Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grammar
Grammar
Uploaded by
sisyphus77447Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grammar
Grammar
Uploaded by
sisyphus77447Copyright:
Available Formats
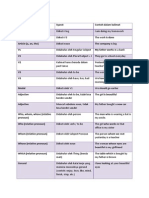
GRAMMAR
Requires a subject Complement Subject performs the action; the object receives Expresses action but has no object
Predicate Patterns
INDEPENDENT
Transitive Verb
Intransitive Verb
Subject + Linking Verb + Adjective Subject Compliment
Subject + T. Verb + Direct Object
Subject + Intransitive Verb
or
Subject + Linking Verb + Adverb Subject Compliment
or
Subject + T. Verb + Indirect Object + Direct Object
or
Subject + Intransitive Verb + Adverb
or
Subject + Linking Verb + Noun Subject Compliment
or
Subject + T. Verb + Direct Object + Object Compliment
or
Subject + Linking Verb + Possessive Subject Compliment
Contains a noun or equivalent, plus modifiers.
SUBJECT
PREDICATE
Contains at least one verb & its modifiers. + one or more compliments
CLAUSE
Subject predicate clause that stands on its own.
INDEPENDENT
DEPENDENT
Subject predicate clause that cannot stand by itself. It must attach to an independent clause, usually begins with an introductory word that signals dependency.
One independent clause.
Simple Sentence
Dependent Clause Functions
Two or more independent clauses.
Compound Sentence
Modifies a noun or pronoun.
Adjective Clause or
Subject Direct Object Subject Complement Object of the preposition
One independent and one or more dependent clauses.
Complex Sentence
Noun Clause or
Two or more independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses.
Compound Sentence
Adverb Clause
Time Cause Purpose Condition Contrast Comparison Place Manner
GRAMMAR
Influences mood
Can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might, & must
Modals
Auxiliaries
Form
S-Form Base Past Past Participle Present Participle
Present & Past Participles
Have, had, has, having
Verb Have
An action that expresses action, occurrence & existence
Base Form
Did, do, & does
Do
Verb Phrase
Predicate Patterns (see clause P1)
A VERB AND ITS AUXILIARIES
Present & Past Participles
is, are, am, was, were, been, being
Be
Verbals
Infinitive
To + Verb
Adverbial Adjectival & Noun Mood Participles
Makes Statements & Asks Questions Past or present, alone or in phrases, modify nouns & pronouns
Indicative Adjectival
Gives commands Positive & Negative
Imperative
Indicates that it isnt a Fact or that it should happen
Gerunds Subjunctive
Present participle functioning as a noun
Noun
Decides the action
Voice Absolutes
Modifies the rest of the sentence
Subject Controls the action
Active Familial Expression
Participle: Speaking of Friends or Infinitive: To tell the Truth
Subject receives the action
Passive
Nominative Absolute
Begins with a noun or pronoun, acts as the subject of the verbal
You might also like
- Business Grammar Practice IntermediateDocument192 pagesBusiness Grammar Practice IntermediateNgô Lê Quỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Grammar Guide (Advanced) - 15 Advanced Grammar Rules You Must Know To Achieve A 100+ Score On The TOEFL Exam!From EverandTOEFL Grammar Guide (Advanced) - 15 Advanced Grammar Rules You Must Know To Achieve A 100+ Score On The TOEFL Exam!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sophomore English Sem1 NotesDocument15 pagesSophomore English Sem1 NotesStudentHelpWW100% (2)
- Grammar PPDocument30 pagesGrammar PPNoor AlhudaNo ratings yet
- Aljerose DolorDocument6 pagesAljerose DolorJaime PandoyNo ratings yet
- Parts of A SentenceDocument7 pagesParts of A SentenceStefan JosephNo ratings yet
- Unit 3,4Document2 pagesUnit 3,4Lucija KljaićNo ratings yet
- The Comparative and The SuperlativeDocument14 pagesThe Comparative and The SuperlativeLuis MiguelNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument14 pagesEnglish Grammarkoala -No ratings yet
- Grammar GlossaryDocument12 pagesGrammar GlossaryJoacoo RodolicoNo ratings yet
- Composition Book PresentationDocument12 pagesComposition Book Presentationsarra AbidiNo ratings yet
- Sentence CorrectionDocument10 pagesSentence CorrectionsanjivsingNo ratings yet
- Linking Words-PhrasesDocument4 pagesLinking Words-PhrasessdNo ratings yet
- Clauses and PhrasesDocument13 pagesClauses and PhrasesFatïma ZohraNo ratings yet
- Phrases: Andi Darmawan 4114110020Document22 pagesPhrases: Andi Darmawan 4114110020Zulfida Fahmi AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Structure I - Pertemuan 8 - Modul 11&12 - Frida&IreneDocument23 pagesStructure I - Pertemuan 8 - Modul 11&12 - Frida&Ireneapi-234714386No ratings yet
- MahinDocument88 pagesMahinMashuk Jahir100% (1)
- 5 - Sintax (Phrase)Document9 pages5 - Sintax (Phrase)Fika OmoluNo ratings yet
- Local Media2228404664060191112Document55 pagesLocal Media2228404664060191112audreyedayan6No ratings yet
- Documento Sin TítuloDocument4 pagesDocumento Sin TítuloElisabethNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: Children SugarDocument2 pagesParts of Speech: Children SugarRicardo CezarNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence PatternsDocument15 pagesBasic Sentence PatternsKRISTER ANN JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence PatternsDocument15 pagesBasic Sentence PatternsJamie JimenezNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence PatternsDocument15 pagesBasic Sentence PatternsKRISTER ANN JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Grammar in ContextDocument36 pagesWeek 9 Grammar in ContextAina MasriNo ratings yet
- Terms Parts of Speech: Alabama, Clarinet, Satisfaction, Socialism)Document6 pagesTerms Parts of Speech: Alabama, Clarinet, Satisfaction, Socialism)Deepak SarhochNo ratings yet
- BAS AARTS (Resumen)Document4 pagesBAS AARTS (Resumen)Agustina Alonso AlbianoNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Verb Prepositional Verb Verb + Adverbial Particle Verb + PrepDocument8 pagesPhrasal Verb Prepositional Verb Verb + Adverbial Particle Verb + PrepNhư QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- The Phrase: By: Nurul Maghfirah PBI 02Document12 pagesThe Phrase: By: Nurul Maghfirah PBI 02nurulNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: by Trisha PatelDocument75 pagesEnglish Grammar: by Trisha PatelPaulina Wanyes100% (1)
- InglesDocument11 pagesInglesSolilisunNo ratings yet
- Grammar Period 7Document4 pagesGrammar Period 7haroldNo ratings yet
- GrammaireDocument15 pagesGrammaireYun LaraNo ratings yet
- OxfordDocument129 pagesOxfords1049447No ratings yet
- English 1010Document1 pageEnglish 1010onewayticketNo ratings yet
- Multi - Word VerbsDocument7 pagesMulti - Word VerbsMagdalenaOgielloNo ratings yet
- 7-Phrase & ClauseDocument26 pages7-Phrase & ClauseMalik DaniyalNo ratings yet
- 14 GrammarDocument89 pages14 GrammarLiu InnNo ratings yet
- English Discoveries StudyDocument383 pagesEnglish Discoveries StudyDANIEL SANCHEZ GARCIANo ratings yet
- Syntaxandothers 1Document11 pagesSyntaxandothers 1shadowhunter022No ratings yet
- The Gerund PhraseDocument3 pagesThe Gerund PhraseDidin MuhidinNo ratings yet
- Eng 2Document4 pagesEng 2Shana PerezNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - VerbDocument26 pagesGroup 3 - VerbErssaanNo ratings yet
- Clause Elements Is A Word/phrase/clause That Fulfills A Syntactic Functions in A Clause or A SentenceDocument1 pageClause Elements Is A Word/phrase/clause That Fulfills A Syntactic Functions in A Clause or A SentenceKhuteibe HashimNo ratings yet
- VerbalsDocument33 pagesVerbalsBaconHairArmyDude - RobloxNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Lessons: Introduction To Sentence StructureDocument26 pagesEnglish Grammar Lessons: Introduction To Sentence StructurecelesteNo ratings yet
- English 10 Parts of Speech Flashcards - Quizlet PDFDocument6 pagesEnglish 10 Parts of Speech Flashcards - Quizlet PDFJustice MervilleNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Content (Open Class) Function (Closed Class)Document4 pagesEnglish Grammar: Content (Open Class) Function (Closed Class)MarienNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Angelica Yan M. 216 4234Document5 pagesEnglish Grammar: Angelica Yan M. 216 4234anyi porfirioNo ratings yet
- English Guide 1Document38 pagesEnglish Guide 1norelkys sanchezNo ratings yet
- Basic English GrammerDocument5 pagesBasic English GrammerhashcedarNo ratings yet
- Course03 Linking Words: 1.liking Words - Result FunctionDocument4 pagesCourse03 Linking Words: 1.liking Words - Result Functionaya rezaiguiaNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Grammar: Read and Make A Summary of Your LearningDocument10 pagesUnit I - Grammar: Read and Make A Summary of Your LearningMariangel PerezNo ratings yet
- Pre - Intermediate: Countable/ UncountableDocument4 pagesPre - Intermediate: Countable/ UncountableAndrea Espinoza YbazetaNo ratings yet
- Sentence: English Grammar Notes PDFDocument37 pagesSentence: English Grammar Notes PDFRANDOM VIDEOS 03No ratings yet
- Phrase Vs ClauseDocument46 pagesPhrase Vs ClauserizkiNo ratings yet
- Sentences and Questions ExplainedDocument3 pagesSentences and Questions ExplainedMelissa OmlNo ratings yet
- TKT GlossaryDocument30 pagesTKT Glossaryerischolar2003No ratings yet
- Overview of Sentence StructureDocument4 pagesOverview of Sentence StructureM MNo ratings yet
- Sight Words 4th Grade Workbook (Baby Professor Learning Books)From EverandSight Words 4th Grade Workbook (Baby Professor Learning Books)No ratings yet
- Reported Speech With Gerund InfinitiveDocument6 pagesReported Speech With Gerund InfinitiveTruong Huynh Minh Thu B2111345No ratings yet
- Intensifiers PDFDocument3 pagesIntensifiers PDFkasuri123No ratings yet
- Unit-1: Nouns Content StructureDocument4 pagesUnit-1: Nouns Content StructureManchia ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- 13 Test Revision 1 - Imperatives, Infintives and VerbsDocument1 page13 Test Revision 1 - Imperatives, Infintives and Verbssc2gjm4j6pNo ratings yet
- Pigamow A - Iňlis Diliniň Amaly grammatikasy-2010'TDMIDocument83 pagesPigamow A - Iňlis Diliniň Amaly grammatikasy-2010'TDMIМенгли МередоваNo ratings yet
- Introductory Question Tags Interactive WorksheetDocument2 pagesIntroductory Question Tags Interactive WorksheetAndrea Sofía Guasca DuránNo ratings yet
- Proper Nouns and Common NounsDocument4 pagesProper Nouns and Common NounsLhaz OrganizerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Infin. and Gerund As Subject and PredicativeDocument9 pagesLecture Infin. and Gerund As Subject and Predicativevprotsenko16No ratings yet
- LEVEL 3c Cambio A 4Document110 pagesLEVEL 3c Cambio A 4Tania CuevasNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument87 pagesEnglish GrammarNori LofindieNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument1 pageTensesharis ilyasNo ratings yet
- Unit-02 TenseDocument18 pagesUnit-02 TenseJahid UllahNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - Self IntroductionDocument15 pagesChapter I - Self IntroductionPutri AristaNo ratings yet
- 01 01 Gopal Parts of SpeechDocument8 pages01 01 Gopal Parts of SpeechRadha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- A Infinitive (Verb 1/ V1) Past Tense (Verb 2/ V2) Past Participle (Verb 3/ V3) ArtiDocument9 pagesA Infinitive (Verb 1/ V1) Past Tense (Verb 2/ V2) Past Participle (Verb 3/ V3) ArtiRezky IndraNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of Speech in EnglishDocument67 pages8 Parts of Speech in Englishtatjanagrujic100% (1)
- Demonstrative, Interrogative, Indefinite, and Relative PronounsDocument9 pagesDemonstrative, Interrogative, Indefinite, and Relative PronounsIavan AlbanoNo ratings yet
- Transitive and Intransitive Verbs: Pay Attention To Particles!Document2 pagesTransitive and Intransitive Verbs: Pay Attention To Particles!eulea larkaroNo ratings yet
- Inglés IDocument78 pagesInglés IAriana M.RNo ratings yet
- PartsofspeechwebquestDocument6 pagesPartsofspeechwebquestapi-282034340100% (1)
- Voice - MeherabDocument13 pagesVoice - MeherabMd. Meherab HossenNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Advanced English Grammar 1St Edition Wendy Wilson PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Advanced English Grammar 1St Edition Wendy Wilson PDFmargarito.phillips676100% (5)
- Junior Two GrammarDocument29 pagesJunior Two GrammarRashid KhanNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Passive VoiceDocument10 pagesFunctions of The Passive VoicevalentinNo ratings yet
- Tabel Error RecognitionDocument4 pagesTabel Error RecognitionNurPiter ThiodorisNo ratings yet
- Colégio Estadual Professora Antonieta Palmeira Ensino MédioDocument8 pagesColégio Estadual Professora Antonieta Palmeira Ensino MédioKarine LimaNo ratings yet
- PossessiveDocument2 pagesPossessiveakashdalwadiNo ratings yet
- STR1 PDFDocument42 pagesSTR1 PDFAjay Chander RNo ratings yet
- Antologia 4° Sem 2024Document64 pagesAntologia 4° Sem 2024Luis Padua DomínguezNo ratings yet