Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet 4
Sheet 4
Uploaded by
Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet 4
Sheet 4
Uploaded by
Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaCopyright:
Available Formats
BENHA UNIVERSITY BANHA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
M578 HYDRAULIC POWER SYSTEMS 5 YEAR PRODUCTION ENGINEERING DR. H. EL-BATSH | ENG. ABDALLA MOHAMED
TH
SHEET4: HYDRAULIC ACTUATORS
REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. What is meant by hydraulic actuators? 2. Classify the types of hydraulic actuators based on motion direction. 3. Discuss briefly the function, construction and operation of hydraulic cylinders. 4. What is meant by cushioning? When is it used? Explain how it is designed to perform its function. 5. Discuss the different methods of mounting of hydraulic cylinders. 6. Classify the types of hydraulic motor. 7. Discuss briefly the function of hydraulic motors giving the mathematical expressions describing the ideal and real motors. 8. Explain the construction and operation of gear motor. 9. Explain the buckling calculations in hydraulic cylinders. 10. Deal with the calculation of the cylinder stroke.
PROPLEMS 1. The same hydraulic circuit in the previous problem is used in a simple hydraulic press. The pressing operation has to exert a force of 15 tonnes with a stroke 1 m. The load is pivoted and guided with front flange mounting method of cylinder. Determine a suitable cylinder checking strength and rigidity, and the pump delivery if the required piston speed is 7 m/min. 2. A three stage displacement type telescopic cylinder is used to tilt the body of a lorry. When the lorry is fully laden the cylinder has to exert a force equivalent to 4000 kg at all points in the stroke. The outside diameters of the tubes forming the three stages are 60, 80, and 100 mm. If the pump powering the cylinder delivers 10 liters per minute, calculate the extend speed and pressure required for each stage of the cylinder when tilting a fully laden lorry.
3. A displacement type cylinder has a rod of 65 mm diameter and is powered by a hand pump with a displacement of 5 ml per double stroke. The maximum operating pressure of the system is to be limited to 350 bar. a. Draw a suitable circuit diagram showing the cylinder, pump and any additional valve. b. Calculate the number of double pumping strokes needed to extend the cylinder rod by 50 mm. c. Calculate the maximum load which could be raised using this system.
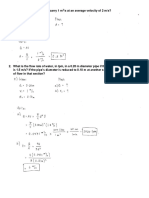
4. A hydraulic cylinder has a bore of 200 mm and a piston rod diameter of 140 mm. For an extend speed of 5 m/min, calculate: a. The supply flow rate (QE) b. The flow rate from the annulus side on exted (qE) c. The retract speed using QE, and d. The flow rate from the full bore end on retract (QR). e. If the maximum pressure applied to the cylinder is 100 bar, calculate the extend and retract thrust. 5. A mass of 2000 kg is to be accelerated horizontally up to a velocity of 1 m/s from rest over a distance of 50 mm. The coefficient of friction between the load and the guides is 0.15. Calculate the bore of the cylinder required to
accelerate this load if the maximum allowable pressure at the full bore is 100 bar. (Take seal friction to be equivalent to a pressure drop of 5 bar. Assume the back pressure at the annulus end of the cylinder is zero)
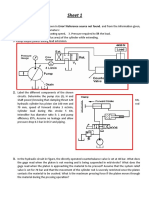
6. The given hydraulic system has the following parameters: Pump Is an axial piston pump of swash plate type Piston diameter 8 mm Pitch circle diameter 3 cm Swash plate inclination angle 20 Mechanical efficiency 0.9 Total efficiency 0.81 Number of pistons 7 Pump speed 3000 rpm Relief valve Is preset at a relief pressure of 10 MPa Hydraulic Is an ideal cylinder, loaded by a cylinder constant load of 160 kN and piston and piston rod diameters are 10 cm and 7 cm respectively. Check valve Is of zero cracking pressure. Throttle valve Is sharp edged of 6 mm2 cross sectional area. Hydraulic oil Is of 850 kg/m3 density.
a. Explain the function of the system. b. Calculate the piston speed and pump driving power at the different positions of the DCV, if the pressure in the pump delivery line doesn't reach the preset relief pressure. Neglect the losses in lines and DCV.
7. For the following system, calculate: a. The pump geometric volume. b. The pump exit pressure. c. The constant K of the relief valve.
8. In the given system, a hydraulic cylinder of 10 cm inner diameter is driving a constant load of 150 kN with a constant speed of 6 cm/s. The pump total efficiency is 0.8. Explain the function of the system and calculate: a. The pump exit pressure and pump flow. b. The pump driving power and torque if the pump input pressure is increased to 0.3 MPa by means of a booster pump, n = 3000 rpm. c. The maximum possible cylinder load and corresponding pump driving power if the maximum pressure preset at the relief valve is 30 MPa.
9. The hydraulic cylinder shown in the figure has a 3 in bore and is to operate at a pressure of 800 psi. With the clevis mount shown, the piston rod should be sized as a column with both ends rounded for any plane buckling. The rod is to be made of forged AISI 1030 steel without further heat treatment.
(a) Use a design factor n=3 and select a preferred size for the rod diameter if the column length is 60 in. (b) Repeat part (a) but for a column of 18 in (c) What factor of safety actually results for each of the cases above
10. A cylinder has to apply extend force of 80 kN and retract force of 10 kN. The retract speed should be 5 m/min using full pump flow. The maximum pump pressure is 150 bar and the pressure drops over the filter is 3 bar and over the directional valve (for each path) is 2 bar. Determine the cylinder size (assuming 2:1 ratio piston area to piston rod area). Determine also the pump size and circuit efficiency during extend and during retract. Note: The available cylinder diameters are: 50 mm, 63 mm, 80 mm, 100 mm, 125 mm, 150 mm, 180 mm, 200 mm
DUE DATE: NEXT WEEK | 1,2 DAYS AFTER D.D.: -10% | 3,7: -20% | 8,14: -40% | >15: 0 PLAGIARISM = 0 | A4 PAPERS | NAME, SECTION & SUBJECT ONLY; CLEAR ON THE 1ST PAPER ONLY
You might also like
- Đề thi HK221Document4 pagesĐề thi HK221Hải NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Oberon 1Document321 pagesOberon 1Grandfather NurgleNo ratings yet
- 2 (Pumps)Document2 pages2 (Pumps)arsenic_94100% (1)
- ME2135E Fluid Mechanics II Tutorial 1Document3 pagesME2135E Fluid Mechanics II Tutorial 1Law Zhan Hong0% (1)
- Microbiological Specifications Nestle PDFDocument24 pagesMicrobiological Specifications Nestle PDFmadiha altafNo ratings yet
- Form To Correct Errors in CGHS CardDocument1 pageForm To Correct Errors in CGHS CardsachinkurhekarNo ratings yet
- Nihongo Connections-Part 1Document285 pagesNihongo Connections-Part 1Julie BruchNo ratings yet
- Contractor Safety Stand Down 2016Document25 pagesContractor Safety Stand Down 2016ekoimampNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6Document5 pagesSheet 6Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- New Sheet - CorrectedDocument19 pagesNew Sheet - CorrectedklashincoviskyNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument27 pagesTutorialbassemNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power Systems - Sheet 2Document4 pagesFluid Power Systems - Sheet 2Mohamed Maher100% (1)
- Steam EnginesDocument6 pagesSteam Engineschat2adiNo ratings yet
- Ajay Kumar Garg Engineering College, Ghaziabad: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesAjay Kumar Garg Engineering College, Ghaziabad: Department of Mechanical EngineeringMradul GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2135 Tutorial 1Document4 pages2135 Tutorial 1Eezhar JumadiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power AutomationquestonsDocument3 pagesFluid Power AutomationquestonsSriram Nanjangud SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt 05Document3 pagesAssignemnt 05Abdalrhman SayedNo ratings yet
- SumsDocument3 pagesSumssp2532658.1970No ratings yet
- Sheet 2 - HydraulicDocument4 pagesSheet 2 - HydraulicbassemNo ratings yet
- r5310302 Hydraulic Machinery and SystemsDocument4 pagesr5310302 Hydraulic Machinery and SystemswirelessandlessNo ratings yet
- Week Two Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerDocument2 pagesWeek Two Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerhellfireNo ratings yet
- Week Two Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerDocument2 pagesWeek Two Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerhellfireNo ratings yet
- Week Two Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerDocument2 pagesWeek Two Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid Powermustafa1011No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of FluidesDocument2 pagesFundamentals of FluidesAbderrahman ZINE EL ABIDINENo ratings yet
- Structural Calculation EOTDocument2 pagesStructural Calculation EOTAmarnath0% (1)
- Week Two Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerDocument2 pagesWeek Two Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerhellfireNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2zul hilmiNo ratings yet
- 9A01308 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument4 pages9A01308 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 New PDFDocument3 pagesSheet 4 New PDFMahmoud GaballaNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt 02Document4 pagesAssignemnt 02Abdalrhman SayedNo ratings yet
- HDM360S Tutorial 2-2024 - Hydraulic PumpsDocument5 pagesHDM360S Tutorial 2-2024 - Hydraulic Pumpssmisosphamandla30No ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document3 pagesAssignment 6Muhammad Jawad IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Muzeyin FocusDocument3 pagesMuzeyin FocuseyobNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4Document5 pagesSheet 4vector mosesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document5 pagesWorksheet 1DANIEL WELDAYNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery II Seme2 2006Document2 pagesFluid Machinery II Seme2 2006Arindam MisraNo ratings yet
- Hy 2nd Exam Spring 2018Document4 pagesHy 2nd Exam Spring 2018FahedNo ratings yet
- AQ Fluid Machinery-1Document3 pagesAQ Fluid Machinery-1Sourabh BelladNo ratings yet
- CH3080 Problem Set1to3 2014Document7 pagesCH3080 Problem Set1to3 2014iifNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 4Document6 pagesChapter No 4gotu123No ratings yet
- Hydarulic SheetsDocument11 pagesHydarulic Sheetsأحمد عبدالجليلNo ratings yet
- FM 15 MarksDocument5 pagesFM 15 MarksPriyanka PrakashNo ratings yet
- 9A01308 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachineryDocument4 pages9A01308 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt 04Document2 pagesAssignemnt 04Abdalrhman SayedNo ratings yet
- DPBC Question BankDocument10 pagesDPBC Question BankshubhamNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document15 pagesProblem Set 1Silva, Joe Mari T.No ratings yet
- Turbo Machinery Tutorial - Jan-Feb 2012Document3 pagesTurbo Machinery Tutorial - Jan-Feb 2012Suchithra RamanNo ratings yet
- MEC 4106 Pumps Tutorial SheetDocument6 pagesMEC 4106 Pumps Tutorial SheetleitchNo ratings yet
- TM 7me4a Question Bank Mid Term IDocument1 pageTM 7me4a Question Bank Mid Term IVijay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sheet5-Centrifugal PumpDocument5 pagesSheet5-Centrifugal Pumpyousef mohamedNo ratings yet
- Fluid MachinesDocument14 pagesFluid MachinesNishankzattNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 Turbomachinery v2Document4 pagesTutorial 4 Turbomachinery v2Nik JaffNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Components and SystemsDocument31 pagesHydraulic Components and SystemsPrasad ChamarajanagarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 HydraulicsDocument31 pagesUNIT 5 Hydraulicsnandu20No ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document3 pagesSheet 2Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- DMM-2 3 1 Q&aDocument6 pagesDMM-2 3 1 Q&aAnand vinayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet PneumaticsDocument2 pagesWorksheet PneumaticsSamuel WozabNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines Question BankDocument11 pagesHydraulic Machines Question BankAdit Gaur100% (3)
- 1.trial On Gear PumpDocument6 pages1.trial On Gear PumpAlmas 1710No ratings yet
- 1.trial On Gear PumpDocument6 pages1.trial On Gear PumpAlmas 1710No ratings yet
- Assignment and WorksheetDocument2 pagesAssignment and WorksheetAbebe AyingdaNo ratings yet
- Assignment I 3rd RegularDocument2 pagesAssignment I 3rd RegularRoha EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Sheet No2Document7 pagesSheet No2Ismail SakrNo ratings yet
- OAFISjLOEeiP Qrke KVoA Setting A Sales Goal AOSDocument1 pageOAFISjLOEeiP Qrke KVoA Setting A Sales Goal AOSAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Engineering From Home: White PaperDocument7 pagesEngineering From Home: White PaperAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Conveyor Systems: TrainingDocument3 pagesHydraulics and Conveyor Systems: TrainingAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Polysulfone / Graphene Oxide / Polyethylene Glycol / Triaminopyrimidine by Using Response Surface MethodologyDocument8 pagesOptimization of Polysulfone / Graphene Oxide / Polyethylene Glycol / Triaminopyrimidine by Using Response Surface MethodologyAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Tensile Properties of Epoxy/graphene Nano-Platelets/ Carboxylated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber Ternary Nanocomposites Using Response Surface MethodologyDocument12 pagesInvestigation On Tensile Properties of Epoxy/graphene Nano-Platelets/ Carboxylated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber Ternary Nanocomposites Using Response Surface MethodologyAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Dd422i Specification Sheet EnglishDocument4 pagesDd422i Specification Sheet EnglishAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Research Grant Donors: ItidaDocument5 pagesResearch Grant Donors: ItidaAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- PublicationDocument1 pagePublicationAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- #Aimenjobs: R&D Senior Researcher in Advanced Materials: Polymer and CompositesDocument2 pages#Aimenjobs: R&D Senior Researcher in Advanced Materials: Polymer and CompositesAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- W 4 Yte 54 SyDocument2 pagesW 4 Yte 54 SyAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Statement: Roberto Silveira Silva FilhoDocument2 pagesTeaching Statement: Roberto Silveira Silva FilhoAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Creating Effective Scientific Figures For PublicationDocument24 pagesCreating Effective Scientific Figures For PublicationAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- ﻝﺎﻤﻟﺍ ﺓﺪﻳﺮﺟ ﺭﺎﺒﺧﺃ ﻢﻫﺃ (Alltopstories - 1.Aspx/) : ﻙﻮـــﻨﺑ (Section/12/1/بنـــوك/)Document9 pagesﻝﺎﻤﻟﺍ ﺓﺪﻳﺮﺟ ﺭﺎﺒﺧﺃ ﻢﻫﺃ (Alltopstories - 1.Aspx/) : ﻙﻮـــﻨﺑ (Section/12/1/بنـــوك/)Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- CourseworkFEA CAD 2015Document4 pagesCourseworkFEA CAD 2015Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis AssignmentDocument1 pageStress Analysis AssignmentAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Formal Supervision Meeting Record Template - PGR-PROG-04Document2 pagesFormal Supervision Meeting Record Template - PGR-PROG-04Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- College of Accountancy, Business, Economics and International Hospitality ManagementDocument32 pagesCollege of Accountancy, Business, Economics and International Hospitality ManagementDavid DinglasanNo ratings yet
- CRM # 4044662347 (Zpec # 5)Document1 pageCRM # 4044662347 (Zpec # 5)Mohammad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Heermm ToolDocument18 pagesHeermm ToolJuan PabloNo ratings yet
- Understanding Order ProcessDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Order ProcessfilipNo ratings yet
- Report - SharifDocument58 pagesReport - SharifNabilNo ratings yet
- Ex-Probation Chief Takes Stand To Defend Child Porn: Ppoossttaall PprroobblleemmDocument28 pagesEx-Probation Chief Takes Stand To Defend Child Porn: Ppoossttaall PprroobblleemmSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Basic Principles of Communication: StructureDocument18 pagesUnit 1 Basic Principles of Communication: Structuresastrylanka_1980No ratings yet
- Prototype TutorialDocument451 pagesPrototype TutorialMariela DemarkNo ratings yet
- Camera Control Pro 2 ManualDocument118 pagesCamera Control Pro 2 ManualBigHeadLittleFeetNo ratings yet
- GTNetS ManualDocument148 pagesGTNetS ManualJatin JaniNo ratings yet
- Extractor de Probetas DEMTECHDocument2 pagesExtractor de Probetas DEMTECHPaul Alex Quiroz BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Imaging CasesDocument278 pagesCardiac Imaging Casesandrew100% (2)
- Market Development ReportDocument121 pagesMarket Development ReportSrivinayaga XNo ratings yet
- Diass New Module 1 2022Document6 pagesDiass New Module 1 2022sheridan dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Old Age Pension VeteranDocument2 pagesOld Age Pension VeteranLADY LYN SANTOSNo ratings yet
- CS Dec 2018-Jan 2019 PDFDocument78 pagesCS Dec 2018-Jan 2019 PDFPavanNo ratings yet
- Added by Guest, Last Edited by Guest On Jun 12, 2007 Show CommentDocument5 pagesAdded by Guest, Last Edited by Guest On Jun 12, 2007 Show CommentNarendrareddy RamireddyNo ratings yet
- Contemp Final ReviewerDocument8 pagesContemp Final ReviewerKen ManilayNo ratings yet
- Sales ManagementDocument26 pagesSales ManagementBenita S MonicaNo ratings yet
- PBM Presentation GroupsDocument7 pagesPBM Presentation GroupsnikhilNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor Specification Sheet: Operating ConditionsDocument6 pagesCentrifugal Compressor Specification Sheet: Operating ConditionsIsmail SayyedNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Module 2Document11 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module 2Glory NeriNo ratings yet
- CrsDocument660 pagesCrsaamirmehmoodkhanNo ratings yet
- Subject - Verb AgreementDocument12 pagesSubject - Verb AgreementRistaNo ratings yet
- An5265 LT5265Document4 pagesAn5265 LT5265maldomattNo ratings yet