Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transistor
Transistor
Uploaded by
Summer WangCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Transistors and Logic GatesDocument17 pagesTransistors and Logic GatesJef SotisNo ratings yet
- TransisterDocument10 pagesTransisterart101988No ratings yet
- TransistorDocument15 pagesTransistorAshvini SugaNo ratings yet
- What Is A TransistorDocument5 pagesWhat Is A TransistorSOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Transistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?Document7 pagesTransistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?study buddyNo ratings yet
- IP 4 TransistorDocument3 pagesIP 4 TransistorRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument22 pagesTransistorRahul DevNo ratings yet
- Transistor As A SwitchDocument5 pagesTransistor As A SwitchGeorge NGNo ratings yet
- NAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorDocument3 pagesNAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorChoiril AthoNo ratings yet
- Introduction TransistorsDocument20 pagesIntroduction Transistorsshahzaib.hasnainNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Aeronaves y LaboratorioDocument5 pagesTransistor: Aeronaves y LaboratorioAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2Document16 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2leon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesBipolar TransistorAndrei Josef NizaNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TransistorsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Transistorsdivya jessiNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Transistors: DiscussionDocument9 pagesTopic 3 Transistors: DiscussionEnitsuj Eam EugarbalNo ratings yet
- Clap SwitchDocument19 pagesClap SwitchNithin Peter80% (5)
- Transistor: Transistor As A SwitchDocument12 pagesTransistor: Transistor As A SwitchBharat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electronic EngeeniringDocument11 pagesElectronic EngeeniringMuataz ZyadaNo ratings yet
- Example of TransistorsDocument12 pagesExample of TransistorslathageethaNo ratings yet
- AbebeDocument25 pagesAbebeAnteneh AbebeNo ratings yet
- Adio's Elect Term PaperDocument13 pagesAdio's Elect Term PaperAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorXhaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXDocument17 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXleon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Transistor&IcDocument66 pagesTransistor&IcmythonyNo ratings yet
- The Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesThe Bipolar TransistorMohammed MushfiqurNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument25 pagesTransistorAdnan Hyder SoomroNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 7: Transistor Characteristics and Its Application As A SwitchDocument3 pagesLab Experiment # 7: Transistor Characteristics and Its Application As A SwitchSaad khanNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument3 pagesTransistorsSohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Musical Siren Lab Project ReportDocument8 pagesMusical Siren Lab Project ReportMahipal_Singh_Deora100% (3)
- Explain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesExplain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsS Dispiser100% (1)
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsAkshay DhandaNo ratings yet
- NextechDocument15 pagesNextechNEXTECH ElectroicsNo ratings yet
- Transistor: by P.Sai SrivathsaDocument15 pagesTransistor: by P.Sai Srivathsak.saikumarNo ratings yet
- L4 Basic-ElectronicsDocument16 pagesL4 Basic-Electronicstheo dominic silvosaNo ratings yet
- For Other UsesDocument11 pagesFor Other Usesashishsharma_1432No ratings yet
- BEC Notes Lecture 11 by Ur Engineering FriendDocument5 pagesBEC Notes Lecture 11 by Ur Engineering FriendsupNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Document8 pagesTransistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Fariz Aditya PutraNo ratings yet
- Transistors Project For IscDocument37 pagesTransistors Project For Iscsandip biswas100% (1)
- What Is A Transistor Circuit Diagram and How Does It WorkDocument10 pagesWhat Is A Transistor Circuit Diagram and How Does It WorkjackNo ratings yet
- LT3A - 06 - Ayu Novita Anggraeni - English Script Topic 4 (AC Transistor)Document5 pagesLT3A - 06 - Ayu Novita Anggraeni - English Script Topic 4 (AC Transistor)Ayu Novita AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Final Project: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsDocument4 pagesBasic Electronics Final Project: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- Electronics by TakDocument7 pagesElectronics by Taktak2020No ratings yet
- Transistor: How Does It Work - NPN & PNPDocument5 pagesTransistor: How Does It Work - NPN & PNPadeelNo ratings yet
- EEE 202 Lecture Note On TransistorDocument7 pagesEEE 202 Lecture Note On Transistoralexapierre08No ratings yet
- TRANSISTORDocument60 pagesTRANSISTORNaty SeyoumNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsDocument103 pagesIntroduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsArinaitwe IvanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DevicesDocument35 pagesSemiconductor DevicesRacknarockNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Transistor)Document6 pagesAppendix 1 Transistor)Achik SniperNo ratings yet
- Task 7Document3 pagesTask 7Nesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- Ewp 5Document12 pagesEwp 5Aakansha PaunikarNo ratings yet
- MODULE5 - Transistor ApplicationDocument21 pagesMODULE5 - Transistor Applicationgreensun_auwrciScribdDBNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsnaidooriNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument7 pagesTransistorsericoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Introduction BJTDocument3 pages2.1 Introduction BJTlizhi0007No ratings yet
- Communication With Laser BeamDocument17 pagesCommunication With Laser BeamJagruti MulayNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument11 pagesBJTVam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- Transistors TutorialDocument92 pagesTransistors TutorialAmit Raj100% (18)
Transistor
Transistor
Uploaded by
Summer WangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transistor
Transistor
Uploaded by
Summer WangCopyright:
Available Formats
Transistor (William Shockley) A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power.
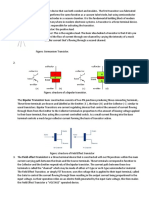
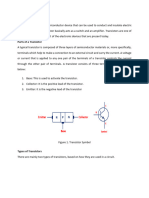
It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current flowing through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be much more than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. Following its release in the early 1950s the transistor revolutionized the field of electronics, and paved the way for smaller and cheaper radios, calculators, and computers, among other things. Importance The transistor is the key active component in practically all modern electronics. Many consider it to be one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century. Its importance in today's society rests on its ability to be mass produced using a highly automated process (semiconductor device fabrication) that achieves astonishingly low per-transistor costs. The invention of the first transistor at Bell Labs was named an IEEE Milestone in 2009. The transistor's low cost, flexibility, and reliability have made it a ubiquitous device. Transistorized mechatronic circuits have replaced electromechanical devices in controlling appliances and machinery. It is often easier and cheaper to use a standard microcontroller and write a computer program to carry out a control function than to design an equivalent mechanical control function. Types of transistors NPN and PNP are the two types of standard transistors, each having different circuit symbols. The letters used in these descriptions are references to what material is used to create these devices. NPN is the most commonly used because they are easily made silicon. A Darlington pair describes a connection of two transistors paired for the purpose of emitting a very high current gain. The PNP Transistor could be considered the reverse opposite of the NPN Transistor. This Transistor employs the two diodes are reversed with respect to the NPN. This type give a Positive-Negative-Positive configuration, which also defines the Emitter terminal. An additional type of transistor is the field-effect transistor, usually referred to as FETs. Simplified operation The essential usefulness of a transistor comes from its ability to use a small signal applied between one pair of its terminals to control a much larger signal at another pair of terminals. This property is called gain. A transistor can control its output in proportion to the input signal; that is, it can act as an amplifier. Alternatively, the transistor can be used to turn current on or off in a circuit as an electrically controlled switch, where the amount of current is determined by other circuit elements. There are two types of transistors, which have slight differences in how they are used in a circuit. A bipolar transistor has terminals labeled base, collector, and emitter. A small current at the base terminal (that is, flowing from the base to the emitter) can control or switch a much larger current between the collector and emitter terminals. For a field-effect transistor, the terminals are labeled gate, source, and drain, and a voltage at the gate can control a current between source and drain. The image to the right represents a typical bipolar transistor in a circuit. Charge will flow between emitter and collector terminals depending on the current in the base. Since internally the base and emitter connections behave like a semiconductor diode, a voltage drop develops between base and emitter while the base current exists. The amount of this voltage depends on the material the transistor is made from, and is referred to as VBE.
You might also like
- Transistors and Logic GatesDocument17 pagesTransistors and Logic GatesJef SotisNo ratings yet
- TransisterDocument10 pagesTransisterart101988No ratings yet
- TransistorDocument15 pagesTransistorAshvini SugaNo ratings yet
- What Is A TransistorDocument5 pagesWhat Is A TransistorSOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Transistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?Document7 pagesTransistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?study buddyNo ratings yet
- IP 4 TransistorDocument3 pagesIP 4 TransistorRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument22 pagesTransistorRahul DevNo ratings yet
- Transistor As A SwitchDocument5 pagesTransistor As A SwitchGeorge NGNo ratings yet
- NAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorDocument3 pagesNAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorChoiril AthoNo ratings yet
- Introduction TransistorsDocument20 pagesIntroduction Transistorsshahzaib.hasnainNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Aeronaves y LaboratorioDocument5 pagesTransistor: Aeronaves y LaboratorioAngel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2Document16 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2leon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesBipolar TransistorAndrei Josef NizaNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TransistorsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Transistorsdivya jessiNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Transistors: DiscussionDocument9 pagesTopic 3 Transistors: DiscussionEnitsuj Eam EugarbalNo ratings yet
- Clap SwitchDocument19 pagesClap SwitchNithin Peter80% (5)
- Transistor: Transistor As A SwitchDocument12 pagesTransistor: Transistor As A SwitchBharat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electronic EngeeniringDocument11 pagesElectronic EngeeniringMuataz ZyadaNo ratings yet
- Example of TransistorsDocument12 pagesExample of TransistorslathageethaNo ratings yet
- AbebeDocument25 pagesAbebeAnteneh AbebeNo ratings yet
- Adio's Elect Term PaperDocument13 pagesAdio's Elect Term PaperAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorXhaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXDocument17 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXleon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Transistor&IcDocument66 pagesTransistor&IcmythonyNo ratings yet
- The Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesThe Bipolar TransistorMohammed MushfiqurNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument25 pagesTransistorAdnan Hyder SoomroNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 7: Transistor Characteristics and Its Application As A SwitchDocument3 pagesLab Experiment # 7: Transistor Characteristics and Its Application As A SwitchSaad khanNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument3 pagesTransistorsSohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Musical Siren Lab Project ReportDocument8 pagesMusical Siren Lab Project ReportMahipal_Singh_Deora100% (3)
- Explain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesExplain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsS Dispiser100% (1)
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsAkshay DhandaNo ratings yet
- NextechDocument15 pagesNextechNEXTECH ElectroicsNo ratings yet
- Transistor: by P.Sai SrivathsaDocument15 pagesTransistor: by P.Sai Srivathsak.saikumarNo ratings yet
- L4 Basic-ElectronicsDocument16 pagesL4 Basic-Electronicstheo dominic silvosaNo ratings yet
- For Other UsesDocument11 pagesFor Other Usesashishsharma_1432No ratings yet
- BEC Notes Lecture 11 by Ur Engineering FriendDocument5 pagesBEC Notes Lecture 11 by Ur Engineering FriendsupNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Document8 pagesTransistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Fariz Aditya PutraNo ratings yet
- Transistors Project For IscDocument37 pagesTransistors Project For Iscsandip biswas100% (1)
- What Is A Transistor Circuit Diagram and How Does It WorkDocument10 pagesWhat Is A Transistor Circuit Diagram and How Does It WorkjackNo ratings yet
- LT3A - 06 - Ayu Novita Anggraeni - English Script Topic 4 (AC Transistor)Document5 pagesLT3A - 06 - Ayu Novita Anggraeni - English Script Topic 4 (AC Transistor)Ayu Novita AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Final Project: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsDocument4 pagesBasic Electronics Final Project: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- Electronics by TakDocument7 pagesElectronics by Taktak2020No ratings yet
- Transistor: How Does It Work - NPN & PNPDocument5 pagesTransistor: How Does It Work - NPN & PNPadeelNo ratings yet
- EEE 202 Lecture Note On TransistorDocument7 pagesEEE 202 Lecture Note On Transistoralexapierre08No ratings yet
- TRANSISTORDocument60 pagesTRANSISTORNaty SeyoumNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsDocument103 pagesIntroduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsArinaitwe IvanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DevicesDocument35 pagesSemiconductor DevicesRacknarockNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Transistor)Document6 pagesAppendix 1 Transistor)Achik SniperNo ratings yet
- Task 7Document3 pagesTask 7Nesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- Ewp 5Document12 pagesEwp 5Aakansha PaunikarNo ratings yet
- MODULE5 - Transistor ApplicationDocument21 pagesMODULE5 - Transistor Applicationgreensun_auwrciScribdDBNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsnaidooriNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument7 pagesTransistorsericoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Introduction BJTDocument3 pages2.1 Introduction BJTlizhi0007No ratings yet
- Communication With Laser BeamDocument17 pagesCommunication With Laser BeamJagruti MulayNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument11 pagesBJTVam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- Transistors TutorialDocument92 pagesTransistors TutorialAmit Raj100% (18)