Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Instructional Shifts For The C C Common Core
Instructional Shifts For The C C Common Core
Uploaded by
gcimorelliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Instructional Shifts For The C C Common Core
Instructional Shifts For The C C Common Core
Uploaded by
gcimorelliCopyright:
Available Formats
Instructional Shifts for the Common Core C C
www.engageNY.org
Instructional Shifts for the Common Core
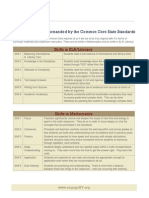
Six Shifts in ELA/Literacy
Balancing Informational and Literary Text y Building Knowledge in the Disciplines Staircase of Complexity p y Text-Based Answers Writing From Sources Academic Vocabulary
Six Shifts in Math
Focus Coherence Fluency Deep Understanding A li ti Applications Dual Intensity
www.engageNY.org
NYS Common Core Standards Shifts Impact NYS Assessments
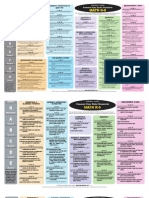
6 Shifts in ELA Literacy
Common Core Implementation
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 5 6.
Balancing Informational and Literary Text Building Knowledge in the Disciplines Staircase of Complexity Text-based Answers Writing from Sources Academic Vocabulary
Common Core Assessments
1 & 2: 3: 4&5: 6: Non-fiction Texts Authentic Texts Higher Level of Text Complexity g Paired Passages Focus on command of evidence from text: rubrics and prompts Academic Vocabulary
6 Shifts in Mathematics
1. 2. 2 3. 4.
Focus Coherence C h Fluency Deep Understanding
1: 2:
Intensive Focus Linking Back
5. Applications
6. Dual Intensity
4, 5, 6: Mathematical Modeling
www.engageNY.org
Six Shifts in ELA/Literacy
Shift 1 PK-5, Balancing Informational & Literary Texts 6-12, Building Knowledge in the Disciplines Staircase of Complexity Students read a true balance of informational and literary texts. Elementary school classrooms are, therefore, places where students access the world science, social studies, the arts and literature through text. At least 50% of what students read is informational.
Shift 2
Content area teachers outside of the ELA classroom emphasize literacy experiences in their planning and instruction. Students learn through domain-specific texts in science and social studies classrooms rather than referring to the text, they are expected to learn from what they read.
Shift 3
In order to prepare students for the complexity of college and career ready texts, each g p p p y g y grade level requires a step q p of growth on the staircase. Students read the central, grade appropriate text around which instruction is centered. Teachers are patient, create more time and space in the curriculum for this close and careful reading, and provide appropriate and necessary scaffolding and supports so that it is possible for students reading below grade level. Students have rich and rigorous conversations which are dependent on a common text. Teachers insist that classroom experiences stay deeply connected to the text on the page and that students develop habits for making evidentiary arguments both in conversation, as well as in writing to assess comprehension of a text. Writing needs to emphasize use of evidence to inform or make an argument rather than the personal narrative and other forms of decontextualized prompts. While the narrative still has an important role, students develop skills through written arguments that respond to the ideas, events, facts, and arguments presented in the texts they read. Students constantly build the vocabulary they need to access grade level complex texts. By focusing strategically on comprehension of pivotal and commonly found words (such as discourse, generation, theory, and principled) and less on esoteric literary terms (such as onomatopoeia or homonym), teachers constantly build students ability to access more complex texts across the content areas.
Shift 4
Text-Based Answers
Shift 5
Writing from Sources
Shift 6
Academic Vocabulary
www.engageNY.org
Six Shifts in Math
Shift 1 Focus Teachers use the power of the eraser and significantly narrow and deepen the scope of how time and energy is spent in the math classroom. They do so in order to focus deeply on only the concepts that are prioritized in the standards so that students reach strong foundational knowledge and deep conceptual understanding and are able to transfer mathematical skills and understanding across concepts and grades. Principals and teachers carefully connect the learning within and across grades so that, for example, fractions or multiplication spiral across grade levels and students can build new understanding onto foundations built in previous years. Teachers can begin to count on deep conceptual understanding of core content and build on it. Each standard is not a new event, but an extension of previous learning. Students are expected to have speed and accuracy with simple calculations; teachers structure class time and/or homework time for students to memorize, through repetition, core functions (found in the attached list of fluencies) such as multiplication tables so that they are more able to understand and manipulate more complex concepts. Teachers teach more than how to get the answer and instead support students ability to access concepts from a number of perspectives so that students are able to see math as more than a set of mnemonics or discrete procedures. procedures Students demonstrate deep conceptual understanding of core math concepts by applying them to new situations. as well as writing and speaking about their understanding. Students are expected to use math and choose the appropriate concept for application even when they are not prompted to do so. Teachers provide opportunities at all grade levels for students to apply math concepts in real world situations. Teachers in content areas outside of math, particularly science, ensure that students are using math at all grade levels to make meaning of and access content content. Students are practicing and understanding. There is more than a balance between these two things in the classroom both are occurring with intensity. Teachers create opportunities for students to participate in drills and make use of those skills through extended application of math concepts. The amount of time and energy spent practicing and understanding learning environments is driven by the specific mathematical concept and therefore, varies throughout the given school year year.
Shift 2
Coherence
Shift 3
Fluency
Shift 4
Deep Understanding
Shift 5
Applications
Shift 6
Dual Intensity
www.engageNY.org
You might also like
- Iep ExampleDocument3 pagesIep Exampleapi-272643348No ratings yet
- DLL in MATH - WEEK 10Document4 pagesDLL in MATH - WEEK 10Norielee Glayze50% (2)
- rdg323 Disciplinary Literacy PaperDocument8 pagesrdg323 Disciplinary Literacy Paperapi-488068102No ratings yet
- Portfolio Pre-Observation Close ReadDocument6 pagesPortfolio Pre-Observation Close Readapi-279291777No ratings yet
- Maternity Leave FAQDocument11 pagesMaternity Leave FAQgcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Name of Teacher: Ria Richelle T. Sicat Date: July 15, 2019 Grade and Section: V-Galilei Time: 8::00-8:50 AM CP: 09068576951Document11 pagesName of Teacher: Ria Richelle T. Sicat Date: July 15, 2019 Grade and Section: V-Galilei Time: 8::00-8:50 AM CP: 09068576951Ria Richelle Pineda TalucodNo ratings yet
- Ccss ShiftsDocument1 pageCcss ShiftsCarolyn CarterNo ratings yet
- Common Core Snapshot: Administrator's Guide to the Common CoreFrom EverandCommon Core Snapshot: Administrator's Guide to the Common CoreNo ratings yet
- Common Core ShiftsDocument1 pageCommon Core ShiftsZeeallNo ratings yet
- Common Core ShiftsDocument1 pageCommon Core Shiftsapi-196719233No ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - TEFL 2Document4 pagesAssignment 3 - TEFL 2LiliskurniaNo ratings yet
- Art Exemplary TeachersDocument14 pagesArt Exemplary TeachersLisa HandlineNo ratings yet
- Disciplinary Literacy A Shift That Makes SenseDocument6 pagesDisciplinary Literacy A Shift That Makes SenseYana ArsyadiNo ratings yet
- rdg323 Final Course ReflectionDocument7 pagesrdg323 Final Course Reflectionapi-488068102No ratings yet
- Shifts in MathematicsDocument1 pageShifts in MathematicsEdison FyeNo ratings yet
- EES 4 Detail 2Document15 pagesEES 4 Detail 2York Daily Record/Sunday NewsNo ratings yet
- District-Wide Instructional Practices - October 2014 With PCC ActivitiesDocument27 pagesDistrict-Wide Instructional Practices - October 2014 With PCC Activitiesapi-289599068No ratings yet
- Precisassignment LessonplanDocument2 pagesPrecisassignment Lessonplanvenkatesh286No ratings yet
- Publishers Criteria For 3-12Document19 pagesPublishers Criteria For 3-12fitness255No ratings yet
- TpesDocument18 pagesTpesapi-419554205No ratings yet
- Directed Learning Experience: Question #9: Focus On Content Area Literacies in Elementary ClassroomsDocument15 pagesDirected Learning Experience: Question #9: Focus On Content Area Literacies in Elementary Classroomsapi-661064468No ratings yet
- Example Research Paper On Learning StylesDocument5 pagesExample Research Paper On Learning Stylesfvg4mn01100% (1)
- Snap Shot of ResponsesDocument2 pagesSnap Shot of Responsesapi-252743869No ratings yet
- Ued 496 Isabella Szczur Student Teaching Rationale and Reflection Paper 3Document7 pagesUed 496 Isabella Szczur Student Teaching Rationale and Reflection Paper 3api-445773759No ratings yet
- Literacy Unit - Ci-5055Document15 pagesLiteracy Unit - Ci-5055api-242111818No ratings yet
- Commo CoreDocument12 pagesCommo CorevalloleticagabNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary CurriculumDocument18 pagesInterdisciplinary CurriculumAndi Ulfa Tenri Pada100% (1)
- Empowerment Through Recognition of Difference: Differentiated Instruction inDocument52 pagesEmpowerment Through Recognition of Difference: Differentiated Instruction inMelchor CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Factors To Consider in Writing IMs (Ornstein), Principles of Materials DesignDocument4 pagesFactors To Consider in Writing IMs (Ornstein), Principles of Materials DesignAlfeo Original100% (1)
- TN Race To The Trough Appendix BDocument259 pagesTN Race To The Trough Appendix BhorbunceNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Factors To Consider in Writing IMs (Ornstein), Principles of Materials DesignDocument4 pagesWeek 3 - Factors To Consider in Writing IMs (Ornstein), Principles of Materials DesignAlfeo Original100% (1)
- Explicit Vocabulary Instruction in MathDocument10 pagesExplicit Vocabulary Instruction in Mathapi-249323843No ratings yet
- Disciplinary Literacy PaperDocument7 pagesDisciplinary Literacy Paperapi-334004109No ratings yet
- HBEL 3203 Teaching of Grammar: Fakulti Pendidikan Dan BahasaDocument22 pagesHBEL 3203 Teaching of Grammar: Fakulti Pendidikan Dan BahasaMilly Hafizah Mohd KanafiaNo ratings yet
- Sample Research Paper Classroom ManagementDocument5 pagesSample Research Paper Classroom Managementxkcwaaqlg100% (1)
- Interacting with Informational Text for Close and Critical ReadingFrom EverandInteracting with Informational Text for Close and Critical ReadingNo ratings yet
- Integrated Method of Teaching by ShilpaDocument8 pagesIntegrated Method of Teaching by ShilpaMayank Jha100% (1)
- Strategy CatalogueDocument5 pagesStrategy Catalogueapi-288560316No ratings yet
- Unit 4 BENLAC A BDocument28 pagesUnit 4 BENLAC A BLeah Angelica BerdulagaNo ratings yet
- Content Area ReadingDocument30 pagesContent Area ReadingJohnjohn GalanzaNo ratings yet
- Eddn680 Siop Lesson 1Document13 pagesEddn680 Siop Lesson 1api-645071941No ratings yet
- Term Paper Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesTerm Paper Lesson Planafmzatvuipwdal100% (2)
- Edu80016 - Assess-Curriculum LinkDocument7 pagesEdu80016 - Assess-Curriculum LinkSalima Abdallah ObeidNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Methodological Approaches: General InformationDocument11 pagesAssignment: Methodological Approaches: General InformationBernar LopezNo ratings yet
- Crosscurricular Teaching and Learning EnglishDocument8 pagesCrosscurricular Teaching and Learning EnglishLug TherapieNo ratings yet
- Full Instructional PlanDocument48 pagesFull Instructional Planapi-308564826No ratings yet
- Midterm - Act 1.Document5 pagesMidterm - Act 1.Lynnah SibongaNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based StrategiesDocument9 pagesEvidence-Based Strategiesapi-534236220No ratings yet
- Artifact #5: Guided Reading Lesson Plan - EDL 550 Developmental LiteracyDocument14 pagesArtifact #5: Guided Reading Lesson Plan - EDL 550 Developmental Literacyapi-288924191No ratings yet
- Ninth Grade Art of Persuasion Unit PlanDocument38 pagesNinth Grade Art of Persuasion Unit Planapi-534313864No ratings yet
- Teaching Math ContextuallyDocument69 pagesTeaching Math ContextuallyBuried_ChildNo ratings yet
- Academic Literacy PDFDocument11 pagesAcademic Literacy PDFLalrinmawiiNo ratings yet
- Theme: What Is Based Curriculum?Document7 pagesTheme: What Is Based Curriculum?Benjamin James Teleb AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Ccss Disciplinary Literacy StatementDocument11 pagesCcss Disciplinary Literacy Statementapi-263457923No ratings yet
- Id490 How Students Learn and StudyDocument4 pagesId490 How Students Learn and StudyB.y. NgNo ratings yet
- How Can You Create Opportunities in Your Courses To Support and Affirm Identity Development of English Learners and Students Exhibiting Math Anxiety?Document10 pagesHow Can You Create Opportunities in Your Courses To Support and Affirm Identity Development of English Learners and Students Exhibiting Math Anxiety?pnewsie324No ratings yet
- Lpcommentary 2Document2 pagesLpcommentary 2api-244609939No ratings yet
- THESIS 1 To 4 Sample FormatDocument123 pagesTHESIS 1 To 4 Sample FormatJwhll MaeNo ratings yet
- 21 Century SUSD CharacteristicsDocument10 pages21 Century SUSD Characteristicscresta2014No ratings yet
- Text 5 - Cross-Curricular Teaching and Learning - Practice MatrixDocument2 pagesText 5 - Cross-Curricular Teaching and Learning - Practice MatrixMaja BušatovićNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary CurriculumDocument4 pagesInterdisciplinary Curriculumapi-2949209900% (1)
- Teaching For UnderstandingDocument3 pagesTeaching For UnderstandingPuspa RosdiNo ratings yet
- Otl565 Module 6Document10 pagesOtl565 Module 6api-250173714No ratings yet
- 6 Grade News: His Month: TDocument5 pages6 Grade News: His Month: TgcimorelliNo ratings yet
- NCCS Young Writers 2015Document575 pagesNCCS Young Writers 2015gcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Media Circut Fall 2012Document2 pagesMedia Circut Fall 2012gcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Enter Grades Through GradebookDocument2 pagesEnter Grades Through GradebookgcimorelliNo ratings yet
- I C To SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesI C To SpreadsheetgcimorelliNo ratings yet
- A-Boght Times: BullyingDocument14 pagesA-Boght Times: BullyinggcimorelliNo ratings yet
- OctoberDocument1 pageOctobergcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Ic 2Document7 pagesIc 2gcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Period 3 GeometryDocument23 pagesPeriod 3 GeometrygcimorelliNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up The Grade Book Navigate To AssignmentsDocument5 pagesHow To Set Up The Grade Book Navigate To AssignmentsgcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Grades KChecklistsfor Common Core CCSSMath Poster SizeDocument12 pagesGrades KChecklistsfor Common Core CCSSMath Poster SizegcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Woman in This PictureDocument31 pagesWoman in This PicturegcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Ela Grade 7Document22 pagesEla Grade 7gcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Test: Book 2Document12 pagesMathematics Test: Book 2gcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Ela Grade 6Document24 pagesEla Grade 6gcimorelli100% (1)
- Math Grade 6Document19 pagesMath Grade 6gcimorelli100% (1)
- Summer 2012 PostingDocument13 pagesSummer 2012 PostinggcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 8Document15 pagesMath Grade 8gcimorelli0% (1)
- Math Grade 5Document13 pagesMath Grade 5gcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 7Document20 pagesMath Grade 7gcimorelliNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 4Document14 pagesMath Grade 4gcimorelliNo ratings yet
- LP 4a'sDocument3 pagesLP 4a'sronald bantuganNo ratings yet
- Mock Trial Lesson Plan 10 - 20 NEWDocument3 pagesMock Trial Lesson Plan 10 - 20 NEWKylie BrunerNo ratings yet
- SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsDocument5 pagesSDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsSalve SerranoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Field StudyDocument9 pagesSyllabus Field Studyjustine100% (2)
- Brielle Welch ResumeDocument2 pagesBrielle Welch Resumeapi-341523362No ratings yet
- DLL - EN6 1st Quarter Week 10 Day 4Document2 pagesDLL - EN6 1st Quarter Week 10 Day 4Jeclyn D. FilipinasNo ratings yet
- Dr.D.Y. Patil College of Education Akurdi-44 MCQ Questions 203 School and Inclusive SchoolDocument24 pagesDr.D.Y. Patil College of Education Akurdi-44 MCQ Questions 203 School and Inclusive SchoolBosky Shah100% (1)
- Iwar 2021Document31 pagesIwar 2021Glenda B. RamosNo ratings yet
- ENG2P Outline 2012-2013Document4 pagesENG2P Outline 2012-2013Danika BarkerNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitaeapi-355257346No ratings yet
- Inquiry Based LearningDocument96 pagesInquiry Based LearninglovechelNo ratings yet
- PR 1 Week 8 Q1 DLLDocument3 pagesPR 1 Week 8 Q1 DLLJap Caranza LagunillaNo ratings yet
- Pulo National High School: Department of EducationDocument3 pagesPulo National High School: Department of EducationËlõysë ÖlbāpNo ratings yet
- Senior High: Lesson Plan 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument2 pagesSenior High: Lesson Plan 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldRigene CalaloNo ratings yet
- ICARE Based Instruction Model On IctDocument24 pagesICARE Based Instruction Model On Ictanon_728564744No ratings yet
- National Reading Program DLLDocument4 pagesNational Reading Program DLLmarissaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Designing and Developing Effective HRD ProgramsDocument37 pagesChapter 8 Designing and Developing Effective HRD ProgramsVincent Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Soc73165 100 - User Training and Adult EducationDocument3 pagesCourse Outline - Soc73165 100 - User Training and Adult Educationapi-382689726No ratings yet
- Teaching Philosophy Statement Example #1Document5 pagesTeaching Philosophy Statement Example #1Dilruk GallageNo ratings yet
- Graduate School ResumeDocument2 pagesGraduate School ResumeDeborah CreekmoreNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in MathematicsDocument1 pageAction Plan in MathematicsPeach CuyosNo ratings yet
- 4 Key Concepts of AndragogyDocument7 pages4 Key Concepts of AndragogyJoshuaNo ratings yet
- 3 MTBDocument3 pages3 MTBAlbert MarzanNo ratings yet
- Lifelong Learning Programme Comenius Application Form 2011 For Comenius Regio PartnershipsDocument37 pagesLifelong Learning Programme Comenius Application Form 2011 For Comenius Regio PartnershipsAlina CaldararuNo ratings yet
- Report For David Kinnersley Lat Trobe Student TeacherDocument2 pagesReport For David Kinnersley Lat Trobe Student Teacherapi-294882880No ratings yet
- Narrative Report PRIMALS PLUSDocument3 pagesNarrative Report PRIMALS PLUSDHEMIE PIODONo ratings yet
- Article ProcrastinationDocument1 pageArticle ProcrastinationAzlinda SamsuriNo ratings yet