Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bonfire Certificate: Priyabrat Prasd Mohapatra Roll No.
Bonfire Certificate: Priyabrat Prasd Mohapatra Roll No.
Uploaded by
Priyabrat PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab 7 (Cascaded Amplifier Design) - Sept 20Document8 pagesLab 7 (Cascaded Amplifier Design) - Sept 20WilfredNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Class 12 - Variation of Conductance of Electrolytes With TemperatureDocument21 pagesChemistry Project Class 12 - Variation of Conductance of Electrolytes With TemperatureHimank Goel47% (15)
- (FESTO) Electropneumatics - Basic LevelDocument270 pages(FESTO) Electropneumatics - Basic Levelprf197588% (8)
- Lab Report For Circuit TheoryDocument28 pagesLab Report For Circuit TheoryMuthmain YusofNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument106 pagesElectricityHartini Mohd RazaliNo ratings yet
- Phy FileDocument14 pagesPhy FileabhayNo ratings yet
- Hemistry Invetigatory PojectDocument14 pagesHemistry Invetigatory Pojectyash TewatiaNo ratings yet
- Ssdsacascchemist Ry Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesSsdsacascchemist Ry Investigatory ProjectShahrukh MominNo ratings yet
- 6 Lesson Plan in ElectricityDocument7 pages6 Lesson Plan in ElectricityJustine Collamar GanabNo ratings yet
- Kartik Soni ProjectDocument12 pagesKartik Soni ProjectgauravNo ratings yet
- Emf Ofa Danienl CellDocument19 pagesEmf Ofa Danienl CellTYAGI JINo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesClass 12 Physics ProjectSRIJAN MANI TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Project by DurgeshDocument10 pagesProject by Durgeshdurgeshshilpi01No ratings yet
- Physics Project 1Document15 pagesPhysics Project 1Mohammed FerozeNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics ProjectRichardNo ratings yet
- Varience of Conductance With Concentration of ElectrolyteDocument20 pagesVarience of Conductance With Concentration of ElectrolyteKarthik BNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics Projectvidushimourya5No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument21 pagesChemistry ProjectAditi JangidNo ratings yet
- Science Question Paper Solutions 2023Document23 pagesScience Question Paper Solutions 2023harshvardhanghodke321No ratings yet
- Class 10 Exp 6,7,8Document6 pagesClass 10 Exp 6,7,8nikhilNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics ProjectRichardNo ratings yet
- Rescue AsdDocument21 pagesRescue Asdraj kamalNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Physics PDFDocument65 pagesLab Manual For Physics PDFpiyushbhandulaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument19 pagesChemistry ProjectIshan AgnohotriNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument16 pagesCHEMISTRYA2 MOTIVATION SPREADING GYANNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PROJET ON EMFDocument19 pagesChemistry PROJET ON EMFArartik TyagiNo ratings yet
- Physics ActivityDocument45 pagesPhysics ActivityHarsh boxNo ratings yet
- Projet On Emf of A CellDocument19 pagesProjet On Emf of A CellTYAGI JINo ratings yet
- Science 10 Prep1 Key AnswerDocument16 pagesScience 10 Prep1 Key AnswerchandanNo ratings yet
- Physics Activity KhushiDocument28 pagesPhysics Activity KhushiAnonymous U3nAjDDLMNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesInvestigatory Projectdurgeshshilpi01No ratings yet
- E.M.F of A Daniel CellDocument13 pagesE.M.F of A Daniel CellVasudevSinghNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics Projectmanasagowda344No ratings yet
- FACTORS - AFFECTING - INTERNAL - RESISTANCE - EM (1) - (2) - 3 (1) BhanuDocument14 pagesFACTORS - AFFECTING - INTERNAL - RESISTANCE - EM (1) - (2) - 3 (1) BhanuBHANU PRATAP SWAINNo ratings yet
- Dainell CellDocument7 pagesDainell Cellhack babaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project-To Study The Change in E.M.F of A DANIEL CELL' Due To Various Factors Such As Change in CONCENTRATION, TEMPERATURE & AREA OF ELECTRODEDocument14 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project-To Study The Change in E.M.F of A DANIEL CELL' Due To Various Factors Such As Change in CONCENTRATION, TEMPERATURE & AREA OF ELECTRODESumit Sapra72% (36)
- Demonstration File: Physics Class: Xii (2010-2011) by - Amitesh RaiDocument12 pagesDemonstration File: Physics Class: Xii (2010-2011) by - Amitesh RaiAmitesh RaiNo ratings yet
- Sachin CheDocument19 pagesSachin CheDevaraj DevaNo ratings yet
- Variation of Conductance in ElectrolytesDocument15 pagesVariation of Conductance in Electrolytesnirmal100% (2)
- Factors Affecting Internal Resistance Em4Document13 pagesFactors Affecting Internal Resistance Em4Harsh BajpaiNo ratings yet
- BHOIDocument18 pagesBHOISoul ViperNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Booklet 2010 PDFDocument52 pagesPhysics Practical Booklet 2010 PDFRashiek SmithNo ratings yet
- Session:-2014-15 Subject: - Factors Affecting Internal Resistance of A Cell Made By: - Kikisha Sahu (Xi - B) - 13 Submitted To: - Mr. G.M. PatilDocument12 pagesSession:-2014-15 Subject: - Factors Affecting Internal Resistance of A Cell Made By: - Kikisha Sahu (Xi - B) - 13 Submitted To: - Mr. G.M. PatilSalilSalviNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Project PDF File ROHITDocument17 pages12th Physics Project PDF File ROHITrohitkumar.rk14822No ratings yet
- Sotyo Proko Blic School: TopicDocument15 pagesSotyo Proko Blic School: TopicYahyouknowme100% (1)
- Chemistry NewDocument20 pagesChemistry NewGaurav Anand56% (9)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: IndexDocument20 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: IndexKushlendra SinhNo ratings yet
- To Study Various Factors On Which The Internal Resistance Emf of A Cell Depends PDFDocument13 pagesTo Study Various Factors On Which The Internal Resistance Emf of A Cell Depends PDFarmonbhuyanNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowDocument32 pages7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowTaner YenerNo ratings yet
- Physics Test 4Document2 pagesPhysics Test 4RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Pps Porject 1Document19 pagesChemistry Pps Porject 1krswastik05No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Internal Resistance em WordDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting Internal Resistance em WordShubham SahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Semiconductor Basics-2-3Document40 pagesChapter 1-Semiconductor Basics-2-3Syed Zubair ZahidNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Project PDFDocument17 pages12th Physics Project PDFRohan MehraNo ratings yet
- Tarika Shree Physics Project FinalDocument11 pagesTarika Shree Physics Project FinalNishanth PNo ratings yet
- Self Inductance of CoilDocument11 pagesSelf Inductance of Coilmandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project-Tangent GalvanometerDocument27 pagesInvestigatory Project-Tangent GalvanometerAswajith K BabuNo ratings yet
- Planck's Constant LABDocument3 pagesPlanck's Constant LAByaduvanshilaxman321No ratings yet
- ThermocoupleDocument19 pagesThermocoupleOgunranti RasaqNo ratings yet
- Fluke111 ManualDocument18 pagesFluke111 ManualPark MinkukNo ratings yet
- ECIL Electrical Question Papers With Answers 2011 PDF Model Question Papers of ECIL Electrical SolvedDocument13 pagesECIL Electrical Question Papers With Answers 2011 PDF Model Question Papers of ECIL Electrical SolvedJaniel Jawahar75% (4)
- Amplificador Marantz Pm580a PDFDocument30 pagesAmplificador Marantz Pm580a PDFJesus Garcia HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 PDFDocument4 pagesLab 4 PDFAisha NurymgaliNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurement: Laboratory ManualDocument6 pagesInstrumentation and Measurement: Laboratory ManualFakharNo ratings yet
- K 57Document3 pagesK 57pamuncakNo ratings yet
- HS3 Oscilloscope, 2 Channel, 100 MS - S USB, C - W 1 HP-3060 Probe - EBayDocument3 pagesHS3 Oscilloscope, 2 Channel, 100 MS - S USB, C - W 1 HP-3060 Probe - EBayhugos31No ratings yet
- Ragu 81D Digital Multimeter Operation ManualDocument40 pagesRagu 81D Digital Multimeter Operation ManualTechnical affairsNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa Servopack RepairDocument19 pagesYaskawa Servopack RepairAraik Ambartsumyan100% (1)
- Experiment SuperpositionDocument6 pagesExperiment SuperpositionShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault DetectionDocument8 pagesCable Fault DetectionSpring SuperbNo ratings yet
- 2000-2001 CR250 Ignition Service ManualDocument13 pages2000-2001 CR250 Ignition Service ManualHeidi Hanson0% (1)
- Accessories & PlugDocument79 pagesAccessories & Plugsugar44No ratings yet
- Lap Report 6 Phy 2Document5 pagesLap Report 6 Phy 2ahmed albualiNo ratings yet
- Craftsman 73754 ManualDocument24 pagesCraftsman 73754 Manualjkchromy945No ratings yet
- NUVEOT90LSERVICEMANUALDocument31 pagesNUVEOT90LSERVICEMANUALMUSTAFANo ratings yet
- KDL 32 Ex 500Document26 pagesKDL 32 Ex 500CesarAgustinAlvaradoNo ratings yet
- RAPTORDocument16 pagesRAPTORp.motortechNo ratings yet
- Kew Analog MultimetersDocument2 pagesKew Analog Multimeterswanna_acNo ratings yet
- Best Note Mobile PhoneDocument4 pagesBest Note Mobile PhonekoangyakNo ratings yet
- KH400 Ignition Testing GuideDocument4 pagesKH400 Ignition Testing Guiderich3677No ratings yet
- DLL Electrical PlanDocument18 pagesDLL Electrical PlanTommy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Home Theatre System Active Speaker SystemDocument42 pagesService Manual: Home Theatre System Active Speaker SystemRuslan IakovenkoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity No 2 SALVILLADocument6 pagesLearning Activity No 2 SALVILLAShiela SalvillaNo ratings yet
- DLP in Multitester Reading AnalogDocument10 pagesDLP in Multitester Reading AnalogKikz Bataller100% (1)
Bonfire Certificate: Priyabrat Prasd Mohapatra Roll No.
Bonfire Certificate: Priyabrat Prasd Mohapatra Roll No.
Uploaded by
Priyabrat PrasadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bonfire Certificate: Priyabrat Prasd Mohapatra Roll No.
Bonfire Certificate: Priyabrat Prasd Mohapatra Roll No.
Uploaded by
Priyabrat PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
ii
Bonfire Certificate
This is to certify that this physics demonstration experiment report has been submitted by:He has successfully completed this report under our guidance in the Physics Laboratory during academic year 200809. I am happy that this piece of report of his hard work and dedication.
Priyabrat Prasd Mohapatra Roll no. :-
Mr. B.M.Dalai
Mr. D.K.Sinha
Mr. J.Roy
Mrs. Poly Pattanaik (Principal)
Declaration
This is to certify that I, Priyabrat Prasad Mohapatra of ClassXII of Mothers Public School, Bhubaneswar, has submitted the Physics Demonstration Experiment Report comprising of two demonstration experiments as the evidence of my work in Physics Laboratory under the efficient guidance of Physics Teachers B.M.Dalai, D.K.Sinha & J.Roy.
Priyabrat Prasad Mohapatra
01
Aim of the Demonstration Experiment1
Effect of temperature on the Resistance of Filament of an Electric
iii
Acknowledgement
I express my deep sense of gratitude to Mr. B.M. Dalai & Mr. D.K. Sinha and Mr. J. Roy, for their dynamic guidance and suggestions in preparation of this demonstration report. I am greatly thankful to my father Mr. Pramod Kumar Mohapatra, being a student of the science background, he gave me a proper idea for the presentation of this project.
Priyabrat Prasad Mohapatra
iv
Content
Sl.no no.
1.
Subject
Aim of Demonstration Experiment no.1. Materials Required. Diagram. Theory. Procedure. Observations. Inference. Aim of Demonstration Experiment no.2. Materials Required. Theory. Procedure. Diagram. Observations. Bibliography.
Page
01 02 03 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 13 14 16 17
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14.
02
Materials Required
Multimeter Electric Bulb Connecting wires A.C. power sources Handkerchief
03
Diagram
eLECtric bulb
04
Diagra m
MULTIMETER
05
Theory
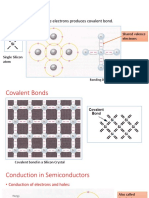
Multimeter: It is a single measuring device acting as an Ammeter as Voltmeter and an Ohmmeter, for this reason, it is also called AVO meter . R = Resistance of material. l = Length of material. A = Area of cross-section of the material. n = No. density. = Relaxation time. e = Electrical charge. m = Mass of filament.
Then, R = ml/ne(for a particular filament). Thus, the resistance of the material depends on the temperature, I A = = Constant Constant
=> R I/
Thus, the resistance of the material depends on the temperature.
06
Procedure
The multimeter knob was turned to Ohmmeter range of 2k. The two lead points were touched with each other and zero reading was confirmed. The bulb was then connected to the two lead points of the multimeter. The resistance of the electric bulb was measured at room temperature. The bulb was then switched on for 5 min., the resistance was measured and was allowed to cool . The electric bulb was again switched for 10 min. and the resistance was measured again. The above procedure was repeated to take one or more set of reading. All the observations were recorded.
07
Observation
Resistance of Resistanc Resistanc the filament e of the e of the Rated Sl.no. at room filament filament Resistanc temperature after after e 5 min. 10 min.
1 2
0.15k 0.15k
0.39k 0.67k 0.38k 0.68k
2.116k 2.116k
08
Inference
The resistance of the filament of an electric bulb increases with increase in temperature. So, the resistance of the filament is directly proportional to temperature.
09
Aim of the Demonstration Experiment2
Study of refraction by keeping a coin at different positions in a beaker containing
10
Materials Required
Glass beaker Water Coin
11
Theory
Refraction: -
The Phenomenon of bending of a ray of light in while traveling from one medium due to change is velocity is called refraction .
Laws Of Refraction: -
There are two laws of refraction: The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal to the interface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane i.e. - they are co-planar. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence (i) to the sine of angle of refraction (r) is constant for any given pair of media. This law is called Snells law.
i.e. sin i /sin r = Constant
12
Total Internal Reflection
The phenomenon by virtue of which a ray of light is sent back to the same medium while traveling from denser medium to rarer medium and angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle is called Total Internal
Reflection. sin c = 1/ c = sin (1/)
13
Procedure
A glass beaker was taken and was filled with clear and transparent water. A coin was dropped in the beaker. The coin was first viewed from the top and then from the side of the container. Then the coin was taken out of the beaker and placed below the container. The coin was again viewed from the top and from the side of the container. The observation was recorded.
14
Diagram
WHEN THE COIN IS INSIDE THE BEAKER
When viewed from the top.
When viewed from any side.
15
Diagram
WHEN THE COIN IS BELOW THE BEAKER
When viewed from the top.
When viewed from any side.
16
Observation
Coin is placed inside the beaker.
a)
When viewed from the top, the coin appears to be raised from its actual position as shown in fig.1.a.
b) The coin is also visible when seen from the sides of the glass container as shown in fig.1.b.
a)
Coin is placed below the container.
The coin is visible and also appears to be raised from its actual position when seen from the top as shown in fig.2.a. The coin is invisible from any other side of the beaker due toTotal Internal Reflection as shown in fig.2.b.
b)
17
Bibliography
NCErt pradeeps fundamental physics move fast with physics internet
MOTHERS PUBLIC SCHOOL
PHYSICS DEMONSTRATION EXPERIMENT REPORTS Submitted By: Priyabrat Prasad Mohapatra Class XII Roll no.: AISSE: - 2008 09 Guided by: Mr. B.M. Dalai Mr. D.K. Sinha Mr. J. Roy
You might also like
- Lab 7 (Cascaded Amplifier Design) - Sept 20Document8 pagesLab 7 (Cascaded Amplifier Design) - Sept 20WilfredNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Class 12 - Variation of Conductance of Electrolytes With TemperatureDocument21 pagesChemistry Project Class 12 - Variation of Conductance of Electrolytes With TemperatureHimank Goel47% (15)
- (FESTO) Electropneumatics - Basic LevelDocument270 pages(FESTO) Electropneumatics - Basic Levelprf197588% (8)
- Lab Report For Circuit TheoryDocument28 pagesLab Report For Circuit TheoryMuthmain YusofNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument106 pagesElectricityHartini Mohd RazaliNo ratings yet
- Phy FileDocument14 pagesPhy FileabhayNo ratings yet
- Hemistry Invetigatory PojectDocument14 pagesHemistry Invetigatory Pojectyash TewatiaNo ratings yet
- Ssdsacascchemist Ry Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesSsdsacascchemist Ry Investigatory ProjectShahrukh MominNo ratings yet
- 6 Lesson Plan in ElectricityDocument7 pages6 Lesson Plan in ElectricityJustine Collamar GanabNo ratings yet
- Kartik Soni ProjectDocument12 pagesKartik Soni ProjectgauravNo ratings yet
- Emf Ofa Danienl CellDocument19 pagesEmf Ofa Danienl CellTYAGI JINo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesClass 12 Physics ProjectSRIJAN MANI TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Project by DurgeshDocument10 pagesProject by Durgeshdurgeshshilpi01No ratings yet
- Physics Project 1Document15 pagesPhysics Project 1Mohammed FerozeNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics ProjectRichardNo ratings yet
- Varience of Conductance With Concentration of ElectrolyteDocument20 pagesVarience of Conductance With Concentration of ElectrolyteKarthik BNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics Projectvidushimourya5No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument21 pagesChemistry ProjectAditi JangidNo ratings yet
- Science Question Paper Solutions 2023Document23 pagesScience Question Paper Solutions 2023harshvardhanghodke321No ratings yet
- Class 10 Exp 6,7,8Document6 pagesClass 10 Exp 6,7,8nikhilNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics ProjectRichardNo ratings yet
- Rescue AsdDocument21 pagesRescue Asdraj kamalNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Physics PDFDocument65 pagesLab Manual For Physics PDFpiyushbhandulaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument19 pagesChemistry ProjectIshan AgnohotriNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument16 pagesCHEMISTRYA2 MOTIVATION SPREADING GYANNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PROJET ON EMFDocument19 pagesChemistry PROJET ON EMFArartik TyagiNo ratings yet
- Physics ActivityDocument45 pagesPhysics ActivityHarsh boxNo ratings yet
- Projet On Emf of A CellDocument19 pagesProjet On Emf of A CellTYAGI JINo ratings yet
- Science 10 Prep1 Key AnswerDocument16 pagesScience 10 Prep1 Key AnswerchandanNo ratings yet
- Physics Activity KhushiDocument28 pagesPhysics Activity KhushiAnonymous U3nAjDDLMNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesInvestigatory Projectdurgeshshilpi01No ratings yet
- E.M.F of A Daniel CellDocument13 pagesE.M.F of A Daniel CellVasudevSinghNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics Projectmanasagowda344No ratings yet
- FACTORS - AFFECTING - INTERNAL - RESISTANCE - EM (1) - (2) - 3 (1) BhanuDocument14 pagesFACTORS - AFFECTING - INTERNAL - RESISTANCE - EM (1) - (2) - 3 (1) BhanuBHANU PRATAP SWAINNo ratings yet
- Dainell CellDocument7 pagesDainell Cellhack babaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project-To Study The Change in E.M.F of A DANIEL CELL' Due To Various Factors Such As Change in CONCENTRATION, TEMPERATURE & AREA OF ELECTRODEDocument14 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project-To Study The Change in E.M.F of A DANIEL CELL' Due To Various Factors Such As Change in CONCENTRATION, TEMPERATURE & AREA OF ELECTRODESumit Sapra72% (36)
- Demonstration File: Physics Class: Xii (2010-2011) by - Amitesh RaiDocument12 pagesDemonstration File: Physics Class: Xii (2010-2011) by - Amitesh RaiAmitesh RaiNo ratings yet
- Sachin CheDocument19 pagesSachin CheDevaraj DevaNo ratings yet
- Variation of Conductance in ElectrolytesDocument15 pagesVariation of Conductance in Electrolytesnirmal100% (2)
- Factors Affecting Internal Resistance Em4Document13 pagesFactors Affecting Internal Resistance Em4Harsh BajpaiNo ratings yet
- BHOIDocument18 pagesBHOISoul ViperNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Booklet 2010 PDFDocument52 pagesPhysics Practical Booklet 2010 PDFRashiek SmithNo ratings yet
- Session:-2014-15 Subject: - Factors Affecting Internal Resistance of A Cell Made By: - Kikisha Sahu (Xi - B) - 13 Submitted To: - Mr. G.M. PatilDocument12 pagesSession:-2014-15 Subject: - Factors Affecting Internal Resistance of A Cell Made By: - Kikisha Sahu (Xi - B) - 13 Submitted To: - Mr. G.M. PatilSalilSalviNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Project PDF File ROHITDocument17 pages12th Physics Project PDF File ROHITrohitkumar.rk14822No ratings yet
- Sotyo Proko Blic School: TopicDocument15 pagesSotyo Proko Blic School: TopicYahyouknowme100% (1)
- Chemistry NewDocument20 pagesChemistry NewGaurav Anand56% (9)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: IndexDocument20 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: IndexKushlendra SinhNo ratings yet
- To Study Various Factors On Which The Internal Resistance Emf of A Cell Depends PDFDocument13 pagesTo Study Various Factors On Which The Internal Resistance Emf of A Cell Depends PDFarmonbhuyanNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowDocument32 pages7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowTaner YenerNo ratings yet
- Physics Test 4Document2 pagesPhysics Test 4RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Pps Porject 1Document19 pagesChemistry Pps Porject 1krswastik05No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Internal Resistance em WordDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting Internal Resistance em WordShubham SahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Semiconductor Basics-2-3Document40 pagesChapter 1-Semiconductor Basics-2-3Syed Zubair ZahidNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Project PDFDocument17 pages12th Physics Project PDFRohan MehraNo ratings yet
- Tarika Shree Physics Project FinalDocument11 pagesTarika Shree Physics Project FinalNishanth PNo ratings yet
- Self Inductance of CoilDocument11 pagesSelf Inductance of Coilmandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project-Tangent GalvanometerDocument27 pagesInvestigatory Project-Tangent GalvanometerAswajith K BabuNo ratings yet
- Planck's Constant LABDocument3 pagesPlanck's Constant LAByaduvanshilaxman321No ratings yet
- ThermocoupleDocument19 pagesThermocoupleOgunranti RasaqNo ratings yet
- Fluke111 ManualDocument18 pagesFluke111 ManualPark MinkukNo ratings yet
- ECIL Electrical Question Papers With Answers 2011 PDF Model Question Papers of ECIL Electrical SolvedDocument13 pagesECIL Electrical Question Papers With Answers 2011 PDF Model Question Papers of ECIL Electrical SolvedJaniel Jawahar75% (4)
- Amplificador Marantz Pm580a PDFDocument30 pagesAmplificador Marantz Pm580a PDFJesus Garcia HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 PDFDocument4 pagesLab 4 PDFAisha NurymgaliNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurement: Laboratory ManualDocument6 pagesInstrumentation and Measurement: Laboratory ManualFakharNo ratings yet
- K 57Document3 pagesK 57pamuncakNo ratings yet
- HS3 Oscilloscope, 2 Channel, 100 MS - S USB, C - W 1 HP-3060 Probe - EBayDocument3 pagesHS3 Oscilloscope, 2 Channel, 100 MS - S USB, C - W 1 HP-3060 Probe - EBayhugos31No ratings yet
- Ragu 81D Digital Multimeter Operation ManualDocument40 pagesRagu 81D Digital Multimeter Operation ManualTechnical affairsNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa Servopack RepairDocument19 pagesYaskawa Servopack RepairAraik Ambartsumyan100% (1)
- Experiment SuperpositionDocument6 pagesExperiment SuperpositionShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault DetectionDocument8 pagesCable Fault DetectionSpring SuperbNo ratings yet
- 2000-2001 CR250 Ignition Service ManualDocument13 pages2000-2001 CR250 Ignition Service ManualHeidi Hanson0% (1)
- Accessories & PlugDocument79 pagesAccessories & Plugsugar44No ratings yet
- Lap Report 6 Phy 2Document5 pagesLap Report 6 Phy 2ahmed albualiNo ratings yet
- Craftsman 73754 ManualDocument24 pagesCraftsman 73754 Manualjkchromy945No ratings yet
- NUVEOT90LSERVICEMANUALDocument31 pagesNUVEOT90LSERVICEMANUALMUSTAFANo ratings yet
- KDL 32 Ex 500Document26 pagesKDL 32 Ex 500CesarAgustinAlvaradoNo ratings yet
- RAPTORDocument16 pagesRAPTORp.motortechNo ratings yet
- Kew Analog MultimetersDocument2 pagesKew Analog Multimeterswanna_acNo ratings yet
- Best Note Mobile PhoneDocument4 pagesBest Note Mobile PhonekoangyakNo ratings yet
- KH400 Ignition Testing GuideDocument4 pagesKH400 Ignition Testing Guiderich3677No ratings yet
- DLL Electrical PlanDocument18 pagesDLL Electrical PlanTommy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Home Theatre System Active Speaker SystemDocument42 pagesService Manual: Home Theatre System Active Speaker SystemRuslan IakovenkoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity No 2 SALVILLADocument6 pagesLearning Activity No 2 SALVILLAShiela SalvillaNo ratings yet
- DLP in Multitester Reading AnalogDocument10 pagesDLP in Multitester Reading AnalogKikz Bataller100% (1)