Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometric Shapes
Geometric Shapes
Uploaded by
Haresh ParmarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Demystifying - Ict @ict - Leaked - CoursesDocument74 pagesDemystifying - Ict @ict - Leaked - CoursesAbhinav Shrivastava95% (38)
- Solid Mensuration FormulasDocument2 pagesSolid Mensuration FormulasAllen Ang Naiba89% (71)
- Trigonometry ReviewerDocument10 pagesTrigonometry ReviewerNiko Ramarama100% (1)
- Trigo IdentitiesDocument29 pagesTrigo IdentitiesKunalKaushikNo ratings yet
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDocument7 pagesCXC MATHS Formula SheetEric D Medeci100% (1)
- 3D-Shapes Symmetry Patterns-Term2 WorksheetDocument3 pages3D-Shapes Symmetry Patterns-Term2 Worksheetmahroof50% (2)
- Geometry: 3. Solid BodiesDocument40 pagesGeometry: 3. Solid BodiesEduardo Tello del PinoNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Geometry (2D)Document26 pagesGeometry (2D)mnashish619No ratings yet
- Mensuration IDocument0 pagesMensuration IBalabhadruni SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Geometry FlashCardsDocument26 pagesGeometry FlashCardsjcargs3100% (1)
- MensurationDocument0 pagesMensurationBalabhadruni SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Cliff S Notes GeometryDocument2 pagesCliff S Notes GeometryKamal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryFranc VenturaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesDocument9 pagesUNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesAaron BrennNo ratings yet
- Math HelpDocument8 pagesMath Helpatiggy05100% (1)
- NGEC 9 Module 1 (Week 2-3) - Student Copy To UploadDocument93 pagesNGEC 9 Module 1 (Week 2-3) - Student Copy To Uploadvjan LeonorNo ratings yet
- Math 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyDocument13 pagesMath 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyArrojo Rhiane Hilary MaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document17 pagesLecture 01David OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 2 MathDocument5 pages2 MathAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Geometryessy_abNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasDocument10 pagesImportant Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasAmey GudigarNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals NotesDocument11 pagesQuadrilaterals NotesJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument36 pagesTrigonometryYoshika GNo ratings yet
- Plane Solid GeometryDocument113 pagesPlane Solid GeometryChalle MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration - Chapter 1Document76 pagesSolid Mensuration - Chapter 1Christian Esteban80% (10)
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Glossary of TermsDocument8 pagesGeometry Glossary of Termsapi-66400853No ratings yet
- Mensuration For Bank ExamsDocument5 pagesMensuration For Bank ExamsRahul Kumar KNo ratings yet
- SM 15161 Mensuration IDocument5 pagesSM 15161 Mensuration Ipavan kumar kvsNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesDocument27 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesArpita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geometric FormulasDocument7 pagesGeometric Formulasprince168No ratings yet
- M911 Les12-13Document5 pagesM911 Les12-13TuyếnĐặngNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulasDocument31 pagesGeometry FormulasJohn Mark IndiongcoNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Quantitative Aptitude Revision Maths ShortcutsDocument108 pagesFlashcards Quantitative Aptitude Revision Maths Shortcutskvdheerajkumar100% (1)
- All Math FormulasDocument27 pagesAll Math FormulasMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument100 pagesChapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsSushanta Singh100% (1)
- KMA002 - L05a - GeometryDocument35 pagesKMA002 - L05a - GeometrymikeyNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Quantitative ReviewDocument108 pagesFlashcards - Quantitative ReviewEduardo KidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Polygons, Triangle, QuadrilateralDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - Polygons, Triangle, QuadrilateralPaulo Bonifacio100% (1)
- Lesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric FunctionsDocument51 pagesLesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric FunctionsSharmaine TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric Functions-CombinedDocument185 pagesLesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric Functions-CombinedSharmaine TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Revcards SSMDocument12 pagesRevcards SSMapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Geometry ReviewDocument2 pagesGeometry ReviewJesuv Cristian CleteNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument5 pagesTriangleEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas - AreaDocument7 pagesImportant Formulas - Areaharit_ecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Maths NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Maths NotesViral DaftaryNo ratings yet
- MH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeDocument12 pagesMH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeNikhil Mahajan100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other Polygons with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other Polygons with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Properties of Corn Cob Ash ConcreteDocument238 pagesProperties of Corn Cob Ash ConcreteENgřMuhăɱɱadRiǺzAhɱad88% (8)
- Coupled LinesDocument10 pagesCoupled LinesFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- WIMO Final 2021 GeneralDocument4 pagesWIMO Final 2021 Generalsusan chuaNo ratings yet
- OOPS ConceptsDocument9 pagesOOPS ConceptsVijay ChikkalaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Math 6Document7 pagesQ2 Math 6JUVY PONTILLASNo ratings yet
- Photoshop-Elements Reference PDFDocument376 pagesPhotoshop-Elements Reference PDFInahoNo ratings yet
- Control System ComponentsDocument29 pagesControl System Componentsshreemanti0% (1)
- LogDocument17 pagesLogErlangga KukuhNo ratings yet
- The Dell Online Store - Build Your SystemDocument3 pagesThe Dell Online Store - Build Your SystemEduardo AguirreNo ratings yet
- Computer Science ISC Sample Paper 2 PDFDocument9 pagesComputer Science ISC Sample Paper 2 PDFNirmal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Python Developer MCQ-QuestionsDocument11 pagesPython Developer MCQ-Questionsrammit2007No ratings yet
- ENGLISH SEMANTICS MID TERM TEST (YerichoApb - E1D118117)Document1 pageENGLISH SEMANTICS MID TERM TEST (YerichoApb - E1D118117)Richo PratamaNo ratings yet
- Achiever DLP Unit Test 3 SoDocument11 pagesAchiever DLP Unit Test 3 SoChetan LaxkarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Wimax: Sector Antenna Installation ManualDocument17 pagesMobile Wimax: Sector Antenna Installation ManualjbonvierNo ratings yet
- EceDocument50 pagesEcemandadi21No ratings yet
- Preparation and Evaluation of Wound Healing Activity of Ursolic Acid Nanoemulgel Formulations in RatsDocument11 pagesPreparation and Evaluation of Wound Healing Activity of Ursolic Acid Nanoemulgel Formulations in RatsRAPPORTS DE PHARMACIENo ratings yet
- Project Noah - Climatex: Accurate Rain Forecasting For The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesProject Noah - Climatex: Accurate Rain Forecasting For The PhilippinesJaja Ordinario Quiachon-AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity Static ElectricityDocument4 pagesStatic Electricity Static ElectricitycashmoneybagsNo ratings yet
- Passing Ability of Self-Consolidating Concrete by J-Ring: Standard Test Method ForDocument5 pagesPassing Ability of Self-Consolidating Concrete by J-Ring: Standard Test Method ForbilalNo ratings yet
- GN CFD I8 3015c 6000w Raycus Technical SolutionDocument23 pagesGN CFD I8 3015c 6000w Raycus Technical SolutionigorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Rutherford ExperimentDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Rutherford ExperimentSana ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Jacques Charles (1746 - 1823)Document5 pagesGas Laws: Jacques Charles (1746 - 1823)cj lequinNo ratings yet
- Delamination Measurement in Glass Fibre Reinforced Poly - 2023 - Composites PartDocument12 pagesDelamination Measurement in Glass Fibre Reinforced Poly - 2023 - Composites PartGUANCI ZHUNo ratings yet
- Technical & Commercial Offer PDFDocument22 pagesTechnical & Commercial Offer PDFMACMET ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Adding Sense To The Internet of Things - An Architecture Framework For Smart Object SystemsDocument19 pagesAdding Sense To The Internet of Things - An Architecture Framework For Smart Object SystemskwxoNo ratings yet
- Application ListDocument30 pagesApplication ListMario AlcazabaNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 Heat Transfer by Conduction2015Document1 pageAssignment1 Heat Transfer by Conduction2015João de QueirozNo ratings yet
- Module 11: Ipv4 Addressing: Introduction To Networks V7.0 (Itn)Document58 pagesModule 11: Ipv4 Addressing: Introduction To Networks V7.0 (Itn)Diana YacchiremaNo ratings yet
Geometric Shapes
Geometric Shapes
Uploaded by
Haresh ParmarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometric Shapes
Geometric Shapes
Uploaded by
Haresh ParmarCopyright:
Available Formats
MathScope Handbook - Plane Geometry
1
Properties of Some Common Geometric Shapes
To return to the place you have come from just use the Back Button
1. PLANE GEOMETRY
A coIIection of usefuI properties of triangIes , quadriIateraIs , poIygons , and circIes .
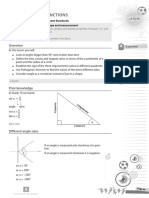
TriangIes
D E J + + = 180
D E J > > > > D E F
T is called an exterior angle.
An exterior angle is equal to the sum of
the two oposite interior angles
T D E = +
Area =
1
2
1
2
1
2
1 2 3
DK EK FK = =
Right-angIed TriangIes
If one of the angles is 90
o
the triangle is called
a right-angIed triangIe
D E F
2 2 2
+ = (Pythagoras Theorem)
and Area =
1
2
DE .
IsosceIes TriangIes
If there are two angles equal it is an
isosceIes triangIe and the sides opposite to
the equal angles are also equal.
Area =
1
4
4
2
E D E
a
b
c
|
o
b
a
c
90
o
|
o
b
a
|
o
o
a
o
E
D
T
c
a
b
h
3
h
1
h
2
Denotes an
angle of 90
o
MathScope Handbook - Plane Geometry
2
EquiIateraI TriangIes
If D E J = = = 60 the triangle is called an
equiIateraI triangIe, and all three sides are
of equal length.
Area =
D
2
3
4
Congruent TriangIes
Two triangles are congruent if they are identical apart from orientation
o o
b
c b c
J
E J E
a a
SimiIar TriangIes
Two triangles are similar if they have the same three angles
B
o | |
A Q C
The ratios of the corresponding sides are equal:-
%& $% $&
34 $3 $4
= =
QuadriIateraIs (Four sides)
D
D E J G + + + = 360 E
G J
a
a
a
60
o
60
o
60
o
MathScope Handbook - Plane Geometry
3
ParaIIeIogram
A quadrilateral with opposite angles
and opposite sides equal andD E + = 180
is called a paraIIeIIogram.
D E + = 180 K
Area = bh = absin o = absin |
If D E = = 90 the figure is
called a rectangIe
Area = ab
A parallelogram with
all sides equal is called a rhombus .
Area = a
2
sin o = a
2
sin |
If D E = = 90 the figure is
called a square.
Area = a
2
Trapezium .
D E + = 180 and J G + = 180
Called a trapezium (or trapezoid)
Area =
1
2
( ) E G K +
a
o
|
b
b
a
a
|
o
o
|
|
o
a
a
a
b
b
a
a
a
a
a
a
h
a
c
b
d
|
o
o
MathScope Handbook - Plane Geometry
4
r
PoIygons
Any plane closed figure having 3 straight sides (3 corners) is called a poIygon.
sum of angles = Q 2 180
If all the angles (and sides) are equal it is called a reguIar poIygon
Angle =
Q
Q
2
180
ExampIes of reguIar poIygons
Pentagon Hexagon Octagon
D = 108 D = 120 D = 135
CircIes
Circle with centre at 0.
Radius 23 U =
Diameter $% U G = = 2
Circumference = 2SU = SG
Area = S S U G
2 2
1
4
=
Straight line 3% is called a chord.
Any triangle inscribed in a semi-circle
is a right angled triangle.
r
o
o
o
o
o o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
0
r
P
B
A
r
0
MathScope Handbook - Plane Geometry
5
CircuIar Measure (Radians)
Arc length $% U = D
Area of sector 2$% U =
1
2
2
D
where D is measured in radians.
1 radian
180
S
degrees
1 degree
S
180
radians.
ExampIes
10
10
180
0174533
=
S
. radians
180 S radians
90
2
S
radians
60
3
S
radians
30
6
S
radians
45
4
S
radians
1 radian 57 2958 . degrees.
o
A
B
0
r
o
r
MathScope Handbook - Plane Geometry
6
2. SOLID GEOMETRY
A coIIection of usefuI properties of paraIIeIepipeds , pyramids , cyIinders ,cones and
spheres .
RectanguIar paraIIeIepiped
6 rectangular faces
Surface are, = 2(,-+,.+-.)
Volume = ,-.
If all faces are square it is called a cube.
6 square faces
Surface area = 6,
2
Volume = ,
3
Pyramids
B = base area, h = height
Triangular base Rectangular base
Volume =
1
3
%K Volume =
1
3
%K
a
b
c
a
a
a
MathScope Handbook - Plane Geometry
7
CyIinders
General cylinder Right circular cylinder
Volume = %K Volume = S U
2
K
Curved surface area = 2S UK
Cones
General cone Right circular cone
Volume =
1
3
%K Volume =
1
3
2
SU K
Curved surface area = SU)
Sphere
Surface area = 4
2
SU
Volume =
4
3
3
SU
Surface area of shaded cap = 4
2
2 2
S
D
U sin .
The quantity 4
2
2
S
D
sin is called the solid angle subtended by the cap at the centre of the
sphere.
h
r
h
h
h
r
)
r r
o
You might also like
- Demystifying - Ict @ict - Leaked - CoursesDocument74 pagesDemystifying - Ict @ict - Leaked - CoursesAbhinav Shrivastava95% (38)
- Solid Mensuration FormulasDocument2 pagesSolid Mensuration FormulasAllen Ang Naiba89% (71)
- Trigonometry ReviewerDocument10 pagesTrigonometry ReviewerNiko Ramarama100% (1)
- Trigo IdentitiesDocument29 pagesTrigo IdentitiesKunalKaushikNo ratings yet
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDocument7 pagesCXC MATHS Formula SheetEric D Medeci100% (1)
- 3D-Shapes Symmetry Patterns-Term2 WorksheetDocument3 pages3D-Shapes Symmetry Patterns-Term2 Worksheetmahroof50% (2)
- Geometry: 3. Solid BodiesDocument40 pagesGeometry: 3. Solid BodiesEduardo Tello del PinoNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Geometry (2D)Document26 pagesGeometry (2D)mnashish619No ratings yet
- Mensuration IDocument0 pagesMensuration IBalabhadruni SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Geometry FlashCardsDocument26 pagesGeometry FlashCardsjcargs3100% (1)
- MensurationDocument0 pagesMensurationBalabhadruni SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Cliff S Notes GeometryDocument2 pagesCliff S Notes GeometryKamal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryFranc VenturaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesDocument9 pagesUNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesAaron BrennNo ratings yet
- Math HelpDocument8 pagesMath Helpatiggy05100% (1)
- NGEC 9 Module 1 (Week 2-3) - Student Copy To UploadDocument93 pagesNGEC 9 Module 1 (Week 2-3) - Student Copy To Uploadvjan LeonorNo ratings yet
- Math 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyDocument13 pagesMath 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyArrojo Rhiane Hilary MaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document17 pagesLecture 01David OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 2 MathDocument5 pages2 MathAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Geometryessy_abNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasDocument10 pagesImportant Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasAmey GudigarNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals NotesDocument11 pagesQuadrilaterals NotesJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument36 pagesTrigonometryYoshika GNo ratings yet
- Plane Solid GeometryDocument113 pagesPlane Solid GeometryChalle MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration - Chapter 1Document76 pagesSolid Mensuration - Chapter 1Christian Esteban80% (10)
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Glossary of TermsDocument8 pagesGeometry Glossary of Termsapi-66400853No ratings yet
- Mensuration For Bank ExamsDocument5 pagesMensuration For Bank ExamsRahul Kumar KNo ratings yet
- SM 15161 Mensuration IDocument5 pagesSM 15161 Mensuration Ipavan kumar kvsNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesDocument27 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesArpita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geometric FormulasDocument7 pagesGeometric Formulasprince168No ratings yet
- M911 Les12-13Document5 pagesM911 Les12-13TuyếnĐặngNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulasDocument31 pagesGeometry FormulasJohn Mark IndiongcoNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Quantitative Aptitude Revision Maths ShortcutsDocument108 pagesFlashcards Quantitative Aptitude Revision Maths Shortcutskvdheerajkumar100% (1)
- All Math FormulasDocument27 pagesAll Math FormulasMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument100 pagesChapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsSushanta Singh100% (1)
- KMA002 - L05a - GeometryDocument35 pagesKMA002 - L05a - GeometrymikeyNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Quantitative ReviewDocument108 pagesFlashcards - Quantitative ReviewEduardo KidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Polygons, Triangle, QuadrilateralDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - Polygons, Triangle, QuadrilateralPaulo Bonifacio100% (1)
- Lesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric FunctionsDocument51 pagesLesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric FunctionsSharmaine TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric Functions-CombinedDocument185 pagesLesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric Functions-CombinedSharmaine TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Revcards SSMDocument12 pagesRevcards SSMapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Geometry ReviewDocument2 pagesGeometry ReviewJesuv Cristian CleteNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument5 pagesTriangleEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas - AreaDocument7 pagesImportant Formulas - Areaharit_ecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Maths NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Maths NotesViral DaftaryNo ratings yet
- MH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeDocument12 pagesMH-CET MBA Geometry FormulaeNikhil Mahajan100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other Polygons with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other Polygons with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Properties of Corn Cob Ash ConcreteDocument238 pagesProperties of Corn Cob Ash ConcreteENgřMuhăɱɱadRiǺzAhɱad88% (8)
- Coupled LinesDocument10 pagesCoupled LinesFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- WIMO Final 2021 GeneralDocument4 pagesWIMO Final 2021 Generalsusan chuaNo ratings yet
- OOPS ConceptsDocument9 pagesOOPS ConceptsVijay ChikkalaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Math 6Document7 pagesQ2 Math 6JUVY PONTILLASNo ratings yet
- Photoshop-Elements Reference PDFDocument376 pagesPhotoshop-Elements Reference PDFInahoNo ratings yet
- Control System ComponentsDocument29 pagesControl System Componentsshreemanti0% (1)
- LogDocument17 pagesLogErlangga KukuhNo ratings yet
- The Dell Online Store - Build Your SystemDocument3 pagesThe Dell Online Store - Build Your SystemEduardo AguirreNo ratings yet
- Computer Science ISC Sample Paper 2 PDFDocument9 pagesComputer Science ISC Sample Paper 2 PDFNirmal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Python Developer MCQ-QuestionsDocument11 pagesPython Developer MCQ-Questionsrammit2007No ratings yet
- ENGLISH SEMANTICS MID TERM TEST (YerichoApb - E1D118117)Document1 pageENGLISH SEMANTICS MID TERM TEST (YerichoApb - E1D118117)Richo PratamaNo ratings yet
- Achiever DLP Unit Test 3 SoDocument11 pagesAchiever DLP Unit Test 3 SoChetan LaxkarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Wimax: Sector Antenna Installation ManualDocument17 pagesMobile Wimax: Sector Antenna Installation ManualjbonvierNo ratings yet
- EceDocument50 pagesEcemandadi21No ratings yet
- Preparation and Evaluation of Wound Healing Activity of Ursolic Acid Nanoemulgel Formulations in RatsDocument11 pagesPreparation and Evaluation of Wound Healing Activity of Ursolic Acid Nanoemulgel Formulations in RatsRAPPORTS DE PHARMACIENo ratings yet
- Project Noah - Climatex: Accurate Rain Forecasting For The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesProject Noah - Climatex: Accurate Rain Forecasting For The PhilippinesJaja Ordinario Quiachon-AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity Static ElectricityDocument4 pagesStatic Electricity Static ElectricitycashmoneybagsNo ratings yet
- Passing Ability of Self-Consolidating Concrete by J-Ring: Standard Test Method ForDocument5 pagesPassing Ability of Self-Consolidating Concrete by J-Ring: Standard Test Method ForbilalNo ratings yet
- GN CFD I8 3015c 6000w Raycus Technical SolutionDocument23 pagesGN CFD I8 3015c 6000w Raycus Technical SolutionigorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Rutherford ExperimentDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Rutherford ExperimentSana ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Jacques Charles (1746 - 1823)Document5 pagesGas Laws: Jacques Charles (1746 - 1823)cj lequinNo ratings yet
- Delamination Measurement in Glass Fibre Reinforced Poly - 2023 - Composites PartDocument12 pagesDelamination Measurement in Glass Fibre Reinforced Poly - 2023 - Composites PartGUANCI ZHUNo ratings yet
- Technical & Commercial Offer PDFDocument22 pagesTechnical & Commercial Offer PDFMACMET ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Adding Sense To The Internet of Things - An Architecture Framework For Smart Object SystemsDocument19 pagesAdding Sense To The Internet of Things - An Architecture Framework For Smart Object SystemskwxoNo ratings yet
- Application ListDocument30 pagesApplication ListMario AlcazabaNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 Heat Transfer by Conduction2015Document1 pageAssignment1 Heat Transfer by Conduction2015João de QueirozNo ratings yet
- Module 11: Ipv4 Addressing: Introduction To Networks V7.0 (Itn)Document58 pagesModule 11: Ipv4 Addressing: Introduction To Networks V7.0 (Itn)Diana YacchiremaNo ratings yet