Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro To Trematodes and Blood Flukes
Intro To Trematodes and Blood Flukes
Uploaded by
Mark Allison BuenaventuraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Table For Cestodes and TrematodesDocument5 pagesTable For Cestodes and TrematodesDawn WRein Legaspi100% (3)
- NCP PreoperativeDocument3 pagesNCP PreoperativeMark Allison Buenaventura75% (4)
- Helminths MCQsDocument21 pagesHelminths MCQsمحمد محمد هشام84% (19)
- Summary (Trematodes)Document4 pagesSummary (Trematodes)Krizia Del Rosario50% (2)
- TREMATODESDocument31 pagesTREMATODESKen Mark ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Phylum Platyheminthes TrematodesDocument12 pagesPhylum Platyheminthes TrematodesRona SalandoNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument10 pagesTrematodesUhjafwnuijhnfa Kmerkgoe100% (1)
- TrematodesDocument9 pagesTrematodesJoseph PerezNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument9 pagesTrematodesLewis P. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Trematodes para ReviewDocument87 pagesTrematodes para ReviewKaycee Ayo100% (1)
- Trematode SDocument4 pagesTrematode SMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument9 pagesTrematodesRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- Medical Helminthology - Chordata and Roundworms - Human ParasitesDocument54 pagesMedical Helminthology - Chordata and Roundworms - Human ParasitesMewa MahartaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lecture 15 - Liver Flukes and Lung FlukeDocument4 pagesParasitology Lecture 15 - Liver Flukes and Lung Flukemiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Trematodes PDFDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Trematodes PDFLyka Villagracia AsiloNo ratings yet
- Trem-Ing pptIIDocument61 pagesTrem-Ing pptIITutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Document94 pages blue_blooded23No ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument75 pagesTrematodesHann SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Trematodes 2Document37 pagesTrematodes 2Akanksha BaireddyNo ratings yet
- Template para Lab Exe 4 The TREMATODES 1 PDFDocument11 pagesTemplate para Lab Exe 4 The TREMATODES 1 PDFCharlie Magne GarciaNo ratings yet
- PARA20 3rd Long ExamDocument4 pagesPARA20 3rd Long ExamEricNo ratings yet
- Trematodes (Flukes)Document35 pagesTrematodes (Flukes)api-3856362No ratings yet
- 1st Lecture - Trematodes - Clinical ParasitologyDocument38 pages1st Lecture - Trematodes - Clinical ParasitologyAhmed MoghazyNo ratings yet
- HelminthsDocument190 pagesHelminthsSarhan AliNo ratings yet
- Parasitesofliver Moin Hydergroup 4Document40 pagesParasitesofliver Moin Hydergroup 4Moeen HyderNo ratings yet
- Flukes in Ruminants in South Africa BBDocument13 pagesFlukes in Ruminants in South Africa BBnigeldkdcNo ratings yet
- Blood Flukes: Richelle D. Sales, RMTDocument20 pagesBlood Flukes: Richelle D. Sales, RMTZairah PascuaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology - Trematodes - S. Mansoni, S. Haematobium, P. WestermaniDocument51 pagesParasitology - Trematodes - S. Mansoni, S. Haematobium, P. WestermaniNicole ManogNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis & FascioliosisDocument40 pagesSchistosomiasis & FascioliosisWahyudi YusmanNo ratings yet
- Para-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Document11 pagesPara-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Aysha AishaNo ratings yet
- Pathology Lec 1 - 211010 - 144130Document83 pagesPathology Lec 1 - 211010 - 144130Daly DaliaNo ratings yet
- Digenean: Schistosoma SPP.: PathologyDocument5 pagesDigenean: Schistosoma SPP.: PathologyBernard Lionel MoreusNo ratings yet
- SchistosomesDocument12 pagesSchistosomesMORDENO, JOHN GABRIEL O. SCINo ratings yet
- FH, F, PW, SDocument56 pagesFH, F, PW, SMo FanNo ratings yet
- Trematode SDocument5 pagesTrematode SAUDREY VERONICA PEREZ100% (1)
- Trematode SDocument26 pagesTrematode SothnielNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Intestinal FlukesDocument76 pages9.2 Intestinal Flukesvader37526No ratings yet
- Trematodes - TransDocument9 pagesTrematodes - TransDenver CarbonNo ratings yet
- Intestinal FlukesDocument3 pagesIntestinal Flukesmiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- Class CESTODADocument65 pagesClass CESTODAKaycee AyoNo ratings yet
- TREMATODA - UsusDocument32 pagesTREMATODA - Usustheo referatNo ratings yet
- 3) TrematodesDocument38 pages3) Trematodesmisgshlove1No ratings yet
- Phylum NematodaDocument285 pagesPhylum NematodaBrielleNo ratings yet
- Para Reviewer (Prelims-Finals)Document15 pagesPara Reviewer (Prelims-Finals)Mafie BarreiroNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Liver and Intestinal FlukesDocument60 pages3.4 Liver and Intestinal FlukesHazel Joyce Gonda RoqueNo ratings yet
- Poraginumus WestermaniDocument23 pagesPoraginumus WestermaniMika AndiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology PDFDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology PDFArianna Aparte AvenidoNo ratings yet
- Trematode NotesDocument3 pagesTrematode NotesGlenn PerezNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document PDFDocument5 pagesUntitled Document PDFRizzy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge ReviewDocument81 pagesKnowledge ReviewAmr EldemardashNo ratings yet
- Six Flukes. TrematodeDocument106 pagesSix Flukes. TrematodeCherenet TomaNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument9 pagesNematodesMomo ShinNo ratings yet
- Cestodes and NematodesDocument19 pagesCestodes and Nematodespancake pancakeNo ratings yet
- Trematoda Usus Hati ParuDocument59 pagesTrematoda Usus Hati ParuRoisah Yunan NegariNo ratings yet
- Parasite Adult OVA Life Cycle Pathology: in CopulaDocument3 pagesParasite Adult OVA Life Cycle Pathology: in CopulaMaria StephanieNo ratings yet
- Amphistomate & Distomate FlukeDocument12 pagesAmphistomate & Distomate FlukeJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Table For Cestodes and TrematodesDocument5 pagesTable For Cestodes and TrematodesMafie Barreiro100% (4)
- Cestodes Trematodes: Agustina Tri Endharti Ssi.,Ph.DDocument42 pagesCestodes Trematodes: Agustina Tri Endharti Ssi.,Ph.DAndre_rarungNo ratings yet
- Class Trematoda: FlukesDocument3 pagesClass Trematoda: FlukesChan LeeNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes (Trematodes and Cestodes)Document6 pagesPlatyhelminthes (Trematodes and Cestodes)Julianna Rheaven JoreNo ratings yet
- AscariasisDocument44 pagesAscariasisMuhammad AuliaNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Orthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic CenterDocument7 pagesOrthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic Centerhannjazz100% (5)
- Drugstudy CastroDocument2 pagesDrugstudy CastroMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument4 pagesNCP PainMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument16 pagesPulmonary EdemaMark Allison Buenaventura100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- SA KALUSUGAN, KALINISAN ANG KAILANGAN Mho SWMDocument21 pagesSA KALUSUGAN, KALINISAN ANG KAILANGAN Mho SWMJoemar CafrancaNo ratings yet
- Trematodes para ReviewDocument87 pagesTrematodes para ReviewKaycee Ayo100% (1)
- Practical Logbook: Medical Parasitology Department GIT Module 104Document16 pagesPractical Logbook: Medical Parasitology Department GIT Module 104Kareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Trematode Lec QuizDocument2 pagesTrematode Lec QuizCia Lomh0% (1)
- Health Promotion Practice: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) For Health Promotion and Public Health: A ReviewDocument12 pagesHealth Promotion Practice: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) For Health Promotion and Public Health: A ReviewFalkneer ReicernageNo ratings yet
- البلهارسيا PDFDocument5 pagesالبلهارسيا PDFbdalftahasamh20No ratings yet
- Micp Report Group 6Document14 pagesMicp Report Group 6Rhelina MinNo ratings yet
- Trematodes and Their Intermediate HostDocument1 pageTrematodes and Their Intermediate HostKriziaoumo P. OrpiaNo ratings yet
- 6 PlatyhelminthesDocument19 pages6 PlatyhelminthesHarun Ft KencolNo ratings yet
- Tre Mad OdesDocument31 pagesTre Mad OdesmoosNo ratings yet
- Document94 pages blue_blooded23No ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument1 pageTrematodesfatima chrystelle nuñalNo ratings yet
- PDF Schistosomiasis Control in China The Successful Example of Jiangxi Province Zhongdao Wu Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Schistosomiasis Control in China The Successful Example of Jiangxi Province Zhongdao Wu Ebook Full Chapterjessica.booth924100% (1)
- Trematodes Final Clin paraDocument17 pagesTrematodes Final Clin paraFiona Isabela CastilloNo ratings yet
- TREMATODESDocument16 pagesTREMATODESBalisi Manuel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Indiv and FamilyDocument123 pagesNCM 104 Indiv and FamilyJames Peter ManatadNo ratings yet
- SchistosomiasisDocument3 pagesSchistosomiasisBeRnAlieNo ratings yet
- Schistosomes Parasite in HumanDocument27 pagesSchistosomes Parasite in HumanAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis JournalDocument3 pagesSchistosomiasis JournalDez TabiosNo ratings yet
- Biology Parasitology Revision NotesDocument29 pagesBiology Parasitology Revision NotesUsman Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- K5 - PPT Trematodes BbsDocument23 pagesK5 - PPT Trematodes Bbsrinaaa20000% (1)
- Schistosomiasis, Group B Presentation-1Document22 pagesSchistosomiasis, Group B Presentation-1Princewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- April 2020 Holiday Tuition Form 3 Biology: Category Notes InstructionDocument8 pagesApril 2020 Holiday Tuition Form 3 Biology: Category Notes InstructionDISHONNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Schistosomiasis in The Department of Agboville in South-Eastern Cote D IvoireDocument8 pagesDistribution of Schistosomiasis in The Department of Agboville in South-Eastern Cote D IvoireIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Travel Medicine: Health Quarantine 2021 Dr. Esther Meylina SipahutarDocument35 pagesTravel Medicine: Health Quarantine 2021 Dr. Esther Meylina SipahutarEsther Meyline XhypaNo ratings yet
- BarramundiDocument1 pageBarramundiJackAsNo ratings yet
- Human SchistosomiasisDocument18 pagesHuman SchistosomiasisbassbngNo ratings yet
- Subkingdom Metazoa 2 (DR - Nagwa)Document28 pagesSubkingdom Metazoa 2 (DR - Nagwa)Ahmed OrabyNo ratings yet
Intro To Trematodes and Blood Flukes
Intro To Trematodes and Blood Flukes
Uploaded by
Mark Allison BuenaventuraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro To Trematodes and Blood Flukes
Intro To Trematodes and Blood Flukes
Uploaded by
Mark Allison BuenaventuraCopyright:
Available Formats
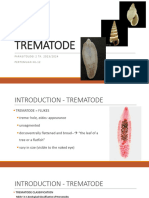
TREMATODES - Body with holes - Presence of acetabula suckers DIECIOUS BLOOD FLUKE SPECIES Schistosoma japonicum Schistosoma mansoni
Schistosoma haematobium
Pattiwatti2011
MONOECIOUS LIVER FLUKE Fasciola hepatica Clonorchis sinensis Opistorchis felineus Opistorchis viverrini
LUNG FLUKE Paragonimus westermani
INTESTINAL FLUKE Fasciolopsis buski Echinostoma ilocanum Heterophyes heterophyes Haplorchis yokogawai Metagonimus yokogawai
GENERAL APPEARANCE No. of Intermediate host Char of Eggs
Cylindrical bodies 1 Non-operculated, embryonated eggs (contains miracidium) Hatches in contact with water SSC
LARVAL DEVT
INFECTIVE STAGE
Intermediate Host: Miracidium Definitive: Fork-tail Cercaria (via skin penetration)
Flattened, leaf-shaped bodies 2, first is always a snail host Operculate eggs Mature (C.s., O.f.H.h., M.y., H.y.), or Immature (F.h., P.w., F.b., E.i.) when laid Mature: Hatches after ingestion of intermediate host Immature: Develops and hatches in water S R C = Clonorchis sinensis, Paragonymus westermani, Heterophyes heterophyes S R R C = Fasciola hepatica, Fasciolopsis buski, Metagonimus yokogawai R R C = Echinostoma Ilocanum 1st Intermediate Host: Egg/ Miracidium Cercaria 2nd Intermediate host: Cercaria Metacercaria Definitive: Metacercaria
ORGAN SYSTEMS: 1. Nervous 2. Excretory
3. Digestive
4. Respiratory/ Circulatory 5. reproductive a. testes b. genital pore c. gynecophoral canal
Paired ganglion at anterior part, back of esophagus/ pharynx Nerve trunk sends fibers to back, lateral, ventral sides of the body Bilaterally symmetrical Opens dorsal and posterior Solenocyte Flame cell basic unit Oral sucker oral cavity pre-pharyngeal tube muscular pharynx esophagus intestinal ceca w/ blind ends usually inverted Y shape NO ANUS! waste excreted through regurgitation, may be branched or straight ABSENT Oxygen taken via Skin Separate sexes Both male and female reproductive organs present in one organism multiple Paired present in both sexes Common opening for male and female reproductive organs present Absent
Clonorchis sinensis, Opistorchis felineus, Metagonymus yokogawai, Heterophyes heterophyes Fish Paragonymus westermani crabs/ crayfish Fasciolopsis buski, Fasciola Hepatica Aquatic vegetation (water cress) Echinostoma ilocanum snail
BLOOD FLUKES: SCHISTOSOMA SPECIES COMMON NAME DISEASE PRODUCED Schistosoma haematobium Vesical blood fluke Vesical schistosomiasis Schistosomal haematobium Schistosomiasis haematobium Urinary bilharziasis Africa and Middle East Vesical plexus Pelvic plexus (drains bladder) Veins of rectum Bulinus Late Intermediate Fine Single 4-5, in cluster Behind ventral sucker Posterior to midpoint Longest 20-30 20-290 Terminal spine Urine > Stool ALL Praziquantel Schistosoma mansoni Mansonis blood fluke Mansonis intestinal schistosomiasis Schistosomiasis mansoni Bilharziasis Africa, South America, Caribbean Inferior mesenteric plexus (drains LI) Vesical plexus (sometimes) Biomphalaria Early Longest Coarse Single 6-9 Posterior and behind ventral sucker Anterior to midpoint Shortest 1-2 100-300 Lateral Spine Stool > Urine ALL Praziquantel Schistosoma japonicum Oriental blood fluke Oriental Schistosomiasis Schistosomiasis japonica Katayama Dse Far East (except Japan & Taiwan) - Bicol, Samar, Leyte, Mindanao Superior mesenteric plexus (drains SI, stomach) Oncomelania quadrasi Very Late Shortest None Double 6-8, in columns/ rows/ clusters midpoint In between 50 1,500-3,000 Abbreviated rudimentary spine Stool ALL Praziquantel
GEOGRAPHICAL DIST. HABITAT
INTERMEDIATE HOST UNION OF INTESTINAL CECA LENGTH OF POST. CECA TUBERCULATION ESOPHAGEAL BULB TESTES OVARIES LENGTH OF UTERUS UTERINE CAPACITY No. OF EGGS/FEMALE/DAY CHAR. Of EGGS DIAGNOSIS PATHOGENIC STAGE TREATMENT
SCHISTOSOMIASIS STAGES STAGE I Stage of Invasion DURATION 0-4 weeks PARASITE STAGE Cercaria skin penetration PATHOLOGY Cellular infiltration CLINICAL Mx Itchiness, redness, edema, congestion, dermatitis, swimmers itch, clam diggers itch Cough, fever Puritus, rashes, urticarial, cough, fever, bronchial asthma, diarrhea GI disturbances, colic pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dysentery LAB Dx IDT (+)
Pattiwatti2011
CHR (+/-)
Schistosomule migrating II Maturation 4-6 weeks Adults in copula Female starts laying eggs
Inflammatory Reaction Allergy
IDT (+) CHR (+)
SE (+/-)
III Established Infection
*Progresses to stage IV if: - Malnourished - Alcoholic - Superinfection
>6 weeks
Massive egg-laying
Pseudogranuloma Fibrosis (small scarring of involved organ) Parasitic Hepatitis
IDT (+) CHR (+) SE (+)
LFT (+/-) COPT (+/-)
IV Late Infection/ Chronic
Uncertain
Decreased egg production
Fibrosis of organ involved Granuloma formation Parasitic Cirrhosis
Portal Hypertension Ascites Hemorrhoids Esophagus Caput Medusa
IDT (+) CHR (+) LFT (+) COPT (+) Biopsy (+)
SE (+/-)
IDT = Intradermal Test; LFT = Liver Function Test; SE = Stool Exam; CHR = Cercaria Huellen Reaction(serum+cercaria) + = shrinking; COPT = Circum Oval Precipitin Test (serum+egg) + = >24 H blebs around egg; >72 H precipitation of filaments; Biopsy = of rectal mucosa (liver = dangerous)
You might also like
- Table For Cestodes and TrematodesDocument5 pagesTable For Cestodes and TrematodesDawn WRein Legaspi100% (3)
- NCP PreoperativeDocument3 pagesNCP PreoperativeMark Allison Buenaventura75% (4)
- Helminths MCQsDocument21 pagesHelminths MCQsمحمد محمد هشام84% (19)
- Summary (Trematodes)Document4 pagesSummary (Trematodes)Krizia Del Rosario50% (2)
- TREMATODESDocument31 pagesTREMATODESKen Mark ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Phylum Platyheminthes TrematodesDocument12 pagesPhylum Platyheminthes TrematodesRona SalandoNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument10 pagesTrematodesUhjafwnuijhnfa Kmerkgoe100% (1)
- TrematodesDocument9 pagesTrematodesJoseph PerezNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument9 pagesTrematodesLewis P. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Trematodes para ReviewDocument87 pagesTrematodes para ReviewKaycee Ayo100% (1)
- Trematode SDocument4 pagesTrematode SMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument9 pagesTrematodesRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- Medical Helminthology - Chordata and Roundworms - Human ParasitesDocument54 pagesMedical Helminthology - Chordata and Roundworms - Human ParasitesMewa MahartaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lecture 15 - Liver Flukes and Lung FlukeDocument4 pagesParasitology Lecture 15 - Liver Flukes and Lung Flukemiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Trematodes PDFDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Trematodes PDFLyka Villagracia AsiloNo ratings yet
- Trem-Ing pptIIDocument61 pagesTrem-Ing pptIITutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Document94 pages blue_blooded23No ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument75 pagesTrematodesHann SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Trematodes 2Document37 pagesTrematodes 2Akanksha BaireddyNo ratings yet
- Template para Lab Exe 4 The TREMATODES 1 PDFDocument11 pagesTemplate para Lab Exe 4 The TREMATODES 1 PDFCharlie Magne GarciaNo ratings yet
- PARA20 3rd Long ExamDocument4 pagesPARA20 3rd Long ExamEricNo ratings yet
- Trematodes (Flukes)Document35 pagesTrematodes (Flukes)api-3856362No ratings yet
- 1st Lecture - Trematodes - Clinical ParasitologyDocument38 pages1st Lecture - Trematodes - Clinical ParasitologyAhmed MoghazyNo ratings yet
- HelminthsDocument190 pagesHelminthsSarhan AliNo ratings yet
- Parasitesofliver Moin Hydergroup 4Document40 pagesParasitesofliver Moin Hydergroup 4Moeen HyderNo ratings yet
- Flukes in Ruminants in South Africa BBDocument13 pagesFlukes in Ruminants in South Africa BBnigeldkdcNo ratings yet
- Blood Flukes: Richelle D. Sales, RMTDocument20 pagesBlood Flukes: Richelle D. Sales, RMTZairah PascuaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology - Trematodes - S. Mansoni, S. Haematobium, P. WestermaniDocument51 pagesParasitology - Trematodes - S. Mansoni, S. Haematobium, P. WestermaniNicole ManogNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis & FascioliosisDocument40 pagesSchistosomiasis & FascioliosisWahyudi YusmanNo ratings yet
- Para-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Document11 pagesPara-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Aysha AishaNo ratings yet
- Pathology Lec 1 - 211010 - 144130Document83 pagesPathology Lec 1 - 211010 - 144130Daly DaliaNo ratings yet
- Digenean: Schistosoma SPP.: PathologyDocument5 pagesDigenean: Schistosoma SPP.: PathologyBernard Lionel MoreusNo ratings yet
- SchistosomesDocument12 pagesSchistosomesMORDENO, JOHN GABRIEL O. SCINo ratings yet
- FH, F, PW, SDocument56 pagesFH, F, PW, SMo FanNo ratings yet
- Trematode SDocument5 pagesTrematode SAUDREY VERONICA PEREZ100% (1)
- Trematode SDocument26 pagesTrematode SothnielNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Intestinal FlukesDocument76 pages9.2 Intestinal Flukesvader37526No ratings yet
- Trematodes - TransDocument9 pagesTrematodes - TransDenver CarbonNo ratings yet
- Intestinal FlukesDocument3 pagesIntestinal Flukesmiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- Class CESTODADocument65 pagesClass CESTODAKaycee AyoNo ratings yet
- TREMATODA - UsusDocument32 pagesTREMATODA - Usustheo referatNo ratings yet
- 3) TrematodesDocument38 pages3) Trematodesmisgshlove1No ratings yet
- Phylum NematodaDocument285 pagesPhylum NematodaBrielleNo ratings yet
- Para Reviewer (Prelims-Finals)Document15 pagesPara Reviewer (Prelims-Finals)Mafie BarreiroNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Liver and Intestinal FlukesDocument60 pages3.4 Liver and Intestinal FlukesHazel Joyce Gonda RoqueNo ratings yet
- Poraginumus WestermaniDocument23 pagesPoraginumus WestermaniMika AndiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology PDFDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology PDFArianna Aparte AvenidoNo ratings yet
- Trematode NotesDocument3 pagesTrematode NotesGlenn PerezNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document PDFDocument5 pagesUntitled Document PDFRizzy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge ReviewDocument81 pagesKnowledge ReviewAmr EldemardashNo ratings yet
- Six Flukes. TrematodeDocument106 pagesSix Flukes. TrematodeCherenet TomaNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument9 pagesNematodesMomo ShinNo ratings yet
- Cestodes and NematodesDocument19 pagesCestodes and Nematodespancake pancakeNo ratings yet
- Trematoda Usus Hati ParuDocument59 pagesTrematoda Usus Hati ParuRoisah Yunan NegariNo ratings yet
- Parasite Adult OVA Life Cycle Pathology: in CopulaDocument3 pagesParasite Adult OVA Life Cycle Pathology: in CopulaMaria StephanieNo ratings yet
- Amphistomate & Distomate FlukeDocument12 pagesAmphistomate & Distomate FlukeJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Table For Cestodes and TrematodesDocument5 pagesTable For Cestodes and TrematodesMafie Barreiro100% (4)
- Cestodes Trematodes: Agustina Tri Endharti Ssi.,Ph.DDocument42 pagesCestodes Trematodes: Agustina Tri Endharti Ssi.,Ph.DAndre_rarungNo ratings yet
- Class Trematoda: FlukesDocument3 pagesClass Trematoda: FlukesChan LeeNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes (Trematodes and Cestodes)Document6 pagesPlatyhelminthes (Trematodes and Cestodes)Julianna Rheaven JoreNo ratings yet
- AscariasisDocument44 pagesAscariasisMuhammad AuliaNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Orthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic CenterDocument7 pagesOrthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic Centerhannjazz100% (5)
- Drugstudy CastroDocument2 pagesDrugstudy CastroMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument4 pagesNCP PainMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument16 pagesPulmonary EdemaMark Allison Buenaventura100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- SA KALUSUGAN, KALINISAN ANG KAILANGAN Mho SWMDocument21 pagesSA KALUSUGAN, KALINISAN ANG KAILANGAN Mho SWMJoemar CafrancaNo ratings yet
- Trematodes para ReviewDocument87 pagesTrematodes para ReviewKaycee Ayo100% (1)
- Practical Logbook: Medical Parasitology Department GIT Module 104Document16 pagesPractical Logbook: Medical Parasitology Department GIT Module 104Kareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Trematode Lec QuizDocument2 pagesTrematode Lec QuizCia Lomh0% (1)
- Health Promotion Practice: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) For Health Promotion and Public Health: A ReviewDocument12 pagesHealth Promotion Practice: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) For Health Promotion and Public Health: A ReviewFalkneer ReicernageNo ratings yet
- البلهارسيا PDFDocument5 pagesالبلهارسيا PDFbdalftahasamh20No ratings yet
- Micp Report Group 6Document14 pagesMicp Report Group 6Rhelina MinNo ratings yet
- Trematodes and Their Intermediate HostDocument1 pageTrematodes and Their Intermediate HostKriziaoumo P. OrpiaNo ratings yet
- 6 PlatyhelminthesDocument19 pages6 PlatyhelminthesHarun Ft KencolNo ratings yet
- Tre Mad OdesDocument31 pagesTre Mad OdesmoosNo ratings yet
- Document94 pages blue_blooded23No ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument1 pageTrematodesfatima chrystelle nuñalNo ratings yet
- PDF Schistosomiasis Control in China The Successful Example of Jiangxi Province Zhongdao Wu Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Schistosomiasis Control in China The Successful Example of Jiangxi Province Zhongdao Wu Ebook Full Chapterjessica.booth924100% (1)
- Trematodes Final Clin paraDocument17 pagesTrematodes Final Clin paraFiona Isabela CastilloNo ratings yet
- TREMATODESDocument16 pagesTREMATODESBalisi Manuel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Indiv and FamilyDocument123 pagesNCM 104 Indiv and FamilyJames Peter ManatadNo ratings yet
- SchistosomiasisDocument3 pagesSchistosomiasisBeRnAlieNo ratings yet
- Schistosomes Parasite in HumanDocument27 pagesSchistosomes Parasite in HumanAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis JournalDocument3 pagesSchistosomiasis JournalDez TabiosNo ratings yet
- Biology Parasitology Revision NotesDocument29 pagesBiology Parasitology Revision NotesUsman Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- K5 - PPT Trematodes BbsDocument23 pagesK5 - PPT Trematodes Bbsrinaaa20000% (1)
- Schistosomiasis, Group B Presentation-1Document22 pagesSchistosomiasis, Group B Presentation-1Princewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- April 2020 Holiday Tuition Form 3 Biology: Category Notes InstructionDocument8 pagesApril 2020 Holiday Tuition Form 3 Biology: Category Notes InstructionDISHONNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Schistosomiasis in The Department of Agboville in South-Eastern Cote D IvoireDocument8 pagesDistribution of Schistosomiasis in The Department of Agboville in South-Eastern Cote D IvoireIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Travel Medicine: Health Quarantine 2021 Dr. Esther Meylina SipahutarDocument35 pagesTravel Medicine: Health Quarantine 2021 Dr. Esther Meylina SipahutarEsther Meyline XhypaNo ratings yet
- BarramundiDocument1 pageBarramundiJackAsNo ratings yet
- Human SchistosomiasisDocument18 pagesHuman SchistosomiasisbassbngNo ratings yet
- Subkingdom Metazoa 2 (DR - Nagwa)Document28 pagesSubkingdom Metazoa 2 (DR - Nagwa)Ahmed OrabyNo ratings yet