Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Example of Gomory's Cutting Plane Method: X X X X X X
Example of Gomory's Cutting Plane Method: X X X X X X
Uploaded by
Suganya SivaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Calculus of A Single Variable 8th Edition: Chapter 2 Answer KeyDocument96 pagesCalculus of A Single Variable 8th Edition: Chapter 2 Answer KeyAlan G.100% (2)
- Solved Simplex Problems PDFDocument5 pagesSolved Simplex Problems PDFSwati Sucharita DasNo ratings yet
- MATH39011 Mathematical Programming I SOLUTIONS To Examples 2Document4 pagesMATH39011 Mathematical Programming I SOLUTIONS To Examples 2Ng Chun HiuNo ratings yet
- MS La Mod5Document28 pagesMS La Mod5Shyme FritsNo ratings yet
- 08 Simplex 3 CDocument31 pages08 Simplex 3 CPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Elimination: × 2 MatrixDocument9 pagesGaussian Elimination: × 2 MatrixMiljan TrivicNo ratings yet
- 15.053 March 13, 2007: Duality 3Document30 pages15.053 March 13, 2007: Duality 3Ehsan SpencerNo ratings yet
- Example 3Document2 pagesExample 3Amit KankarwalNo ratings yet
- CJ - ZJ Method SimplexDocument7 pagesCJ - ZJ Method SimplexChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Simplex Method ProblemsDocument5 pagesSimplex Method Problemsirshad_ktNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document21 pagesLecture 5AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 3Document6 pagesMathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 3Ng Chun HiuNo ratings yet
- Zeros Below The Diagonal: Row I Column I I NDocument4 pagesZeros Below The Diagonal: Row I Column I I NরোদেলাদুপুরেরফুলNo ratings yet
- Modular Arithmetic and The RSA CryptosystemDocument92 pagesModular Arithmetic and The RSA CryptosystemWa Ode MuslimahNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document8 pagesCH 10Amit KankarwalNo ratings yet
- MTH 234 Exam Review 3 SolutionsDocument11 pagesMTH 234 Exam Review 3 SolutionsDonald ChurchNo ratings yet
- Step 2011 Paper 2 Question 2Document3 pagesStep 2011 Paper 2 Question 2Kyle ByrneNo ratings yet
- Thomas AlgorithmDocument3 pagesThomas AlgorithmAdithya AiyaswamiNo ratings yet
- Addition of A New ConstraintDocument22 pagesAddition of A New ConstraintPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Linear-Programming 101Document13 pagesLinear-Programming 101Rabin Bajagain.No ratings yet
- Assign 3 SolsDocument4 pagesAssign 3 SolsAvik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Simplex Method: Example 1: Maximize Z 3x + 2xDocument17 pagesSimplex Method: Example 1: Maximize Z 3x + 2xtesfaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Math SolutionsDocument7 pagesAdvanced Engineering Math Solutionsblazinlyfe42No ratings yet
- Exercice 1.2.1Document17 pagesExercice 1.2.1Amine BrahmiNo ratings yet
- Press 08Document16 pagesPress 08katodativa23No ratings yet
- Matrix Algorithms (Part 1)Document28 pagesMatrix Algorithms (Part 1)Debangan DeyNo ratings yet
- 2010 AJC Paper 1solDocument6 pages2010 AJC Paper 1solnothingtodo1992No ratings yet
- 30 2 Gaussian ElimDocument9 pages30 2 Gaussian ElimralpholicNo ratings yet
- 6 Sensitivity Analysis: 6.1 Changes in Right-Hand Side BDocument5 pages6 Sensitivity Analysis: 6.1 Changes in Right-Hand Side Bhatemakeedy1969No ratings yet
- Non-Normal Linear Programming Problem: in Case of Maximization ProblemDocument5 pagesNon-Normal Linear Programming Problem: in Case of Maximization ProblemTóth PéterNo ratings yet
- Math1314 Matrix Solutions To Linear EquationsDocument10 pagesMath1314 Matrix Solutions To Linear Equationsاحمد الشوافيNo ratings yet
- John S. Loucks: Slides Prepared byDocument42 pagesJohn S. Loucks: Slides Prepared byRokib RonyNo ratings yet
- Solution BBADocument1 pageSolution BBAShweta SinghNo ratings yet
- 11.4 Inverse Matrix: M MM M IDocument6 pages11.4 Inverse Matrix: M MM M IAli AkbarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 4Document5 pagesMathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 4Ng Chun HiuNo ratings yet
- Problem 5 Problem Set 3.4B Pages 101-102 Maximize Subject To The ConstraintsDocument30 pagesProblem 5 Problem Set 3.4B Pages 101-102 Maximize Subject To The ConstraintsPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- The Simplex Method - MaximizationDocument23 pagesThe Simplex Method - MaximizationfatinNo ratings yet
- 8 3 Gauss ElimDocument11 pages8 3 Gauss ElimajayNo ratings yet
- Gauss Elimanation MethodDocument3 pagesGauss Elimanation MethodRamzi YahyaNo ratings yet
- Solving Systems of Equations With Three VariablesDocument8 pagesSolving Systems of Equations With Three VariablesSsNo ratings yet
- Quadratic ProgrammingDocument38 pagesQuadratic ProgrammingAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Duality 2. The Dual Problem: 15.053 March 8, 2007Document50 pagesDuality 2. The Dual Problem: 15.053 March 8, 2007Ehsan SpencerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04.??: Effect of Significant Digits On Solution of Simultaneous Linear Equations?Document9 pagesChapter 04.??: Effect of Significant Digits On Solution of Simultaneous Linear Equations?oasisdesertNo ratings yet
- Advance Operations ResearchDocument255 pagesAdvance Operations Researchgoldy243usNo ratings yet
- Simplex Method: Theory at A Glance (For IES, GATE, PSU) General Linear Programming ProblemDocument12 pagesSimplex Method: Theory at A Glance (For IES, GATE, PSU) General Linear Programming Problemganesh gowthamNo ratings yet
- Duality in LPPDocument8 pagesDuality in LPPTibelchNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Solving Linear SystemDocument6 pages1.3 Solving Linear SystemCT MarNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Real Zeros of PolynomialDocument35 pages2.3 Real Zeros of PolynomialYukiC123No ratings yet
- 12 Maths CBSE Exam Papers 2015 Chennai Set 1 AnswerDocument16 pages12 Maths CBSE Exam Papers 2015 Chennai Set 1 AnswerGeeteshGuptaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Matrix Inverse: Zar97/09/03 Numerical Methods For Engineers Page 3-22Document5 pages3.2 Matrix Inverse: Zar97/09/03 Numerical Methods For Engineers Page 3-22Muhammad FirdawsNo ratings yet
- In This Presentation We Illustrate The Ideas Developed in The Previous Presentation With Two More ProblemsDocument21 pagesIn This Presentation We Illustrate The Ideas Developed in The Previous Presentation With Two More ProblemsPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming 1Document4 pagesLinear Programming 1Özlem YurtseverNo ratings yet
- GaussElim PDFDocument15 pagesGaussElim PDFMuhammad Tariq SadiqNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionetome05No ratings yet
- Indr262LectureNotes 8-DualSimplexDocument4 pagesIndr262LectureNotes 8-DualSimplexHotatmoon HGNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Consolidated List of Scrips - Blocked-Allowed by RMSDocument55 pagesConsolidated List of Scrips - Blocked-Allowed by RMSSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- Match The Poems With The PoetsDocument4 pagesMatch The Poems With The PoetsSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- Current Affirs Question SeptDocument84 pagesCurrent Affirs Question SeptSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- Ad Technical Faculty OctDocument4 pagesAd Technical Faculty OctSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- 8th Social Science Question Paper 2015 - 2016Document5 pages8th Social Science Question Paper 2015 - 2016Suganya Siva100% (1)
- Of November - Time of Day - in The Morning/ in The Evening Except Night - Year - in 2006 - After A Certain Period of Time - in An HourDocument1 pageOf November - Time of Day - in The Morning/ in The Evening Except Night - Year - in 2006 - After A Certain Period of Time - in An HourSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Thiyalnayaki 010118 Sid No Name: Dr.M.Balamurugan - MD (Path) ., S.Sampathkumar - MSC Mlt.,Mba.Document1 pageMrs. Thiyalnayaki 010118 Sid No Name: Dr.M.Balamurugan - MD (Path) ., S.Sampathkumar - MSC Mlt.,Mba.Suganya SivaNo ratings yet
Example of Gomory's Cutting Plane Method: X X X X X X
Example of Gomory's Cutting Plane Method: X X X X X X
Uploaded by
Suganya SivaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Example of Gomory's Cutting Plane Method: X X X X X X
Example of Gomory's Cutting Plane Method: X X X X X X
Uploaded by
Suganya SivaCopyright:
Available Formats
Gomorys Cutting Plane Method
Page 1 of 3
Example of Gomorys Cutting Plane Method
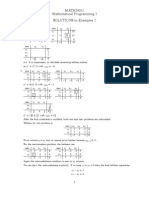
Consider the linear program
min 2x 1 + 15x 2 + 18x 3
Subject to
-x 1 + 2x 2 - 6x 3 -10 x 2 + 2x 3 6 2x 1 + 10x 3 19 -x 1 + x 2 -2 x 1, x 2, x 3 0
We can solve this problem the dual simplex method algorithm. The final tableau is as follows: x1 x1 z2 x3 z4 1 0 0 0 0 x2 10 5 2 11 31 x3 0 0 1 0 0 z1 5 2 1 5 8 z2 0 1 0 0 0 z3 3 1 3 3 z4 0 0 0 1 0 7 5 5 23
Which corresponds to the solution
x1 = 7 x2 = 0 x3 =
1 2
Objective function = 23
Now, imagine that we need x1, x2 and x3 to be integers. The third row reads
-2x 2 + x 3 - z 1 - 1 z 3 = 1 2 2 1 -2x 2 + x 3 - z 1 - 2 z 3 1 2 1 -2x 2 + x 3 - z 1 - z 3 2
If all the variables are integers, we also have that
1 -2x 2 + x 3 - z 1 - z 3 2 -2x 2 + x 3 - z 1 - z 3 0
We can add this new inequality to our tableau in the form
-2x 2 + x 3 - z 1 - z 3 + z 5 = 0
Daniel Guetta, 2010
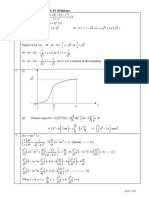
Gomorys Cutting Plane Method Inserting this inequality into our tableau, we obtain x1 x1 z2 x3 z4 z5 1 0 0 0 0 0 x2 10 5 2 11 2 31 x3 0 0 1 0 1 0 z1 5 2 1 5 1 8 z2 0 1 0 0 0 0 z3 3 1 3 1 3 z4 0 0 0 1 0 0 z5 0 0 0 0 1 0
Page 2 of 3
7 5 5 0 23
The matrix in the body of the tableau is AB 1A . Thus, those columns corresponding to basis variables should give AB 1AB = I . Looking at the
highlighted basis columns above, this is clearly not the case in the x3 column. We fix this by subtracting the x3 row from the last row: x1 x1 z2 x3 z4 z5 1 0 0 0 0 0 x2 10 5 2 11 0 31 x3 0 0 1 0 0 0 z1 5 2 1 5 0 8 z2 0 1 0 0 0 0 z3 3 1 3 3 z4 0 0 0 1 0 0 z5 0 0 0 0 1 0 7 5 5 23
z5 is negative, and we therefore pivot on that row. The only column with a negative entry in that row is z3, so we pivot there. x1 x1 z2 x3 z4 z5 1 0 0 0 0 0 x2 10 5 2 11 0 31 x3 0 0 1 0 0 0 z1 5 2 1 5 0 8 z2 0 1 0 0 0 0 z3 0 0 0 0 1 0 z4 0 0 0 1 0 0 z5 6 2 1 6 2 6 4 4 1 2 1 26
Daniel Guetta, 2010
Gomorys Cutting Plane Method
Page 3 of 3
This solution is both primal and dual optimal, with only integer solution.
x1 = 4 x2 = 0 x3 = 1 Objective function = 26
Daniel Guetta, 2010
You might also like
- Calculus of A Single Variable 8th Edition: Chapter 2 Answer KeyDocument96 pagesCalculus of A Single Variable 8th Edition: Chapter 2 Answer KeyAlan G.100% (2)
- Solved Simplex Problems PDFDocument5 pagesSolved Simplex Problems PDFSwati Sucharita DasNo ratings yet
- MATH39011 Mathematical Programming I SOLUTIONS To Examples 2Document4 pagesMATH39011 Mathematical Programming I SOLUTIONS To Examples 2Ng Chun HiuNo ratings yet
- MS La Mod5Document28 pagesMS La Mod5Shyme FritsNo ratings yet
- 08 Simplex 3 CDocument31 pages08 Simplex 3 CPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Elimination: × 2 MatrixDocument9 pagesGaussian Elimination: × 2 MatrixMiljan TrivicNo ratings yet
- 15.053 March 13, 2007: Duality 3Document30 pages15.053 March 13, 2007: Duality 3Ehsan SpencerNo ratings yet
- Example 3Document2 pagesExample 3Amit KankarwalNo ratings yet
- CJ - ZJ Method SimplexDocument7 pagesCJ - ZJ Method SimplexChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Simplex Method ProblemsDocument5 pagesSimplex Method Problemsirshad_ktNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document21 pagesLecture 5AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 3Document6 pagesMathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 3Ng Chun HiuNo ratings yet
- Zeros Below The Diagonal: Row I Column I I NDocument4 pagesZeros Below The Diagonal: Row I Column I I NরোদেলাদুপুরেরফুলNo ratings yet
- Modular Arithmetic and The RSA CryptosystemDocument92 pagesModular Arithmetic and The RSA CryptosystemWa Ode MuslimahNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document8 pagesCH 10Amit KankarwalNo ratings yet
- MTH 234 Exam Review 3 SolutionsDocument11 pagesMTH 234 Exam Review 3 SolutionsDonald ChurchNo ratings yet
- Step 2011 Paper 2 Question 2Document3 pagesStep 2011 Paper 2 Question 2Kyle ByrneNo ratings yet
- Thomas AlgorithmDocument3 pagesThomas AlgorithmAdithya AiyaswamiNo ratings yet
- Addition of A New ConstraintDocument22 pagesAddition of A New ConstraintPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Linear-Programming 101Document13 pagesLinear-Programming 101Rabin Bajagain.No ratings yet
- Assign 3 SolsDocument4 pagesAssign 3 SolsAvik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Simplex Method: Example 1: Maximize Z 3x + 2xDocument17 pagesSimplex Method: Example 1: Maximize Z 3x + 2xtesfaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Math SolutionsDocument7 pagesAdvanced Engineering Math Solutionsblazinlyfe42No ratings yet
- Exercice 1.2.1Document17 pagesExercice 1.2.1Amine BrahmiNo ratings yet
- Press 08Document16 pagesPress 08katodativa23No ratings yet
- Matrix Algorithms (Part 1)Document28 pagesMatrix Algorithms (Part 1)Debangan DeyNo ratings yet
- 2010 AJC Paper 1solDocument6 pages2010 AJC Paper 1solnothingtodo1992No ratings yet
- 30 2 Gaussian ElimDocument9 pages30 2 Gaussian ElimralpholicNo ratings yet
- 6 Sensitivity Analysis: 6.1 Changes in Right-Hand Side BDocument5 pages6 Sensitivity Analysis: 6.1 Changes in Right-Hand Side Bhatemakeedy1969No ratings yet
- Non-Normal Linear Programming Problem: in Case of Maximization ProblemDocument5 pagesNon-Normal Linear Programming Problem: in Case of Maximization ProblemTóth PéterNo ratings yet
- Math1314 Matrix Solutions To Linear EquationsDocument10 pagesMath1314 Matrix Solutions To Linear Equationsاحمد الشوافيNo ratings yet
- John S. Loucks: Slides Prepared byDocument42 pagesJohn S. Loucks: Slides Prepared byRokib RonyNo ratings yet
- Solution BBADocument1 pageSolution BBAShweta SinghNo ratings yet
- 11.4 Inverse Matrix: M MM M IDocument6 pages11.4 Inverse Matrix: M MM M IAli AkbarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 4Document5 pagesMathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 4Ng Chun HiuNo ratings yet
- Problem 5 Problem Set 3.4B Pages 101-102 Maximize Subject To The ConstraintsDocument30 pagesProblem 5 Problem Set 3.4B Pages 101-102 Maximize Subject To The ConstraintsPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- The Simplex Method - MaximizationDocument23 pagesThe Simplex Method - MaximizationfatinNo ratings yet
- 8 3 Gauss ElimDocument11 pages8 3 Gauss ElimajayNo ratings yet
- Gauss Elimanation MethodDocument3 pagesGauss Elimanation MethodRamzi YahyaNo ratings yet
- Solving Systems of Equations With Three VariablesDocument8 pagesSolving Systems of Equations With Three VariablesSsNo ratings yet
- Quadratic ProgrammingDocument38 pagesQuadratic ProgrammingAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- Duality 2. The Dual Problem: 15.053 March 8, 2007Document50 pagesDuality 2. The Dual Problem: 15.053 March 8, 2007Ehsan SpencerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04.??: Effect of Significant Digits On Solution of Simultaneous Linear Equations?Document9 pagesChapter 04.??: Effect of Significant Digits On Solution of Simultaneous Linear Equations?oasisdesertNo ratings yet
- Advance Operations ResearchDocument255 pagesAdvance Operations Researchgoldy243usNo ratings yet
- Simplex Method: Theory at A Glance (For IES, GATE, PSU) General Linear Programming ProblemDocument12 pagesSimplex Method: Theory at A Glance (For IES, GATE, PSU) General Linear Programming Problemganesh gowthamNo ratings yet
- Duality in LPPDocument8 pagesDuality in LPPTibelchNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Solving Linear SystemDocument6 pages1.3 Solving Linear SystemCT MarNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Real Zeros of PolynomialDocument35 pages2.3 Real Zeros of PolynomialYukiC123No ratings yet
- 12 Maths CBSE Exam Papers 2015 Chennai Set 1 AnswerDocument16 pages12 Maths CBSE Exam Papers 2015 Chennai Set 1 AnswerGeeteshGuptaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Matrix Inverse: Zar97/09/03 Numerical Methods For Engineers Page 3-22Document5 pages3.2 Matrix Inverse: Zar97/09/03 Numerical Methods For Engineers Page 3-22Muhammad FirdawsNo ratings yet
- In This Presentation We Illustrate The Ideas Developed in The Previous Presentation With Two More ProblemsDocument21 pagesIn This Presentation We Illustrate The Ideas Developed in The Previous Presentation With Two More ProblemsPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming 1Document4 pagesLinear Programming 1Özlem YurtseverNo ratings yet
- GaussElim PDFDocument15 pagesGaussElim PDFMuhammad Tariq SadiqNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionetome05No ratings yet
- Indr262LectureNotes 8-DualSimplexDocument4 pagesIndr262LectureNotes 8-DualSimplexHotatmoon HGNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Consolidated List of Scrips - Blocked-Allowed by RMSDocument55 pagesConsolidated List of Scrips - Blocked-Allowed by RMSSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- Match The Poems With The PoetsDocument4 pagesMatch The Poems With The PoetsSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- Current Affirs Question SeptDocument84 pagesCurrent Affirs Question SeptSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- Ad Technical Faculty OctDocument4 pagesAd Technical Faculty OctSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- 8th Social Science Question Paper 2015 - 2016Document5 pages8th Social Science Question Paper 2015 - 2016Suganya Siva100% (1)
- Of November - Time of Day - in The Morning/ in The Evening Except Night - Year - in 2006 - After A Certain Period of Time - in An HourDocument1 pageOf November - Time of Day - in The Morning/ in The Evening Except Night - Year - in 2006 - After A Certain Period of Time - in An HourSuganya SivaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Thiyalnayaki 010118 Sid No Name: Dr.M.Balamurugan - MD (Path) ., S.Sampathkumar - MSC Mlt.,Mba.Document1 pageMrs. Thiyalnayaki 010118 Sid No Name: Dr.M.Balamurugan - MD (Path) ., S.Sampathkumar - MSC Mlt.,Mba.Suganya SivaNo ratings yet