Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Android Michaelmorckos May 13 09
Android Michaelmorckos May 13 09
Uploaded by
Recursive EnumerableOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Android Michaelmorckos May 13 09
Android Michaelmorckos May 13 09
Uploaded by
Recursive EnumerableCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Android Architecture
Michael Y. Morckos
German Univeristy in Cairo
May 13, 2009
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
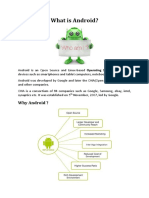
What is Android
What is Android
Android is an operating system for mobile devices Its an integrated open source software stack for mobile device
Operating system Middleware Key mobile applications
Went open source in late 2008. Released under the Apache v2 license
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
History
Google acquired Android Inc. in July 2005
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
History
Google acquired Android Inc. in July 2005 The Android team, led by Andy Rubin, developed a mobile device platform powered by Linux operating system
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
History
Google acquired Android Inc. in July 2005 The Android team, led by Andy Rubin, developed a mobile device platform powered by Linux operating system This signaled Googles entry into the mobile-phone market
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
Open Handset Alliance
A consortium established by Google in November 2007
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
Open Handset Alliance
A consortium established by Google in November 2007 34 members including key companies in mobile handsets, application developments and mobile chips industries.
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
Open Handset Alliance
A consortium established by Google in November 2007 34 members including key companies in mobile handsets, application developments and mobile chips industries. The consortium aim at providing open standards for mobile devices for richer capabilities and reduced cost
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
Open Handset Alliance
A consortium established by Google in November 2007 34 members including key companies in mobile handsets, application developments and mobile chips industries. The consortium aim at providing open standards for mobile devices for richer capabilities and reduced cost On the same month Android was unveilled, marking it the agship product of the OHA consortium
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
Open Handset Alliance
A consortium established by Google in November 2007 34 members including key companies in mobile handsets, application developments and mobile chips industries. The consortium aim at providing open standards for mobile devices for richer capabilities and reduced cost On the same month Android was unveilled, marking it the agship product of the OHA consortium The T-Mobile G1 (HTC Dream) was the rst mobile device powered by Android. Released on October 2008
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
What is Android
Innovative Features
Linux kernel Open system Component based Java programming language for applications development Enable mobile applications to exploit full advantage of all a handset has to oer No boundaries Fast & easy development
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Contents
Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Android Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Android Stack
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Android Architecture
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Kernel
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Overview
Android uses a heavily modied GNU/Linux kernel version 2.6 for handling core system infrastructure services as security, memory management, process management, network stack, and driver model The kernel provides an abstraction layer between the hardware and the rest of the software stack Include many enhancements and modications
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Android Power Management
A light-weight power managemenr driver built atop the standard linux power management Constrainted power management policy
CPU shouldnt consume power if no applications or services require power Components make requests to keep the power on through Wake Locks
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Binder
An OpenBinder-based driver to facilitate inter-process communication (IPC) on the Android platform OpenBinder provides:
High performance through shared memory Per-process thread pool for processing requests Synchronous calls between processes
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Memory Management
Low Memory Killer: based on feedbacks from user applications, the low memory killer can kill processes to free up memory as necessary Provides more exibility than the Out Of Memory (OOM) killer in the standard kernel Android PMEM: the PMEM (physical memory) driver is used to provide contiguous physical memory regions to userspace libraries that interact with the processor and other hardware
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Other Components
Logger: A light weight logging device used to capture system, radio, logdata, etc. Android Alarm: A driver which provides timers that can wake the device up from sleep and a monotonic timebase that runs while the device is asleep M-Systems: for memory cards and other ash media storage Other conventional drivers:
Bluetooth Display Keypad Audio ...
Michael Y. Morckos Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Runtime
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Overview
A vital component in the Android stack
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Overview
A vital component in the Android stack Composed of two major parts:
The Dalvik virtual machine Core libraries
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Dalvik Virual Machine
One of the most important components in Android
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Dalvik Virual Machine
One of the most important components in Android Developed by Dan Bornstein, and named after the Dalvik village in Iceland
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Dalvik Virual Machine
One of the most important components in Android Developed by Dan Bornstein, and named after the Dalvik village in Iceland Three main design targets:
runs on a limited CPU and RAM (250-500MHz) (20-40 MB) runs atop an OS with no swap space runs on a device with limited power
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
From .class to .dex
Dalvik replaces the JVM in providing the runtime environment to Java platform applications
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
From .class to .dex
Dalvik replaces the JVM in providing the runtime environment to Java platform applications The VM runs Java applications which have been converted to the Dalvik Executable format .dex
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
From .class to .dex
Dalvik replaces the JVM in providing the runtime environment to Java platform applications The VM runs Java applications which have been converted to the Dalvik Executable format .dex The dx tool available in the SDK converts Java bytcode to DVM bytcode at build time
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
From .class to .dex
Dalvik replaces the JVM in providing the runtime environment to Java platform applications The VM runs Java applications which have been converted to the Dalvik Executable format .dex The dx tool available in the SDK converts Java bytcode to DVM bytcode at build time The dx format is a highly ecient and compact bytecode
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
From .class to .dex
Dalvik replaces the JVM in providing the runtime environment to Java platform applications The VM runs Java applications which have been converted to the Dalvik Executable format .dex The dx tool available in the SDK converts Java bytcode to DVM bytcode at build time The dx format is a highly ecient and compact bytecode dx les can be installed on dierent devices and can be further modied after being installed to increase eciency
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Dalvik Features
Highly CPU optimized interpreter No just-in-time compiling Shared constants pool and data structures Static linking Bytes reordering
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Core Libraries
Androids core libraries provide most of the functionality available in the core libraries of Java needed for applications development:
I/O functionalities Collections File access ...
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Native Libraries
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Overview
This layer houses the core libraries providing the bulk of Android functionalities Implemented in C/C++ Developers can exploit the full capabilities of these libs through the application framework layer
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Bionic (libC)
A BSD-based implementation of the standard C library, tuned for embedded Linux-based devices 200 KB in size, roughly half the size of the standard GNU C library libc Bionic includes a very fast and small custom POSIX-thread implementation Compatability issue with GNU libc
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
SQLite
A powerful lightweight embedded relational database management system contained in a relatively small ( 500 kb) C library The engine is not a standalone entity. Instead, a SQLite database is just another program linked in and thus becomes an integral part of the program The database is stored as a single cross-platform le on the host machine Application access SQLite through conventional simple function calls
Michael Y. Morckos Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Surface Manager
Responsible for composing dierent drawing surfaces on the mobile screen Manages access for dierent processes to the underlying display subsystem and composites 2D and 3D graphic layers from multiple applications Layers passed as buers via Binder IPC calls Use OpenGL/ES and 2D hardware accelerator for its compositions
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
OpenGL/ES & SGL
Subset of the OpenGL 3D graphics API designed for embedded devices Dened and promoted by the Khronos Group, a graphics hardware and software industry consortium Can use either hardware 3D acceleration (hardware dependent) or the included highly optimized 3D software rasterize SGL is Androids specialized 2D graphics library
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Media Framework
Provided by PacketVideos multimedia package OpenCore The OpenCore provides a universal structure for mobile multimedia applications Support for standard video, audio, still-frame formats (MPEG4, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, and PNG, H.264) Support for codec plug-ins
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
FreeType
Implements a font rasterization engine Written in C It is used to rasterize characters into bitmaps and provides support for other font-related operations
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
LibWebCore (WebKit)
A framework providing the basis for building a web browser based on the open source WebKit browser Written in C++ Rendering of pages in full (desktop) view Support for modern web technologies; CSS, JavaScript, DOM, AJAX
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Audio Manager (Audio Flinger)
Processing multiple audio streams into PCM audio out paths
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Framework Overview
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Overview
A general purpose toolkit that all applications use Written in Java Enable reuse and replacement of components
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
View System
Enabling applications to access data from other applications or to share their own data
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Resource Manager
Providing access to non-code resources (localized string, graphics, and layout les)
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Notication Manager
Enabling all applications to display customer alerts in the status bar
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Activity Manager
Managing the lifecycle of applications and providing a common navigation backstack
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Telephony Manager
Provides core telephoning functionalities
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
XMPP Service
An Open, XML-based protocol originally aimed at near-real-time, extensible instant messaging Largely extended. VoIP Aims to:
Send simple P2P message between handsets Send and receive IMs using Googles Talk
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Location Manager
Allows applications to obtain periodic updates
devices geographical location triggers an application-specied event when the device enters the proximity of a given geographical location
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Window Manager
The window manager creates display surfaces for the application Responsible for organizing the screen and display of dierent layers of application
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Contents Overview Linux Kernel Android Runtime Native Libraries Application Framework Applications
Applications
Android comes with a bundle of core applications: email client SMS program calendar maps browser contacts ...
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Overview
Written in Java (as you know)
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Overview
Written in Java (as you know) The compiled application is bundled by the aapt tool into an Android package .apk
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Overview
Written in Java (as you know) The compiled application is bundled by the aapt tool into an Android package .apk Like .jad & .jar in J2ME, .apk les are distributed and installed on Android powered devices
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Basic Facts
Every application: is a single Linux process has its own VM instance is assigned a unique Linux user ID
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Basic Facts
A key feature of Android is that applications can publish their functionalities An application can use other functionalities provided by other applications Android applications dont have a single entry point
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Application Diagram
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Activities
Class in the API An activity presents the user with a visual UI for a specic functionality Application can have several activities Each activity is given a default window to draw in The visual content of the window is provided by a hierarchy of views User interacts with activities through the views Android provides several built-in views:
Buttons Menus Text elds ...
Michael Y. Morckos Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Services
Background functionalities Run in the applicationss thread
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Content Provider
Provides applications with required applications data Data stored in a SQLite DB Applications talk to content provider through a content resolver
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Broadcast Receiver
Receive and react to broadcast announcements Many originate from system level Persistent
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Activation
Content providers are activated when targeted by applications (implicit activation) Broadcast receivers are activated when receiving Services and activities are activated by intent msgs Intent messages contains ID of component to be activated + URI of data to be used Intent lters
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Deactivation
Content providers and broadcast receivers are shut down once they are done Activities and services require explicit shutdown Components might also be shut down by the system to reclaim memory for higher priority components (life cycle)
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Tasks
Dierent activities can be activated on demand A group of activities composes a task. They are maintained in a stack Users experience of an application can actually be a task consisting of dierent activities from dierent applications Can have a stack of tasks as well
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Activity
Activities can be in one of these states at an instance: Active: has the users focus, displayed in the foreground Paused: still visible but under another active activity Stopped: completely obscured by another activity, no longer visible If an activity is paused or stopped, the system can drop it from memory. When the user returns to it, the system must restore it to its previous state
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Activity
Entire lifetime: from the moment the activity is created till destroyed Visible lifetime: from the moment the activity activated till stopped Foreground lifetime: between resuming and pausing an activity
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Activity Lifecycle
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Service
Services can be shutdown explicity or implicitly Entire lifetime: from creation till destruction Active lifetime: from activation
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Introduction Application Components Components Activation/Deactivation Tasks Components Lifecycle
Broadcast Receiver
Broadcast receiver is active when receiving and reacting to a notication A process with an active broadcast receiver is protected from being killed Active lifetime: from activation
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Overview
The SDK includes a full set of tools for developing and debugging application Designing UIs Major components in version 1.5:
Android Development Tools Plugin (for the Eclipse IDE) Android Emulator Android Virtual Devices (AVDs); speciying dierent platform, hardware options, skins... Dalvik Debug Monitor Service (ddms) Android Asset Packaging Tool (aapt) sqlite3 dx tool
Michael Y. Morckos Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Standard Procedure: Hello, World
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Summary
Whats Android Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
Android Closing...
Questions? Thank you for your attention!
Michael Y. Morckos
Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
References
http://developer.android.com/ http://androidlinux.com/ http://www.dalvikvm.com/ http://www.bindaaspoll.com/googleandroid/index.htm http://benno.id.au/blog/2007/11/26/what-is-android http://it.toolbox.com/wiki/index.php/Dalvik virtual machine http://blog.codebeach.com/2007/11/android-architectureoverview.html http://stuthathappens.com/blog/2009/04/12/google-io2008-dalvik-virtual-machine-internals/
Michael Y. Morckos Android Architecture
Introduction Android Architecture Android Application Fundamentals Android SDK Summary
References
http://www.kandroid.org/android pdk/intro source code.html http://sites.google.com/site/io/dalvik-vm-internals http://www.brighthub.com/mobile/googleandroid/articles/17822.aspx http://glab.wordpress.com/2008/05/21/android-a-quickoverview/ http://moss.csc.ncsu.edu/ mueller/g1/slides/platform.ppt http://www.softdevtube.com/2008/09/16/inside-the-androidapplication-framework/ http://groups.google.com/group/androidframework/browse thread/thread/34a635dd68c8b4f4
Michael Y. Morckos Android Architecture
You might also like
- Simple Introduction To Angle Resolve Photo Emission Spectroscopy ARPESDocument7 pagesSimple Introduction To Angle Resolve Photo Emission Spectroscopy ARPESousolidNo ratings yet
- GereeceDocument35 pagesGereeceAbhishekNo ratings yet
- My AndroidDocument26 pagesMy AndroidLê Thu HiềnNo ratings yet
- Pen Viva QuesDocument14 pagesPen Viva QuesJanvi WaghmodeNo ratings yet
- Best PDFDocument79 pagesBest PDFbalew ayalewNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 NOTES Android and It's ToolsDocument9 pagesUNIT 1 NOTES Android and It's Toolstoxawib889No ratings yet
- Android Application DevelopmentDocument32 pagesAndroid Application DevelopmentAmi VermaNo ratings yet
- Android VersionsDocument26 pagesAndroid VersionsDamayanti Pawar-BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Ch-2-Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesCh-2-Literature ReviewChandro KironNo ratings yet
- Unit No.1Document23 pagesUnit No.1Atharv KadamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Android Development: The Open Source Appliance PlatformDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Android Development: The Open Source Appliance PlatformToni_RodriguezNo ratings yet
- " Android Os ": A Seminar Synopsis Report ONDocument25 pages" Android Os ": A Seminar Synopsis Report ONAbhishek SaxenaNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report ON Android: Prepared byDocument39 pagesA Seminar Report ON Android: Prepared bySanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Android DevelopmentDocument46 pagesAndroid DevelopmentanjeruNo ratings yet
- Ieee Paper Based On Android Applications With Its Recent TechnologiesDocument6 pagesIeee Paper Based On Android Applications With Its Recent TechnologiesSuganya PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- 6 ChaptersDocument25 pages6 Chaptersumesh patilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Android Dev..Document15 pagesIntroduction To Android Dev..motashNo ratings yet
- A Developer's First Look At: AndroidDocument3 pagesA Developer's First Look At: AndroidanimatedjadeNo ratings yet
- MAD Lab DocumentDocument32 pagesMAD Lab DocumentDhyan MohanNo ratings yet
- QB Solution PT-1 MADDocument31 pagesQB Solution PT-1 MADAryan BuchakeNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With AndroidDocument36 pagesGetting Started With AndroidRaj SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- AndroidDocument22 pagesAndroidSPSINGH RathourNo ratings yet
- Android Development Slides Lec 01 GCUFDocument16 pagesAndroid Development Slides Lec 01 GCUFcode with joeyNo ratings yet
- Android TechnologyDocument28 pagesAndroid TechnologysuchetanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument229 pagesUnit 1 Notessainath chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Mohammad Ali Jauhar University: A Seminar OnDocument29 pagesMohammad Ali Jauhar University: A Seminar OnAhmadNo ratings yet
- What Is Android?Document17 pagesWhat Is Android?Sagar BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Android Development TutorialDocument50 pagesAndroid Development TutorialShailesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Mad Lab ManualDocument173 pagesMad Lab ManualPRIYA RAJI100% (2)
- MAD LabmanualDocument70 pagesMAD LabmanualRiya PatelNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To AndroidDocument24 pages1 Introduction To AndroidSamson OkumuNo ratings yet
- AndroidDocument122 pagesAndroidrahul kadianNo ratings yet
- "Android": Boon For Mobile Operating SystemsDocument15 pages"Android": Boon For Mobile Operating SystemsAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument42 pagesQuestion Bank02 - CM Ankita AdamNo ratings yet
- Unit-1-Android-And-Its-Tools MADDocument10 pagesUnit-1-Android-And-Its-Tools MADAryan BuchakeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AndroidDocument25 pagesIntroduction To AndroidMehdi 'Bada' Ben LazregNo ratings yet
- Soar12.0 Class09Document14 pagesSoar12.0 Class09sarafarajnasardi786No ratings yet
- 11.intro AndrDocument30 pages11.intro AndrRavi 1 91 8 9 TejaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 1 - AndroidIntroduction - SettingUpYourEnvironment PDFDocument36 pagesUnit 1 - 1 - AndroidIntroduction - SettingUpYourEnvironment PDFPreethiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To: AndroidDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To: AndroidAbhiram HollaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Unit AndroidDocument50 pages2nd Unit AndroidNitesh SainiNo ratings yet
- MADDocument12 pagesMADP.subhaNo ratings yet
- Mad Part 1 NotesDocument10 pagesMad Part 1 NotesVeeresh NikeeNo ratings yet
- Android Technology SeminarDocument31 pagesAndroid Technology SeminarArchie Srivastava0% (1)
- Android Report - ابانوب عماد فارسDocument22 pagesAndroid Report - ابانوب عماد فارسAbanob EmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document51 pagesUnit 5yunoedits324No ratings yet
- Android App DevelopmentDocument40 pagesAndroid App Developmentnaman sethiNo ratings yet
- Android MosDocument14 pagesAndroid MosPranusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACT: Android Is A Software Stack For Mobile Devices ThatDocument29 pagesABSTRACT: Android Is A Software Stack For Mobile Devices That12345mtp69% (13)
- Summer Training Project Report: Submitted byDocument34 pagesSummer Training Project Report: Submitted byShivam JhaNo ratings yet
- Android 130923124440 Phpapp01Document22 pagesAndroid 130923124440 Phpapp01Aaditya BaidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1notesDocument10 pagesUnit 1notesJidnyasa ChavanNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentIJERDNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey On Android 3Document5 pagesLiterature Survey On Android 3AkshayHanumanteNo ratings yet
- Android Application Development Tutorial: by Chau Ngo EEL 6788-Advanced Topics in Wireless NetworksDocument61 pagesAndroid Application Development Tutorial: by Chau Ngo EEL 6788-Advanced Topics in Wireless Networksjagdishmehta_onlineNo ratings yet
- Mad NotesDocument376 pagesMad NotesDivya RahaneNo ratings yet
- Mad - Notes - I, IiDocument34 pagesMad - Notes - I, IiDivya RahaneNo ratings yet
- Android Programming For Beginners: The Ultimate Android App Developer's GuideFrom EverandAndroid Programming For Beginners: The Ultimate Android App Developer's GuideNo ratings yet
- Convegenious - AMITY STAGE 1 2023Document247 pagesConvegenious - AMITY STAGE 1 2023ConanNo ratings yet
- Sample Technical Writing Mechanism DescriptionDocument3 pagesSample Technical Writing Mechanism DescriptionAcatech CabNo ratings yet
- Helmer FreezerDocument26 pagesHelmer FreezerBrent EnciniasNo ratings yet
- Fairfield Atlas Limited: 6.1 - Minimum 5 Samples Per Heat Batch To Be CheckedDocument3 pagesFairfield Atlas Limited: 6.1 - Minimum 5 Samples Per Heat Batch To Be CheckedAndras StegerNo ratings yet
- Iae v2500 FlyerDocument2 pagesIae v2500 FlyerkevnwongNo ratings yet
- WR3072 RevDocument39 pagesWR3072 RevJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Selected AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter Four Selected AnswersByron BanzonNo ratings yet
- 7800 User Manual 6.0Document12 pages7800 User Manual 6.0sajal99No ratings yet
- 19 2 1mm Bronze II Stranded ConductorDocument1 page19 2 1mm Bronze II Stranded ConductorCarlos PanccaNo ratings yet
- Wiseco 16ST Engine 999 1071Document73 pagesWiseco 16ST Engine 999 1071Danno N0% (1)
- Gear Crack Detection Using Modified TSA and Proposed Fault Indicators For Fluctuating Speed ConditionsDocument16 pagesGear Crack Detection Using Modified TSA and Proposed Fault Indicators For Fluctuating Speed ConditionsPradeep KunduNo ratings yet
- Single Stage DistillationDocument15 pagesSingle Stage DistillationFatimah MauludiyahNo ratings yet
- DIP2Document80 pagesDIP2gigabyte1812No ratings yet
- FFV4Q4-65B-R7 Product SpecificationsDocument6 pagesFFV4Q4-65B-R7 Product SpecificationsyohnnisNo ratings yet
- Chesterton PDFDocument96 pagesChesterton PDFPedro DonayreNo ratings yet
- BBS - 1-22-0 CulvertDocument2 pagesBBS - 1-22-0 Culvertshakti panda0% (1)
- Astronomical Reflexes in Ancient CoinsDocument30 pagesAstronomical Reflexes in Ancient CoinsAnitaVasilkovaNo ratings yet
- WPS D1.3 RF 40Document8 pagesWPS D1.3 RF 40RodolfoNo ratings yet
- Evermotion Archmodels 31 PDFDocument2 pagesEvermotion Archmodels 31 PDFJessicaNo ratings yet
- Arcsight TrainingDocument329 pagesArcsight TrainingsrujanNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Switching Transients ProblemsDocument5 pagesCapacitor Switching Transients Problemsaris09yekofNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - SoftwareDocument10 pagesModule 3 - SoftwareRoden LacabaNo ratings yet
- Barry - Modern Political TheoryDocument23 pagesBarry - Modern Political TheoryilseNo ratings yet
- LabDocument4 pagesLabjohn mark100% (1)
- Voltage and Reactive Power Control: Code: EEE 574Document34 pagesVoltage and Reactive Power Control: Code: EEE 574Fuh Vallery100% (1)
- Aa Microlab300 Cat 8Document52 pagesAa Microlab300 Cat 8DARWIN FERNANDO MONTOYA GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - EEConDocument27 pagesMODULE 2 - EEConMark Anthony GarciaNo ratings yet
- CANQUE - Optical PropertiesDocument5 pagesCANQUE - Optical PropertiesAvelyn Mary Canque ClarionNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety and Alert System Using Arduino Sensors With Iot IntegrationDocument6 pagesFire Safety and Alert System Using Arduino Sensors With Iot IntegrationSAURAV PANDEYNo ratings yet