Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lenr Elements Selection
Lenr Elements Selection
Uploaded by
xarnixCopyright:
You might also like
- ESG 332 Test 1 Review SheetDocument12 pagesESG 332 Test 1 Review SheetAshish JohnsonNo ratings yet
- UW CHEM 5100 Homework SolutionDocument11 pagesUW CHEM 5100 Homework Solutionibrahim6muddasserNo ratings yet
- Metallic Oxides by GoodenoughDocument255 pagesMetallic Oxides by Goodenoughmuk_hawkNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Flare Tower Subjected To Wind LoadingDocument99 pagesAnalysis and Design of Flare Tower Subjected To Wind Loadingajivakkom50% (2)
- F321 PeriodicityDocument3 pagesF321 PeriodicityDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Superheavy Elements: Existence, Classification and ExperimentDocument45 pagesSuperheavy Elements: Existence, Classification and ExperimentMerlita TuralbaNo ratings yet
- Bai GiangDocument104 pagesBai GiangminhyNo ratings yet
- 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p: ExamplesDocument104 pages1s 2s 2p 3s 3p: ExamplesminhyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Bonding NotesMohammed YusufNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Galvanic Cells, The Nernst Equation: Chemistry For Engineers LaboratoryDocument8 pagesExperiment 4: Galvanic Cells, The Nernst Equation: Chemistry For Engineers Laboratoryjamila milanoNo ratings yet
- Kevin M. Jones Et Al - Ultracold Photoassociation Spectroscopy: Long-Range Molecules and Atomic ScatteringDocument53 pagesKevin M. Jones Et Al - Ultracold Photoassociation Spectroscopy: Long-Range Molecules and Atomic ScatteringItama23No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Ramez MezNo ratings yet
- Bond and StructureDocument30 pagesBond and StructureRadu StafiNo ratings yet
- CHEM 221/PHY 335 - Molecular Symmetry IDocument50 pagesCHEM 221/PHY 335 - Molecular Symmetry Ipaul javedNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Atomic StructureDocument10 pages1.1. Atomic Structurelilysingh2006No ratings yet
- MST, Module 1, NotesDocument22 pagesMST, Module 1, NotesChandrashekhar KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Atomic Structure PDFDocument10 pages1.1. Atomic Structure PDFi don't have enough money for chicken nuggetsNo ratings yet
- Longuet-Higgins: Studies in Molecular Orbital Theory I: Resonance & Molecular Orbitals in Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument11 pagesLonguet-Higgins: Studies in Molecular Orbital Theory I: Resonance & Molecular Orbitals in Unsaturated HydrocarbonsvanalexbluesNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Metallic BondingDocument7 pagesLec 1 Metallic BondingkenzoNo ratings yet
- Physics Theory-FinalDocument26 pagesPhysics Theory-Finaladibsadman10No ratings yet
- (@TEAMFLOOD) Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument6 pages(@TEAMFLOOD) Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSaksham Singh SakshamNo ratings yet
- Tesi Di Laurea Commissioning With Cosmic Rays of The ALICE Muon Trigger SystemDocument94 pagesTesi Di Laurea Commissioning With Cosmic Rays of The ALICE Muon Trigger SystemgeklaudioNo ratings yet
- A Thank You From Wikipedia Founder Jimmy Wales: Atoms in MoleculesDocument3 pagesA Thank You From Wikipedia Founder Jimmy Wales: Atoms in MoleculesCA Meenaxi SoniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureELVIS BoradNo ratings yet
- Textbook Theory of Molecular Collisions Gabriel G Balint Kurti Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Theory of Molecular Collisions Gabriel G Balint Kurti Ebook All Chapter PDFtim.bass844100% (1)
- Predicting New Simple Inorganic Species by Quantum PDFDocument11 pagesPredicting New Simple Inorganic Species by Quantum PDFNandini GattadahalliNo ratings yet
- Metal Structure and Bonding in MaterialsDocument95 pagesMetal Structure and Bonding in MaterialsTeptep GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Notes On Semiconductor Physics For Electronic DevicesDocument27 pagesNotes On Semiconductor Physics For Electronic DevicesspyseetunaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Ferroelectrics: Pblittlewood January 27, 2002Document26 pagesPhysics of Ferroelectrics: Pblittlewood January 27, 2002Muhammd Usman MalikNo ratings yet
- Elements From The SeaDocument11 pagesElements From The SeaLaurenNo ratings yet
- Book WikiDocument68 pagesBook Wikialice.medeirosNo ratings yet
- 1 Final Session G12: Solid State PhysicsDocument65 pages1 Final Session G12: Solid State PhysicsAhmed ElabasyNo ratings yet
- PH-155 Measurement of Ge Bandgap Using Ge Thin Film Using Four Probe MethodDocument6 pagesPH-155 Measurement of Ge Bandgap Using Ge Thin Film Using Four Probe MethodAmit RajNo ratings yet
- Animation of Figure 5.1: Class 5: Free Electron Gas?Document7 pagesAnimation of Figure 5.1: Class 5: Free Electron Gas?Steel BeingNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument185 pagesChemistryAshutosh Shaw100% (1)
- Calculate Effective No of Atom, Packing Factor EtcDocument7 pagesCalculate Effective No of Atom, Packing Factor EtcTARUN DHUNNANo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodicity - Jack Barrett - 2002Document188 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodicity - Jack Barrett - 2002Cayo Farias100% (2)
- Handbook No.1Document125 pagesHandbook No.1Dhinakar AnnaduraiNo ratings yet
- Band of StabilityDocument8 pagesBand of StabilityDaneilla BanksNo ratings yet
- D Block Elemnets Theory EDocument31 pagesD Block Elemnets Theory EKenny FernandoNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureDocument14 pages2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureAdwaar HassanNo ratings yet
- Science Fundamentals NotesDocument4 pagesScience Fundamentals NotesFaiyaz ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Hydron ColliderDocument6 pagesHydron ColliderrupeshNo ratings yet
- WIEN2k PaperDocument31 pagesWIEN2k Paperdaniel.fidelisNo ratings yet
- (BEST) Chem 16 LE1 Samplex + Answers PDFDocument8 pages(BEST) Chem 16 LE1 Samplex + Answers PDFChris Andrew Mendoza100% (1)
- SLG 5.3.1 Isotopes, Isotones, IsobarsDocument7 pagesSLG 5.3.1 Isotopes, Isotones, IsobarsPaul CustodioNo ratings yet
- The Application of Atomic Absorption Spectra To Chemical AnalysisDocument10 pagesThe Application of Atomic Absorption Spectra To Chemical Analysistenorio pauloNo ratings yet
- Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter: Chapter 3 ReviewDocument8 pagesAtoms: The Building Blocks of Matter: Chapter 3 Reviewshahad mohammadNo ratings yet
- KURENAI: Kyoto University Research Information RepositoryDocument5 pagesKURENAI: Kyoto University Research Information RepositoryDiêgo GuedesNo ratings yet
- Apparent Inverse Gibbs-Thomson Effect in Dealloyed Nanoporous NanoparticlesDocument5 pagesApparent Inverse Gibbs-Thomson Effect in Dealloyed Nanoporous NanoparticlesParamita HaldarNo ratings yet
- Relativistic Effects in Structural ChemistryDocument32 pagesRelativistic Effects in Structural ChemistryEdison FlorezNo ratings yet
- Atoms in MoleculesDocument23 pagesAtoms in MoleculesLuis SosaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Unit1Document20 pagesChemistry - Unit1Mahatma MurthiNo ratings yet
- Elementary Particle Physics in a NutshellFrom EverandElementary Particle Physics in a NutshellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Supercritical TechnologyDocument24 pagesSupercritical TechnologyBv RaoNo ratings yet
- Astm E974 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm E974 PDFHabibie RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lagrange SolutionsDocument5 pagesLagrange SolutionsOwais IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Beam To Col. Pin Connection DesignDocument2 pagesBeam To Col. Pin Connection DesignmaheshbandhamNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: Class I X Ss2 Science-ChemistryDocument6 pagesAtoms and Molecules: Class I X Ss2 Science-ChemistryKhyati BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Review Activity WordDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Review Activity WordsaramafareNo ratings yet
- Aerogel Applications 1998Document8 pagesAerogel Applications 1998EemedellinNo ratings yet
- 1996 CJP KordyukDocument2 pages1996 CJP KordyukXan TolusNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationDocument5 pagesComparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSiva ShankarNo ratings yet
- Slow ReactionDocument27 pagesSlow Reactionmd mithuNo ratings yet
- Antenna 1Document53 pagesAntenna 1Heart StealerNo ratings yet
- Kuznetsov EinsteinDocument387 pagesKuznetsov EinsteinIván Sanchez RojoNo ratings yet
- Resistivity, Conductivity & ResistanceDocument3 pagesResistivity, Conductivity & ResistanceWilson (Electrical Engineer)No ratings yet
- 20020043078Document284 pages20020043078Aaron HarriganNo ratings yet
- Calculus and Analytical Geometry MA101Document1 pageCalculus and Analytical Geometry MA101Mansoor KasiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Particle Physics 4th Edition Martin Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Particle Physics 4th Edition Martin Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterbeswikemysteryy6rp100% (21)
- WME01 01 Que 20220510Document15 pagesWME01 01 Que 20220510muhammad awaisNo ratings yet
- Talk (Hehl & Obukhov)Document22 pagesTalk (Hehl & Obukhov)Nilson Yecid BautistaNo ratings yet
- S1Document37 pagesS1sbpathiNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanNur Kamelia AlyahNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission NotesDocument21 pagesHVDC Transmission NotesHariShankarSharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of deDocument1 pageBasic Concept of derosdianaNo ratings yet
- Program: The 14th Asian Congress of Fluid Mechanics (14 ACFM)Document46 pagesProgram: The 14th Asian Congress of Fluid Mechanics (14 ACFM)TiendatHoangNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Models of SystemsDocument45 pagesMathematical Models of SystemsSaid Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- 7075 Fatigue LimitDocument30 pages7075 Fatigue LimitCasey FordyceNo ratings yet
- Kisssoft Tut 008 E Cylindrical GearpairDocument19 pagesKisssoft Tut 008 E Cylindrical GearpairJorge Ronald Cabrera ÑaupaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Unit - SVDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Unit - SVGiang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Magnetic Blueprint by Albert Roy DavisDocument67 pagesThe Magnetic Blueprint by Albert Roy DavisElena Anca100% (1)
Lenr Elements Selection
Lenr Elements Selection
Uploaded by
xarnixCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Lenr Elements Selection
Lenr Elements Selection
Uploaded by
xarnixCopyright:
Page 1
Date : March 27,2012
Selection of elements for participation in LENR reactions involving proton absorption V G kulkarni Mo. +917587098357 e-mail: vilas1.kulkarni@gmail.com
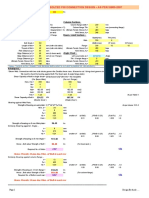
Page 2 Recently E-CAT (which is a LENR based heat source invented by Mr. Andrea Rossi) is in news. Here Ni gets converte into Cu by absorption of a proton. The exact mechanism is yet not clear. In this document I wish to put forth some guideleines using which we can identify elements which can particip[ate in LENR reactions by absorbing protons. Kindly refer to chart 1 on Page 4.The chart shows the transition elements with some of their relevant properties. Note the pairs of elements which are highlighted in color. What are the peculiarities of these pairs of elements? 1) They are all solid at relevant temperatures expected in LENR reactions. 2) The members of each pair are adjacent in with same period numbers of elements. 3) The crystal structure of both the mebers in a given pair is same type. 4) The cell parameters are nearly equal as compared to pairs which are not highlighted but are adjacent to each other. For example in the case of the Ni/Cu pair the cell parameters differ by about 9 pm(picometre) while for a non highlighted pair like Y/Zr, eventhough the cell type is same viz hcp in this case, the cell parameters differ by at least 40 pm. 5) A smaller atomic number is more favorable for participation in LENR than a higher atomic number. Element pair Period 4 V/Cr Ni/Cu Period 5 Nb/Mo Tc/Ru Rh/Pd Period 6 Ta/W Re/Os Ir/Pt Page 3 bcc hcp ccp 14 3 9 bcc hcp ccp 16 3 1 bcc ccp 12 9 Cell type Cell Parameter Difference (pm)
Pairs of elements with members in adjacent positions in periodic table and with small differences in cell parameters and with same type of cell structure and also solid at relevant temperatures are listed above. These are the elements which should be experimented with in LENR involving absorption of a proton. The requirement of element being solid at the relevant temperature is to restrain the absorbing nucleus from moving away due to elctrostatic repulsion between it and the approching proton. For the same reason fcc crystal structure will be more suitable than hcp and hcp will be more suitable than bcc. Similarly an element with a lower atomic number will be more suitable than an element with a higher atomic number again due to lower electrostatic repulsion in the former case. Similar study was made for most other elements in the periodic table but were not found suitable due to above criteria. Lanthanides and Actinoids due to their very high atomic numbers may be rejected straightaway. Therefore following criteria are proposed: a) The selected element for proton adsorption and its adjacent neighbour should be solid at the relevant temperatures. b) The crystal structures of both the elements should be same. c) The cell dimensions should differ as little as possible(like for example the difference should be less than 20 pm). d) A smaller atomic number is more suitable than a larger atomic number. e) Crystal structures ccp and hcp are more preferable than bcc and other structures as these structures constraint the participating nucleus more than do the loosely packed structures. Criteria a and e help in constraining the participating nucleus into a fixed position in face of the electrostatic repulsion from the approaching proton. Criterion b helps in ensuring that all the atoms surrounding the participating nuleus are disturbed very little and a major rearrangement of all atoms is not required during the proton absorption. Criterion d helps in reducing the electrostatic repulsion between the participating nucleus and the proton.
Page 4 Transition Elements:
You might also like
- ESG 332 Test 1 Review SheetDocument12 pagesESG 332 Test 1 Review SheetAshish JohnsonNo ratings yet
- UW CHEM 5100 Homework SolutionDocument11 pagesUW CHEM 5100 Homework Solutionibrahim6muddasserNo ratings yet
- Metallic Oxides by GoodenoughDocument255 pagesMetallic Oxides by Goodenoughmuk_hawkNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Flare Tower Subjected To Wind LoadingDocument99 pagesAnalysis and Design of Flare Tower Subjected To Wind Loadingajivakkom50% (2)
- F321 PeriodicityDocument3 pagesF321 PeriodicityDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Superheavy Elements: Existence, Classification and ExperimentDocument45 pagesSuperheavy Elements: Existence, Classification and ExperimentMerlita TuralbaNo ratings yet
- Bai GiangDocument104 pagesBai GiangminhyNo ratings yet
- 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p: ExamplesDocument104 pages1s 2s 2p 3s 3p: ExamplesminhyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Bonding NotesMohammed YusufNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Galvanic Cells, The Nernst Equation: Chemistry For Engineers LaboratoryDocument8 pagesExperiment 4: Galvanic Cells, The Nernst Equation: Chemistry For Engineers Laboratoryjamila milanoNo ratings yet
- Kevin M. Jones Et Al - Ultracold Photoassociation Spectroscopy: Long-Range Molecules and Atomic ScatteringDocument53 pagesKevin M. Jones Et Al - Ultracold Photoassociation Spectroscopy: Long-Range Molecules and Atomic ScatteringItama23No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Ramez MezNo ratings yet
- Bond and StructureDocument30 pagesBond and StructureRadu StafiNo ratings yet
- CHEM 221/PHY 335 - Molecular Symmetry IDocument50 pagesCHEM 221/PHY 335 - Molecular Symmetry Ipaul javedNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Atomic StructureDocument10 pages1.1. Atomic Structurelilysingh2006No ratings yet
- MST, Module 1, NotesDocument22 pagesMST, Module 1, NotesChandrashekhar KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Atomic Structure PDFDocument10 pages1.1. Atomic Structure PDFi don't have enough money for chicken nuggetsNo ratings yet
- Longuet-Higgins: Studies in Molecular Orbital Theory I: Resonance & Molecular Orbitals in Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument11 pagesLonguet-Higgins: Studies in Molecular Orbital Theory I: Resonance & Molecular Orbitals in Unsaturated HydrocarbonsvanalexbluesNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Metallic BondingDocument7 pagesLec 1 Metallic BondingkenzoNo ratings yet
- Physics Theory-FinalDocument26 pagesPhysics Theory-Finaladibsadman10No ratings yet
- (@TEAMFLOOD) Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument6 pages(@TEAMFLOOD) Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSaksham Singh SakshamNo ratings yet
- Tesi Di Laurea Commissioning With Cosmic Rays of The ALICE Muon Trigger SystemDocument94 pagesTesi Di Laurea Commissioning With Cosmic Rays of The ALICE Muon Trigger SystemgeklaudioNo ratings yet
- A Thank You From Wikipedia Founder Jimmy Wales: Atoms in MoleculesDocument3 pagesA Thank You From Wikipedia Founder Jimmy Wales: Atoms in MoleculesCA Meenaxi SoniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureELVIS BoradNo ratings yet
- Textbook Theory of Molecular Collisions Gabriel G Balint Kurti Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Theory of Molecular Collisions Gabriel G Balint Kurti Ebook All Chapter PDFtim.bass844100% (1)
- Predicting New Simple Inorganic Species by Quantum PDFDocument11 pagesPredicting New Simple Inorganic Species by Quantum PDFNandini GattadahalliNo ratings yet
- Metal Structure and Bonding in MaterialsDocument95 pagesMetal Structure and Bonding in MaterialsTeptep GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Notes On Semiconductor Physics For Electronic DevicesDocument27 pagesNotes On Semiconductor Physics For Electronic DevicesspyseetunaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Ferroelectrics: Pblittlewood January 27, 2002Document26 pagesPhysics of Ferroelectrics: Pblittlewood January 27, 2002Muhammd Usman MalikNo ratings yet
- Elements From The SeaDocument11 pagesElements From The SeaLaurenNo ratings yet
- Book WikiDocument68 pagesBook Wikialice.medeirosNo ratings yet
- 1 Final Session G12: Solid State PhysicsDocument65 pages1 Final Session G12: Solid State PhysicsAhmed ElabasyNo ratings yet
- PH-155 Measurement of Ge Bandgap Using Ge Thin Film Using Four Probe MethodDocument6 pagesPH-155 Measurement of Ge Bandgap Using Ge Thin Film Using Four Probe MethodAmit RajNo ratings yet
- Animation of Figure 5.1: Class 5: Free Electron Gas?Document7 pagesAnimation of Figure 5.1: Class 5: Free Electron Gas?Steel BeingNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument185 pagesChemistryAshutosh Shaw100% (1)
- Calculate Effective No of Atom, Packing Factor EtcDocument7 pagesCalculate Effective No of Atom, Packing Factor EtcTARUN DHUNNANo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodicity - Jack Barrett - 2002Document188 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodicity - Jack Barrett - 2002Cayo Farias100% (2)
- Handbook No.1Document125 pagesHandbook No.1Dhinakar AnnaduraiNo ratings yet
- Band of StabilityDocument8 pagesBand of StabilityDaneilla BanksNo ratings yet
- D Block Elemnets Theory EDocument31 pagesD Block Elemnets Theory EKenny FernandoNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureDocument14 pages2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureAdwaar HassanNo ratings yet
- Science Fundamentals NotesDocument4 pagesScience Fundamentals NotesFaiyaz ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Hydron ColliderDocument6 pagesHydron ColliderrupeshNo ratings yet
- WIEN2k PaperDocument31 pagesWIEN2k Paperdaniel.fidelisNo ratings yet
- (BEST) Chem 16 LE1 Samplex + Answers PDFDocument8 pages(BEST) Chem 16 LE1 Samplex + Answers PDFChris Andrew Mendoza100% (1)
- SLG 5.3.1 Isotopes, Isotones, IsobarsDocument7 pagesSLG 5.3.1 Isotopes, Isotones, IsobarsPaul CustodioNo ratings yet
- The Application of Atomic Absorption Spectra To Chemical AnalysisDocument10 pagesThe Application of Atomic Absorption Spectra To Chemical Analysistenorio pauloNo ratings yet
- Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter: Chapter 3 ReviewDocument8 pagesAtoms: The Building Blocks of Matter: Chapter 3 Reviewshahad mohammadNo ratings yet
- KURENAI: Kyoto University Research Information RepositoryDocument5 pagesKURENAI: Kyoto University Research Information RepositoryDiêgo GuedesNo ratings yet
- Apparent Inverse Gibbs-Thomson Effect in Dealloyed Nanoporous NanoparticlesDocument5 pagesApparent Inverse Gibbs-Thomson Effect in Dealloyed Nanoporous NanoparticlesParamita HaldarNo ratings yet
- Relativistic Effects in Structural ChemistryDocument32 pagesRelativistic Effects in Structural ChemistryEdison FlorezNo ratings yet
- Atoms in MoleculesDocument23 pagesAtoms in MoleculesLuis SosaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Unit1Document20 pagesChemistry - Unit1Mahatma MurthiNo ratings yet
- Elementary Particle Physics in a NutshellFrom EverandElementary Particle Physics in a NutshellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Supercritical TechnologyDocument24 pagesSupercritical TechnologyBv RaoNo ratings yet
- Astm E974 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm E974 PDFHabibie RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lagrange SolutionsDocument5 pagesLagrange SolutionsOwais IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Beam To Col. Pin Connection DesignDocument2 pagesBeam To Col. Pin Connection DesignmaheshbandhamNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: Class I X Ss2 Science-ChemistryDocument6 pagesAtoms and Molecules: Class I X Ss2 Science-ChemistryKhyati BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Review Activity WordDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Review Activity WordsaramafareNo ratings yet
- Aerogel Applications 1998Document8 pagesAerogel Applications 1998EemedellinNo ratings yet
- 1996 CJP KordyukDocument2 pages1996 CJP KordyukXan TolusNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationDocument5 pagesComparison Between Edge and Screw DislocationAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSiva ShankarNo ratings yet
- Slow ReactionDocument27 pagesSlow Reactionmd mithuNo ratings yet
- Antenna 1Document53 pagesAntenna 1Heart StealerNo ratings yet
- Kuznetsov EinsteinDocument387 pagesKuznetsov EinsteinIván Sanchez RojoNo ratings yet
- Resistivity, Conductivity & ResistanceDocument3 pagesResistivity, Conductivity & ResistanceWilson (Electrical Engineer)No ratings yet
- 20020043078Document284 pages20020043078Aaron HarriganNo ratings yet
- Calculus and Analytical Geometry MA101Document1 pageCalculus and Analytical Geometry MA101Mansoor KasiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Particle Physics 4th Edition Martin Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Particle Physics 4th Edition Martin Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterbeswikemysteryy6rp100% (21)
- WME01 01 Que 20220510Document15 pagesWME01 01 Que 20220510muhammad awaisNo ratings yet
- Talk (Hehl & Obukhov)Document22 pagesTalk (Hehl & Obukhov)Nilson Yecid BautistaNo ratings yet
- S1Document37 pagesS1sbpathiNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanNur Kamelia AlyahNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission NotesDocument21 pagesHVDC Transmission NotesHariShankarSharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of deDocument1 pageBasic Concept of derosdianaNo ratings yet
- Program: The 14th Asian Congress of Fluid Mechanics (14 ACFM)Document46 pagesProgram: The 14th Asian Congress of Fluid Mechanics (14 ACFM)TiendatHoangNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Models of SystemsDocument45 pagesMathematical Models of SystemsSaid Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- 7075 Fatigue LimitDocument30 pages7075 Fatigue LimitCasey FordyceNo ratings yet
- Kisssoft Tut 008 E Cylindrical GearpairDocument19 pagesKisssoft Tut 008 E Cylindrical GearpairJorge Ronald Cabrera ÑaupaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Unit - SVDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Unit - SVGiang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Magnetic Blueprint by Albert Roy DavisDocument67 pagesThe Magnetic Blueprint by Albert Roy DavisElena Anca100% (1)