Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
lutherlynOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
lutherlynCopyright:
Available Formats
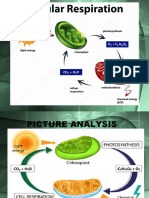
Aerobic Cellular Respiration The process by which the energy from glucose is released in the presence of oxygen is called
aerobic cellular respiration. Aerobic cellular respiration takes place only if oxygen is available. For instance, if glucose were oxidized, the result would be energy, carbon dioxide and water. Take a look at the chemical formula given below. C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) In simple words, Glucose + Oxygen = Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP) In brief, aerobic cellular respiration helps in release of maximum energy and also gets rid of carbon dioxide and excess water. Three Stages of Aerobic Cellular Respiration There are three stages of aerobic cellular respiration. They are
Glycolysis - The process of Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of the cell. In this stage of the aerobic cellular respiration, glucose is partially oxidized and is broken down into 3 carbon molecules of pyruvate. This process of glycolysis produces energy - 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) molecules. Each NADH molecule carries 2 energy electrons. The cells later use these electrons.
Krebs Cycle - This is the next stage of aerobic cellular respiratory. In Krebs cycle, pyruvate molecules are processed to release the energy that is stored between their molecular bonds. The energy is released in the form of ATP. This cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle.
Electron Transport Chain - This is the final stage of aerobic cellular respiratory. During glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle, entire energy was not released from the glucose. In this stage of aerobic respiration, remaining energy from the glucose will be released by the electron transport chain. The network of electrons carrying proteins to the inner membrane of the cell is known as electron transport chain. Eventually, in this stage the electrons along with the protons will be added to oxygen. When electrons and protons are added to oxygen, it produces water and not ATP (energy). Actually, ATP is produced when the protons are moved across the cell membrane. This is known as chemiosis.
A point worth mentioning here is, while glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell, the Krebs Cycle and electron transport takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. Oxygen plays a major role in aerobic cellular respiration because it is a great electron acceptor. It plays an active role in preventing the electrons from building up in the electron transport system.
Breathing is the process that moves air in and out of the lungs of terrestrial vertebrates. Aerobic organisms of these types--such as reptiles, birds and mammals--require oxygen to release energy via respiration, in the form of the metabolism of energy-rich molecules such asglucose.
Breathing is only one process that delivers oxygen to where it is needed in the body and removes carbon dioxide. Another important process involves the movement of blood by the circulatory system. Gas exchange occurs in the pulmonary alveoli by passive diffusion of gases between the alveolar gas and the blood in lung capillaries. Once these dissolved gases are in the blood, the heart powers their flow around the body (via the circulatory system). The medical term for normal relaxed breathing is eupnea. In addition to removing carbon dioxide, breathing results in loss of water from the body. Exhaled air has a relative humidity of 100% because of water diffusing across the moist surface of breathing passages and alveoli.
2.
You might also like
- Laboratory 1 Mech 285 (UVic)Document11 pagesLaboratory 1 Mech 285 (UVic)MechLoretteNo ratings yet
- Small Clear Specimens of Timber: Standard Test Methods ForDocument31 pagesSmall Clear Specimens of Timber: Standard Test Methods ForCaro ChasipantaNo ratings yet
- Sri Yantra (PDFDrive) PDFDocument158 pagesSri Yantra (PDFDrive) PDFAnoventia OrxswixyNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDocument3 pagesRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument14 pagesCellular Respirationcleahveil badanNo ratings yet
- Lesson-9 1Document26 pagesLesson-9 1Aihk kenneth BaronaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Lecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Document14 pagesLecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Andre NesbethNo ratings yet
- Respiration CycleDocument1 pageRespiration CycleEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Exchange Gases, Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesExchange Gases, Cellular RespirationGISRemoteSensingNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Lab.3 PhysicsDocument4 pagesLab.3 Physicsksoo5118No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Respiratory SystemPiyush RoyNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 7Document4 pagesBiology Class 7Jon Williams100% (4)
- Mechanics of BreathingDocument5 pagesMechanics of BreathingMark Lyndon M OrogoNo ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4Mohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- Summary of Aerob RespirationDocument3 pagesSummary of Aerob RespirationHenry AndersonNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in Elementary GradesDocument2 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary GradesJenniferChantengcoCatacutan50% (2)
- Measure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerDocument17 pagesMeasure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerTootsie100% (12)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q2 Week 3 Module 5 Aerobic Vs Anaerobic RespirationDocument8 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q2 Week 3 Module 5 Aerobic Vs Anaerobic RespirationReygie Ann SuenoNo ratings yet
- Biology U2Document10 pagesBiology U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- Biology ClassDocument1 pageBiology ClasswwxlzpriestNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration in Animals.Document4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals.studyklieNo ratings yet
- Ange EeeeeDocument4 pagesAnge EeeeeHazel BandayNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ExplanationDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration Explanationvestermail50% (2)
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesCellular Respirationmanojtbgri5793No ratings yet
- Las Q4 WK3.1Document8 pagesLas Q4 WK3.1Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Study Guide 2015Document7 pagesCH 9 Study Guide 2015dickbeater73No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY 11 - Energy For Life, Catabolic Pathways, Redox ReactionDocument4 pagesBIOLOGY 11 - Energy For Life, Catabolic Pathways, Redox ReactionApril Rose CortesNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio W3-5Document9 pagesGen Bio W3-5Alyson EscuderoNo ratings yet
- CellrespDocument1 pageCellrespojggxgqbqhyqqltcksNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Metabolism Glycolysis and T.C.A. CycleDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Metabolism Glycolysis and T.C.A. Cycleمحمد جانNo ratings yet
- Katriel Ziv Batutay - Refective QuestionsDocument2 pagesKatriel Ziv Batutay - Refective QuestionsKatriel Ziv LasNo ratings yet
- Grade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialDocument19 pagesGrade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialJake LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1Document50 pagesQuarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1champimiloNo ratings yet
- BioDocument18 pagesBiomarcneil773No ratings yet
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document8 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Waleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Slide 1Document1 pageSlide 1NickTheTurtleNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 13 To 15: Energy TransformationDocument8 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 13 To 15: Energy Transformationkent ignacioNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 12Document13 pagesModule 5 Lesson 12John eric CatayongNo ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Student Module 2 Genbio1Document5 pagesStudent Module 2 Genbio1Lezel LaracasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NcellularrespirationDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis NcellularrespirationBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document10 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Yana LouisseNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismDocument12 pagesRespiration in OrganismopsharpedgeNo ratings yet
- Bio AP CHP 9 NotesDocument13 pagesBio AP CHP 9 Noteslauren roNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in PlantsAadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- Bio 123Document2 pagesBio 123SHEMAR STEWARTNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodDocument28 pagesCellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeashNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespDocument3 pagesCellular Resptruckerrr1No ratings yet
- 2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoDocument6 pages2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoLucas BuSheaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument5 pagesRespirationDivyansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument49 pagesCell RespirationJanine CambaNo ratings yet
- 3 ReviewDocument5 pages3 ReviewJNo ratings yet
- Durasquirt DownloadDocument7 pagesDurasquirt DownloadEngr Ahmed FadulNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena Question 1Document4 pagesTransport Phenomena Question 1Nadia KamaNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument296 pagesCapacitorTomtopNo ratings yet
- Inductive LoopDocument8 pagesInductive LoopKrishna Pavan100% (2)
- High-Strength Aluminium Alloys and Their Use in Foundry IndustryDocument7 pagesHigh-Strength Aluminium Alloys and Their Use in Foundry Industryferhat aydoganNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Punching Machine DesignDocument3 pagesPneumatic Punching Machine DesignAmrinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of The Weibull Distribution, This Issue - S Reliability BasicDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of The Weibull Distribution, This Issue - S Reliability BasicmarsulexNo ratings yet
- Hron 2012Document15 pagesHron 2012Maica SantosNo ratings yet
- 6 Delay Fault Testing TutorialDocument35 pages6 Delay Fault Testing TutorialjagruthimsNo ratings yet
- CV AzharDocument2 pagesCV AzharAzhar MansuriNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Telescopic BoomDocument6 pagesOptimization of Telescopic BoomVinod YbNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityPARMAR MAHENDRANo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering: Indian Society OF Structural EngineersDocument24 pagesStructural Engineering: Indian Society OF Structural Engineerssuresh_501No ratings yet
- Design of FoundationDocument8 pagesDesign of FoundationRajib BagNo ratings yet
- Stellariswiki MapDocument8 pagesStellariswiki MapberapiNo ratings yet
- PDF (Texts) - RW - Unit 9 - Lesson 4 - The Use of Boldface, Italics, and Underline - DrillsDocument2 pagesPDF (Texts) - RW - Unit 9 - Lesson 4 - The Use of Boldface, Italics, and Underline - DrillsErlie BagnolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PID ControlDocument56 pagesChapter 6 PID ControlHana Muhammad100% (1)
- BTU MeterDocument2 pagesBTU Meternareshbv749No ratings yet
- Curve FittingDocument18 pagesCurve FittingManoj ThapaNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesHeat Exchangerskats2404No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering SeminorsDocument15 pagesElectrical Engineering SeminorsmANOHARNo ratings yet
- DR.M.G.R Educational and Research Institute University: Entrance Examination For PH.D Admission (March 2012)Document3 pagesDR.M.G.R Educational and Research Institute University: Entrance Examination For PH.D Admission (March 2012)Krishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- ch03 PDFDocument11 pagesch03 PDFFarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Boiler OptimizationDocument10 pagesBoiler Optimizationrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- 5.movement Optimization of Robotic Arms For EnergyDocument4 pages5.movement Optimization of Robotic Arms For Energyrajmeet singhNo ratings yet
- ASDA A2 ManualDocument583 pagesASDA A2 ManualClaudio Lourenço da Silva100% (1)