Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Nature of The Solutions To A Quadratic B Ac B X A BXC Ax
The Nature of The Solutions To A Quadratic B Ac B X A BXC Ax
Uploaded by
Sam ShahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Nature of The Solutions To A Quadratic B Ac B X A BXC Ax
The Nature of The Solutions To A Quadratic B Ac B X A BXC Ax
Uploaded by
Sam ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:____________________________
Date:_________________
Band:________
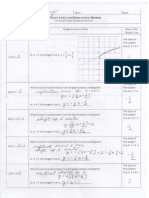
Algebra II | Packer Collegiate Institute The nature of solutions and x-intercepts The nature of the solutions to a quadratic The quadratic formula is: x = a true statement. We have gotten all sorts of different solutions to quadratics For x 2 3 x + 7 = 0 , the solutions are x =
x 1.5 2.18i )
b b 2 4ac . It tells us the x values that make ax 2 + bx + c = 0 2a
3 19i 3 19i & x= (or x 1.5 + 2.18i and + 2 2 2 2
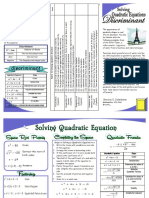
5 13 5 13 For 3 x 2 + 5 x + 1 = 0 , the solutions are x = + & x= (or x 0.23 and x 1.43 ) 6 6 6 6 For x 2 4 x + 4 = 0 , the solution is x = 2 . Some of the quadratics have solutions with imaginary numbers ( i ), while others dont. Look at the quadratic formula. Circle the part of the formula which determines whether there is an imaginary number in the solutions or not:
b b 2 4 ac x= 2a
This expression is known as: When this expression is negative, we know we will have ____ non-real solution(s) (solutions involving i ). This is because: When this expression is positive, we know we will have ____ real solution(s) (solutions not involving i ). This is because: When this expression is zero, we know we will have ____ real solution(s). This is because:
Lets check this out. 1
For the examples above, find the value of the discriminant: For x 2 3 x + 7 = 0 , the discriminant is ______. Thus, there is/are ______________ solution(s). For 3 x 2 + 5 x + 1 = 0 , the discriminant is ______. Thus, there is/are ______________ solution(s). For x 2 4 x + 4 = 0 , discriminant is ______. Thus, there is/are ______________ solution(s). The discriminant doesnt tell us what the solutions are, but they do tell us what these solutions look like.
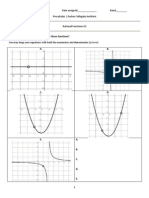
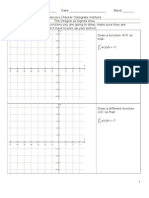
The x-intercepts of a quadratic What do we mean when we say x-intecept? ______________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________. What is true about the y-coordinate of all x-intercepts? _______________________________________. On your graphing calculators, graph the following, and find the x-intercepts. Use ZOOM STANDARD. Calculator Instruction: To find the x-intercepts, go to CALC > ZERO > then pick the left bound and right bound so youre to the left and right of the x-intercept. y = x 2 3x + 7 y = 3x 2 + 5x + 1 y = x2 4 x + 4
x-intercept(s):
x-intercept(s):
x-intercept(s):
Look at the x-intercepts. What do you notice? Recall, since x-intercepts occur when y=0, what were really doing is finding the solutions to x 2 3 x + 7 = 0 , 3 x 2 + 5 x + 1 = 0 , and x 2 4 x + 4 = 0 . Heres where things get interesting The first parabola has ______ x-intercepts because: The second parabola has _____ x-intercepts because: The third parabola has _____ x-intercepts because:
Check yoself before you wreck yoself: How many x-intercepts do the following parabolas have? (a) f ( x) = 2 x 2 3x + 1 (b) y = 2 x 2 + 2 x + 1
(c) g ( x) = x 2 3 x + 10
(d) h( x) = 25 x 2 + 20 x + 4
Lets summarize the discriminant: For a quadratic equation 0 = ax 2 + bx + c a positive discriminant means: a negative discriminant means: a zero discriminant means: For a quadratic equation y = ax 2 + bx + c a positive discriminant means: a negative discriminant means: a zero discriminant means:
You might also like
- 2013-05-13 Rational Functions 1Document9 pages2013-05-13 Rational Functions 1Sam Shah100% (1)
- 2012-09-12 Learning To Count CommentsDocument10 pages2012-09-12 Learning To Count CommentsSam Shah100% (1)
- 2013-05-15 Rational Functions 2Document4 pages2013-05-15 Rational Functions 2Sam Shah100% (2)
- Insight 2015 Mathematical Methods Examination 1Document15 pagesInsight 2015 Mathematical Methods Examination 1nochnoch0% (1)
- Quadratic BrochureDocument2 pagesQuadratic BrochureJemarjo Salandanan60% (5)
- Binomial Theorem by RobertDocument7 pagesBinomial Theorem by RobertBilal GulNo ratings yet
- MathBasics EverythingAboutAlgebra PDFDocument4 pagesMathBasics EverythingAboutAlgebra PDFShane LambertNo ratings yet
- Calg t3 4Document23 pagesCalg t3 4api-261379705No ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document30 pagesAlgebra 2Cuthbert YedwaNo ratings yet
- GSE Algebra I Unit 2B Day 03 Solving Linear Systems by GraphingDocument4 pagesGSE Algebra I Unit 2B Day 03 Solving Linear Systems by GraphingYishuo ShenNo ratings yet
- To Graph An Equation or An Inequality, One Must Consider The Solution Set: Integers or RealDocument4 pagesTo Graph An Equation or An Inequality, One Must Consider The Solution Set: Integers or RealpianoNdarkNo ratings yet
- 1.linear Equations in Two Variables ExplainedDocument10 pages1.linear Equations in Two Variables ExplainedmouneshskNo ratings yet
- Review of Essential Algebra Concepts and Skills For Calculus Autor Utah State UniversityDocument23 pagesReview of Essential Algebra Concepts and Skills For Calculus Autor Utah State UniversityDavid Franz GicainNo ratings yet
- DiophantDocument8 pagesDiophantRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- High School Secrets: 1 Translation and Rotation MatterDocument6 pagesHigh School Secrets: 1 Translation and Rotation MatterViet Quoc Hoang100% (2)
- UNIT 2 AlgebraDocument37 pagesUNIT 2 AlgebraDeneika MorganNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document10 pagesModule 5KC BeltranNo ratings yet
- Finding The Roots of Polynomial Equations 1Document2 pagesFinding The Roots of Polynomial Equations 1Dorinda F. Barredo100% (1)
- Module 11 (Polynomial Equations) : Learning Activity Sheet in Mathematics 10Document2 pagesModule 11 (Polynomial Equations) : Learning Activity Sheet in Mathematics 10Jeanie PeNo ratings yet
- Elementary MathematicsDocument14 pagesElementary MathematicsViet Quoc Hoang100% (1)
- Factorising Quadratics: © Skillbank Solutions Limited 2010Document10 pagesFactorising Quadratics: © Skillbank Solutions Limited 2010Aldo Peña RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 EquationsDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 7 EquationsSathish Sarma SathianarayananNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document12 pagesChap 4bhaskarNo ratings yet
- Solumn Mathematics Module 1 (Algebra)Document7 pagesSolumn Mathematics Module 1 (Algebra)PHILIP1001No ratings yet
- BM 1 PDFDocument37 pagesBM 1 PDFAnish ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Revision Form 3Document28 pagesRevision Form 3Karvesh Gopaul100% (1)
- Mathematics: First Quarter - Week 3Document9 pagesMathematics: First Quarter - Week 3MARIE GRACE APARRE100% (1)
- 6 QuadraticDocument10 pages6 Quadraticmaths_5555No ratings yet
- AlgebraicDocument16 pagesAlgebraiczohabnoor63No ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Two Variables 55Document7 pagesLinear Equations in Two Variables 55Manoj CBSNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Inequalities: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesModule 6: Inequalities: ObjectivesmoreNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-AntiderivativesDocument5 pagesLesson Plan-AntiderivativesRaine G. DulayNo ratings yet
- G9MATHQ1M2Document46 pagesG9MATHQ1M2SITTIE FARISHA MAGAPISANo ratings yet
- CHAP07 Logs and ExponentialsDocument6 pagesCHAP07 Logs and ExponentialsRenaldyNo ratings yet
- Math Basic PrinciplesDocument9 pagesMath Basic PrinciplesRakesh BussaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument12 pagesLinear Equations in Two VariablesVimala ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- Algebra Basics: For Friends .AdarshDocument11 pagesAlgebra Basics: For Friends .AdarshAdarsh RonNo ratings yet
- Algebra Worksheet 2 - Simultaneous Equations and Manipulating SurdsDocument4 pagesAlgebra Worksheet 2 - Simultaneous Equations and Manipulating SurdsJane ChangNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document20 pagesBasic Calculus: Quarter 1 - Module 3Angelie Limbago CagasNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math II ADocument4 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math II ABrenda OpawNo ratings yet
- MAT Reasoning About Solutions Practice: Non CalculatorDocument5 pagesMAT Reasoning About Solutions Practice: Non CalculatorSanil KatulaNo ratings yet
- ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Final Project For Final SemDocument21 pagesELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Final Project For Final SemJulita AleonarNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions DefinitionDocument8 pagesAlgebraic Expressions Definitionapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Investigating Simultaneous EquationsDocument2 pagesInvestigating Simultaneous Equationsbellays96No ratings yet
- Linear Equation (Slope and Y-Intercept)Document21 pagesLinear Equation (Slope and Y-Intercept)AJ SaysonNo ratings yet
- Operation ResearchDocument131 pagesOperation ResearchmariaNo ratings yet
- 06 Manipulating and Solving Equations I & IIDocument15 pages06 Manipulating and Solving Equations I & IIharshilNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation With Two VariablesDocument194 pagesLinear Equation With Two VariablesJagabandhu KarNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 9Document7 pagesMath Grade 9Pede CasingNo ratings yet
- Differentiation of Logarithmic FunctionsDocument24 pagesDifferentiation of Logarithmic FunctionsNorman CruzNo ratings yet
- w10 HDTBasMathDocument3 pagesw10 HDTBasMathKhaeroni KhaeroniNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Day 1Document12 pages2.7 Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Day 1Jaycher BagnolNo ratings yet
- Functions of Several VariablesDocument21 pagesFunctions of Several VariablesVishnu Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Iemh 104Document5 pagesIemh 104saptarshibnrj2003No ratings yet
- Simultaneous EquationsDocument3 pagesSimultaneous EquationsHamza KahemelaNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 9: Pasay - M9 - Q1-W1-02Document5 pagesModule in Mathematics 9: Pasay - M9 - Q1-W1-02Shein SheilaNo ratings yet
- Linear Inequalities: 6.1 OverviewDocument16 pagesLinear Inequalities: 6.1 OverviewSprihanjayNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Attacking Problems in Logarithms and Exponential FunctionsFrom EverandAttacking Problems in Logarithms and Exponential FunctionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2013 10 17 Quadric SurfacesDocument5 pages2013 10 17 Quadric SurfacesSam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2013-11-14 Tangent Lines and Derivatives SolutionsDocument2 pages2013-11-14 Tangent Lines and Derivatives SolutionsSam ShahNo ratings yet
- T P R: T T T: HE Ower ULE Ying Hings OgetherDocument4 pagesT P R: T T T: HE Ower ULE Ying Hings OgetherSam ShahNo ratings yet
- Letter of Recommendation Questionnaire 2012-2013 ShahDocument1 pageLetter of Recommendation Questionnaire 2012-2013 ShahSam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2013-05-15 Rational Functions 3Document4 pages2013-05-15 Rational Functions 3Sam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2013-05-24 Assessment On Rational FunctionsDocument6 pages2013-05-24 Assessment On Rational FunctionsSam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2012-2013 Senior LetterDocument3 pages2012-2013 Senior LetterSam ShahNo ratings yet
- GeoGebra InstructionsDocument3 pagesGeoGebra InstructionsSam ShahNo ratings yet
- Conics ProjectDocument4 pagesConics ProjectSam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2013-04-25 Integral As Signed Area ActivityDocument2 pages2013-04-25 Integral As Signed Area ActivitySam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2013 04 29 Polynomial FunctionsDocument4 pages2013 04 29 Polynomial FunctionsSam ShahNo ratings yet
- Section 1: Puzzles! Puzzle #1Document29 pagesSection 1: Puzzles! Puzzle #1Sam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2012-11-30 Investigating Sound RevisedDocument4 pages2012-11-30 Investigating Sound RevisedSam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2012-11-26 Solving Basic Trig Equations and Graphing Basic Trig FunctionsDocument6 pages2012-11-26 Solving Basic Trig Equations and Graphing Basic Trig FunctionssamjshahNo ratings yet
- Learning To CountDocument7 pagesLearning To CountSam ShahNo ratings yet
- 2012-09-12 Learning To Count No CommentsDocument10 pages2012-09-12 Learning To Count No CommentsSam ShahNo ratings yet
- Advice From Calculus Students PastDocument6 pagesAdvice From Calculus Students PastSam ShahNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series No CommentsDocument33 pagesSequences and Series No CommentsSam Shah100% (1)
- TMC 2012 ProgramDocument5 pagesTMC 2012 ProgramSam ShahNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series With CommentsDocument33 pagesSequences and Series With CommentsSam Shah50% (2)
- Learning To CountDocument7 pagesLearning To CountSam ShahNo ratings yet
- TMC 2012 ProgramDocument5 pagesTMC 2012 ProgramSam ShahNo ratings yet
- TMC 2012 ProgramDocument6 pagesTMC 2012 ProgramSam ShahNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit Wise Important QDocument2 pagesDAA Unit Wise Important QMUSHAM HARI KIRAN6737No ratings yet
- 1617 Level MS-NA Math Periodic Revision Sheet T2 Wk7 PDFDocument10 pages1617 Level MS-NA Math Periodic Revision Sheet T2 Wk7 PDFAndrewNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Elliptic Partial Differential Equations by Haar Wavelet Operational Matrix MethodDocument100 pagesNumerical Solution of Elliptic Partial Differential Equations by Haar Wavelet Operational Matrix Methodsashankchappidigmail100% (1)
- Some Examples of Non-Measurable Lebesgue Functions Some Examples of Non-Measurable Lebesgue FunctionsDocument3 pagesSome Examples of Non-Measurable Lebesgue Functions Some Examples of Non-Measurable Lebesgue FunctionsFahad MajeedNo ratings yet
- Module-3 Finite Differences and Interpolation: Example: For 0Document10 pagesModule-3 Finite Differences and Interpolation: Example: For 0Jawa freakNo ratings yet
- Meccademia Education Institute Grade: Mathematics Time: 1 Hours 30 Minutes Marks: 40 HLT-1Document4 pagesMeccademia Education Institute Grade: Mathematics Time: 1 Hours 30 Minutes Marks: 40 HLT-1AnujNo ratings yet
- Fem Assignment Question Bank Unit 1&2 PDFDocument1 pageFem Assignment Question Bank Unit 1&2 PDFSudhakar UppalapatiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Final Test Math 7Document3 pages2nd Quarter Final Test Math 7Jingle Pagas CelestianNo ratings yet
- 2005level2 SolutionsDocument8 pages2005level2 SolutionsRaghav guptaNo ratings yet
- The Real Number SystemDocument11 pagesThe Real Number SystemProf. David G.No ratings yet
- OE5170 Notes 08Document3 pagesOE5170 Notes 08dhruvbhagtaniNo ratings yet
- MS-E2148 Dynamic OptimizationDocument85 pagesMS-E2148 Dynamic Optimizationpancho_davNo ratings yet
- (London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series 420) Luis Dieulefait, Gerd Faltings, D. R. Heath-Brown, Yu. v. Manin, B. Z. Moroz, Jean-Pierre Wintenberger - Arithmetic and Geometry-Cambridge UniversDocument539 pages(London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series 420) Luis Dieulefait, Gerd Faltings, D. R. Heath-Brown, Yu. v. Manin, B. Z. Moroz, Jean-Pierre Wintenberger - Arithmetic and Geometry-Cambridge Universalvarezdiaz_11921176No ratings yet
- Ma8352 IqDocument17 pagesMa8352 IqBkNo ratings yet
- ISI Mathematical Talent Reward Programme 2019Document3 pagesISI Mathematical Talent Reward Programme 2019ElevenPlus ParentsNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation and Diffraction: Igor T. Selezov Yuriy G. Kryvonos Ivan S. GandzhaDocument251 pagesWave Propagation and Diffraction: Igor T. Selezov Yuriy G. Kryvonos Ivan S. Gandzhapuceiroale100% (1)
- Iii. Union and Intersection of Events Complement of An Event Odds Unions and IntersectionsDocument8 pagesIii. Union and Intersection of Events Complement of An Event Odds Unions and IntersectionsKristhel Pecolados RombaoaNo ratings yet
- Quarterly of Applied Mathematics: T, - For SuchDocument7 pagesQuarterly of Applied Mathematics: T, - For SuchSuriyunNo ratings yet
- MAT-0201 (Lec-10) Vector AlgebraDocument4 pagesMAT-0201 (Lec-10) Vector AlgebraMd JishanNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Exemplar Answer PDFDocument18 pages11 Maths Exemplar Answer PDFsmitsanghaviNo ratings yet
- Numerical SolveDocument9 pagesNumerical SolveT024KOUSTAV CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- Wavelet Toolbox™ User's Guide PDFDocument617 pagesWavelet Toolbox™ User's Guide PDFVictor Colpo NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Exponential FormsDocument4 pagesExponential FormsWella Wella WellaNo ratings yet
- CouStudy 201718Document332 pagesCouStudy 201718mp SinghNo ratings yet
- LS - 0 - 2 - 1 - 023e7404312ef-Trigonometry Bhagwati Maths 51 To 134Document6 pagesLS - 0 - 2 - 1 - 023e7404312ef-Trigonometry Bhagwati Maths 51 To 134Nitin DangiNo ratings yet
- The Bogoliubov-De Gennes and Andreev Equations: Andreev ReflectionDocument9 pagesThe Bogoliubov-De Gennes and Andreev Equations: Andreev ReflectionHercules De Souza SantanaNo ratings yet
- Single Degree of Freedom: 2.1.1 Undamped Free VibrationDocument8 pagesSingle Degree of Freedom: 2.1.1 Undamped Free VibrationMohammad Muhtasim Mashfy, 170011054No ratings yet
- 2019 3U - ST - George - GirlsDocument40 pages2019 3U - ST - George - GirlsJaniceNo ratings yet