Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care and Parents Contribution in The Care of Their Childern With Hypospadias
Nursing Care and Parents Contribution in The Care of Their Childern With Hypospadias
Uploaded by
cumiasamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care and Parents Contribution in The Care of Their Childern With Hypospadias
Nursing Care and Parents Contribution in The Care of Their Childern With Hypospadias
Uploaded by
cumiasamCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Caring Sciences 2010 September-December Vol 3 Issue 3 106 REVIEW PAPER Nursing Care and Parents
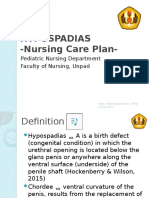
Contribution in the Care of their Childern with Hypospadias Maria Tsiligiri, PhD Assistant Professor , Physical Therapy Department, Alexander Technological Educational Institute of Thessaloniki, Greece Zioga Dimitra Nursing student , Alexander Technological Educational Institute of Thessaloniki, Greece Orfanidou Marianna Nursing student, Alexander Technological Educational Institute of Thessaloniki, Greece Correspondence: Maria Tsiligiri, Assistant Professor , Alexander Technological Educational Institute of Thessaloniki, Greece, Marion.87@windowslive.com Abstract: The term hypospadias is derived from the Greek language and refers to the pathological condition of urethra, which the vestibule, by the time of embryology is imperfect. Approximately 1 to 300 male births appear this problem. The aim of this study is the best quality of nursing management. It is proved that the child recover earlier when the parents involved in care, so it is important to explain the procedure, educate parents about the care after leaving the hospital and to make sure that there are no questions unanswered. The new techniques, the nursing management and the parents contribution in care promote to reduce hypospadias hospitalization and so, the less suffering. KEY-WORDS: Urinary system, surgery, paediatric nursing, catheter, treatment, home dressing removal. The children as hospitalized patients need special care not only because they are in a stage in which they built their bodily systems but also because they don t understand what happened to them, where they are and who all this strange people around them are Nurses should approach them properly forgaining their trust and then take care of them. Parents are the only persons who the children trust, so it is important for nurses to collaborate with them for achieving a better quality of care for their patients. In this collaborative process, nurses have to educate parents how to reduce their stress and how to give support to their child. This article aims to describe the way in which nursing care can improve the patient journey for children with hypospadias and their families Hypospadias is a common abnormality in boys with an incidence in the general population estimated at 3 to 4 per 1000 live births (Thomas and Barker, 1997, Caroline Sanders 2006). Hypospadias refers to a condition in which the urethral opening is located below the glans penis or anywhere along the ventral surface (underside) of the penile shaft. (Whaley 1997) The reason why the penis does not develop properly is still not clear, but it is most likely polygenic because of the higher familial incidence. The development of the penis whilst the baby is growing in the womb is partly dependent on the male sex hormones such as testosterone. The effects of the testosterone on the growing penis may be blocked in some way. Genetic factors are likely involved in at least some cases, as there is about 7% familial recurrence risk. (Duckett 1982)
Historically, classification of Hypospadias has been based on meatal position. The types of hypospadias are: glanular, coronal, distal, mid, and proximal shaft, penoscrotal, scrotal, and perineal. (Duckett 1982) Historically, classification of Hypospadias has been based on meatal position. The types of hypospadias are: glanular, coronal, distal, mid, and proximal shaft, penoscrotal, scrotal, and perineal. (Duckett 1982) Surgical correction is necessary to repair the defects (restore the urethral meatus to its normal position on the glans, correct penile curvature and create a urethral that allows urination with a controlled stream). There are 300 different operations for hypospadias repair being cited in the literature (Winslow Devine, 1996). However, Magpi, Mathieu, Duckett, Snodgrass and Onlay Island flap repair are common one-stage repairs. Ultimately the nature of the repair is a consultant decision and is influenced by the position of the meatus, the position of distal urethra, the presence or absence of associated chordee and the quality and size of the foreskin (Sanders 2006) The repair is being done at progressively younger ages between 6 to 18 months of age, to minimize the traumatic effects of this experience. (Ball 1995) Some complications of this surgery are: meatal stenosis and urethrocutaneous fistula. (Duckett 1982) How to Inform Parents? Parents need information about the forthcoming procedure, such as length of stay, outcome of operation and management at home. Pre-admission information and education about a forthcoming procedure tends to complement the delivery of a good quality service. (Price, 1991).Nurses and doctors provide the necessary information however the parents because of their stress or because of the lapse of the time between assessment and admission can lead to the family generating questions that need answering, and this may further heighten anxiety. Written information is important, but it needs to be relevant and accessible to the family (Crawford, 1992).This information helps the parents to feel more confident because they curb the main points care. Multimedia sources including the internet can provide information about variance in surgical approaches, timing of surgery and outcome. Although this information may confuse them and some sources may be inaccurate or unreliable. A list of reliable places in internet where parents can inform, it would be necessary to be provided. Dressing Removal There are many different types of hypospadias dressings: all are designed to protect the suture line, reduce swelling and immobilize the penis. Home dressing removal protocol A full explanation regarding dressing removal is given to parents prior to discharge. Parents are advised that the penis may look red and swollen following dressing removal. Photographs of a penis following dressing removal are shown. Dressings are removed in the home at a pre-arranged time. Families are contacted half an hour before dressing removal and asked to administer the prescribed analgesia and put the patient in the bath with the dressing fully submerged. Dressings and stent are removed. Parents are given written and verbal information regarding wound care and returning to normal activities.
Parents are given advice regarding the administration of regular analgesia. Parents are given advice regarding increasing their child s fluid intake. Parents contact the urology nursing service when the child has passed urine. If a dressing is too tight, it has the potential to cause pain and possibly necrosis of some parts of the penis by vascular occlusion. The length of time that the dressing will remain in place is determined by the individual repair performed and is specified by the consultant following surgery, the time span being usually between two and 10 days. It is difficult to anchor a dressing to the area, especially when the child is an active toddler. Although the child is not encouraged to be mobile and is nursed in a pushchair, a cot or a playpen, it is very difficult to practicably manage, and parents do become stressed trying to minimize activity. Many families identified removal of the catheter and dressing a stressful event. Parents used words such as traumatic, very stressful and distressing. Despite children being given analgesia and the use of distraction, this aspect of admission remained of greatest concern to many parents and carers. It is recognized that removal of dressings and catheters post-operatively has the potential to be painful for the child and stressful for the family. McLorie et al (2001) reported significant pain at removal with both biofilm and compression dressings. PARENTS TEACHING Use the double-diapering technique, to protect thestent (the small tube that drains the urine) Restrict the infant or toddler from activities (e.g. playing on riding toys) that put a pressure on the surgical site. Avoid holding the infant or child straddled on the hip. Limit the children activity for two weeks. Encourage the infant or toddler to drink fluids to ensure adequate hydration. Provided fluids in a pleasant environment or using a special cup. Offer fruit juice, fruit-flavored ice pops, fruit-flavored juices, flavored ice cubes, and gelatin. Be sure to give the complete course of prescribed antibiotics to avoid infection. Watch for signs of infection: fever, swelling, redness, pain, strong-smelling urine or chance in flow of the urinary stream. The urine will be blood tinged for several days. Call the physician if urine is seen leaking from any area than the penis. Difficulties post operatively, such as pulling on the catheter, urinary obstruction/blocked catheter, erections, straining due to constipation and interference with dressings, can influence surgical outcome negatively (Grobbelaar et al 1996). Positive management of both the dressing and catheter is important to possibly minimize failure of surgery. It would appear that the information given at the pre-admission clinic goes some way to help the family manage the dressing and prepare for the potentially stressful and unpleasant experience of removal, but further study is needed to determine how best to manage a post-operative dressing or, indeed, if one is needed at all. Nursing Management It is important for the nurse to address parents concerns at the time of birth. Preoperative teaching can relieve some of their anxiety about the future appearance and functioning of the penis. Postoperative care focuses on protecting the surgical site from injury. The infant or child returns from surgery with the penis wrapped in a pressure dressing and a urethral stent (a devise used to maintain patency of the urethral canal) in place to keep the new urethral canal open. Use of arm and leg restraints prevents inadvertent removal of the stent (Wong et al 1995). Encourage fluid intake to maintain adequate urinary output and patency of the stent. Accurate documentation of intake and output is essential. Notify the physician if there is no urine drainage for
1 hour as this may indicate kinks in the system or obstruction by sediment. Pain may be associated with bladder spasms. Anticholinergic medications such as oxybutynin or hyoscyamine may be prescribed. Acetaminophen may also be given for pain. Antibiotics are often prescribed until the urinary stent falls out. Patients are often discharged within 1 day of surgery. Discharged teaching should include instructions for parents about care of the reconstructed area, fluid intake, medication administration, and signs and symptoms of infection. Inform parents of the need to go to the physician s office for dressing removal about 4 days after surgery Discussion and Conclusion In order to ensure that parents and patients needs were being met, informal discussions with parents would identify areas for service developments. Two main areas for Improvement were highlighted: 1) the need for improved pre- and postoperative Information.2) the discovery of a better method of dressing s removal. Hypospadias is a condition in which the urethral opening is located below the glans penis or anywhere along the urethral surface surgical correction is necessary to repair the defects. After leaving the hospital the nursing care is entrusted to the parents so they must learn how to use the double-diapering technique, them to protect the stent and to urge them to involve in care of their child and to watch for signs of infection. Postoperative care focuses on protecting the surgical site from complications and injury. References Ball J, Bindler R (1995). Pediatric nursing caring for the physician s office children, Appleton and Lange Stamford Washington, U.S.A Fletcher J. (1999) A Practical Approach to Dressing Wounds in Difficult Positions ,British Journal of Nursing 8(12): 779 86. Gormley A, Fishwick J, Whitnall B (2007). Home dressing removal following hypospadias repair. Journal of Child Health Care, 11:158-166 Price S. (1991) Preparing Children for Admission to Hospital, Nursing Times 87(9): 46 9. Robertson M, Walker D. (1975) .Psychological Factors in Hypospadias Repair, Journal of Urology 113(5): 698 700. Sanders C (2002). A Review of Current Practice for Boys Undergoing Hypospadias Repair: From Pre-Operative Work up to Removal of Dressing Post-Surgery. Journal of Child Health Care, 6:60-69 Stone K, Glasper E. (1997) .Can Leaflets Assist Parents in Preparing Children for Hospital? British Journal of Nursing 6(18): 1054 8. Teare J. (2001).Professional Relationships: CCNs and Primary Care Nurses, Journal of Child Health Care 5(2): 60 5. Thomas D. (2004) Hypospadiology: Science and Surgery, British Journal of Urology International 93(4): 470 3. Winslow B.H, Devine C.J. (1996) Principles in of Hypospadias, Seminars in Paediatric Surgery 5(1): 41 8. Wong D, Whaley, Wilson D, Vaughn A (1995).Nursing care in infants and children, Oklahoma, U.S.A
Jurnal Ilmu Merawat 2010 September-Desember Vol 3 Edisi 3 106 TINJAUAN KERTAS Perawatan dan Kontribusi Orang tua dalam Perawatan childern mereka dengan Hipospadia Maria Tsiligiri, PhD Asisten Profesor, Departemen Terapi Fisik, Alexander Lembaga Pendidikan Teknologi Thessaloniki, Yunani Zioga Dimitra Keperawatan mahasiswa, Alexander Institut Pendidikan Teknologi Thessaloniki, Yunani Orfanidou Marianna Keperawatan mahasiswa, Alexander Institut Pendidikan Teknologi Thessaloniki, Yunani Korespondensi: Maria Tsiligiri, Asisten Profesor, Alexander Teknologi Pendidikan Institut Thessaloniki, Yunani, Marion.87 @ windowslive.com Abstrak: Para Istilah hipospadia berasal dari bahasa Yunani dan mengacu pada kondisi patologis uretra, yang ruang depan, pada saat embriologi tidak sempurna. Sekitar 1 sampai 300 kelahiran laki-laki muncul masalah ini. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah kualitas terbaik dari manajemen keperawatan. Hal ini membuktikan bahwa anak memulihkan sebelumnya ketika orang tua terlibat dalam perawatan, sehingga sangat penting untuk menjelaskan prosedur, mendidik orang tua tentang perawatan setelah meninggalkan rumah sakit dan untuk memastikan bahwa tidak ada pertanyaan yang belum terjawab. Teknik-teknik baru, manajemen keperawatan dan kontribusi orang tua dalam perawatan mempromosikan untuk mengurangi rawat inap hipospadia dan begitu, penderitaan kurang. KUNCI-KATA: sistem kemih, operasi, perawatan anak, kateter, perawatan, rumah penghapusan ganti. Anak-anak sebagai pasien rumah sakit membutuhkan perawatan khusus bukan hanya karena mereka berada dalam tahap di mana mereka membangun sistem tubuh mereka tetapi juga karena mereka tidak mengerti apa yang terjadi pada mereka, di mana mereka dan yang semua ini orang aneh di sekitar mereka adalah Perawat harus mendekati mereka dengan baik forgaining kepercayaan mereka dan kemudian mengurus mereka. Orang tua adalah orang-orang yang hanya anak-anak kepercayaan, sehingga sangat penting bagi perawat untuk berkolaborasi dengan mereka untuk mencapai kualitas pelayanan yang lebih baik bagi pasien mereka. Dalam proses kolaboratif, perawat harus mendidik orang tua bagaimana mengurangi stres mereka dan bagaimana memberi dukungan kepada anak mereka. Artikel ini bertujuan untuk menggambarkan cara di mana perawatan dapat meningkatkan perjalanan pasien untuk anak-anak dengan hipospadia dan keluarga mereka Hipospadia adalah kelainan umum pada anak laki-laki dengan kejadian pada populasi umum diperkirakan mencapai 3 sampai 4 per 1000 kelahiran hidup (Thomas dan Barker, 1997, Caroline Sanders 2006). Hipospadia mengacu pada suatu kondisi di mana pembukaan uretra terletak di bawah glans penis atau di mana saja sepanjang permukaan ventral (bawah) dari batang penis. (Whaley 1997)
Alasan mengapa penis tidak berkembang dengan baik masih belum jelas, tetapi poligenik kemungkinan besar karena insiden familial yang lebih tinggi. Perkembangan penis sementara bayi tumbuh dalam rahim sebagian bergantung pada hormon seks pria seperti testosteron. Efek testosteron pada penis berkembang dapat diblokir dalam beberapa cara. Faktor genetik yang mungkin terlibat dalam setidaknya beberapa kasus, seperti ada sekitar 7% risiko kekambuhan keluarga. (Duckett 1982) Secara historis, klasifikasi Hipospadia telah didasarkan pada posisi meatus. Jenis-jenis hipospadia adalah: poros glanular, coronal, distal, mid, dan proksimal, penoscrotal, skrotum, dan perineum. (Duckett 1982) Secara historis, klasifikasi Hipospadia telah didasarkan pada posisi meatus. Jenis-jenis hipospadia adalah: poros glanular, coronal, distal, mid, dan proksimal, penoscrotal, skrotum, dan perineum. (Duckett 1982) Koreksi bedah diperlukan untuk memperbaiki cacat (mengembalikan meatus uretra ke posisi normal pada kelenjar, kelengkungan penis yang benar dan membuat uretra yang memungkinkan buang air kecil dengan aliran terkendali). Ada 300 operasi yang berbeda untuk perbaikan hipospadia yang dikutip dalam literatur (Winslow Devine, 1996). Namun, Magpi, Mathieu, Duckett, Snodgrass dan onlay perbaikan Pulau flap yang umum satu tahap perbaikan. Akhirnya sifat perbaikan adalah keputusan konsultan dan dipengaruhi oleh posisi meatus, posisi distal uretra, ada atau tidak adanya asosiasi chordee dan kualitas dan ukuran kulup (Sanders 2006) Perbaikan yang dilakukan pada usia semakin muda antara 6 sampai 18 bulan, untuk meminimalkan efek traumatis dari pengalaman ini. (Ball 1995) Beberapa komplikasi dari operasi ini adalah: Stenosis meatus dan fistula urethrocutaneous. (Duckett 1982) Bagaimana untuk Menginformasikan Orang tua? Orangtua perlu informasi tentang prosedur yang akan datang, seperti lama tinggal, hasil operasi dan manajemen di rumah. Pra-masuk informasi dan pendidikan tentang prosedur yang akan datang cenderung untuk melengkapi pengiriman layanan berkualitas baik. (Price, 1991) Perawat dan. Dokter memberikan informasi yang diperlukan namun orang tua karena stres atau karena selang waktu antara penilaian dan penerimaan dapat menyebabkan keluarga menghasilkan pertanyaanpertanyaan yang perlu menjawab, dan ini lebih lanjut dapat meningkatkan kecemasan. Informasi tertulis adalah penting, tetapi harus relevan dan dapat diakses oleh keluarga (Crawford, 1992). Informasi ini membantu orang tua untuk merasa lebih percaya diri karena mereka mengekang perawatan poin utama. Sumber multimedia termasuk internet dapat memberikan informasi tentang varians dalam pendekatan bedah, waktu operasi dan hasil. Walaupun informasi ini dapat membingungkan mereka dan beberapa sumber mungkin tidak akurat atau tidak dapat diandalkan. Sebuah daftar tempattempat terpercaya di internet di mana orang tua dapat menginformasikan, itu akan diperlukan untuk disediakan. Dressing Penghapusan Ada berbagai jenis dressing hipospadia: semua dirancang untuk melindungi garis jahitan, mengurangi pembengkakan dan melumpuhkan penis. Depan protokol ganti penghapusan
Penjelasan lengkap mengenai penghapusan saus diberikan kepada orang tua sebelum dibuang. Orang tua disarankan bahwa penis mungkin terlihat merah dan bengkak ganti penghapusan berikut. Foto-foto penghapusan ganti penis berikut muncul di layar. Dressing dikeluarkan di rumah pada waktu yang telah diatur sebelumnya. Keluarga dihubungi setengah jam sebelum berpakaian penghapusan dan diminta untuk mengelola analgesia yang ditentukan dan menempatkan pasien di bak mandi dengan saus sepenuhnya terendam. Dressing dan stent dihapus. Orangtua diberikan informasi tertulis dan verbal tentang perawatan luka dan kembali ke kegiatan normal. Orang tua diberi saran mengenai pemberian analgesik biasa. Orangtua diberikan nasihat mengenai meningkatkan asupan cairan anak mereka. Orangtua hubungi pelayanan keperawatan urologi ketika anak telah lulus urin. Jika dressing yang terlalu ketat, ia memiliki potensi untuk menyebabkan nekrosis nyeri dan mungkin beberapa bagian penis dengan oklusi pembuluh darah. Lamanya waktu yang ganti akan tetap berlaku ditentukan oleh perbaikan individu dilakukan dan ditentukan oleh konsultan operasi berikut, rentang waktu yang biasanya antara dua sampai 10 hari. Sulit untuk jangkar ganti untuk daerah tersebut, terutama ketika anak adalah anak yang aktif. Meskipun anak tidak didorong untuk menjadi mobile dan dirawat di sebuah kursi dorong, dipan atau boks, sangat sulit untuk dengan praktis mengelola, dan orangtua menjadi stres mencoba untuk meminimalkan aktivitas. Banyak keluarga diidentifikasi penghapusan kateter dan ganti acara stres. Orang tua digunakan katakata seperti trauma, sangat menegangkan dan menyedihkan. Meskipun anak-anak yang diberikan analgesia dan penggunaan distraksi, aspek penerimaan tetap menjadi perhatian terbesar bagi banyak orang tua dan wali. Diakui bahwa penghapusan dressing dan kateter pasca bedah memiliki potensi untuk menjadi menyakitkan bagi anak dan menegangkan bagi keluarga. McLorie et al (2001) melaporkan nyeri signifikan pada penghapusan dengan kedua biofilm dan dressing kompresi. ORANG TUA PENGAJARAN Gunakan teknik double popok, untuk melindungi thestent (tabung kecil yang mengalir urin) Batasi bayi atau balita dari kegiatan (misalnya bermain di naik mainan) yang menempatkan tekanan di situs bedah. Hindari memegang bayi atau anak mengangkangi di pinggul. Batasi kegiatan anak-anak selama dua minggu. Mendorong bayi atau balita untuk minum cairan untuk memastikan hidrasi yang cukup. Diperoleh cairan dalam lingkungan yang menyenangkan atau menggunakan gelas khusus. Menawarkan jus buah, rasa buah es muncul, rasa buah jus, es batu rasa, dan gelatin. Pastikan untuk memberikan kursus lengkap diresepkan antibiotik untuk menghindari infeksi. Perhatikan tanda-tanda infeksi: demam, pembengkakan, kemerahan, nyeri, berbau tajam urin atau kesempatan dalam aliran dari aliran kemih. Urin akan diwarnai darah selama beberapa hari. Hubungi dokter jika air seni terlihat bocor dari setiap area dari penis. Kesulitan posting bedah, seperti menarik kateter, obstruksi kemih / kateter diblokir, ereksi, berusaha karena sembelit dan gangguan dengan perban, dapat mempengaruhi hasil bedah negatif (Grobbelaar dkk 1996). Manajemen positif dari kedua dressing dan kateter penting untuk meminimalkan kemungkinan kegagalan operasi. Ia akan muncul bahwa informasi yang diberikan di klinik pra-masuk berjalan beberapa cara untuk membantu keluarga mengelola saus dan mempersiapkan diri untuk pengalaman berpotensi stres dan tidak menyenangkan dari penghapusan, tetapi penelitian lebih lanjut diperlukan untuk menentukan cara terbaik untuk mengelola pascaoperasi dressing atau, bahkan, jika ada yang dibutuhkan sama sekali.
Manajemen Keperawatan Hal ini penting bagi perawat untuk menangani kekhawatiran orang tua pada saat lahir. Pengajaran pra operasi dapat meringankan kecemasan mereka tentang masa depan penampilan dan fungsi penis. Perawatan pasca operasi berfokus pada melindungi situs bedah dari cedera. Kembali bayi atau anak dari operasi dengan penis yang terbungkus pembalut tekanan dan stent uretra (a Rancangan digunakan untuk mempertahankan patensi dari kanal uretra) di tempat untuk menjaga kanal uretra baru terbuka. Penggunaan lengan dan kaki pengekangan mencegah penghapusan tidak disengaja dari stent (Wong et al 1995). Mendorong asupan cairan untuk mempertahankan output urin yang memadai dan patensi dari stent. Dokumentasi yang akurat asupan dan keluaran adalah penting. Beritahu dokter jika tidak ada drainase urin selama 1 jam karena hal ini dapat menunjukkan Kinks dalam sistem atau obstruksi oleh sedimen. Nyeri mungkin berhubungan dengan kejang kandung kemih. Obat antikolinergik seperti oxybutynin atau hiosiamin dapat diresepkan. Acetaminophen juga dapat diberikan untuk nyeri. Antibiotik sering diresepkan sampai stent kemih jatuh keluar. Pasien sering habis dalam waktu 1 hari operasi. Pengajaran habis harus mencakup instruksi untuk orang tua tentang perawatan daerah direkonstruksi, asupan cairan, administrasi pengobatan, dan tanda-tanda dan gejala infeksi. Menginformasikan orang tua dari kebutuhan untuk pergi ke kantor dokter untuk ganti penghapusan sekitar 4 hari setelah operasi Diskusi dan Kesimpulan Untuk memastikan bahwa orang tua dan pasien 'kebutuhan itu terpenuhi, diskusi informal dengan orang tua akan mengidentifikasi area untuk pengembangan layanan. Dua bidang utama untuk Perbaikan yang disorot: 1) kebutuhan untuk Information.2 pra dan pasca operasi membaik) penemuan metode yang lebih baik penghapusan saus itu. Hipospadia adalah suatu kondisi di mana pembukaan uretra terletak di bawah glans penis atau di mana saja di sepanjang permukaan uretra koreksi bedah diperlukan untuk memperbaiki cacat. Setelah meninggalkan rumah sakit asuhan keperawatan dipercayakan kepada orang tua sehingga mereka harus belajar bagaimana menggunakan teknik double popok, itu untuk melindungi stent dan mendesak mereka untuk terlibat dalam mengasuh anak mereka dan untuk memperhatikan tandatanda infeksi. Perawatan pasca operasi berfokus pada melindungi situs bedah dari komplikasi dan cedera. Referensi Bola J, Bindler R (1995). Keperawatan anak merawat anak-anak kantor dokter, Appleton dan Lange Stamford Washington, Amerika Serikat Fletcher J. (1999) Pendekatan Praktis untuk Dressing Luka di Posisi Sulit, British Journal of Nursing 8 (12): 779-86. Gormley A, Fishwick J, Whitnall B (2007). Rumah ganti penghapusan mengikuti perbaikan hipospadia. Jurnal Perawatan Kesehatan Anak, 11:158-166 Harga S. (1991) Mempersiapkan Anak untuk Masuk ke Rumah Sakit, Keperawatan Times, 87 (9): 469. Robertson M, D. Walker (1975) Faktor Psikologis di Hipospadia Perbaikan, Jurnal Urologi 113 (5):. 698-700. Sanders C (2002). Sebuah Tinjauan Praktek Saat Ini untuk Boys Menjalani Perbaikan Hipospadia: Dari Pra-Operative Kerja hingga Penghapusan Dressing Pasca Bedah. Jurnal Perawatan Kesehatan Anak, 6:60-69 Batu K, Glasper E. (1997). Dapatkah Leaflet Membantu Orang tua dalam Mempersiapkan Anak untuk Rumah Sakit? British Journal of Nursing 6 (18): 1054-8.
. Teare J. (2001) Hubungan Profesional: CCNs dan Perawat Perawatan Primer, Jurnal Perawatan Kesehatan Anak 5 (2): 60-5. Thomas D. (2004) Hypospadiology: Sains dan Bedah, British Journal of Urology International 93 (4): 470-3. Winslow BH, Devine CJ (1996) Prinsip dalam dari Hipospadia, Seminar Bedah Pediatri di 5 (1): 41-8. Wong D, Whaley, Wilson D, Vaughn A (1995) Keperawatan perawatan. Pada bayi dan anak, Oklahoma, Amerika Serikat
You might also like
- Vol3 Issue3 04 TsiligiriDocument4 pagesVol3 Issue3 04 TsiligiriMaria Avin FjlNo ratings yet
- Procedures Used in The Management of DystociaDocument17 pagesProcedures Used in The Management of DystociaRavi RokkamNo ratings yet
- CHApter 27 MCN 2023Document76 pagesCHApter 27 MCN 2023Gwen De CastroNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument11 pagesDownloadhasan nazzalNo ratings yet
- 107 Lec Finals 3RD LessonDocument8 pages107 Lec Finals 3RD LessonChona CastorNo ratings yet
- Water Birth Research PaperDocument6 pagesWater Birth Research Papergw10ka6s100% (1)
- 110613pyloricstenosis PDFDocument8 pages110613pyloricstenosis PDFSandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Dissertation TopicsDocument8 pagesNeonatal Dissertation TopicsPaperWritersCollegeSingapore100% (1)
- Activity #1 Nupc110-CmcrpDocument4 pagesActivity #1 Nupc110-CmcrpMelody BoadoNo ratings yet
- Ob Gyn ThesisDocument8 pagesOb Gyn Thesisafktbwqoqnevso100% (2)
- Thesis Topics Gynaecology ObstetricsDocument7 pagesThesis Topics Gynaecology Obstetricsoaehviiig100% (2)
- Nursing Crib ThesisDocument8 pagesNursing Crib ThesisProfessionalCollegePaperWritersMcAllen100% (1)
- NCM 109 L - Cesarean DeliveryDocument74 pagesNCM 109 L - Cesarean DeliveryRon Ar IcaNo ratings yet
- Rectal & Large Intestinal Atresia/Stenosis: Minnesota Department of Health Fact Sheet November 2005Document3 pagesRectal & Large Intestinal Atresia/Stenosis: Minnesota Department of Health Fact Sheet November 2005chuck55No ratings yet
- International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology: Mark W. Steehler, Matthew K. Steehler, Earl H. HarleyDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology: Mark W. Steehler, Matthew K. Steehler, Earl H. HarleyJohan Sebastian Perea PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Procedures Used in The Management of DystociaDocument17 pagesProcedures Used in The Management of DystociaVeterinary Online InstituteNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario: Anesthesia For Maternal-Fetal Surgery: The Ex Utero Intrapartum Therapy (EXIT) ProcedureDocument7 pagesCase Scenario: Anesthesia For Maternal-Fetal Surgery: The Ex Utero Intrapartum Therapy (EXIT) ProcedureHilton EmilNo ratings yet
- Neonatology Thesis TopicsDocument7 pagesNeonatology Thesis Topicspwqlnolkd100% (1)
- Hernia InguinalDocument18 pagesHernia InguinalisabellaNo ratings yet
- 05 N006 5660Document24 pages05 N006 5660DeepaRamaniNo ratings yet
- NUR 145 - SAS 16-18 Activity For THF GroupDocument10 pagesNUR 145 - SAS 16-18 Activity For THF Groupella retizaNo ratings yet
- Circumcision in Baby BoysDocument6 pagesCircumcision in Baby BoysJbl2328No ratings yet
- MM Guidelines 2010Document5 pagesMM Guidelines 2010Arimbi DrestiNo ratings yet
- Abortion PaperbackDocument89 pagesAbortion PaperbackLarryNo ratings yet
- Reading On Imperforate AnusDocument4 pagesReading On Imperforate AnusHUSAIN, HAIZIAH-YASMINNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Nursing ClinicsDocument133 pagesCritical Care Nursing ClinicsJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Current Trends in ObstetricsDocument6 pagesCurrent Trends in ObstetricsShyrra Edades Pinder100% (1)
- UNIT 6 The Nursing Role in Supporting The Health of Ill Children and Their FamiliesDocument5 pagesUNIT 6 The Nursing Role in Supporting The Health of Ill Children and Their FamiliesStephanie LeeNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Obstetric FistulaDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Obstetric Fistulaikofdvbnd100% (1)
- Symptoms of Talipes DiseaseDocument6 pagesSymptoms of Talipes DiseaseJustine DumaguinNo ratings yet
- Bladder PhysioDocument4 pagesBladder PhysiovishnupriyaNo ratings yet
- CBT Reviewer 4Document11 pagesCBT Reviewer 4Cindy TanchuanNo ratings yet
- STS MODULE Final 100 108Document9 pagesSTS MODULE Final 100 108The GreatNo ratings yet
- Obs and Gynae Thesis TopicsDocument6 pagesObs and Gynae Thesis Topicsdwfz48q3100% (2)
- Bowel Training Call - Et - Al-2017-Journal - of - Applied - Behavior - AnalysisDocument13 pagesBowel Training Call - Et - Al-2017-Journal - of - Applied - Behavior - AnalysisgggNo ratings yet
- First Do No HarmDocument10 pagesFirst Do No Harmaperfectcircle7978No ratings yet
- Vaginal Agenesis PDFDocument4 pagesVaginal Agenesis PDFBill HarmanNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice in Relation To Labor InterventionDocument19 pagesEvidence Based Practice in Relation To Labor Interventionnathsujitkr1980No ratings yet
- HYPOSPADIUSDocument21 pagesHYPOSPADIUSLady350zNo ratings yet
- The First Step in Treating Your Child Is Forming An Accurate and Complete DiagnosisDocument3 pagesThe First Step in Treating Your Child Is Forming An Accurate and Complete DiagnosisDimpuulina Erna Mariati SihombingNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Exclusive Breastfeeding PDFDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Exclusive Breastfeeding PDFegtwfsaf100% (1)
- Educacion A Familias Niños TQTDocument12 pagesEducacion A Familias Niños TQTPauli VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Preterm Birth DissertationDocument9 pagesPreterm Birth DissertationPaperWritingServicesLegitimateSingapore100% (1)
- Neonatal Research PaperDocument5 pagesNeonatal Research Paperkrqovxbnd100% (1)
- Guest Editorial: The Surgical NeonateDocument2 pagesGuest Editorial: The Surgical NeonateNovita ApramadhaNo ratings yet
- Pearls of Tomorrow - Birth Intervention and The Astrological Face of A New Generation by Wendy StaceyDocument10 pagesPearls of Tomorrow - Birth Intervention and The Astrological Face of A New Generation by Wendy StaceySultanademerkadilloNo ratings yet
- Gastrostomy: The Children's HospitalDocument16 pagesGastrostomy: The Children's Hospitalikke alma alukaNo ratings yet
- Water Birth Dissertation IdeasDocument8 pagesWater Birth Dissertation IdeasCanSomeoneWriteMyPaperForMeUK100% (1)
- Research Paper On Exclusive BreastfeedingDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Exclusive Breastfeedingmadywedykul2100% (1)
- Hypospadias - Nursing Care Plan-: Pediatric Nursing Department Faculty of Nursing, UnpadDocument20 pagesHypospadias - Nursing Care Plan-: Pediatric Nursing Department Faculty of Nursing, UnpadAnastasia Yovita SariNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Seminar in NursingDocument12 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Seminar in NursingAnni BarbaNo ratings yet
- 9 Labor and DeliveryDocument6 pages9 Labor and DeliveryUri Perez MontedeRamosNo ratings yet
- 1.assig-Bma New-1Document9 pages1.assig-Bma New-1Ramya SriNo ratings yet
- ClubfootDocument27 pagesClubfootJaya Prabha100% (1)
- CircumcisionDocument8 pagesCircumcisionJoan Marie BelegaNo ratings yet
- BGD Tutorial 2015 - Applied Embryology and TeratologyDocument10 pagesBGD Tutorial 2015 - Applied Embryology and TeratologyRendy YogaNo ratings yet
- Contemprory Issues in ObstetricsDocument6 pagesContemprory Issues in ObstetricsDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- Best Practices in Maternity CareDocument32 pagesBest Practices in Maternity CareFev BanataoNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dystocia and Birth Injury: Prevention and TreatmentFrom EverandShoulder Dystocia and Birth Injury: Prevention and TreatmentNo ratings yet