Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study Guide 1
Study Guide 1
Uploaded by
msmickey24Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Guide 1
Study Guide 1
Uploaded by
msmickey24Copyright:
Available Formats
1.
BSC 1093 Study Questions CHAPTER 1: The Human Body Define: anatomy: Study of the structure of body parts and their relationship to each other principle of complementarity: the relationship between a structure and its function positive feedback: the result or response enhanced the original stimulus so that the response is accelerated. physiology: concerns the function of the body; how body parts work and carry out their life sustaining activities. homeostasis: A state of body equilibrium or stable internal environment of the body. negative feedback: the most common homeostatic control mechanism. The net effect is that the output of the system shuts off the original stimulus or reduces its intensity.
2.
3.
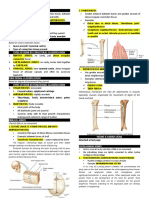
What are three essential concepts related to the human body? Explain each concept, and give an example of each The Complenetarity of Structure: -function is dependent on structure -changes in structure may change function Hierarchy of Structural Organization: -see #3 Homeostasis: -Maintaining a stable internal environment through contol mechanisms. What are the 6 levels of organization, and define what makes up each level (i.e. Chemical Level: Atoms Molecules Cellular: Tissue Level: Epithelium Muscle Connective Tissue Nervous Tissue Organs: Liver Brain Blood Vessels Organ System Level: Cardiovascular Integumentary Muscular Nervous
4.
Endocrine Lymphatic Repiratory Digestive Urinary Reproductive Organismal Level: Humans What are the major functions of the organ systems? organs that work together to perform a specific function in the body. maintain homeostasis
5.
6.
7.
8.
List the 8 functions required for life, and give an example of each. Maintain their boundaries Move Respond to environmental changes Take in and digest nutrients Carry our Metabolism Dispose of wastes Reproduce themselves Grow What are the 5 survival needs? Nutrients Oxygen Water Appropriate temperature Atmospheric pressure What is the purpose of a homeostatic control mechanism? What are the 5 main parts of the mechanism and what is each parts function? Stimulus: Produces change variable. Receptor: detects change. Input: Information sent along afferent pathway to control center. Output: Info sent along efferent pathway to effector. Response: effector feeds bck to reduce the effect of stimuls and returns variable to homeostatic level. Compare and Contrast negative and positive feedback mechanisms, and give an example of each. Negative Feedback takes a stimulus stops or slows it down, which causes variable to change in opposite direction of initial change returning to ideal value. example would be AC set on 70* temp drops below 70* heater kicks on and increases temp above 70* which then turns the heater off.
Positive Feedback is a response that enhanced original stimulus so response is accelerated. change proceeds in same direction as initial change causing it to deviate further from original value. 9. What does a homeostatic imbalance often result in? Disease
You might also like
- Speech 30 SyllabusDocument7 pagesSpeech 30 SyllabusHaruki AkemiNo ratings yet
- EClinicalWorks How To Add Global Alert To Patient's ChartDocument2 pagesEClinicalWorks How To Add Global Alert To Patient's Chartcindi swiftNo ratings yet
- AAP Module 9 SupplementDocument20 pagesAAP Module 9 Supplementmaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- Brainstroming and OrganizingDocument9 pagesBrainstroming and OrganizingFadly ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter One, Structure and Bonding in Organic MoleculesDocument4 pagesChapter One, Structure and Bonding in Organic MoleculesAmin JamjahNo ratings yet
- Intro To Philosophy Notes Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesIntro To Philosophy Notes Cheat SheetLucy100% (1)
- The Impact of Vitamin D Pathway Genetic Variation and Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D On Cancer Outcome. Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument19 pagesThe Impact of Vitamin D Pathway Genetic Variation and Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D On Cancer Outcome. Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDaniel AriasNo ratings yet
- Imaging of UroradiologyDocument32 pagesImaging of UroradiologyAdib Ul IslamNo ratings yet
- Im Dude HandoutDocument1 pageIm Dude Handoutapi-535001113No ratings yet
- The Cell in Its Environment SummaryDocument1 pageThe Cell in Its Environment Summaryapi-292648627100% (1)
- Cognitive Dissonance TheoryDocument2 pagesCognitive Dissonance TheoryRavimohan RajmohanNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue by Dr. Gironella PDFDocument3 pagesConnective Tissue by Dr. Gironella PDFFatima RadeenaNo ratings yet
- Skin InfectionsDocument22 pagesSkin InfectionsoktafNo ratings yet
- Buletin Lp.3Document2 pagesBuletin Lp.3Joana B. NikolovaNo ratings yet
- PainGone Acupoint GuideDocument8 pagesPainGone Acupoint GuideRachel Greene100% (1)
- B Vitamins 1Document1 pageB Vitamins 1api-245692797No ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument12 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptPablo BaudinoNo ratings yet
- The Cell MembraneDocument9 pagesThe Cell MembraneShuchi HossainNo ratings yet
- 3D Printer InformationDocument16 pages3D Printer Informationmahesh mulikNo ratings yet
- Blood and Its Components-NotesDocument10 pagesBlood and Its Components-NotesKelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pearls DermatologíamatologyDocument4 pagesClinical Pearls DermatologíamatologyMaritza24No ratings yet
- 2013 Connective Tissue Quiz ReviewDocument3 pages2013 Connective Tissue Quiz ReviewCarl WeinfieldNo ratings yet
- Classification of Joints 1Document30 pagesClassification of Joints 1Asmat Ullah QureshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Cell Energy Guided NotesDocument3 pagesUnit 3 - Cell Energy Guided NotesKaylee Lopez Student - KnightdaleHSNo ratings yet
- Joints TransesDocument19 pagesJoints TransesskidamarinkNo ratings yet
- Metformin: Its Botanical Background: Practical Diabetes International April 2004Document4 pagesMetformin: Its Botanical Background: Practical Diabetes International April 2004made dwi novitasariNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis: Dr. TonnyDocument10 pagesUrinalysis: Dr. TonnyrkyaritonangNo ratings yet
- What Is Healing Energy - Part 5 Gravity, Structure, and EmotionsDocument9 pagesWhat Is Healing Energy - Part 5 Gravity, Structure, and EmotionsDianaNo ratings yet
- To Remember The Four Causes of Cell InjuryDocument43 pagesTo Remember The Four Causes of Cell Injuryapi-3825096No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument999 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyNacel CelesteNo ratings yet
- Review 4 Chap 12-16Document21 pagesReview 4 Chap 12-16j_docsNo ratings yet
- Cell Fucking MembraneDocument12 pagesCell Fucking MembraneColeen ParejaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Body Systems NotesDocument5 pages2013 Body Systems Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- Cellular Basis of HeredityDocument12 pagesCellular Basis of HeredityLadyvirdi CarbonellNo ratings yet
- Direct File Topic DownloadDocument33 pagesDirect File Topic DownloadJass Sidhu100% (1)
- Panic (Critical) Values 06-14-2021 0Document2 pagesPanic (Critical) Values 06-14-2021 0JorgeNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine: Nendyah RoestijawatiDocument17 pagesFamily Medicine: Nendyah RoestijawatiAuliya SyismaNo ratings yet
- 16.classification of JointsDocument19 pages16.classification of JointsdenekeNo ratings yet
- Concept 3 Notes - Anatomy Basics For StudentsDocument39 pagesConcept 3 Notes - Anatomy Basics For StudentsKaranNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping and Cross MatchingDocument8 pagesBlood Grouping and Cross MatchingJeevitha Vanitha100% (2)
- Nervous System Study GuideDocument4 pagesNervous System Study Guidewalnutqb8No ratings yet
- Chapter 6. HistologyDocument22 pagesChapter 6. Histologymaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- Vitamin What The Vitamin Does Significant Food Sources B1 (Thiamin)Document4 pagesVitamin What The Vitamin Does Significant Food Sources B1 (Thiamin)Safi BroNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Double Effect Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyDocument9 pagesDoctrine of Double Effect Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyCarlos TrNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy Physiology Week 2 3 For LmsDocument88 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy Physiology Week 2 3 For LmsClaire Jasmine Ilao100% (1)
- Disorders Due To Hormone Deficiency (Hyposecretion) : List of Hormonal DisordersDocument2 pagesDisorders Due To Hormone Deficiency (Hyposecretion) : List of Hormonal Disordersritik shuklaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Lecturs 27Document27 pagesImmunology Lecturs 27Rolls SaeedNo ratings yet
- Parameter: ALT AST Parameter AlbuminDocument2 pagesParameter: ALT AST Parameter AlbuminJoe-Anne Eliz WillsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Anatomy and Physiology QuizDocument53 pagesChapter 1 Anatomy and Physiology QuizAylie PilobelloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Related To Clinical PathologyDocument110 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Related To Clinical PathologyMike JohnsonNo ratings yet
- High School Science Virtual Learning: Biology Homeostasi SDocument20 pagesHigh School Science Virtual Learning: Biology Homeostasi SEdchel EspeñaNo ratings yet
- 03 Adaptive Immune SystemDocument14 pages03 Adaptive Immune SystemEnea NastriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document13 pagesAssignment 1Luna100% (1)
- Biochemistry NotesDocument2 pagesBiochemistry NotesFatima Nur Faiza HandaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Yr1Document32 pagesConnective Tissue Yr1aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology The Muscular System MCQ QuizDocument32 pagesAnatomy Physiology The Muscular System MCQ QuizKanwal KhanNo ratings yet
- BIO 230 Exam 1 ReviewDocument31 pagesBIO 230 Exam 1 ReviewRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Major Organic Molecules SlidesDocument13 pagesMajor Organic Molecules Slidesapi-189616674No ratings yet
- Hyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Maintaining A Balance Part 5Document43 pagesMaintaining A Balance Part 5educator56No ratings yet
- Science 6 TG q2Document112 pagesScience 6 TG q2Pinaka ShungaNo ratings yet
- List of English Roots Suffixes and PrefixesDocument44 pagesList of English Roots Suffixes and PrefixesJithin VijayanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Skin Pekan 4 Kelompok 15 Blok Skin FixedDocument17 pagesTutorial Skin Pekan 4 Kelompok 15 Blok Skin Fixedkiki tuanaya1No ratings yet
- Scheuermanns DiseaseDocument26 pagesScheuermanns DiseaseMihnea VulpeNo ratings yet
- Lower Lingual Holding ArchDocument23 pagesLower Lingual Holding ArchJasmine Rey Quinto100% (1)
- Knowledge Regarding Prevention of Helminthic Disease Among School ChildrenDocument5 pagesKnowledge Regarding Prevention of Helminthic Disease Among School ChildrenIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument1 pagePulmonary EdemaLeonardo ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Getting Your Baby To Sleep: by Doctor Kevin and Kate Buchanan-DunneDocument8 pagesGetting Your Baby To Sleep: by Doctor Kevin and Kate Buchanan-Dunneapi-233455171No ratings yet
- Motoric SystemDocument32 pagesMotoric SystemAnisa Zulfiya RahmahNo ratings yet
- ConsiderationDocument3 pagesConsiderationAsvogelNo ratings yet
- Syllabus SCSIDocument92 pagesSyllabus SCSIDcStrokerehab100% (1)
- Therenin Angiotensinaldosteronesystem Final 120401080848 Phpapp02Document53 pagesTherenin Angiotensinaldosteronesystem Final 120401080848 Phpapp02andre kesumaNo ratings yet
- KZN LFSC Grade 10 Step Ahead Learner Support Document 2023Document46 pagesKZN LFSC Grade 10 Step Ahead Learner Support Document 2023jurrymakgoba671No ratings yet
- 11.pharyngeal ApparatusDocument47 pages11.pharyngeal ApparatusChipego NyirendaNo ratings yet
- Body Condition Score Cat Updated August 2020Document1 pageBody Condition Score Cat Updated August 2020Illias AmariciNo ratings yet
- Investigation Methods in HematologyDocument32 pagesInvestigation Methods in HematologyCarmen DuranNo ratings yet
- List Pasien Bedah Rsud DR Pirngadi MedanDocument16 pagesList Pasien Bedah Rsud DR Pirngadi MedanDiah FebruarieNo ratings yet
- 3Document265 pages3Carlos HernándezNo ratings yet
- Yersinia EnterocoliticaDocument5 pagesYersinia EnterocoliticaRahul SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Animal Research Has Been Used For Several Centuries As Part of Efforts To Better Understand The World Around UsDocument2 pagesAnimal Research Has Been Used For Several Centuries As Part of Efforts To Better Understand The World Around UsAshwiniNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cementum: Shreya Das Intern Department of PeriodontiaDocument57 pagesSeminar On Cementum: Shreya Das Intern Department of Periodontiashreya dasNo ratings yet
- Nclex 2Document147 pagesNclex 2Habet Fidem100% (6)
- Annotated BibliographyDocument3 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-354673353No ratings yet
- CBCDocument1 pageCBCAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Case Study RevisedDocument8 pagesCase Study RevisedKjetil Rossignol100% (1)
- Periyar University: B.Sc. ZoologyDocument38 pagesPeriyar University: B.Sc. ZoologyMathematics KingNo ratings yet
- Application Form Health Examination Form Parents Consent Form Camper'SDocument1 pageApplication Form Health Examination Form Parents Consent Form Camper'SRozane Ell JimenezNo ratings yet
- Epi ReviewerDocument4 pagesEpi ReviewerHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy Management of Complications in Patients With Motor Neuron Disease (MND)Document10 pagesPhysiotherapy Management of Complications in Patients With Motor Neuron Disease (MND)YangNo ratings yet
- Clinical Consensus Guidelines DemodicosisDocument44 pagesClinical Consensus Guidelines DemodicosisAnggit StephanieNo ratings yet