Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sources of Energy
Sources of Energy
Uploaded by
Diochel BasaloOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sources of Energy
Sources of Energy
Uploaded by
Diochel BasaloCopyright:
Available Formats
Sources of Energy
Introduction:
As you have learned, energy is the ability to do work. By doing work, you can move things, change things, and make things happen. Energy is one of your everyday needs, something you never could do without. All energy sources have advantages and disadvantages. Think of all the way you use energy. It warms your home in winter or cools it in summer. It supplies heat for warm showers and washing machines. Energy makes stoves, refrigerators, computers and television to work. Office buildings and factories depend on energy too. Like your home these building need heating, cooling, and lighting. Without realizing it people use large amounts of energy everyday. Fuels supply the energy needed by buses, trucks, cars, and airplanes. People also use energy to grow and ship foods. Electricity is a familiar form of energy. Every time you turn on a television or flip a light switch, you use electrical energy. If you multiply the amount of energy you use by the number of people in your neighborhood, you can imagine how much energy people use. Just think what would happen if we ever ran out of energy? The electricity people use is not a source of energy. It is, rather, a convenient way to move energy around. It does not come from mines, as coal and uranium do, or from wells, as oil and natural gas do. People must use energy sources to make electricity. There will always be a great need for energy. Because of this need, some sources are beginning to run out. The day may come when there is no enough gasoline for cars, because the world is running out of petroleum, oil where gas is made. So a great way of conservation must be made and practiced by people today as consumption of men increases to avoid energy shortage. According to the Law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor it can be destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to the other, so where the energy does comes from? Energy is stored in the nature in various sources and in various forms. The sources of energy available in the nature are divided into two main types: renewable energy sources and non-renewable energy sources. The energy which replenishes itself quickly and which is available in never ending supply is called renewable energy. The energy sources that cannot be recreated and which go on depleting as we use them are non-renewable energy.
Sources of Energy Renewable Energy are those energy sources that can be regenerated by natural processes. are those that either do not run out or can be replaced in a few years. energy whose sources can easily supply or replenish the current demand or usage.
They replace themselves or are continuously present as a feature of the solar system. In its various forms, it can be derived directly from the sun or from heat generated deep within the earth such as solar, wind, ocean, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal resources. They are renewable resources because they are continuously available. A. Solar Energy It is the energy that which comes directly from the sun. Solar energy can be used to make electricity and to heat water. The sun is often mentioned as the ultimate answer to the worlds energy problems. It provides a continuous supply of energy that far exceeds the worlds demands. The major problem with solar energy is its intermittent nature. It is only available during the day when it is sunny and less available in cloudy weather. All systems that use solar energy must store or use supplementary sources of energy when sunlight is not available. Solar technologies are characterized as either: active solar and passive solar depending on the way they capture, convert, and distribute solar energy. 1. In a passive solar technology, the suns energy is converted directly into heat for use at the site where it is collected. It is a means of using sunlight for useful energy without the use of active mechanical system. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air. 2. In an active solar technology, the suns energy is converted into heat, but the heat must be transferred from the collection area to the place of use. It converts solar energy into usable light or store heat for future use. It includes the use of solar thermal collectors to harness the energy. B. Wind Energy The term Wind Energy describes effectively the process of generating energy using the wind. The kinetic (motion) energy in the wind is transformed by wind turbines into mechanical power. This power can in turn be exploited for tasks like pumping water or grinding grain or be fed into a generator to generate electricity, powering homes, schools and businesses. It is one of the fastest growing types of alternative energy used today. Since humans first took to the sea in primitive sailboats, wind has used for its awesome power. For centuries, windmills have been used to aid milling and grinding. But today, humans harness renewable wind power by connecting modern windmills or turbines to power-collection systems. Energy the wind turbines harvest from the motion caused by wind is what is called wind energy. In a way, wind energy is a form of solar energy as wind is caused by uneven heating of the atmosphere. As for flow pattern, wind is influenced by the earth terrain, vegetative cover and bodies of water. The mechanism of wind turbines can be explained as the opposite of a fan. The fan moves to generate wind while the wind turbine lets itself moved by the wind to create kinetic energy. There are two types of wind turbines, the horizontal axis type which looks like the classic windmills and the vertical axis turbine. Most used wind turbines these days are the horizontal axis turbines. C. Geothermal Energy
Super-heated water or steam from earth's interior utilized in running the turbines of a conventional power plant to generate electricity. Such plants are usually small and suitable only for the needs of a local community. Typically found near geysers or tectonic plate boundaries, geothermal plants now exist in dozens of countries around the world. Iceland, Italy, New Zealand, Russia, and the US are among the few countries having the right-sized geothermal energy fields. Geothermal plants are responsible for over 15% of all energy production. D. Hydro-electric power For centuries, people used the energy of falling water to do work. It is made by turning the energy of moving water into electricity. Water from a reservoir flows rapidly through a dam. This fast flowing water spins a turbine which generates electricity. The sun is responsible for the energy in falling water. Energy from the sun drives the water cycle. In the water cycle, the water evaporates from the earths surface and falls again as rain. Rivers carry excess water from land to oceans. Most hydro-electric power plants, which generally include dams, are built along river banks. It is an important source of energy in mountainous areas with a high rainfall. E. Biomass Energy It is defined by any organic materials that can be burned and used as a source of fuel. Wood being the main source of biomass such as saw-dust or any type of waste from wood is processed to make wood-pellets and used as fuel for wood pellet boilers and stoves. Farm waste such as cow manure is processed into biomass to form biogas. It can be used in bottled gas for gas cooking appliances. Crops such as switch-grass, corn and sugarcane are produced to form ethanol which can be used to fuel vehicles and presently are so, to great success. Waste heat harnessed by waste-to-energy plants can generate electricity for heating buildings. Among energy sources referred to as biofuels is domestic rubbish. About 15% of municipal solid waste is burned.Biomass can further be broken down into more specific categorys which have different types of uses. Biomass that comes from wood keeps its form and is formed into pellet size uniformity to be used for biomass heating systems and electricity. F. Biofuel Fuel produced from renewable biomass material, commonly used as an alternative, cleaner fuel source. Biofuels are a wide range of fuels which are in some way derived from biomass. The term covers solid biomass, liquid fuels and various biogases. Biofuels are gaining increased public and scientific attention, driven by factors such as oil price spikes, the need for increased energy security, and concern over greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels. Biofuel, such as ethanol or biodiesel, is an area currently undergoing considerable research. When looking at the green clumpy mass cluttering up a backyard pond, it is difficult to imagine that it could power a car. Algae biodiesel, however, is becoming the focus of considerable attention one of the newer renewable sources of energy. Algae, easily grown and produced in lakes or laboratory settings, may be one of the answers to depleted stocks of fossil fuels. Non-renewable Energy
A non-renewable resource is a natural resources which cannot be replaced once they have been used or the energy sources that cannot be recreated and which go on depleting as we use them. They are also the resource which cannot be produced, grown, generated, or used on a scale which can sustain its consumption rate. These resources often exist in a fixed amount and finite, or are consumed much faster than they can be produced by the nature. At present most of the needs of the world are fulfilled by non-renewable sources of energy. The most extensively used non-renewable energy sources are the fossil fuels that consist of oil, natural gas, and coal. Other problems occur with the use of fossil fuels includes the pollution it will cause. When they burn, the fossil fuels release harmful waste products-or- pollutants-into the air. These pollutants include compounds of oxygen joined with nitrogen and sulfur, carbon monoxide, and small particles. In addition, it can damage buildings. It can also harm plant and animal life. It can trigger health problems such as pneumonia, emphysema, and other lung illnesses. Burning fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide which might change the earths climate. A. Oil It is a kind of fossil fuel. It is a thick, dark liquid which is made of hydrocarbons. They probably originated from microscopic marine organisms. When these organisms died and accumulated on the ocean bottom and were buried by sediments, their breakdown released oil droplets. Gradually the muddy sediment formed rock called shale, which contained dispersed oil droplets. It is made up largely of silt mixed with a kind of matter known as kerogen. Extraction from shale is difficult because the oil is not concentrated. An area containing reserves of oil is called an oil field. Oil and oil products are sometimes called petroleum. The well pumped up the oil from deep underground to the surface. It can be transported from one nation to another or within one nation. The energy released by burning can be used to move vehicles or to heat water and buildings. But burning oil causes air pollution and water pollution. It can take many years for an area to recover from the effects of oil spill. B. Coal It is the worlds most abundant fossil fuel, but it supplies only about 27 percent of the energy used in the world. It varies in quality and is generally classified in three categories: lignite, bituminous, and anthracite. Lignite coal also referred to as brown coal; is the lowest rank of coal and used almost exclusively as fuel for electric power generation. Bituminous coal is the most widely used because it is the easiest to mine and the most abundant. It supplies about 20 percent of the worlds energy requirements. Coal is primarily used for electric power generation and other industrial uses. For most uses, anthracite coal is the most desirable because it furnishes more energy than the other grades and is the cleanest burning. But anthracite is not as
common and is usually more expensive because it is found at greater depths and is difficult to obtain.
PLANTS CONTAINING CARBON COMPOUNDS
WHEN PLANTS DIE, THEY ONLY PARTIALLY DECAY
FOR A MILLION OF YEARS, PLANTS COMPRESSED FORMING PEAT
COMPRESSION AND HEAT FORCES IN THE EARTH OVER TIME TRANSFORMING PEAT TO COAL
Man has realized that coal is a carbon-based mineral that can be used as fuel. This is a result of a half a million to even a several million years of compression and heat applied to decaying plants growing in bogs or swampy areas. C. Natural Gas The main ingredient in natural gas is methane, a gas (or compound) composed of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. Millions of years ago, the remains of plants and animals (diatoms) decayed and built up in thick layers. This decayed matter from plants and animals is called organic material it was once alive. Over time, the sand and silt changed to rock, covered the organic material, and trapped it beneath the rock. Pressure and heat changed some of this organic material into coal, some into oil (petroleum) and some into natural gas tiny bubbles of odorless gas. D. Nuclear Energy It is energy in the nucleus (core) of an atom. Atoms are tiny particles that make up every object in the universe. There is enormous energy in the bonds that hold atoms together. Nuclear energy is released by the nucleus of an atom as the result of nuclear fission, nuclear fusion, or radioactive decay.
Bibliography: Books: Arturo N. Villegas; Physics: a Conceptual Approach; Academe Publishing House; 1993
Internet:
Eldon Enger & Bradley Smith; Environmental Science 6th edition; The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc.; 1998 Michael Magnoli, ibid.; Experiences in Physical Science; Glencoe Publishing Co.; 1985 Martin Walters & Felicity Trotman; Earth Sciences; Merlion Publishing Ltd.; 1991 Gil Nonato C. Santos & Jorge Ocampo; Science and Technology; 2003 Basa, Erlinda, Integrated Science third edition. Diwa Scholastic Press Inc. 1999 Santos, Gil Nonato. Science and Technology The Next Generation. Rex Bookstore, Inc. 2003. http://www.brighthub.com/environment/renewableenergy/articles/5029.aspx#ixzz16B 3TTxDj http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/nuclear+energy http://www.clean-energy-ideas.com/energy_definitions/definition_of_biofuel.html http://www.techstore.ie/Renewable-Energy/Biomass-Energy/Definition-of-BiomassEnergy.htm http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/geothermal-energy.html http://ezinearticles.com/?Wind-Energy---Definition,-Mechanism-andAdvantages&id=4380565
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Letter For AWOL (Job Abandonment)Document2 pagesLetter For AWOL (Job Abandonment)Diochel Basalo96% (25)
- Letter For AWOL (Job Abandonment)Document2 pagesLetter For AWOL (Job Abandonment)Diochel Basalo96% (25)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- UNIT 7 Voc - Exercises (11868)Document6 pagesUNIT 7 Voc - Exercises (11868)Аманта ЛиньковаNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- RESR Executive Project SummaryDocument39 pagesRESR Executive Project SummaryhandsoloknowsNo ratings yet
- In Depth On SSS MembershipDocument64 pagesIn Depth On SSS MembershipDiochel BasaloNo ratings yet
- PSA 810 Revised and RedraftedDocument28 pagesPSA 810 Revised and RedraftedJohn Erol BulacanNo ratings yet
- 7 Wonders of I.WDocument10 pages7 Wonders of I.WDiochel BasaloNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Wind Turbines Based On DFIGDocument8 pagesModeling of Wind Turbines Based On DFIGAida AdylbekovaNo ratings yet
- Pssewindandsolarmodels CasestudiesDocument69 pagesPssewindandsolarmodels Casestudiespra0% (1)
- IEEE ConferenceDocument7 pagesIEEE ConferenceTural AliyevNo ratings yet
- Bremskerl Company ProfileDocument20 pagesBremskerl Company ProfileDhan CNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Market ReportDocument119 pagesOffshore Wind Market ReportTaimoorAsim100% (1)
- Sources of ElectricityDocument3 pagesSources of ElectricityhamidalkorbiNo ratings yet
- Windmill Digital ElxDocument9 pagesWindmill Digital ElxElleNo ratings yet
- Wind Future in Asia Report (Final) Updated23Aug12 - 0 PDFDocument104 pagesWind Future in Asia Report (Final) Updated23Aug12 - 0 PDFSahil GargNo ratings yet
- Overview of MULTI Megawatt WIND TURBINES and Wind ParkDocument24 pagesOverview of MULTI Megawatt WIND TURBINES and Wind ParkPrakash MishraNo ratings yet
- Wind Solar Hybrid ControllerDocument6 pagesWind Solar Hybrid ControllerBogdan IlieNo ratings yet
- November 25, 2015Document12 pagesNovember 25, 2015The Delphos HeraldNo ratings yet
- Ppimagazine201104 DLDocument52 pagesPpimagazine201104 DLMertol SerbanNo ratings yet
- Small and Hybrid Wind TurbinesDocument23 pagesSmall and Hybrid Wind Turbinesk rajendraNo ratings yet
- FanusDocument19 pagesFanusfanusNo ratings yet
- IRENA Tracking COP28 Outcomes 2024Document20 pagesIRENA Tracking COP28 Outcomes 2024HASSAN AGOUZOULNo ratings yet
- Khossain 2007Document33 pagesKhossain 2007Humayun Kabir JimNo ratings yet
- Economic Evaluation and Determination of Optimal Hybrid Energy Supply Systems For Residential and Healthcare Facilities in Rural and Urban AreasDocument36 pagesEconomic Evaluation and Determination of Optimal Hybrid Energy Supply Systems For Residential and Healthcare Facilities in Rural and Urban Areasomotayo jamiuNo ratings yet
- 2017-Selection of Sustainable Development Indicators For The Assessment of Electricity Production in EgyptDocument9 pages2017-Selection of Sustainable Development Indicators For The Assessment of Electricity Production in EgyptA.HassanNo ratings yet
- DronesDocument24 pagesDronesTiviz Rooban67% (3)
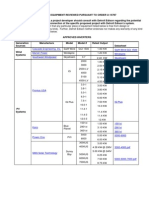
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : Wind Turbine GeneratorDocument2 pagesOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : Wind Turbine GeneratorSupratno ArhamNo ratings yet
- PRDCNL Jan Jun2016Document36 pagesPRDCNL Jan Jun2016debajyoti ghoshNo ratings yet
- Francesco Paraggio Wind Farm Dev Puglia-PrintDocument14 pagesFrancesco Paraggio Wind Farm Dev Puglia-PrintFrancesco ParaggioNo ratings yet
- Reporte HOMER WIND 5kW-PV 6.36kWDocument10 pagesReporte HOMER WIND 5kW-PV 6.36kWlandoa junNo ratings yet
- Wind HVDC SlidesDocument50 pagesWind HVDC Slidessandeep kumar mishraNo ratings yet
- Small Wind Turbine Blade Design and OptiDocument14 pagesSmall Wind Turbine Blade Design and OptiIsmadi IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Cascade Engineering, Inc. Swift Wind GCI 1500 Mariah Power Windspire Southwest Windpower SkystreamDocument4 pagesCascade Engineering, Inc. Swift Wind GCI 1500 Mariah Power Windspire Southwest Windpower SkystreamGLCIINo ratings yet
- Fuzzy TOPSIS Method For Ranking Renewable Energy Supply Systems in TurkeyDocument9 pagesFuzzy TOPSIS Method For Ranking Renewable Energy Supply Systems in TurkeyJorge BessaNo ratings yet
- ABEN50 Lab 6 Assessment of The Renewable Energy in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesABEN50 Lab 6 Assessment of The Renewable Energy in The Philippinescjcaporado18No ratings yet