicsTateszNo ratings yet
- TRACE 1300 Series GC User GuideDocument384 pagesTRACE 1300 Series GC User GuideFabián B. Fernández ReyesNo ratings yet
- NSH 7 Element 2 Meter Beam AntennaDocument3 pagesNSH 7 Element 2 Meter Beam AntennaGeroldo 'Rollie' L. QuerijeroNo ratings yet
- Vpa Data 5k8,5k5,2k2Document5 pagesVpa Data 5k8,5k5,2k2sv6jhaNo ratings yet
- Telecom & Data InfraDocument6 pagesTelecom & Data InfraMohammad Ather SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- UHF-VHF Yagi ConstructionDocument8 pagesUHF-VHF Yagi Constructionmukhlison1989100% (1)
- UniFi Quick GuideDocument2 pagesUniFi Quick GuideAndhika TharunaNo ratings yet
- Pragati Maidan Exhibition DetailsDocument10 pagesPragati Maidan Exhibition DetailsDr-Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- RTL - SDR DIY KITs Installation InstructionsDocument22 pagesRTL - SDR DIY KITs Installation InstructionsSergio OlivieriNo ratings yet
- Navy Supplement To The DOD Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms, 2011Document405 pagesNavy Supplement To The DOD Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms, 2011bateljupko100% (1)
- CradlePoint COR IBR6x0 DataSheet 10.22.12Document8 pagesCradlePoint COR IBR6x0 DataSheet 10.22.12Buchi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Atif Jamil HuaweiDocument21 pagesMuhammad Atif Jamil Huaweifatemeh sameniNo ratings yet
- ImcDocument30 pagesImcMuhammad Qasim0% (1)