Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DSLR Camera
DSLR Camera
Uploaded by
Abdelrahman HassanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DSLR Camera
DSLR Camera
Uploaded by
Abdelrahman HassanCopyright:
Available Formats
How does a DSLR Camera work?
The lens in a standard DSLR camera is a normal curved piece of glass or plastic. Its job is to take the beams of light reflecting off of an object and redirect them so they come together to form a real image As light travels from one medium to another, it changes speed. Light travels more quickly through air than it does through glass, so a lens slows it down. When light waves enter a piece of glass at an angle, one part of the wave will reach the glass before another and so will start slowing down first. Light bends in one direction. It bends again when it exits the glass because parts of the light wave enter the air and speed up before other parts of the wave. This is known as refraction. In a standard convex lens, one or both sides of the glass curves out. This means rays of light passing through will bend toward the center of the lens on entry. Also, curving the lens out increases the distance between different points on the lens, This increases the amount of time that one part of the light wave is moving faster than another part, so the light makes a sharper turn. In a lens with a flatter shape, light beams will not turn as sharply. Consequently, the light beams will converge farther away from the lens. To put it another way, the focused real image forms farther away from the lens when the lens has a flatter surface.
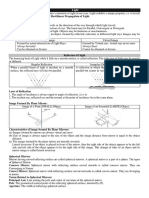
Images form in mirrors via three important Laws: Law of Reflection: When a light ray reaches upon a flat shiny surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Both of these angles are measured relative to a normal drawn to the surface. The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane. Diffuse reflection: When rays are reflected from a rough surface, they are reflected in many directions and no clear image is formed, they are dispersed. Regular reflection: When rays are reflected from a smooth surface, they are reflected so that a clear image is formed.
There are also 3 types of mirrors which form those images: Plane mirrors: Is a flat mirror that reflects light rays in the same order and angle as they reach the mirror. Concave mirrors: A converging mirror; with the surface slightly protruding away, light rays that strike the mirror surface are reflected so that they converge, or "come together," at a point Convex mirrors: A diverging mirror; with surface slightly bending inwards, light rays that strike the mirror surface are reflected so that they diverge, or "go apart," and they never come to a point.
An image sensor is found in a DSLR camera and it is basically a device that converts an optical image into an electronic signal. A CCD image sensor is an analog device. When light strikes the chip it is held as a small electrical charge in each photo sensor. The charges are converted to voltage one pixel at a time as they are read from the chip. Additional circuitry in the camera converts the voltage into digital information. By Abdelrahman Hassan
You might also like
- English 2.06Document2 pagesEnglish 2.06brody100% (3)
- E111 - AgustinDocument20 pagesE111 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- CemeraDocument84 pagesCemerashyam prakash sharmaNo ratings yet
- Refraction by LensesDocument5 pagesRefraction by LensesJanis Micaela EsmasNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical MirrorsDocument9 pagesPlane and Spherical Mirrorschinkayaby16No ratings yet
- 12th Feb 2024Document3 pages12th Feb 2024tanvir.md.ahsanNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Chapter 6 NoteDocument4 pagesGrade 6 Chapter 6 NotesiyaNo ratings yet
- Camera Quiz Autofocus CameraDocument7 pagesCamera Quiz Autofocus CameraKeval KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Question 8KdDocument5 pagesQuestion 8KdShihabsirNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Light NotesDocument5 pagesClass 7 Light Noteschotu bhanuNo ratings yet
- Refraction Lesson 5Document29 pagesRefraction Lesson 5Yohanes Fevian100% (2)
- Additional Notes - LightDocument10 pagesAdditional Notes - LightsidharthNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Image Formation in LensesDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Image Formation in LensesRhian PanaganeNo ratings yet
- Lecture On LightDocument4 pagesLecture On LightAshly DeniseNo ratings yet
- Optics NotesDocument6 pagesOptics Notesvihaanrawal2No ratings yet
- Reflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument11 pagesReflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionmathclubNo ratings yet
- Optics - Reflection, Refraction and LensesDocument46 pagesOptics - Reflection, Refraction and LensesBrianna Malcolm100% (1)
- LensesDocument17 pagesLensesMeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Light Gr.10Document5 pagesLight Gr.10Himayu RanpariaNo ratings yet
- La Martiniere College, Lucknow: Digital Academic ServicesDocument18 pagesLa Martiniere College, Lucknow: Digital Academic ServicesShreya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Document6 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- Concave and Convex LensDocument7 pagesConcave and Convex LensannmarieNo ratings yet
- Course of Lectures Contemporary Physics: Part2 : Lecture 1Document64 pagesCourse of Lectures Contemporary Physics: Part2 : Lecture 1Dana SatybaldyNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection & RefractionDocument29 pagesLight Reflection & Refractionmacff217No ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction - CBSE - XDocument7 pagesReflection and Refraction - CBSE - Xvidyamane23100% (1)
- Principal Focus. Secondary Focus, F' Focal LengthDocument6 pagesPrincipal Focus. Secondary Focus, F' Focal LengthMikkaella BaleñaNo ratings yet
- Lens & MirrorsDocument219 pagesLens & MirrorsChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision NotesDocument35 pagesChapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision Notesprateeksahu1111No ratings yet
- Laws of ReflectionDocument3 pagesLaws of ReflectionMarion Denn GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Notes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 pagesNotes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionShardul SumantNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Lenses: and How Brain Adapts To The Image Reflected or AbsorbedDocument20 pagesMirrors and Lenses: and How Brain Adapts To The Image Reflected or AbsorbedJoy Perez100% (1)
- Light - Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument9 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction NotesRaviraj Desai100% (2)
- Reflection of LightDocument8 pagesReflection of LightShivani ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light Revision NotesDocument28 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light Revision NotesPRATUL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Science Notes6Document37 pagesScience Notes6abhyudai.edwardsNo ratings yet
- Physics - Convex LensDocument15 pagesPhysics - Convex LensdivyapriyaNo ratings yet
- Spherical MirrorsDocument8 pagesSpherical MirrorsJunaid HussainNo ratings yet
- Physics - Light Reflection N Refraction Class 10Document11 pagesPhysics - Light Reflection N Refraction Class 10M S SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - LightDocument35 pagesChapter 10 - LightMadhanNo ratings yet
- LensDocument13 pagesLensDebkanta ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision NotesDocument51 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision Notesved bhaskerNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Images by Convex Concave R ExplainedDocument11 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Images by Convex Concave R ExplainedSeetha SenthilNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesPhysics ProjectRaghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument35 pagesChapter 1 PDFHarshil SagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 Light Final - Ejrm4pw4gjcvtmnndtktDocument17 pagesChapter-10 Light Final - Ejrm4pw4gjcvtmnndtktSarveshyaNo ratings yet
- Mirrors: Law of ReflectionDocument4 pagesMirrors: Law of Reflectionblackmoon_boyzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NoteDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NoteJay Maki100% (1)
- Light PDFDocument5 pagesLight PDFAninda RoyNo ratings yet
- Light ReflectionandnrhehrDocument16 pagesLight ReflectionandnrhehrRaghav NegiNo ratings yet
- 004 - Option C Chapter 15 Imaging PDFDocument67 pages004 - Option C Chapter 15 Imaging PDFAdarsh BhimrajkaNo ratings yet
- Geometric OpticsDocument3 pagesGeometric OpticsYeizmin KimNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction 2Document63 pagesReflection and Refraction 2Alaa Asim OsmanNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light at Plane SurfacesDocument2 pagesRefraction of Light at Plane SurfacesShaik HidayathullaNo ratings yet
- P102LN2324Document35 pagesP102LN2324Ayush Birla100% (1)
- Print - Light WavesDocument22 pagesPrint - Light WavesantonellidejanNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectDocument103 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectRishi Bhatia100% (1)
- Light EnergyDocument5 pagesLight Energyammarahn0No ratings yet
- Reflection of Light by Different SurfacesDocument6 pagesReflection of Light by Different SurfacesShaik HidayathullaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Plane Mirrors LessonDocument23 pages6 - Plane Mirrors LessondaregumacalNo ratings yet
- Victorian LiteratureDocument46 pagesVictorian Literatureraquel395No ratings yet
- Tone - 8 - Plagal 4 - 10 June 2012 - 1 AP - 1 Matt - All SaintsDocument8 pagesTone - 8 - Plagal 4 - 10 June 2012 - 1 AP - 1 Matt - All SaintsMarguerite PaizisNo ratings yet
- Should: "This Is My Fault."Document2 pagesShould: "This Is My Fault."shivani bhaktaNo ratings yet
- Assignment PPD 1Document33 pagesAssignment PPD 1Runaway Shuji33% (3)
- Is The Fourth Dimension TimeDocument5 pagesIs The Fourth Dimension TimejonNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Evaluation Second Edition PDFDocument281 pagesOutcome Based Evaluation Second Edition PDFochay1806100% (2)
- Umberto Eco - The Role of The ReaderDocument140 pagesUmberto Eco - The Role of The ReaderPahomy4100% (14)
- What Is The Purpose of The Message?Document22 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of The Message?gio4sauquilloNo ratings yet
- IAPM PM Guide v05Document29 pagesIAPM PM Guide v05Andre Njotohusodo100% (1)
- Week 2-Chapter 1 - Philosophical Thoughts On EducationDocument6 pagesWeek 2-Chapter 1 - Philosophical Thoughts On EducationJuan Miguel Sapad AlpañoNo ratings yet
- Idealism PPTDocument40 pagesIdealism PPTphoon bookNo ratings yet
- UAP CV FormatDocument4 pagesUAP CV FormatMd. RuHul A.No ratings yet
- CFA New Generation Research Exchange 2023Document3 pagesCFA New Generation Research Exchange 2023Fanat ŠpadiNo ratings yet
- Job Interview Questions For Financial AnalystsDocument5 pagesJob Interview Questions For Financial AnalystsPabitha MonishaNo ratings yet
- The Search For A Unified Theory of Language Learning: 7 Great Theories About Language Learning by Brilliant ThinkersDocument5 pagesThe Search For A Unified Theory of Language Learning: 7 Great Theories About Language Learning by Brilliant ThinkersjamesramilNo ratings yet
- The Zoo Story - Juni ZarlinaDocument2 pagesThe Zoo Story - Juni ZarlinaJuni Zarlina0% (1)
- Leaders Make A Real Difference in An OrganizationDocument4 pagesLeaders Make A Real Difference in An Organization12345No ratings yet
- XI P Notes Projectile MotionDocument33 pagesXI P Notes Projectile Motionsarawalem1No ratings yet
- Sample Narrative Essay - 30th April 2023Document2 pagesSample Narrative Essay - 30th April 2023Dale QuadrosNo ratings yet
- 6003 22562 1 PBDocument19 pages6003 22562 1 PBDwi AsriNo ratings yet
- 1000-Word PhilosophyDocument5 pages1000-Word Philosophyapi-664974041No ratings yet
- 2014 Advent DevotionalDocument30 pages2014 Advent DevotionalestillnazNo ratings yet
- Helping Students With Mathematical Disabilities To SucceedDocument12 pagesHelping Students With Mathematical Disabilities To SucceedAsyraf Jamil100% (1)
- Shell in Nigeria: Corporate Social Responsibility and The Ogoni CrisisDocument17 pagesShell in Nigeria: Corporate Social Responsibility and The Ogoni Crisisモーラーリー いたちNo ratings yet
- Talking Therapies For MaoriDocument68 pagesTalking Therapies For MaoriRobert Ford100% (2)
- Abdul Salam Federal CT DecisionDocument14 pagesAbdul Salam Federal CT DecisionpolismiliterNo ratings yet
- Tes Profil Pribadi - Definisi Kata: NamaDocument8 pagesTes Profil Pribadi - Definisi Kata: Namareadme345No ratings yet
- Safety Aspects TrainingDocument65 pagesSafety Aspects Trainingmujeebmehar100% (4)
- 1-Quantitative Decision Making and Overview PDFDocument14 pages1-Quantitative Decision Making and Overview PDFAbhilashNo ratings yet