Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Remaining Life of Pipeline
Remaining Life of Pipeline
Uploaded by
rathore_mbm2002Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HDD Calculation (Template)Document4 pagesHDD Calculation (Template)bebas_amarah87% (15)
- API 579 Section 5 Level 2 AssessmentDocument18 pagesAPI 579 Section 5 Level 2 AssessmentJavierSeiman100% (1)
- Retiring Wall Thickness Calculation For PipeDocument4 pagesRetiring Wall Thickness Calculation For PipeFares JawadNo ratings yet
- Api 579 PDFDocument60 pagesApi 579 PDFJavierSeiman100% (5)
- API 510 Corrosion Rate and Remaining Life CalculationsDocument2 pagesAPI 510 Corrosion Rate and Remaining Life Calculationshirenpatel_6233% (6)
- Asme b31g Calculation Eml-4Document3 pagesAsme b31g Calculation Eml-4GRANRICKY100% (4)
- Section-4 Assessment of General Metal Loss API 579 - FFSDocument69 pagesSection-4 Assessment of General Metal Loss API 579 - FFSNDTInstructor80% (5)
- API 1104 InterpretationDocument40 pagesAPI 1104 Interpretationrathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- 8.inspection CalculationDocument38 pages8.inspection CalculationAMAL VISHNUNo ratings yet
- Remaining Life of A PipelineDocument2 pagesRemaining Life of A Pipelinefaisalf100% (4)
- Asme b31g Level 2 A1Document27 pagesAsme b31g Level 2 A1finiteinjustice78% (9)
- B31 G Level 1 EvaluationDocument5 pagesB31 G Level 1 EvaluationmmNo ratings yet
- Signal FFS Software DatasheetDocument2 pagesSignal FFS Software DatasheetMirtunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Assessment As Per API 579-1ASME FFS-1 For Pressure Vessel General Metal Loss by Using FEA TechniquesDocument21 pagesLevel 3 Assessment As Per API 579-1ASME FFS-1 For Pressure Vessel General Metal Loss by Using FEA TechniquesKingston RivingtonNo ratings yet
- API 510 Spreadsheet To Calculate (Welding ScwiDocument2 pagesAPI 510 Spreadsheet To Calculate (Welding Scwibryandown100% (1)
- Retirement ThicknessDocument7 pagesRetirement ThicknessKamal UddinNo ratings yet
- RSTRENG Report - 08 - 07 - 2015 - 10 - 12 - 14Document2 pagesRSTRENG Report - 08 - 07 - 2015 - 10 - 12 - 14Mustafa Akbar100% (2)
- MAWP CalculationDocument2 pagesMAWP CalculationMuhammad Zeeshan Wasi60% (5)
- Integrity Evaluation of Small Bore Connections (Branch Connections) PDFDocument9 pagesIntegrity Evaluation of Small Bore Connections (Branch Connections) PDFHendra YudistiraNo ratings yet
- FFS, 579 - Seminar Ata, 1389Document68 pagesFFS, 579 - Seminar Ata, 1389전상문100% (3)
- Asme 31 GDocument48 pagesAsme 31 GShriram Avasarkar100% (2)
- API 579 - Fitness For Service SummaryDocument12 pagesAPI 579 - Fitness For Service SummaryJustin OnisoruNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The API Section 10Document18 pagesAn Overview of The API Section 10api-3855165100% (1)
- APPENDIX D - CORROSION RATE and REMAINING LIFE CALCULATIONDocument6 pagesAPPENDIX D - CORROSION RATE and REMAINING LIFE CALCULATIONPhornlert Wana100% (2)
- Advanced Integrity Assessment of Pipeline Dents Using ILI DataDocument27 pagesAdvanced Integrity Assessment of Pipeline Dents Using ILI DataMuhammad ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Detailed Fitness For Service Per API 579Document3 pagesDetailed Fitness For Service Per API 579Sajal KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- ASME B31.3.4.8 Wall Thickness CalculatorDocument26 pagesASME B31.3.4.8 Wall Thickness Calculatoreko123100% (1)
- Integrity Assessment of Pressure VesselDocument6 pagesIntegrity Assessment of Pressure Vesselmrb193100% (1)
- Elbow Thickness CalculatorDocument7 pagesElbow Thickness Calculatorvijayakumar2015100% (1)
- Asme API 579 SI HandoutsDocument196 pagesAsme API 579 SI Handoutsronfrend94% (17)
- API579 EXAMPLE CalculationsDocument4 pagesAPI579 EXAMPLE CalculationsJaclyn Henderson80% (5)
- Assessment of Corrosion in PipelinesDocument31 pagesAssessment of Corrosion in PipelinesRicardo Andres Santamaria Torres100% (2)
- B31GDocument3 pagesB31GHendra YudistiraNo ratings yet
- API 579 SI Handouts PDFDocument196 pagesAPI 579 SI Handouts PDFshakeelahmadjsr100% (1)
- API 579 Part 5 Local Metal LossDocument41 pagesAPI 579 Part 5 Local Metal LossAli SASSINo ratings yet
- 5 16259779815014437Document26 pages5 16259779815014437Hafizul Hisyam Maysih Luzifah100% (1)
- API 579 Section 5 Level 2 AssessmentDocument18 pagesAPI 579 Section 5 Level 2 AssessmentcutefrenzyNo ratings yet
- Boxup Clamp DesignDocument5 pagesBoxup Clamp DesignGohar ZamanNo ratings yet
- Draft Report RLA Pipeline PDFDocument47 pagesDraft Report RLA Pipeline PDFTengku Nizarul AslamiNo ratings yet
- Pipelines Defects Assements - Will Defect Fails ?Document22 pagesPipelines Defects Assements - Will Defect Fails ?api-3784571100% (4)
- Buch 15 Corrosion Under Pipe SupportsDocument8 pagesBuch 15 Corrosion Under Pipe SupportsTrajko GorgievskiNo ratings yet
- Remaining Life of A PipelineDocument38 pagesRemaining Life of A Pipelineochable100% (2)
- Corrosion Rate CalculationsDocument51 pagesCorrosion Rate CalculationsJosé Ignacio Mendieta CamargoNo ratings yet
- F.sq-p.003 Rev. 0 Procedure For Repair, Alteration, and Modification Pressure VesselDocument7 pagesF.sq-p.003 Rev. 0 Procedure For Repair, Alteration, and Modification Pressure VesselIksan Adityo MulyoNo ratings yet
- Pdam Corrosion AssessmentDocument31 pagesPdam Corrosion AssessmentЛюдмила МуравьеваNo ratings yet
- Pipíng & Stress Analysis Ref - Sofware Caesar II. 06-09-2017 Autor - Ing R L Morard - U T N 1Document9 pagesPipíng & Stress Analysis Ref - Sofware Caesar II. 06-09-2017 Autor - Ing R L Morard - U T N 1Oswaldo GuerraNo ratings yet
- Design of Repair Clamp For Online Elimination of Leakage From Bolted Flanged JointsDocument7 pagesDesign of Repair Clamp For Online Elimination of Leakage From Bolted Flanged JointsAlberto Fernando Leon Arismendy100% (1)
- 510 y Asme PCC-2 Insert PlatesDocument3 pages510 y Asme PCC-2 Insert PlatesJuan Jose Espinoza BarandiaranNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Rate API 581Document6 pagesCorrosion Rate API 581Indra Mulyana100% (2)
- API 510 Rerating Extract PDFDocument3 pagesAPI 510 Rerating Extract PDFmjmehta81No ratings yet
- Api 579-2 - 4.4Document22 pagesApi 579-2 - 4.4Robiansah Tri AchbarNo ratings yet
- Hydro Testing in Crosscountry PipelineDocument22 pagesHydro Testing in Crosscountry Pipelinemadhunikhil50% (8)
- 13.api 570 Open BookDocument60 pages13.api 570 Open BookAMAL VISHNUNo ratings yet
- Api-510 - Corrosion RateDocument2 pagesApi-510 - Corrosion RateRana krupalNo ratings yet
- Pipe Support Systems (2 PDH) Course No. M-2018Document17 pagesPipe Support Systems (2 PDH) Course No. M-2018arsssyNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE CalculationsDocument4 pagesEXAMPLE CalculationszaheermechNo ratings yet
- D6543-Standard Guide To The Evaluation of Measurements Made by On-Line Coal AnalyzersDocument10 pagesD6543-Standard Guide To The Evaluation of Measurements Made by On-Line Coal AnalyzersAyaNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Hydraulic Network Models by Lindell and Lingereddy 1997Document28 pagesCalibration of Hydraulic Network Models by Lindell and Lingereddy 1997Jhosep Mendoza ComunNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Steam Reformer Tube Inspection and Remaining Life Assessment ApproachDocument4 pagesEnhanced Steam Reformer Tube Inspection and Remaining Life Assessment Approachbigsteve9088No ratings yet
- API 570 GuideDocument4 pagesAPI 570 GuideSharon FreemanNo ratings yet
- Condition Assessment of BoilerDocument8 pagesCondition Assessment of BoilerEzhil Vendhan PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsFrom EverandEngineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsNo ratings yet
- Steady-State Flow of Gas Through PipesDocument71 pagesSteady-State Flow of Gas Through PipesAgustin SaezNo ratings yet
- Cfo CalculatorDocument20 pagesCfo Calculatorrathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- OPENMAT Entrance Test Form XL and XLIDocument2 pagesOPENMAT Entrance Test Form XL and XLIrathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- API Flange SelectorDocument1 pageAPI Flange Selectorrathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- A113 Thermal Growth Calculation Form (Old)Document1 pageA113 Thermal Growth Calculation Form (Old)rathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- Alignment TipsDocument4 pagesAlignment TipsUdhaya KumarNo ratings yet
Remaining Life of Pipeline
Remaining Life of Pipeline
Uploaded by
rathore_mbm2002Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Remaining Life of Pipeline
Remaining Life of Pipeline
Uploaded by
rathore_mbm2002Copyright:
Available Formats
API 570 "Piping System Repair, Alteration, Re-rating & Pressure Testing" is a very good reference for calculating
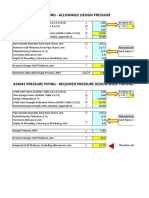
the remaining life for a pipeline in service. Also ASME B31G "Determining the Remaining Strength of Corroded Pipelines" is also a very good reference. To do that as per API 570, Section 7 "Inspection Data Evaluation, Analysis, and Recording", you have to get a full history of that pipeline regarding the average of corrosion rates that occurred at last 5 years (Short-Term corrosion rate, ST), in addition to the average corrosion rate occurred along the full period from the moment of installation till the instant moment (Long Term corrosion rate, LT). The corrosion rate used in equation for calculating the remaining life of that pipeline shall be the max. of LT & ST. Remaining life = (tactual - trequired) / Corrosion Rate Free download an example demonstrating calculation of remaining life of inservice pipeline:Remaining_life_of_inserivce_Pipeline.
See the following paragraphs are extracted from API 570: 7.1.2 Newly Installed Piping Systems or Changes in Service. For new piping systems and piping systems for which service conditions are being changed, one of the following methods shall be employed to determine the probable rate of corrosion from which the remaining wall thickness at the time of the next inspection can be estimated: a. A corrosion rate for a piping circuit may be calculated from data collected by the owner/user on piping systems of similar material in comparable service. b. If data for the same or similar service are not available, a corrosion rate for a piping circuit may be estimated from the owner/user's experience or from published data on piping systems in comparable service. c. If the probable corrosion rate cannot be determined by either method listed in item a or item b, the initial thickness measurement determinations shall be made after no more than 3 months of service by using nondestructive thickness measurements of the piping system. Corrosion monitoring devices, such as corrosion coupons or corrosion probes, may be useful in establishing the timing of these thickness measurements. Subsequent measurements shall be made after appropriate intervals until the corrosion rate is established.
7.1.3 Existing Piping Systems. Corrosion rates shall be calculated on either a short-term or a long-term basis. If calculations indicate that an inaccurate rate of corrosion has been assumed, the rate to be used for the next period shall be adjusted to agree with the actual rate found.
You might also like
- HDD Calculation (Template)Document4 pagesHDD Calculation (Template)bebas_amarah87% (15)
- API 579 Section 5 Level 2 AssessmentDocument18 pagesAPI 579 Section 5 Level 2 AssessmentJavierSeiman100% (1)
- Retiring Wall Thickness Calculation For PipeDocument4 pagesRetiring Wall Thickness Calculation For PipeFares JawadNo ratings yet
- Api 579 PDFDocument60 pagesApi 579 PDFJavierSeiman100% (5)
- API 510 Corrosion Rate and Remaining Life CalculationsDocument2 pagesAPI 510 Corrosion Rate and Remaining Life Calculationshirenpatel_6233% (6)
- Asme b31g Calculation Eml-4Document3 pagesAsme b31g Calculation Eml-4GRANRICKY100% (4)
- Section-4 Assessment of General Metal Loss API 579 - FFSDocument69 pagesSection-4 Assessment of General Metal Loss API 579 - FFSNDTInstructor80% (5)
- API 1104 InterpretationDocument40 pagesAPI 1104 Interpretationrathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- 8.inspection CalculationDocument38 pages8.inspection CalculationAMAL VISHNUNo ratings yet
- Remaining Life of A PipelineDocument2 pagesRemaining Life of A Pipelinefaisalf100% (4)
- Asme b31g Level 2 A1Document27 pagesAsme b31g Level 2 A1finiteinjustice78% (9)
- B31 G Level 1 EvaluationDocument5 pagesB31 G Level 1 EvaluationmmNo ratings yet
- Signal FFS Software DatasheetDocument2 pagesSignal FFS Software DatasheetMirtunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Assessment As Per API 579-1ASME FFS-1 For Pressure Vessel General Metal Loss by Using FEA TechniquesDocument21 pagesLevel 3 Assessment As Per API 579-1ASME FFS-1 For Pressure Vessel General Metal Loss by Using FEA TechniquesKingston RivingtonNo ratings yet
- API 510 Spreadsheet To Calculate (Welding ScwiDocument2 pagesAPI 510 Spreadsheet To Calculate (Welding Scwibryandown100% (1)
- Retirement ThicknessDocument7 pagesRetirement ThicknessKamal UddinNo ratings yet
- RSTRENG Report - 08 - 07 - 2015 - 10 - 12 - 14Document2 pagesRSTRENG Report - 08 - 07 - 2015 - 10 - 12 - 14Mustafa Akbar100% (2)
- MAWP CalculationDocument2 pagesMAWP CalculationMuhammad Zeeshan Wasi60% (5)
- Integrity Evaluation of Small Bore Connections (Branch Connections) PDFDocument9 pagesIntegrity Evaluation of Small Bore Connections (Branch Connections) PDFHendra YudistiraNo ratings yet
- FFS, 579 - Seminar Ata, 1389Document68 pagesFFS, 579 - Seminar Ata, 1389전상문100% (3)
- Asme 31 GDocument48 pagesAsme 31 GShriram Avasarkar100% (2)
- API 579 - Fitness For Service SummaryDocument12 pagesAPI 579 - Fitness For Service SummaryJustin OnisoruNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The API Section 10Document18 pagesAn Overview of The API Section 10api-3855165100% (1)
- APPENDIX D - CORROSION RATE and REMAINING LIFE CALCULATIONDocument6 pagesAPPENDIX D - CORROSION RATE and REMAINING LIFE CALCULATIONPhornlert Wana100% (2)
- Advanced Integrity Assessment of Pipeline Dents Using ILI DataDocument27 pagesAdvanced Integrity Assessment of Pipeline Dents Using ILI DataMuhammad ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Detailed Fitness For Service Per API 579Document3 pagesDetailed Fitness For Service Per API 579Sajal KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- ASME B31.3.4.8 Wall Thickness CalculatorDocument26 pagesASME B31.3.4.8 Wall Thickness Calculatoreko123100% (1)
- Integrity Assessment of Pressure VesselDocument6 pagesIntegrity Assessment of Pressure Vesselmrb193100% (1)
- Elbow Thickness CalculatorDocument7 pagesElbow Thickness Calculatorvijayakumar2015100% (1)
- Asme API 579 SI HandoutsDocument196 pagesAsme API 579 SI Handoutsronfrend94% (17)
- API579 EXAMPLE CalculationsDocument4 pagesAPI579 EXAMPLE CalculationsJaclyn Henderson80% (5)
- Assessment of Corrosion in PipelinesDocument31 pagesAssessment of Corrosion in PipelinesRicardo Andres Santamaria Torres100% (2)
- B31GDocument3 pagesB31GHendra YudistiraNo ratings yet
- API 579 SI Handouts PDFDocument196 pagesAPI 579 SI Handouts PDFshakeelahmadjsr100% (1)
- API 579 Part 5 Local Metal LossDocument41 pagesAPI 579 Part 5 Local Metal LossAli SASSINo ratings yet
- 5 16259779815014437Document26 pages5 16259779815014437Hafizul Hisyam Maysih Luzifah100% (1)
- API 579 Section 5 Level 2 AssessmentDocument18 pagesAPI 579 Section 5 Level 2 AssessmentcutefrenzyNo ratings yet
- Boxup Clamp DesignDocument5 pagesBoxup Clamp DesignGohar ZamanNo ratings yet
- Draft Report RLA Pipeline PDFDocument47 pagesDraft Report RLA Pipeline PDFTengku Nizarul AslamiNo ratings yet
- Pipelines Defects Assements - Will Defect Fails ?Document22 pagesPipelines Defects Assements - Will Defect Fails ?api-3784571100% (4)
- Buch 15 Corrosion Under Pipe SupportsDocument8 pagesBuch 15 Corrosion Under Pipe SupportsTrajko GorgievskiNo ratings yet
- Remaining Life of A PipelineDocument38 pagesRemaining Life of A Pipelineochable100% (2)
- Corrosion Rate CalculationsDocument51 pagesCorrosion Rate CalculationsJosé Ignacio Mendieta CamargoNo ratings yet
- F.sq-p.003 Rev. 0 Procedure For Repair, Alteration, and Modification Pressure VesselDocument7 pagesF.sq-p.003 Rev. 0 Procedure For Repair, Alteration, and Modification Pressure VesselIksan Adityo MulyoNo ratings yet
- Pdam Corrosion AssessmentDocument31 pagesPdam Corrosion AssessmentЛюдмила МуравьеваNo ratings yet
- Pipíng & Stress Analysis Ref - Sofware Caesar II. 06-09-2017 Autor - Ing R L Morard - U T N 1Document9 pagesPipíng & Stress Analysis Ref - Sofware Caesar II. 06-09-2017 Autor - Ing R L Morard - U T N 1Oswaldo GuerraNo ratings yet
- Design of Repair Clamp For Online Elimination of Leakage From Bolted Flanged JointsDocument7 pagesDesign of Repair Clamp For Online Elimination of Leakage From Bolted Flanged JointsAlberto Fernando Leon Arismendy100% (1)
- 510 y Asme PCC-2 Insert PlatesDocument3 pages510 y Asme PCC-2 Insert PlatesJuan Jose Espinoza BarandiaranNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Rate API 581Document6 pagesCorrosion Rate API 581Indra Mulyana100% (2)
- API 510 Rerating Extract PDFDocument3 pagesAPI 510 Rerating Extract PDFmjmehta81No ratings yet
- Api 579-2 - 4.4Document22 pagesApi 579-2 - 4.4Robiansah Tri AchbarNo ratings yet
- Hydro Testing in Crosscountry PipelineDocument22 pagesHydro Testing in Crosscountry Pipelinemadhunikhil50% (8)
- 13.api 570 Open BookDocument60 pages13.api 570 Open BookAMAL VISHNUNo ratings yet
- Api-510 - Corrosion RateDocument2 pagesApi-510 - Corrosion RateRana krupalNo ratings yet
- Pipe Support Systems (2 PDH) Course No. M-2018Document17 pagesPipe Support Systems (2 PDH) Course No. M-2018arsssyNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE CalculationsDocument4 pagesEXAMPLE CalculationszaheermechNo ratings yet
- D6543-Standard Guide To The Evaluation of Measurements Made by On-Line Coal AnalyzersDocument10 pagesD6543-Standard Guide To The Evaluation of Measurements Made by On-Line Coal AnalyzersAyaNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Hydraulic Network Models by Lindell and Lingereddy 1997Document28 pagesCalibration of Hydraulic Network Models by Lindell and Lingereddy 1997Jhosep Mendoza ComunNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Steam Reformer Tube Inspection and Remaining Life Assessment ApproachDocument4 pagesEnhanced Steam Reformer Tube Inspection and Remaining Life Assessment Approachbigsteve9088No ratings yet
- API 570 GuideDocument4 pagesAPI 570 GuideSharon FreemanNo ratings yet
- Condition Assessment of BoilerDocument8 pagesCondition Assessment of BoilerEzhil Vendhan PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsFrom EverandEngineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsNo ratings yet
- Steady-State Flow of Gas Through PipesDocument71 pagesSteady-State Flow of Gas Through PipesAgustin SaezNo ratings yet
- Cfo CalculatorDocument20 pagesCfo Calculatorrathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- OPENMAT Entrance Test Form XL and XLIDocument2 pagesOPENMAT Entrance Test Form XL and XLIrathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- API Flange SelectorDocument1 pageAPI Flange Selectorrathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- A113 Thermal Growth Calculation Form (Old)Document1 pageA113 Thermal Growth Calculation Form (Old)rathore_mbm2002No ratings yet
- Alignment TipsDocument4 pagesAlignment TipsUdhaya KumarNo ratings yet