Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Logical Channels in GSM: Downlink
Logical Channels in GSM: Downlink
Uploaded by
chillcasterOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Logical Channels in GSM: Downlink
Logical Channels in GSM: Downlink
Uploaded by
chillcasterCopyright:
Available Formats
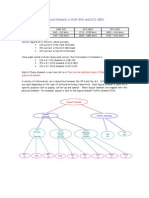
Logical channels in GSM The main types of signalling chnnels are: i) ii) iii) iv) Broadcast Channels BCH
Common Control Channels CCCH Associated Control Channels ACCH Standalone Dedicated Control Channel SDCCH
Broadcast Channels This channel is transmitted from BTS to MS. This channel comprise of information about system parameters including network identification, synchronization time, frequency with network etc. Broadcast channels include: Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH) Synchronization Channel (SCH) Cell Broadcast Channel (CBCH)
Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) - DOWNLINK - This channel contains system parameters needed to identify the network and gain access. These parameters include the Location Area Code (LAC), the Mobile Network Code (MNC), the frequencies of neighboring cells, and access parameters. Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH) - DOWNLINK - This channel is used by the MS as a frequency reference. This channel contains frequency correction bursts. Synchronization Channel (SCH) - DOWNLINK - This channel is used by the MS to learn the Base Station Information Code (BSIC) as well as the TDMA frame number (FN). This lets the MS know what TDMA frame they are on within the hyperframe. Cell Broadcast Channel (CBCH) - DOWNLINK - This channel is not truly its own type of logical channel. The CBCH is for point-to-omnipoint messages. It is used to broadcast specific information to network subscribers; such as weather, traffic, sports, stocks, etc. Messages can be of any nature depending on what service is provided. Messages are normally public service type messages or announcements. The CBCH isnt allocated a slot for itself, it is assigned to an SDCCH. It only occurs on the downlink. The CBCH usually occupies the second subslot of the SDCCH. The mobile will not acknowledge any of the messages.
Common Control Channels CCCH is used for signalling between BTS and MS and its purpose is to request as well as grant network access to the subscriber.
Common Control Channels include: Paging Channel (PCH) Random Access Channel (RACH) Access Grant Channel (AGCH)
Paging Channel (PCH) - DOWNLINK - This channel is used to inform the MS that it has incoming traffic. The traffic could be a voice call, SMS, or some other form of traffic. Random Access Channel (RACH) - UPLINK This channel is used by a MS to request an initial dedicated channel from the BTS. This would be the first transmission made by a MS to access the network and request radio resources. The MS sends an Access Burst on this channel in order to request access. Access Grant Channel (AGCH) - DOWNLINK - This channel is used by a BTS to notify the MS of the assignement of an initial SDCCH for initial signaling.
Dedicated Control Channels This channel is used during the process of call setup and its activation. Dedicated control channels include: Standalone Dedicated Control Channel (SDCCH) Fast Associated Control Channel (FACCH) Slow Associated Control Channel (SACCH)
Standalone Dedicated Control Channel (SDCCH) - UPLINK/DOWNLINK - This channel is used for signaling and call setup between the MS and the BTS. Fast Associated Control Channel (FACCH) - UPLINK/DOWNLINK - This channel is used for control requirements such as handoffs. There is no TS and frame allocation dedicated to a FAACH. The FAACH is a burst-stealing channel, it steals a Timeslot from a Traffic Channel (TCH). Slow Associated Control Channel (SACCH) - UPLINK/DOWNLINK - This channel is a continuous stream channel that is used for control and supervisory signals associated with the traffic channels.
Associated Control Channels This channel is used for signaling associated with calls and call-setup. An ACCH is always allocated along with a TCH or a SDCCH.
You might also like
- GSM Channel TypesDocument3 pagesGSM Channel Typessanu81No ratings yet
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationFrom EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Subnetting Questions 1Document12 pagesSubnetting Questions 1smzohaibabbasNo ratings yet
- GSM Radio ConceptsDocument3 pagesGSM Radio ConceptsMD SahidNo ratings yet
- Logical Channels in GSMDocument10 pagesLogical Channels in GSMshridon123No ratings yet
- Lec1 (Channels)Document29 pagesLec1 (Channels)Nazir AhmadNo ratings yet
- 7GSM ChannelsDocument24 pages7GSM ChannelsNishant Amit MehtaNo ratings yet
- 7.GSM ChannelsDocument24 pages7.GSM Channelsmanthasaikarthik100% (1)
- 2G Logical ChannelsDocument14 pages2G Logical ChannelsAkhtar Khan100% (1)
- GSM Channel ConceptDocument1 pageGSM Channel Conceptarvind yadavNo ratings yet
- GSM Logical ChannelsDocument8 pagesGSM Logical ChannelsfarhadfzmNo ratings yet
- GSM Physical and Logical ChannelsDocument20 pagesGSM Physical and Logical ChannelsJamshid IbragimovNo ratings yet
- GSM ChannelsDocument20 pagesGSM Channelsshashikala kotiNo ratings yet
- GSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelDocument20 pagesGSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelNguyễn HùngNo ratings yet
- GSM ChannelsDocument46 pagesGSM ChannelsAshish KushwahNo ratings yet
- Logical Channels of GSMDocument7 pagesLogical Channels of GSMAhmad HusaeriNo ratings yet
- Broadcast Control ChannelDocument3 pagesBroadcast Control Channeltelecomstuffs7931No ratings yet
- Vikas GSM NotesDocument27 pagesVikas GSM NotesVicky SehrawatNo ratings yet
- GSM Logical ChannelsDocument8 pagesGSM Logical ChannelsTri NguyenNo ratings yet
- GSM Channels1 PDFDocument46 pagesGSM Channels1 PDFNutan Prakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Various Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarDocument43 pagesVarious Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarKuldeep BishtNo ratings yet
- GSM ChannelsDocument3 pagesGSM ChannelsImran AslamNo ratings yet
- MC NotesDocument109 pagesMC Notesprithwirajsrimani2No ratings yet
- Call ProcessingDocument38 pagesCall ProcessingPrakasam ArulappanNo ratings yet
- GSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelDocument20 pagesGSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir Shakeelhi2nazirNo ratings yet
- GSM Logical ChannelsDocument5 pagesGSM Logical ChannelsRahul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 2G Channels and 3GDocument5 pages2G Channels and 3Gkn09No ratings yet
- 1 Broadcast Control ChannelDocument3 pages1 Broadcast Control ChannelRaafat YounisNo ratings yet
- GSM Frame StructureDocument25 pagesGSM Frame StructureVarun SoodNo ratings yet
- GSM Channels & Air InterfaceDocument31 pagesGSM Channels & Air InterfaceCabdallaNo ratings yet
- BTS Make-Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Alcatel Etc. 2206,2964 MCC, IMSI (International Subscriber Identity Moduel) SIM (Subscriber Identity Module)Document4 pagesBTS Make-Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Alcatel Etc. 2206,2964 MCC, IMSI (International Subscriber Identity Moduel) SIM (Subscriber Identity Module)AnujNo ratings yet
- E1-E2 - Text - Chapter 2. GSM Gprs Logical Channels and CallDocument16 pagesE1-E2 - Text - Chapter 2. GSM Gprs Logical Channels and Callmayank guptaNo ratings yet
- Logical Channels & Multi-Frame StructuresDocument20 pagesLogical Channels & Multi-Frame Structuresfahadmalik89No ratings yet
- Frequency Channels in GSMDocument34 pagesFrequency Channels in GSMFarzeen FatimaNo ratings yet
- ChannelsDocument27 pagesChannelsRaju KumarNo ratings yet
- Base Station SubsystemDocument25 pagesBase Station SubsystemNdambuki Mang'uuNo ratings yet
- Canales Logicos GSMDocument15 pagesCanales Logicos GSMOscar JaraNo ratings yet
- GSM ChannelsDocument27 pagesGSM ChannelsSarah AndersonNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Channels in GSMDocument13 pagesConcepts of Channels in GSMSana DanyalNo ratings yet
- Interfaces: by Bssrao Sde GSM FacultyDocument22 pagesInterfaces: by Bssrao Sde GSM FacultydavinderNo ratings yet
- 13.1 WCDMA Channel StructureDocument3 pages13.1 WCDMA Channel StructureKamal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Logical Channels: Broadcast Channels (BCH) (Downlink Only)Document3 pagesLogical Channels: Broadcast Channels (BCH) (Downlink Only)Samir SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- GSM Channels - MyDocument11 pagesGSM Channels - MyDeepan BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- 02 Channels - PpsDocument27 pages02 Channels - PpsAbdul HameedNo ratings yet
- 02 ChannelsDocument27 pages02 ChannelsRathnaKumarNo ratings yet
- 3G ChannelsDocument6 pages3G ChannelsAmit BasraNo ratings yet
- 3G UMTS Data Channels: Physical Logical TransportDocument6 pages3G UMTS Data Channels: Physical Logical TransportRoland Nnadi100% (1)
- 3G Channel StructuresDocument3 pages3G Channel StructureshamidboulahiaNo ratings yet
- WcdmaDocument3 pagesWcdmaSangeen AliNo ratings yet
- 3G UMTS Channel StructuresDocument3 pages3G UMTS Channel StructuresVishalNo ratings yet
- 3G UMTS Data ChannelsDocument6 pages3G UMTS Data ChannelsMark EmakhuNo ratings yet
- UMTS / WCDMA Channels: - Tutorial, or Overview of The Basics of UMTS / WCDMA Logical, Physical and Transport ChannelsDocument4 pagesUMTS / WCDMA Channels: - Tutorial, or Overview of The Basics of UMTS / WCDMA Logical, Physical and Transport ChannelsDiwakar MishraNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Oversimplified Ham Exam for Technician Class License (2022-2026)From EverandOversimplified Ham Exam for Technician Class License (2022-2026)No ratings yet
- Radio Access Networks for UMTS: Principles and PracticeFrom EverandRadio Access Networks for UMTS: Principles and PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsFrom EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 34.123 Protocol Conformance SpecificationDocument539 pages3GPP TS 34.123 Protocol Conformance Specificationptt3iNo ratings yet
- DoS Host Alert 84961Document5 pagesDoS Host Alert 84961siriomNo ratings yet
- The Rule of GRFU&DRFU Positions and CPRI CableDocument20 pagesThe Rule of GRFU&DRFU Positions and CPRI CableFerry KurniawanNo ratings yet
- The Evolution and Future of Wired CommunicationsDocument2 pagesThe Evolution and Future of Wired CommunicationsHubert SemenianoNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between IEEE 802.11af and 802.11ah - PDFDocument10 pagesWhat's The Difference Between IEEE 802.11af and 802.11ah - PDFsorinproiecteNo ratings yet
- Convert Serial To IPsec VPNDocument6 pagesConvert Serial To IPsec VPNĐỗ Văn Tùng0% (1)
- Training ITP C Production Configuration v0.2Document45 pagesTraining ITP C Production Configuration v0.2bayoubgoorNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Computer SOPDocument2 pagesElectrical and Computer SOPYASIN ISMAILNo ratings yet
- RRU3971 Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument15 pagesRRU3971 Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDArturo Cadena100% (1)
- Telecom Core Network Manager Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesTelecom Core Network Manager Job Descriptionhmyousuf100% (3)
- Bluetooth PresentationDocument18 pagesBluetooth Presentationarjun_rathore8178No ratings yet
- AVC Metric Definition GuideDocument68 pagesAVC Metric Definition GuideGregg HarrisNo ratings yet
- Accedian Paa Vs Cisco Ip SlaDocument2 pagesAccedian Paa Vs Cisco Ip SlaSaleh M. Al-QasimNo ratings yet
- Call Drop AnalysisDocument153 pagesCall Drop Analysisashu gupta100% (1)
- DTMF Signalling in 3gDocument10 pagesDTMF Signalling in 3gFaheem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 3G Communication Protocols: 4.1 UTRAN Protocol Structure: The Encryption Mechanism Is Built Into RadioDocument9 pages3G Communication Protocols: 4.1 UTRAN Protocol Structure: The Encryption Mechanism Is Built Into RadioSithija AlwisNo ratings yet
- 3G Core NewDocument46 pages3G Core NewPaul Joseph100% (1)
- 11.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Port Forwarding On A Linksys Router InstructionsDocument2 pages11.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Port Forwarding On A Linksys Router InstructionsLiyanNo ratings yet
- Unstructured Supplementary Service DataDocument3 pagesUnstructured Supplementary Service Datadarezzo.guido100% (1)
- A Comparison Between GPON and EPONDocument4 pagesA Comparison Between GPON and EPONCelesteYangNo ratings yet
- Wifi Security 6 3Document7 pagesWifi Security 6 3Flávio OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Huawei Ficha AP5030 Access Points Datasheet PDFDocument12 pagesHuawei Ficha AP5030 Access Points Datasheet PDFfahmi1987No ratings yet
- Getting Started With at Commands - RevCDocument23 pagesGetting Started With at Commands - RevCkalyanmn100% (3)
- Eci - XDM 1000 - 2000 at SheetDocument11 pagesEci - XDM 1000 - 2000 at SheetPradeep Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- ZXSS10 Network Design Scheme (LLD) - Template - 361048Document16 pagesZXSS10 Network Design Scheme (LLD) - Template - 361048Mahmoud KarimiNo ratings yet
- IManager M2000 V200R013 Basic Feature Description (GSM&UMTS<E)Document176 pagesIManager M2000 V200R013 Basic Feature Description (GSM&UMTS<E)Christopher BennettNo ratings yet
- Network Administration and Mikrotik Router ConfigurationDocument17 pagesNetwork Administration and Mikrotik Router ConfigurationbiswasjoyNo ratings yet
- Dram ParticularsDocument7 pagesDram ParticularsnagulapallisagarNo ratings yet
- BRKSPG 2116Document104 pagesBRKSPG 2116Daniel VieceliNo ratings yet