Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculus: R Differential Calculus: Concept
Calculus: R Differential Calculus: Concept
Uploaded by
Nasir UddinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Data Analyst Associate Cert Training ResourcesDocument4 pagesData Analyst Associate Cert Training ResourcesjoseNo ratings yet
- Most Repeated Questions - Maths Class 10 by PadhleDocument68 pagesMost Repeated Questions - Maths Class 10 by PadhleSahanaa0% (1)
- 2Document35 pages2Avinash Katragadda100% (1)
- Math Finance Assignment Session 1718Document11 pagesMath Finance Assignment Session 1718Fani Masturina100% (1)
- (The Addison-Wesley Series in Finance) Bruno H. Solnik, Dennis W. McLeavey - International Investments (2004, Addison-Wesley) PDFDocument786 pages(The Addison-Wesley Series in Finance) Bruno H. Solnik, Dennis W. McLeavey - International Investments (2004, Addison-Wesley) PDFElma Ummati100% (1)
- INCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHDocument38 pagesINCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHCA Harshil ShethNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 - Unconstrained OptimizationDocument3 pagesTutorial 6 - Unconstrained OptimizationsurojiddinNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS For Field Study 1 - The Learner's Development and Environment by Prof. Eric Datu AgustinDocument5 pagesSYLLABUS For Field Study 1 - The Learner's Development and Environment by Prof. Eric Datu AgustinRoxane Rivera83% (12)
- Ch6 MGT Mathematics Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesCh6 MGT Mathematics Lecture NotesSamoWadaag Online BusinessNo ratings yet
- Sanam MathDocument13 pagesSanam MathAbrar Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument36 pagesLinear ProgrammingHSNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Linear ProgrammingDocument35 pagesLesson 2 Linear ProgrammingalecksgodinezNo ratings yet
- Target Mathematics By:-Agyat Gupta: Pre-Board Examination 2010 - 11 Class - Xii Cbse MathematicsDocument4 pagesTarget Mathematics By:-Agyat Gupta: Pre-Board Examination 2010 - 11 Class - Xii Cbse MathematicsNitin JainNo ratings yet
- BBA 2019 Reg Final ExamDocument8 pagesBBA 2019 Reg Final ExamBinod KhatriNo ratings yet
- All Bank Written Math Solution - 2015 16 PDFDocument33 pagesAll Bank Written Math Solution - 2015 16 PDFAshief Ahmed100% (1)
- Linear Programming in Operations ResearchDocument15 pagesLinear Programming in Operations ResearchAli MemonNo ratings yet
- SSC Maths Quiz 13 PDFDocument9 pagesSSC Maths Quiz 13 PDFTarun PandeyNo ratings yet
- CALCULUSDocument5 pagesCALCULUSVongai MushabaNo ratings yet
- CMAT 2020 by CrackuDocument39 pagesCMAT 2020 by Crackuaadeshmogarge1998No ratings yet
- CLAT Maths Quiz 42Document7 pagesCLAT Maths Quiz 42Pooja DiveNo ratings yet
- SBI PO Previous Year Question Paper 2019: Quantitative Aptitude (Questions & Solutions)Document20 pagesSBI PO Previous Year Question Paper 2019: Quantitative Aptitude (Questions & Solutions)Ananiya TiwariNo ratings yet
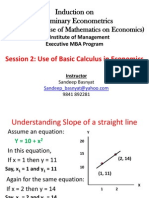
- Induction On Preliminary Econometrics: (Basics On The Use of Mathematics On Economics)Document25 pagesInduction On Preliminary Econometrics: (Basics On The Use of Mathematics On Economics)Dhananjay ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- BCOM Maths Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesBCOM Maths Practice QuestionsVishwanth Sagar SNo ratings yet
- Quarterly QP AKDocument7 pagesQuarterly QP AKhangezoe68khpNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics Assignment 1Document5 pagesBusiness Mathematics Assignment 1Tayyaba YounasNo ratings yet
- Solution of Test Qaure RootDocument7 pagesSolution of Test Qaure RootBrijesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Assignment (Solved)Document14 pagesMathematics Assignment (Solved)tabizhNo ratings yet
- Math 1001 Practice Test 3Document6 pagesMath 1001 Practice Test 3JINGYLINGYNo ratings yet
- MATH 142-511, 516, 517 Spring 2010 Solutions For The Sample Problems For The FinalDocument17 pagesMATH 142-511, 516, 517 Spring 2010 Solutions For The Sample Problems For The FinalAsmady AhmadNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Applied Mathematics Term - I Code-241: Q.N. Correct Option Hints/Solutions Section - A C A C D D A C A CDocument3 pagesMarking Scheme Applied Mathematics Term - I Code-241: Q.N. Correct Option Hints/Solutions Section - A C A C D D A C A CDp MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Actual CAT Problems 1998-2008 Algebra (Answers and Explanations)Document15 pagesActual CAT Problems 1998-2008 Algebra (Answers and Explanations)Avdesh KothariNo ratings yet
- Solution+V1 VG MVG MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesDocument16 pagesSolution+V1 VG MVG MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions - MSC DelhiDocument18 pagesSample Questions - MSC DelhiPriyanath PaulNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 SMU 3013 Mathematics SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2018/2019Document12 pagesAssignment 1 SMU 3013 Mathematics SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2018/2019ainie khalimNo ratings yet
- The Management Life and Social Sciences 10th Edition Harshbarger and Reynolds 1133106234 9781133106234Document36 pagesThe Management Life and Social Sciences 10th Edition Harshbarger and Reynolds 1133106234 9781133106234rachael.stookey199100% (17)
- CMAT 2020 by CrackuDocument39 pagesCMAT 2020 by CrackuCommon PhoneNo ratings yet
- Graphical Method of Solving Linear Programming ProblemDocument25 pagesGraphical Method of Solving Linear Programming ProblemGuruvayur Maharana67% (3)
- Vg/Mvg-Level Test On Algebra and Functions: Quadratic Equations, Exponential Equations, Logarithms, Simultaneous Equations Mac1Nvco08 InstructionsDocument7 pagesVg/Mvg-Level Test On Algebra and Functions: Quadratic Equations, Exponential Equations, Logarithms, Simultaneous Equations Mac1Nvco08 InstructionsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer 1ST QuarterDocument4 pagesMath Reviewer 1ST QuarterSofia Marmel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Nov'23 Math 04 - 09 Nov 2023Document26 pagesNov'23 Math 04 - 09 Nov 2023Rhowelle TibayNo ratings yet
- SSC CHSL 6 March 2018 Afternoon Shift by CrackuDocument38 pagesSSC CHSL 6 March 2018 Afternoon Shift by CrackuSayantani NathNo ratings yet
- Most Repeated Questions - Maths Class 10 by PadhleDocument67 pagesMost Repeated Questions - Maths Class 10 by Padhleaprajita royNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Integer ProgrammingDocument41 pagesChapter 6 - Integer ProgrammingNhư TâmNo ratings yet
- Math 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsDocument3 pagesMath 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Business MathematicsDocument10 pagesBusiness MathematicsDipesh Raj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics January 2020 Paper 2Document34 pagesMathematics January 2020 Paper 2Tamera Green100% (1)
- Csec Math January 2020 Paper 2Document34 pagesCsec Math January 2020 Paper 2Simion MillwoodNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Quadratic Equations in PDFDocument13 pagesGrade 10 Quadratic Equations in PDFSaurabh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- North South University: Dy DXDocument5 pagesNorth South University: Dy DXRifat Tasfia OtriNo ratings yet
- The Remainder and Factor TheoremDocument7 pagesThe Remainder and Factor TheoremOwen CheongNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Board Class 10 Mathematics Paper I March 2019 Question Paper SolutionDocument14 pagesMaharashtra Board Class 10 Mathematics Paper I March 2019 Question Paper Solutionkzakiya17No ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1Document12 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Applied Maths MSDocument10 pagesApplied Maths MSVaradNo ratings yet
- Math 24 SG 5Document12 pagesMath 24 SG 5MysteryAliNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 LPPDocument16 pagesChap 12 LPPShivamNo ratings yet
- Operations Research More or ModelsDocument31 pagesOperations Research More or ModelsGunaseelan RvNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk 22 May 2016: Downloaded From Https://cracku - inDocument48 pagesSBI Clerk 22 May 2016: Downloaded From Https://cracku - inRishabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegrationDocument17 pagesDefinite IntegrationAc CruzNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 7Document21 pagesSelina Solutions Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 7Madhura ChobeNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Previous Questions With Explanation - Part 2Document12 pagesTNPSC Previous Questions With Explanation - Part 2PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseFrom EverandGCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in BankingDocument105 pagesRisk Management in BankingNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Forex Risk ManagementDocument114 pagesForex Risk ManagementNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Case PresentaionDocument53 pagesCase PresentaionNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Ja Accounts Provati 2012 Audit Opu Update2Document11 pagesJa Accounts Provati 2012 Audit Opu Update2Nasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Modern Portfolio Theory and Investment AnalysisDocument11 pagesModern Portfolio Theory and Investment AnalysisNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument4 pagesTime Value of MoneyNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Walmart CaseDocument21 pagesWalmart CaseNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Correct Your SentencesDocument8 pagesCorrect Your SentencesNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Skylab 3 PAO Mission Commentary 3 of 6Document851 pagesSkylab 3 PAO Mission Commentary 3 of 6Bob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Research On Moment of Inertia Measurement Method2019Document7 pagesResearch On Moment of Inertia Measurement Method2019ait oubella marouaneNo ratings yet
- Web Pages With MVC3 and Razor SyntaxDocument282 pagesWeb Pages With MVC3 and Razor Syntaxozamaro100% (1)
- Tutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BDocument18 pagesTutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- WA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Document2 pagesWA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Daily Kos ElectionsNo ratings yet
- Caesar II TutorialDocument35 pagesCaesar II TutorialOctavio fnNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32davieNo ratings yet
- WPQR3Document3 pagesWPQR3Dimitris NikouNo ratings yet
- 1 L.M. College of Pharmacy Gujarat (Government of Gujarat) Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination Question Paper 2016Document9 pages1 L.M. College of Pharmacy Gujarat (Government of Gujarat) Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination Question Paper 2016pratyush swarnkarNo ratings yet
- Chem 120.1 Lab Sheet (Exercise No. 1)Document2 pagesChem 120.1 Lab Sheet (Exercise No. 1)Giema OrocNo ratings yet
- Physics Standard Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesDocument17 pagesPhysics Standard Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesjszNo ratings yet
- Agriculture AhmedabadDocument33 pagesAgriculture AhmedabadKrupam Thetenders.com100% (1)
- C32 - PFRS 5 Noncurrent Asset Held For SaleDocument4 pagesC32 - PFRS 5 Noncurrent Asset Held For SaleAllaine ElfaNo ratings yet
- C BAND Satellites Recivable in A INDIA PDFDocument3 pagesC BAND Satellites Recivable in A INDIA PDFchidambaram kasiNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Arena VerdeDocument12 pagesMSDS - Arena VerdeSoledad OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan Prodi Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesFakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan Prodi Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisAlya Mahastra PutriNo ratings yet
- Some Facts About PractoDocument2 pagesSome Facts About PractoinfoNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Lesson, The Students Will Be Able To Apply The Indefinite Articles in The Given SentencesDocument11 pagesAt The End of The Lesson, The Students Will Be Able To Apply The Indefinite Articles in The Given SentencesRhielle Dimaculangan CabañezNo ratings yet
- Eco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbDocument10 pagesEco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbsanchiNo ratings yet
- M Britt Profiles - Grab N Go PackDocument6 pagesM Britt Profiles - Grab N Go PackpavelscribdNo ratings yet
- Diamond Kipah For JDocument3 pagesDiamond Kipah For JM MilliganNo ratings yet
- Rag & Bone - Fragments: Free Content Friday - Outbreak: Undead.. September 2021Document7 pagesRag & Bone - Fragments: Free Content Friday - Outbreak: Undead.. September 2021Brian PayneNo ratings yet
- Can You Dribble The Ball Like A ProDocument4 pagesCan You Dribble The Ball Like A ProMaradona MatiusNo ratings yet
- Nurse Resume ConstructionDocument4 pagesNurse Resume ConstructionNelly Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Connolly Ryan Acit 1 To 1 3 22 17 644Document10 pagesConnolly Ryan Acit 1 To 1 3 22 17 644api-356586426No ratings yet
- Call CardsDocument1 pageCall CardsFarmers CooperativeNo ratings yet
Calculus: R Differential Calculus: Concept
Calculus: R Differential Calculus: Concept
Uploaded by
Nasir UddinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculus: R Differential Calculus: Concept
Calculus: R Differential Calculus: Concept
Uploaded by
Nasir UddinCopyright:
Available Formats
Application of Mathematics in Business
Md. Nasir Uddin; BBA (Finance), DU. Cell: 01924 75 65 94; 01683 20 27 52
E-mail: nasir_findu@yahoo.com Page 1
Calculus
Differential calculus: concept, general rules, mathematical problems, practical problems related to
differential calculus.
Integral calculus: concept, general rules, mathematical problems, practical problems related to
integral calculus.
Differential calculus: concept
General rules
1. Derivative of any constant is 0. ( derivative o ).
If y = 2,
= 0. If f(x) = a,
= 0
2. Derivative of a constant time a function equals the constant times the derivative of the
function. ( " derivative
.
If y = 2
, ,
= 2 . 2
= 4x. If f(x) = 2
= 2. 2
= 4x.
3. Derivative of an expression can be taken term by term. (expression
derivative 4)
If y = 2
+ 2x - 10
= 2 . 2
+ 2 .
- 0
= 4x + 2
Practical problem solving related to differential calculus
Constant: , a, b,
Expression
y = 2
+ 2x 10
Term Term Term
Application of Mathematics in Business
Md. Nasir Uddin; BBA (Finance), DU. Cell: 01924 75 65 94; 01683 20 27 52
E-mail: nasir_findu@yahoo.com Page 2
Problem1: A manufacturing firm has the following cost function:
C =
+ 5x + 100; where x is the units of production. Find: a) FC, b) VC, c) AC, d) AVC, e) AFC.
Solution:
a) FC = 100 ( o} constant change i o}
fixed cost)
b) VC =
+ 5x (fixed cost y cost function o "} i
c) AC =
= x + 5 +
( AC = TC/Q)
d) AVC =
= x + 5
e) AFC =
Problem 2: A producers pattern of total revenue is described by the relation:
Y =
; where y is the total revenue and x is the number of units sold.
Requirement:
a) Units sold that maximizes total revenue
b) Amount of this maximum revenue
c) Total revenue if 15 units were sold
Solution:
a) Given that, Y =
= 100 (
- 20x + 100) =
+ 20x
Application of Mathematics in Business
Md. Nasir Uddin; BBA (Finance), DU. Cell: 01924 75 65 94; 01683 20 27 52
E-mail: nasir_findu@yahoo.com Page 3
= 2x + 20
For maximum or minimum first condition,
= 0
2x +20 = 0
x = 10
Now,
= 2x + 20
= 2 <0. So the revenue function is maximum at x = 10. ( " 4 y}
Therefore, revenue maximizing units = 10 units.
b) Amount of maximum revenue =
= 100 0 = Tk. 100
c) If 15 units are sold, total revenue =
= 100
= Tk. 75
Problem 3: Total cost function of a firm is C =
Where c is the total cost and x is the output, and price under perfect competition is given as tk. 6,
find for what output the profit will be maximized.
Solution:
Given that, C =
Price, p = tk. 6 and Quantity, q = x
Revenue, R = p.q = 6x
Therefore, profit, TP= R C
= 6x (
)
=
Application of Mathematics in Business
Md. Nasir Uddin; BBA (Finance), DU. Cell: 01924 75 65 94; 01683 20 27 52
E-mail: nasir_findu@yahoo.com Page 4
(TP)=
For maximum or minimum first condition,
= 0
= 0
= 0
(x 6) (x 4) = 0
x = 6 or x = 4
Now,
= 2x + 10
When x = 6,
= 2.6 + 10 = <0 .So the profit is maximum at x = 6. (" 4
Therefore, profit maximizing output = 6 units.
Problem 4: For a unit demand function of p = 24 8x, where x is the number of units in thousands
and p is the price in taka, find the sales function. If the average cost per unit is Tk. 8, find
a) The profit function
b) The number of unit that maximize the profit function
Solution:
a) Given that, p = 24 8x, average cost, AC = Tk. 8
Total Revenue, TR = PQ = (24 8x). x = 24x 8
Total Cost, TC = = x = 8x
Therefore, Total profit, TP = TR TC = 24x 8
8x = 16x 8
b) Total profit, TP= 16x 8
Application of Mathematics in Business
Md. Nasir Uddin; BBA (Finance), DU. Cell: 01924 75 65 94; 01683 20 27 52
E-mail: nasir_findu@yahoo.com Page 5
(TP)=
For maximum or minimum first condition,
= 0
= 0
x = 0
Now,
=
Therefore, profit maximizing output = 1 unit.
Problem 4: If the cost function is C(x) = 4x + 9 and the revenue function is R(x) = 9x
, where x
is the number of units produced. Find the following:
b) Marginal revenue at x=5, x=6
d) Fixed cost
e) Variable cost at x=5
f) Breakeven point, that is R(x)= C(x)
g) Profit function
^ o)
i) Marginal revenue at most profitable output ( ^ o J
k) Variable cost at most profitable output
Solution:
Application of Mathematics in Business
Md. Nasir Uddin; BBA (Finance), DU. Cell: 01924 75 65 94; 01683 20 27 52
E-mail: nasir_findu@yahoo.com Page 6
Given that, R(x) = 9x
Marginal revenue, MR =
= 9 2 x
b) Marginal revenue at x=5, x=6 :
When x=5, MR = 9 2. 5 = 1
When x=6, MR = 9 2. 6 = 3
Given that, C(x) = 4x + 9
Marginal cost, MC =
= 4
d) Fixed cost:
Given that, C(x) = 4x + 9. Fixed cost, FC = 9
e) Variable cost at x=5:
Given that, C(x) = 4x + 9. Variable cost, VC = 4x
Therefore, variable cost = 4.5 = 20
f) Breakeven point, that is R(x)= C(x):
At breakeven point, R(x) = C(x)
9x
= 4x + 9
- 5x +9 =0
=
g) Profit function:
Profit, TP = R(x) C(x) = 9x
4x + 9 = 5x
9
middle term factor 4
x o
formula:
a
+ bx + c = 0
=
Application of Mathematics in Business
Md. Nasir Uddin; BBA (Finance), DU. Cell: 01924 75 65 94; 01683 20 27 52
E-mail: nasir_findu@yahoo.com Page 7
^ o):
Profit, TP = 5x
(TP)=
For maximum or minimum first condition,
= 0
= 0
x = 2.5
Now,
=
Therefore, profit maximizing output = 2.5 units.
i) Marginal revenue at most profitable output ( ^ o
When x = 2.5, MR = 9 2 x = 9 2. 2.5 = Tk. 4
When x = 2.5, R = 9x
= 9. 2.5
= Tk. 16.25
k) Variable cost at most profitable output
When x = 2.5,VC = 4x = 4. 2.5 = Tk. 10
Application of Mathematics in Business
Md. Nasir Uddin; BBA (Finance), DU. Cell: 01924 75 65 94; 01683 20 27 52
E-mail: nasir_findu@yahoo.com Page 8
Slope of the marginal revenue =
= - 2
You might also like
- Data Analyst Associate Cert Training ResourcesDocument4 pagesData Analyst Associate Cert Training ResourcesjoseNo ratings yet
- Most Repeated Questions - Maths Class 10 by PadhleDocument68 pagesMost Repeated Questions - Maths Class 10 by PadhleSahanaa0% (1)
- 2Document35 pages2Avinash Katragadda100% (1)
- Math Finance Assignment Session 1718Document11 pagesMath Finance Assignment Session 1718Fani Masturina100% (1)
- (The Addison-Wesley Series in Finance) Bruno H. Solnik, Dennis W. McLeavey - International Investments (2004, Addison-Wesley) PDFDocument786 pages(The Addison-Wesley Series in Finance) Bruno H. Solnik, Dennis W. McLeavey - International Investments (2004, Addison-Wesley) PDFElma Ummati100% (1)
- INCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHDocument38 pagesINCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHCA Harshil ShethNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 - Unconstrained OptimizationDocument3 pagesTutorial 6 - Unconstrained OptimizationsurojiddinNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS For Field Study 1 - The Learner's Development and Environment by Prof. Eric Datu AgustinDocument5 pagesSYLLABUS For Field Study 1 - The Learner's Development and Environment by Prof. Eric Datu AgustinRoxane Rivera83% (12)
- Ch6 MGT Mathematics Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesCh6 MGT Mathematics Lecture NotesSamoWadaag Online BusinessNo ratings yet
- Sanam MathDocument13 pagesSanam MathAbrar Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument36 pagesLinear ProgrammingHSNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Linear ProgrammingDocument35 pagesLesson 2 Linear ProgrammingalecksgodinezNo ratings yet
- Target Mathematics By:-Agyat Gupta: Pre-Board Examination 2010 - 11 Class - Xii Cbse MathematicsDocument4 pagesTarget Mathematics By:-Agyat Gupta: Pre-Board Examination 2010 - 11 Class - Xii Cbse MathematicsNitin JainNo ratings yet
- BBA 2019 Reg Final ExamDocument8 pagesBBA 2019 Reg Final ExamBinod KhatriNo ratings yet
- All Bank Written Math Solution - 2015 16 PDFDocument33 pagesAll Bank Written Math Solution - 2015 16 PDFAshief Ahmed100% (1)
- Linear Programming in Operations ResearchDocument15 pagesLinear Programming in Operations ResearchAli MemonNo ratings yet
- SSC Maths Quiz 13 PDFDocument9 pagesSSC Maths Quiz 13 PDFTarun PandeyNo ratings yet
- CALCULUSDocument5 pagesCALCULUSVongai MushabaNo ratings yet
- CMAT 2020 by CrackuDocument39 pagesCMAT 2020 by Crackuaadeshmogarge1998No ratings yet
- CLAT Maths Quiz 42Document7 pagesCLAT Maths Quiz 42Pooja DiveNo ratings yet
- SBI PO Previous Year Question Paper 2019: Quantitative Aptitude (Questions & Solutions)Document20 pagesSBI PO Previous Year Question Paper 2019: Quantitative Aptitude (Questions & Solutions)Ananiya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Induction On Preliminary Econometrics: (Basics On The Use of Mathematics On Economics)Document25 pagesInduction On Preliminary Econometrics: (Basics On The Use of Mathematics On Economics)Dhananjay ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- BCOM Maths Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesBCOM Maths Practice QuestionsVishwanth Sagar SNo ratings yet
- Quarterly QP AKDocument7 pagesQuarterly QP AKhangezoe68khpNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics Assignment 1Document5 pagesBusiness Mathematics Assignment 1Tayyaba YounasNo ratings yet
- Solution of Test Qaure RootDocument7 pagesSolution of Test Qaure RootBrijesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Assignment (Solved)Document14 pagesMathematics Assignment (Solved)tabizhNo ratings yet
- Math 1001 Practice Test 3Document6 pagesMath 1001 Practice Test 3JINGYLINGYNo ratings yet
- MATH 142-511, 516, 517 Spring 2010 Solutions For The Sample Problems For The FinalDocument17 pagesMATH 142-511, 516, 517 Spring 2010 Solutions For The Sample Problems For The FinalAsmady AhmadNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Applied Mathematics Term - I Code-241: Q.N. Correct Option Hints/Solutions Section - A C A C D D A C A CDocument3 pagesMarking Scheme Applied Mathematics Term - I Code-241: Q.N. Correct Option Hints/Solutions Section - A C A C D D A C A CDp MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Actual CAT Problems 1998-2008 Algebra (Answers and Explanations)Document15 pagesActual CAT Problems 1998-2008 Algebra (Answers and Explanations)Avdesh KothariNo ratings yet
- Solution+V1 VG MVG MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesDocument16 pagesSolution+V1 VG MVG MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions - MSC DelhiDocument18 pagesSample Questions - MSC DelhiPriyanath PaulNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 SMU 3013 Mathematics SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2018/2019Document12 pagesAssignment 1 SMU 3013 Mathematics SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2018/2019ainie khalimNo ratings yet
- The Management Life and Social Sciences 10th Edition Harshbarger and Reynolds 1133106234 9781133106234Document36 pagesThe Management Life and Social Sciences 10th Edition Harshbarger and Reynolds 1133106234 9781133106234rachael.stookey199100% (17)
- CMAT 2020 by CrackuDocument39 pagesCMAT 2020 by CrackuCommon PhoneNo ratings yet
- Graphical Method of Solving Linear Programming ProblemDocument25 pagesGraphical Method of Solving Linear Programming ProblemGuruvayur Maharana67% (3)
- Vg/Mvg-Level Test On Algebra and Functions: Quadratic Equations, Exponential Equations, Logarithms, Simultaneous Equations Mac1Nvco08 InstructionsDocument7 pagesVg/Mvg-Level Test On Algebra and Functions: Quadratic Equations, Exponential Equations, Logarithms, Simultaneous Equations Mac1Nvco08 InstructionsEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer 1ST QuarterDocument4 pagesMath Reviewer 1ST QuarterSofia Marmel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Nov'23 Math 04 - 09 Nov 2023Document26 pagesNov'23 Math 04 - 09 Nov 2023Rhowelle TibayNo ratings yet
- SSC CHSL 6 March 2018 Afternoon Shift by CrackuDocument38 pagesSSC CHSL 6 March 2018 Afternoon Shift by CrackuSayantani NathNo ratings yet
- Most Repeated Questions - Maths Class 10 by PadhleDocument67 pagesMost Repeated Questions - Maths Class 10 by Padhleaprajita royNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Integer ProgrammingDocument41 pagesChapter 6 - Integer ProgrammingNhư TâmNo ratings yet
- Math 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsDocument3 pagesMath 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Business MathematicsDocument10 pagesBusiness MathematicsDipesh Raj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics January 2020 Paper 2Document34 pagesMathematics January 2020 Paper 2Tamera Green100% (1)
- Csec Math January 2020 Paper 2Document34 pagesCsec Math January 2020 Paper 2Simion MillwoodNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Quadratic Equations in PDFDocument13 pagesGrade 10 Quadratic Equations in PDFSaurabh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- North South University: Dy DXDocument5 pagesNorth South University: Dy DXRifat Tasfia OtriNo ratings yet
- The Remainder and Factor TheoremDocument7 pagesThe Remainder and Factor TheoremOwen CheongNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Board Class 10 Mathematics Paper I March 2019 Question Paper SolutionDocument14 pagesMaharashtra Board Class 10 Mathematics Paper I March 2019 Question Paper Solutionkzakiya17No ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1Document12 pagesSolutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Applied Maths MSDocument10 pagesApplied Maths MSVaradNo ratings yet
- Math 24 SG 5Document12 pagesMath 24 SG 5MysteryAliNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 LPPDocument16 pagesChap 12 LPPShivamNo ratings yet
- Operations Research More or ModelsDocument31 pagesOperations Research More or ModelsGunaseelan RvNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk 22 May 2016: Downloaded From Https://cracku - inDocument48 pagesSBI Clerk 22 May 2016: Downloaded From Https://cracku - inRishabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegrationDocument17 pagesDefinite IntegrationAc CruzNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 7Document21 pagesSelina Solutions Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 7Madhura ChobeNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Previous Questions With Explanation - Part 2Document12 pagesTNPSC Previous Questions With Explanation - Part 2PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseFrom EverandGCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in BankingDocument105 pagesRisk Management in BankingNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Forex Risk ManagementDocument114 pagesForex Risk ManagementNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Case PresentaionDocument53 pagesCase PresentaionNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Ja Accounts Provati 2012 Audit Opu Update2Document11 pagesJa Accounts Provati 2012 Audit Opu Update2Nasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Modern Portfolio Theory and Investment AnalysisDocument11 pagesModern Portfolio Theory and Investment AnalysisNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument4 pagesTime Value of MoneyNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Walmart CaseDocument21 pagesWalmart CaseNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Correct Your SentencesDocument8 pagesCorrect Your SentencesNasir UddinNo ratings yet
- Skylab 3 PAO Mission Commentary 3 of 6Document851 pagesSkylab 3 PAO Mission Commentary 3 of 6Bob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Research On Moment of Inertia Measurement Method2019Document7 pagesResearch On Moment of Inertia Measurement Method2019ait oubella marouaneNo ratings yet
- Web Pages With MVC3 and Razor SyntaxDocument282 pagesWeb Pages With MVC3 and Razor Syntaxozamaro100% (1)
- Tutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BDocument18 pagesTutorial Letter 203/2/2017: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- WA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Document2 pagesWA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Daily Kos ElectionsNo ratings yet
- Caesar II TutorialDocument35 pagesCaesar II TutorialOctavio fnNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32davieNo ratings yet
- WPQR3Document3 pagesWPQR3Dimitris NikouNo ratings yet
- 1 L.M. College of Pharmacy Gujarat (Government of Gujarat) Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination Question Paper 2016Document9 pages1 L.M. College of Pharmacy Gujarat (Government of Gujarat) Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination Question Paper 2016pratyush swarnkarNo ratings yet
- Chem 120.1 Lab Sheet (Exercise No. 1)Document2 pagesChem 120.1 Lab Sheet (Exercise No. 1)Giema OrocNo ratings yet
- Physics Standard Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesDocument17 pagesPhysics Standard Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesjszNo ratings yet
- Agriculture AhmedabadDocument33 pagesAgriculture AhmedabadKrupam Thetenders.com100% (1)
- C32 - PFRS 5 Noncurrent Asset Held For SaleDocument4 pagesC32 - PFRS 5 Noncurrent Asset Held For SaleAllaine ElfaNo ratings yet
- C BAND Satellites Recivable in A INDIA PDFDocument3 pagesC BAND Satellites Recivable in A INDIA PDFchidambaram kasiNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Arena VerdeDocument12 pagesMSDS - Arena VerdeSoledad OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan Prodi Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesFakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan Prodi Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisAlya Mahastra PutriNo ratings yet
- Some Facts About PractoDocument2 pagesSome Facts About PractoinfoNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Lesson, The Students Will Be Able To Apply The Indefinite Articles in The Given SentencesDocument11 pagesAt The End of The Lesson, The Students Will Be Able To Apply The Indefinite Articles in The Given SentencesRhielle Dimaculangan CabañezNo ratings yet
- Eco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbDocument10 pagesEco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbsanchiNo ratings yet
- M Britt Profiles - Grab N Go PackDocument6 pagesM Britt Profiles - Grab N Go PackpavelscribdNo ratings yet
- Diamond Kipah For JDocument3 pagesDiamond Kipah For JM MilliganNo ratings yet
- Rag & Bone - Fragments: Free Content Friday - Outbreak: Undead.. September 2021Document7 pagesRag & Bone - Fragments: Free Content Friday - Outbreak: Undead.. September 2021Brian PayneNo ratings yet
- Can You Dribble The Ball Like A ProDocument4 pagesCan You Dribble The Ball Like A ProMaradona MatiusNo ratings yet
- Nurse Resume ConstructionDocument4 pagesNurse Resume ConstructionNelly Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Connolly Ryan Acit 1 To 1 3 22 17 644Document10 pagesConnolly Ryan Acit 1 To 1 3 22 17 644api-356586426No ratings yet
- Call CardsDocument1 pageCall CardsFarmers CooperativeNo ratings yet