Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition
Definition
Uploaded by
Jaydison AniwerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition
Definition
Uploaded by
Jaydison AniwerCopyright:
Available Formats
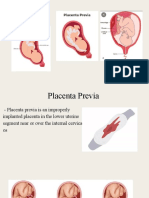
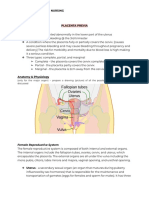
Definition Placenta previa is a condition that occurs during pregnancy when the placenta is abnormally placed, and partially
or totally covers the cervix. Sign and Symptoms Sudden, painless vaginal bleeding that is light to heavy. The blood is often bright red. Symptoms of early labor, such as regular contraction and aches or pains in your lower back or belly. Medium to severe vaginal bleeding during the first trimester. Any vaginal bleeding in the second or third trimesters. Laboratory test
Placenta previa is diagnosed through ultrasound, either during a routine prenatal appointment or after an episode of vaginal bleeding.
A definitive diagnosis may require a combination of abdominal ultrasound and transvaginal ultrasound, which is done through a wand-like device placed inside your vagina. Your health care provider will closely monitor the location of the transducer in your vagina to prevent any bleeding. In rare instances, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to clearly determine the placental location.
If your health care provider suspects that you may have placenta previa, he or she will avoid routine vaginal exams to reduce the risk of heavy bleeding. You may need additional ultrasounds to determine the exact location of your placenta before delivery. Your baby's heartbeat may be tracked as well.
NCP Assessment
S-O-> Bleeding Episodes (amount, duration) > Facial Grimace dueof Pain > Complaintof pain Abdomen soft/hard when palpated > Manifest Body Weakness > Low BP Increased HR
Nursing Dx
Deficient Fluid Volume r/t Active Blood Loss Secondary to Disrupted Placental Implantation.
Planning
Short Term:After 4 hours of NI, the pt will verbalize understanding of causative factors.Long Term: After 4 days of NI, the pt will maintain fluid volume at a functional level AEB individually adequate urinary output and stable vital signs.
Nursing Interventions
1. Establish Rapport2. Monitor Vital Signs3. Assess color, odor, consistency and amount of vaginal bleeding; weigh pads 4. Assess hourly intake and output. 5. Assess
Rationale
1. To gain patients trust2. To obtain baseline data3. Provides information about active bleeding versus old blood, tissue loss and degree of blood loss 4. Provides information about maternal and fetal physiologic compensation to blood loss
Expected Outcome
Short Term:The pt shall have verbalized understanding of causative factors.Long Term: The pt shall have maintained fluid volume at a functional level AEB individually adequate urinary output and stable vital signs.
baseline data and
Decreased RR Fetal HR >120-160 bpm > Decreased Urine Out > Increased Urine Concentration > Pale, Cool Skin >Increased Capillary Refill
note changes. Monitor FHR. 6. Assess
5.
Assessment
provides information about possible infection, placenta previa or abruption. Warm, moist, bloody environment is ideal for growth of microorganisms. 6. Detecting
abdomen for tenderness or rigidity- if present, measure abdomen at umbilicus (specify time interval) 7. Assess SaO2,
increased in measurement of abdominal girth suggests active abruption 7. Assessment
skin color, temp, moisture, turgor, capillary refill (specify frequency) 8. note forcomplaints of thirst or apprehension 9. Provide supplemental O2 as ordered via facemask or nasal cannula @ 10-12 L/min. 10. Initiate IV fluids as ordered (specify fluid type and rate). Assess for
changes in LOC:
provides information about blood vol., O2 saturation and peripheral perfusion 8. To detect
signs of cerebral perfusion 9. Intervention
increases available O2 to saturate decreased hemoglobin 10. For 11. Position Pt. in supine with hips elevated if ordered or left lateral position. 12. Monitor lab. Work as obtained: Hgb & Hct, Rh and type, cross match for 2 units RBCs, urinalysis, etc. Scheduled for 11. Position decreases pressure on placenta andcervical os. Left lateral position improves placental perfusion 12. Lab. Work provides replacement of fluid vol. loss
ultrasound as ordered.
information about degree of blood loss; prepares for possibletransfusion. Ultra sound provides info about the cause of bleeding
You might also like
- Obstetric Ultrasound Report FormatDocument3 pagesObstetric Ultrasound Report Formatሀይደር ዶ.ር67% (6)
- Unit VI L&D Case StudyDocument6 pagesUnit VI L&D Case StudyBrooke Misty Ann BaileyNo ratings yet
- Postnatal AssessmentDocument10 pagesPostnatal AssessmentVijith.V.kumar81% (26)
- NCLEX Questions - OB MATERNITY QUESTIONS PDFDocument17 pagesNCLEX Questions - OB MATERNITY QUESTIONS PDFAnneRaquelTalentoNo ratings yet
- Word Association TestDocument4 pagesWord Association TestLouRaine TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)Document7 pagesGovernment College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)priyankaNo ratings yet
- Annual Agreement TemplateDocument4 pagesAnnual Agreement TemplateAngie CrutchfieldNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Is Defined As A Placenta Implanted in The Lower Segment of The UterusDocument21 pagesPlacenta Previa Is Defined As A Placenta Implanted in The Lower Segment of The UterusSundari AtmanegaraNo ratings yet
- 3 Placenta Previa Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages3 Placenta Previa Nursing Care PlansAjay RajpootNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Document6 pagesPlacenta Previa NCP 1Faye Nervanna Alecha Alferez83% (18)
- Case Study Group 2 Chapter 21Document4 pagesCase Study Group 2 Chapter 21Arnold ZamoroNo ratings yet
- LEORAG OBGYN FORMULATION wk1Document2 pagesLEORAG OBGYN FORMULATION wk1FreakyRustlee LeoragNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument87 pagesPlacenta PreviaKaye Cueto100% (1)
- PartographDocument6 pagesPartographalyssa marie salcedo100% (2)
- Ob Ati StudyDocument22 pagesOb Ati Studylpirman0580% (5)
- Partograph HandoutsDocument5 pagesPartograph HandoutsJozarine Chelsea LopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Family During Labor and BirthhhDocument6 pagesNursing Care of Family During Labor and BirthhhAudreySalvadorNo ratings yet
- Final Ob ChecklistDocument21 pagesFinal Ob ChecklistAlbino Fulgencio Santos III100% (1)
- LEORAG OBGYN Formulation wk5Document3 pagesLEORAG OBGYN Formulation wk5FreakyRustlee LeoragNo ratings yet
- NCP ApDocument2 pagesNCP Aprix07No ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Abruptio PlacentaDocument32 pagesPlacenta Previa Abruptio PlacentaQuinonez Anna MarieNo ratings yet
- CH 10 - Antepartum Fetal AssessmentDocument8 pagesCH 10 - Antepartum Fetal Assessmentnat0118100% (1)
- Assigment VDocument4 pagesAssigment VJoey ParkNo ratings yet
- Position Pt. in Supine With Hips Elevated If Ordered or Left Lateral PositionDocument2 pagesPosition Pt. in Supine With Hips Elevated If Ordered or Left Lateral PositionNicole ArandingNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Well BeingDocument29 pagesAssessment of Fetal Well Beingmalaika khanNo ratings yet
- 6 PartographDocument50 pages6 PartographEdelyn Arguelles100% (1)
- Miwfrey Osce GuideDocument49 pagesMiwfrey Osce GuideDramoyo GeofreyNo ratings yet
- Abruptio NCPDocument4 pagesAbruptio NCPShien Samalea Vasquez100% (1)
- Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument9 pagesNeonatal Sepsis NCPHollan Galicia100% (1)
- HematometrocolposDocument7 pagesHematometrocolposanna carmela rani montalboNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Hemorrhage: Client Assessment Data Base: General Findings CirculationDocument11 pagesPrenatal Hemorrhage: Client Assessment Data Base: General Findings CirculationLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Assessment CiDocument5 pagesPost Partum Assessment CiSupremo Manuel M DeluaoNo ratings yet
- PARTOGRAPH ModuleDocument11 pagesPARTOGRAPH ModuleWynjoy NebresNo ratings yet
- Placenta InsufficiencyDocument39 pagesPlacenta InsufficiencyslyfoxkittyNo ratings yet
- Resume Nasogastric Tube InstallationDocument17 pagesResume Nasogastric Tube InstallationRedmy LasmanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment: Vital SignsDocument6 pagesAssessment: Vital SignsDaisy AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- CC C C: June 8, 2011 By: Santos, Edilberto DBDocument63 pagesCC C C: June 8, 2011 By: Santos, Edilberto DBHakugeiNo ratings yet
- Basics of UltrasoundDocument55 pagesBasics of UltrasoundDrChauhan100% (4)
- PLACENTA PREVIA TOTALIS CaseDocument19 pagesPLACENTA PREVIA TOTALIS CasebobtagubaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Haemorrhage (PPH) : DR - Shameem R. AlaasamDocument41 pagesPostpartum Haemorrhage (PPH) : DR - Shameem R. Alaasamمصطفى محمدNo ratings yet
- Routine Problems of Pregnancy5Document7 pagesRoutine Problems of Pregnancy5elgitharahayu67No ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDocument5 pagesPlacenta Previa Case StudyKristine Castillo100% (2)
- H MoleDocument27 pagesH MoleAnjela Fae Jintalan Amador100% (1)
- 2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Document75 pages2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Mary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- The PartogramDocument6 pagesThe PartogramCamille AliNo ratings yet
- Example Nursing Diagnosis and Careplan For N205 Mini Careplanspote Ntial ForDocument25 pagesExample Nursing Diagnosis and Careplan For N205 Mini Careplanspote Ntial ForCorina RadulescuNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Normal LaborDocument31 pagesConduct of Normal LaborMASIINo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument12 pagesPlacenta PreviaAyen Fajardo-HernalNo ratings yet
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument11 pagesPostpartum HemorrhageColeen Aubrey TanNo ratings yet
- H-Mole (Case Study)Document28 pagesH-Mole (Case Study)Mary Ann Lumbay Paye50% (4)
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument11 pagesAbruptio PlacentaAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Postpartal HemorrhageDocument9 pagesPostpartal HemorrhageJkimNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa InfoDocument5 pagesPlacenta Previa Infoirene joyNo ratings yet
- Care of The High Risk NewbornDocument309 pagesCare of The High Risk NewbornClaire Alvarez OngchuaNo ratings yet
- New Born NCPDocument8 pagesNew Born NCPCarl Vincent Marrion Rejuso100% (1)
- Related To Dimminshed Gag Reflexand Impaired Swallowing AbilityDocument5 pagesRelated To Dimminshed Gag Reflexand Impaired Swallowing AbilityFerwina SakiliNo ratings yet
- 1 GYNE 3 - History, PE, Prevention Interaction of Disease and PhysiologyDocument6 pages1 GYNE 3 - History, PE, Prevention Interaction of Disease and PhysiologyIrene FranzNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of the Pregnant PatientFrom EverandDental Management of the Pregnant PatientChristos A. SkouterisNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Blood in Stools, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Blood in Stools, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Recurrent Pregnancy LossFrom EverandRecurrent Pregnancy LossOle Bjarne ChristiansenNo ratings yet
- Gios-Samar V DOTCDocument2 pagesGios-Samar V DOTCJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- STAT CON 2019 - OutlineDocument4 pagesSTAT CON 2019 - OutlineJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- Etude in A Minor (Sky Guitar #111) L1 (TAB)Document3 pagesEtude in A Minor (Sky Guitar #111) L1 (TAB)Jaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- About Application Procedure of Criminal Background CertificateDocument3 pagesAbout Application Procedure of Criminal Background CertificateJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- PRPA ChecklistDocument1 pagePRPA ChecklistJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- Why I Favor Marcos To Be Buried in The L PDFDocument4 pagesWhy I Favor Marcos To Be Buried in The L PDFJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- 24 UCPB Vs UyDocument2 pages24 UCPB Vs UyJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- Japan Visa ApplicationDocument3 pagesJapan Visa ApplicationJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- Pnpacat 2015 Final List of Qualified Examinees 001-Ilcos Sur National High School, Vigan CityDocument1,269 pagesPnpacat 2015 Final List of Qualified Examinees 001-Ilcos Sur National High School, Vigan CityJaydison Aniwer100% (1)
- Private Media-Related Organizations: Agorilla Alvarez Brito Ibis SurioDocument14 pagesPrivate Media-Related Organizations: Agorilla Alvarez Brito Ibis SurioJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- Classlist NSTP As2 - BreakoutDocument5 pagesClasslist NSTP As2 - BreakoutJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- DialogueDocument2 pagesDialogueJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- Elgar - Enigma VariationsDocument146 pagesElgar - Enigma VariationsJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- STS Grades Complete For StudentsDocument38 pagesSTS Grades Complete For StudentsJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- Exercises AttendanceDocument10 pagesExercises AttendanceJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- University of The Philippines Los Baños: Application Form Undergraduate Student AssistantshipDocument3 pagesUniversity of The Philippines Los Baños: Application Form Undergraduate Student AssistantshipJaydison AniwerNo ratings yet
- Tracing Family Traits Using A GenogramDocument3 pagesTracing Family Traits Using A GenogramArvin VelascoNo ratings yet
- Introduction by GMCKSDocument2 pagesIntroduction by GMCKSapi-3822407No ratings yet
- Comparison of Two Different Dry-Needling TechniquesDocument8 pagesComparison of Two Different Dry-Needling TechniquesmozarzamNo ratings yet
- Lucid Dreaming For HealingDocument32 pagesLucid Dreaming For HealingDstringz672880% (5)
- PolicyRenewal 0000000006381920-01Document37 pagesPolicyRenewal 0000000006381920-01Hemant TiwariNo ratings yet
- TranceDocument11 pagesTranceadeblarNo ratings yet
- Apocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsDocument11 pagesApocrine Gland: Sweat Glands Eccrine Gland LipoproteinsSourav DasNo ratings yet
- Lder ARE: Pedal Edema in Older AdultsDocument2 pagesLder ARE: Pedal Edema in Older AdultsIseth ISethNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Diabetis and AnemiaDocument21 pagesCase Study On Diabetis and AnemiaAfna SyedNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Spine AssessmentDocument26 pagesLumbar Spine Assessmentyoyo_pt2007100% (1)
- Listening To and Making Facilitates Brain Recovery ProcessesDocument2 pagesListening To and Making Facilitates Brain Recovery Processestonylee24100% (1)
- Pub 005940 PDFDocument31 pagesPub 005940 PDFkurniaNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument21 pagesLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder Screener GAD7Document2 pagesGeneralized Anxiety Disorder Screener GAD7Indira Damar PangestuNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument4 pagesNCP ErljarseniornNo ratings yet
- Path of Reiki First Degree Manual PDFDocument87 pagesPath of Reiki First Degree Manual PDFsakinehNo ratings yet
- First Aid Pocket GuideDocument24 pagesFirst Aid Pocket GuideHarsh Chadda67% (3)
- Operant Conditioning HandoutDocument12 pagesOperant Conditioning HandoutRotsen YodicoNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of LevofloxacinDocument8 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of LevofloxacinPharma Research LibraryNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For The Prevention and Treatment of Pressure UlcersDocument15 pagesBest Practices For The Prevention and Treatment of Pressure UlcersViroj รักเมืองไทยNo ratings yet
- Acls Drug OverviewDocument2 pagesAcls Drug OverviewBruce Abramowitz100% (1)
- HerbsDocument68 pagesHerbsCharanjeet Singh100% (2)
- Introduction To LocomotorDocument148 pagesIntroduction To LocomotorsherinprinceNo ratings yet
- ND Annual: Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology ReviewDocument12 pagesND Annual: Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology Reviewsulai701280No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communities Research ReportDocument25 pagesTherapeutic Communities Research ReportMentari Prima OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument7 pagesSpinal Cord CompressionMarius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- AnxietydisordersDocument82 pagesAnxietydisordersmayshiaNo ratings yet
- Systematic Review of Rehabilitation Intervention in Palliative Care For Cancer PatientsDocument6 pagesSystematic Review of Rehabilitation Intervention in Palliative Care For Cancer Patientstri indahNo ratings yet