Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chorda Tympani..
Chorda Tympani..
Uploaded by
Sheeba NoorOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chorda Tympani..
Chorda Tympani..
Uploaded by
Sheeba NoorCopyright:
Available Formats
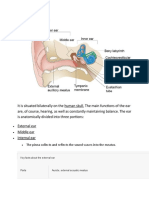
Chorda tympani From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Nerve: Chorda tympani
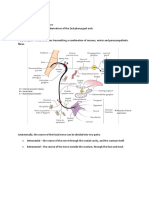
The right membrana tympani with the hammer and the chorda tympani, viewed from within, from behind, and from above. Gray'ssubject #231 1047 From facial nerve MeSH Chorda+Tympani+Nerve The chorda tympani is a nerve that branches from the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) inside the facial canal, just before the facial nerve exits the skull via the Stylomastoid foramen. It serves the taste buds in the front of the tongue, runs through the middle ear, and carries taste messages to the brain. The chorda tympani is part of one of three cranial nerves that are involved in taste. The taste system involves a complicated feedback loop, with each nerve acting to inhibit the signals of other nerves. The chorda tympani appears to exert a particularly strong inhibitory influence on other taste nerves, as well as on pain fibers in the tongue. When the chorda tympani is damaged, its inhibitory function is disrupted, leading to less inhibited activity in the other nerves. Contents [hide] 1 Nerve fibers 2 Path 3 Additional images 4 References and notes 5 External links [edit]Nerfibers
The chorda tympani carries two types of nerve fibers from their origin with the facial nerve to the lingual nerve that carries them to their destinations: Special sensory fibers providing taste sensation from the anterior two-thirds
of the tongue. Presynaptic parasympathetic fibers to the submandibular ganglion, providing secretomotor innervation to two salivary glands: the submandibular gland and sublingual gland and to the vessels of the tongue, which when stimulated, cause a dilatation of blood vessels of the tongue. [edit]Pathfibers
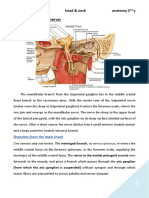
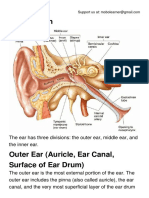
Enters the skull through the internal acoustic meatus as part of the facial nerve, then it travels through the middle ear, where it runs from posterior to anterior across the tympanic membrane. It passes between the malleus and the incus, on the medial surface of the neck of the malleus. The nerve continues through the petrotympanic fissure, after which it emerges from the skull into the infratemporal fossa. It soon combines with the larger lingual nerve, a branch of the mandibular nerve The fibers of the chorda tympani travel with the lingual nerve to the submandibular ganglion. Here, the preganglionic fibers of the chorda tympani synapse with postganglionic fibers which go on to innervate the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Special sensory (taste) fibers also extend from the chorda tympani to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue via the lingual nerve. [edit]Additional imageshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Striae_medullares chorda tympani nerve (kord timpn), n a nerve branch of the facial nerve that passes through the tympanic cavity to join the lingual branch of the mandibular nerve; it conveys taste sensation from the anterior two thirds of the tongue and carries parasympathetic preganglionic fibers to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.
Chondrosarcoma. Mosby's Dental Dictionary, 2nd edition. 2008 Elsevier, Inc. All righ
You might also like
- Cranial Nerves Important To SpeechDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves Important To SpeechMike SwiesNo ratings yet
- Gu LJMDocument2 pagesGu LJMJery JsNo ratings yet
- Lect11-Facial Nerve (CNVII)Document17 pagesLect11-Facial Nerve (CNVII)Nayela AkramNo ratings yet
- The Facial Nerve NotesDocument5 pagesThe Facial Nerve NotesSimphiwe CebisaNo ratings yet
- Os 3Document11 pagesOs 3مرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Mandibular NerveDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy Mandibular Nerveمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument2 pagesTrigeminal NerveVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 AnatomyDocument14 pagesLecture 3 AnatomyZA IDNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs - EarsDocument37 pagesSensory Organs - Earsapi-324160601No ratings yet
- Salivary Glands & PharynxDocument8 pagesSalivary Glands & Pharynxزين العابدين محمد عويشNo ratings yet
- Human Function AnatomyDocument8 pagesHuman Function AnatomyaishbiyaNo ratings yet
- The Ear: Head & Neck Unit - مسعسلا ليلج رديح .دDocument20 pagesThe Ear: Head & Neck Unit - مسعسلا ليلج رديح .دStevanovic StojaNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument74 pagesTrigeminal NerveSanat KhanapuriNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve VDocument4 pagesTrigeminal Nerve Vm1m2mNo ratings yet
- Mandibular NerveDocument6 pagesMandibular NerveCatalina Stoicescu100% (1)
- 8 Mandibular NerveDocument6 pages8 Mandibular NerveAaaNo ratings yet
- Underlying Blood Vessels: Innervation Trigeminal Maxillary NervesDocument4 pagesUnderlying Blood Vessels: Innervation Trigeminal Maxillary NervesbangpatuiNo ratings yet
- Telinga LuarDocument3 pagesTelinga LuarMarco fransNo ratings yet
- The Facial NerveDocument6 pagesThe Facial NerveRahul Raj SNo ratings yet
- Physiology Aspect of The Special SensesDocument31 pagesPhysiology Aspect of The Special SensesDaniel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Presentation ScriptDocument2 pagesAnatomy Presentation ScriptMikey ZhitnitskyNo ratings yet
- The Glossopharyngeal Nerve (N. Glossopharyngeus Ninth Nerve)Document15 pagesThe Glossopharyngeal Nerve (N. Glossopharyngeus Ninth Nerve)viorel79No ratings yet
- Mandibular Nerve, Chorda Tympani Nerve, Otic GanglionDocument33 pagesMandibular Nerve, Chorda Tympani Nerve, Otic Ganglionwaniya irumNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument33 pagesAnatomy of The EarRichard HadinataNo ratings yet
- The EarDocument13 pagesThe EarOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- The Pharynx and LarynxDocument18 pagesThe Pharynx and Larynxrusseljay1216No ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument126 pagesTrigeminal NerveAsha Praveena100% (4)
- InfraTemporal FossaDocument34 pagesInfraTemporal FossaAhmed JawdetNo ratings yet
- Fracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Document67 pagesFracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Arafat Masud NiloyNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiAlexAlxNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument63 pagesMuscles of Facial Expressionraphaelyohana140No ratings yet
- NervesDocument16 pagesNervesDerahNo ratings yet
- L3 Infratemporal RegionDocument29 pagesL3 Infratemporal RegionMohammad HilmiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy EarDocument20 pagesAnatomy EarRod HilalNo ratings yet
- Patients With Ruptured or Absent Tympanic Membranes Have Extreme Difficulty in Hearing, and Possibly Even Complete Hearing LossDocument3 pagesPatients With Ruptured or Absent Tympanic Membranes Have Extreme Difficulty in Hearing, and Possibly Even Complete Hearing LossminaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology THT - Dr. AriefDocument88 pagesAnatomy and Physiology THT - Dr. AriefGilbert Sterling OctaviusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The EarDarkAngelNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve.. EditedDocument61 pagesFacial Nerve.. EditedmfaisalzargarNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 Slide 2 Lingual NerveDocument1 pageSlide 1 Slide 2 Lingual NerveBogdan Robert CNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument17 pagesAnatomy of Earkresha solankiNo ratings yet
- The Ear (DR Anani)Document28 pagesThe Ear (DR Anani)blissjames249No ratings yet
- Special Senses (EAR) : Sumera AfzalDocument74 pagesSpecial Senses (EAR) : Sumera AfzalAmbreen GhafoorNo ratings yet
- The MouthDocument23 pagesThe MouthgcamaymayanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesNuardi YusufNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument48 pagesTrigeminal NervebhalaashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Are Twelve Pairs of Nerves That Exit The Brain and The BrainstemDocument5 pagesCranial Nerves Are Twelve Pairs of Nerves That Exit The Brain and The BrainstemFarena LazimNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Auriculotemporal Nerve: SupplyDocument1 pageAuriculotemporal Nerve: SupplyBogdan Robert CNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Trigeminal NerveDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Trigeminal NerveNicky RomeoNo ratings yet
- Vagus Cranial NerveDocument6 pagesVagus Cranial NervedimiNo ratings yet
- Glossopharyngeal NerveDocument8 pagesGlossopharyngeal NerveGEORGE MATHIASNo ratings yet
- Parotid GlandDocument2 pagesParotid Glandneleh grayNo ratings yet
- Nerves of The NeckDocument47 pagesNerves of The NeckAbrar SabawiNo ratings yet
- 8 The Special SensesDocument7 pages8 The Special SensesSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- 10 - Anatomy of The Ear (Edited)Document26 pages10 - Anatomy of The Ear (Edited)Enlighten usNo ratings yet
- 7 Infratemporal RegionDocument8 pages7 Infratemporal RegionNur Ain Faezah RoslanNo ratings yet
- Nervous IntermediusDocument1 pageNervous IntermediusGhaly AmirNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity Salivary GlandsDocument36 pagesOral Cavity Salivary GlandsSaifNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear PDFDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Ear PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear - Earth's LabDocument1 pageMiddle Ear - Earth's Labmfk5p77t8mNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ento 131Document61 pagesEnto 131Donbor Shisha PohsngapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Textile IndustryDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Textile IndustryAlice ChepkuruiNo ratings yet
- 0653 Combined ScienceDocument131 pages0653 Combined ScienceGodfrey RugareNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsDocument302 pagesRecent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsPedro CastroNo ratings yet
- Mirjam Van Weissenbruch - Neonatal HypoglycaemiaDocument57 pagesMirjam Van Weissenbruch - Neonatal Hypoglycaemiabenny christantoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chiral or Optical IsomersDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Chiral or Optical IsomersSeepana Dayakar100% (1)
- Atrial FlutterDocument2 pagesAtrial FlutterDhiaNo ratings yet
- Stanislas Dehaene Le Code La Conscience PDF 5Document21 pagesStanislas Dehaene Le Code La Conscience PDF 5geroimoNo ratings yet
- H3 Lab Report Wu YanlongDocument8 pagesH3 Lab Report Wu YanlongLuke Alan SkaiwalkerNo ratings yet
- Minutes of EC Metting of SBTC Held On 05.04.11Document7 pagesMinutes of EC Metting of SBTC Held On 05.04.11Ram Mohan SNo ratings yet
- Pampas Cat GroupDocument36 pagesPampas Cat GrouppristidactylusNo ratings yet
- Protein Lab ReportDocument9 pagesProtein Lab ReportAxelBlomNo ratings yet
- GayaHidup August 2010Document32 pagesGayaHidup August 2010Elena Doina CristacheNo ratings yet
- BIO 160 SyllabusDocument15 pagesBIO 160 SyllabusjoanneoellersNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument10 pagesWorksheetMomay RojalesNo ratings yet
- Initial and Annual Medical Examination FormDocument2 pagesInitial and Annual Medical Examination Formsonny7220No ratings yet
- STEMI Algorithm Poster 18x24Document1 pageSTEMI Algorithm Poster 18x24OgizWaraNo ratings yet
- Neutrophils in DiseaseDocument16 pagesNeutrophils in DiseaseAbhishaik SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 Handling Common Problems Pitfalls Pravit Edited DemoDocument5 pages4 Handling Common Problems Pitfalls Pravit Edited DemoBambang DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Al Esraa GroupDocument9 pagesAnatomy: Al Esraa Groupوحش الصاعقهNo ratings yet
- STUDY OF BODY'S ENERGY CHANGES IN NON-TOUCH ENERGY HEALING 1. PRANIC HEALING PROTOCOL APPLIED FOR A BREAST CANCER SUBJECT Koji TsuchiyaDocument16 pagesSTUDY OF BODY'S ENERGY CHANGES IN NON-TOUCH ENERGY HEALING 1. PRANIC HEALING PROTOCOL APPLIED FOR A BREAST CANCER SUBJECT Koji TsuchiyaCambiador de MundoNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: Epithelium EpitheliumDocument87 pagesConnective Tissue: Epithelium EpitheliumDo Van TienNo ratings yet
- Intro 70Document75 pagesIntro 70bockoneNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of RhinoplastyDocument21 pagesBasic Principles of Rhinoplastydrbantm100% (2)
- Metabolic SyndromeDocument9 pagesMetabolic SyndromeThomasManuelWasuwayNo ratings yet
- Patho DiagramDocument4 pagesPatho DiagramNielArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Techniques of Internal Fixation of FracturesDocument56 pagesBasic Principles and Techniques of Internal Fixation of FracturesRudi haris munandarNo ratings yet
- SpermatogenesisDocument31 pagesSpermatogenesiselzenyNo ratings yet
- Resistant Hypertension. AHADocument38 pagesResistant Hypertension. AHAEderEmmanuelMartinezRuiz100% (1)