Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry Exam Questions
Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry Exam Questions
Uploaded by
Taarikuu TaaddaseeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry Exam Questions
Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry Exam Questions
Uploaded by
Taarikuu TaaddaseeCopyright:
Available Formats
MEDICAL CHEMISTRY AND BIOCHEMISTRY EXAM QUESTIONS
I. PHYSICAL, BIOANORGANIC AND BIOORGANIC CHEMISTRY
1. 2.
Water- physical and chemical properties and importance in human organism Solubility of compounds, analytical and colloidal dispersions, diffusion, osmosis, osmotic and oncotic pressure, dialysis, biochemical examples
3.
Energetics of chemical reactions, , Gibbs energy and entropy, metabolic applications
4.
Kinetics and energetics of reversible and consecutive reactions, chemical equilibrium,the Guldberg-Waage law , application to enzymology
5.
Basic
techniques
for
the
separation
of
macromolecules
(electrophoresis,
chromatography) and their application in clinical practice 6. 7. Spectrophotometry, application in clinical practice Electrolytic dissociation, dissociation constant, strong and weak electrolytes, biochemical examples 8. Brnsteds theory of acids and bases, equilibrium in protolytic reaction, biochemical examples. Ionic product of water, pH and its importance for medicine 9. Ampholytes - properties, biochemical examples
10. Buffer solution, pH calculation, importance in human organism 11. Oxidation and reduction, redox potential, dependency on the concentration of the reactants and pH, biochemical examples 12. Precipitation reactions, solubility product, formation of complex compounds, examples and importance for biochemistry and medicine 13. Chemical properties of basic biogenic elements 14. Oxygen and reactive forms of oxygen. Lipid peroxidation 15. Biologically and toxicologically important elements of the periodic table with the exclusion of basic biogenic elements, the mechanism of action of selected toxic compounds (CO, KCN, HCN, H2S, heavy metals 16. Trace elements , biological and metabolic importance 17. Structure of organic compounds, isomerism, examples in metabolic pathways
18. Halogen and nitroderivatives of carbohydrates, examples of medically and toxicologically important compounds 19. Sulphur-containing derivatives of carbohydrates, examples of medically important compounds 20. Amines - importance in biochemistry 21. Alcohols, phenols, aldehydes, ketones, biochemical examples 22. Carboxylic acids, functional and substituted derivatives of carboxylic acids, biochemical examples 23. Importance of nitrogen, oxygen and sulphur-containing heterocycles 24. Structural characteristic of amino acids, clasification, reactions, importance, peptides, peptide bond, examples of biologically important peptides 25. Proteins - structure, properties and functions 26. Saccharides - classification, structure, stereochemistry, biological importance 27. Reactions of monosaccharides, disaccharides, O- and N- glykosidic bound, examples 28. Homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharides - structure and importance in organism 29. Proteoglycanes, glycoproteins - structure, properties, examples 30. Lipids - definition, classification, structure, properties, function in organism 31. Phospho- anf sphingolipids - structure, properties and importance in organism 32. Sterols, bile acids and steroid hormones - structure, function and importance in organism
II. METABOLISM
1. Structure of enzymes (cofactors, coenzymes, oligomeric structure), multiple forms of enzymes and isoenzymes, medical application of enzymology 2. Enzymatic activity, influence of physical and chemical conditions, regulation (expression, allosteric effects, covalent modification). Detection of enzymatic activity - methods of measuring (temperature, kinetic versus endpoint measurement) 3. 4. Respiratory chain, oxidative phosphorylation Energy-rich compounds, substrate level phosphorylation, drive of endergonic reactions 5. Citric acid cycle, amphibolic character of the citric acid cycle, regulation
6.
Common mechanisms of amino acids - metabolism, deamination, transamination, nitrogen balance
7.
Formation and detoxification of ammonia, urea cycle and its regulation, hyperammonaemia
8.
Metabolism of the carbon skeleton of amino acids converted into pyruvate, oxalacetate, 2-oxoglutarate, succinyl CoA and branched chain amino acids, integration of amino acids into metabolic pathways
9.
Metabolism of aromatic amino acids, defects of metabolism
10. Metabolism of sulphur-containing amino acids 11. Biosynthesis, biodegradation and function of the most important biogenic amines 12. Conversion of amino acids into special products (formation, conversion and importance of creatine and S-adenosylmethionine, creatinin clearence) 13. Glycolysis, regulation 14. Gluconeogenesis, regulation 15. Degradation and synthesis of glycogen, regulation, inherited disorders 16. Pentose phosphate pathway, regulation 17. Metabolism of galactose and fructose, inherited disorders 18. Metabolism of glucuronic acid and its metabolic importance 19. Biosynthesis of fatty acids 20. Formation of ketone bodies from acetyl-CoA, metabolic causes, importance 21. Carnitine system, oxidation of fatty acids, energy balance 22. Biosynthesis and biodegradation of triacylglycerols 23. Structure, metabolism and function of phospholipids and sphingolipids 24. Synthesis and degradation of eicosanoids, cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways 25. Biosynthesis of cholesterol and its regulation, role of HMG-CoA reductase, transport of the endogenic and exogenic cholesterol 26. Conversion and excretion of cholesterol, bile acids 27. Biosynthesis and biodegradation of steroid hormones 28. Transport of lipids, role of lipoproteins, structure of lipoprotein particles (formation and conversion, role of chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL lipoproteins). Lipoprotein electrophoresis 29. Biosynthesis and degradation of tetrapyrroles, disorders
30. Important blood plasma proteins (albumin, immunoglobulins, complement system, acute-phase proteins, transport proteins) 31. Pyrimidine nucleotides - metabolism, regulation, inhibitors, metabolic disorders 32. Purine nucleotides - metabolism, regulation, inhibitors, metabolic disorders
III. FUNDAMENTALS OF ORGAN AND FUNCTIONAL BIOCHEMISTRY
1. 2. Regulation and coordination of metabolism of carbohydrates and other nutrients Glycaemia and its regulation, diagnostics,(glucose tolerance test. glycosylated haemoglobin) 3. 4. Metabolism of fat tissue Regulation of haem biosynthesis; differences between the hepatocyte and erythroid cell; iron metabolism 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Hormonal regulation of water and mineral metabolism Regulation of bone metabolism Hormonal regulation of energy metabolism Biochemical processes in digestion of nutrients Biochemical functions of hepatocytes and liver; assessment of liver function and damage 10. Biotransformation of endogenous and exogenous compounds; types of the biotransformation processes. Toxic and carcinogenic compounds in the environment 11. Buffer systems of the organism, their significance in maintaining the acido-base balance 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Erythrocyte metabolism Haemocoagulation, cascade of coagulation factors, function of platelets Urine, physiological and pathological constituents Collagen - structure, properties, metabolism Biochemistry of connective tissue (cartilage and bone) Biochemistry of the skin. Biochemical basis of touch. Contractile apparatus, the control of smooth and skeletal muscle contraction. myocardial markers and their importance 19. 20. Biochemistry of vision - Wald cycle, transducin cycle Biochemistry of hearing, taste and olfaction
21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. .
Biochemical events in the synapsis; neurotransmitters Steroid hormones and their functions in regulatory processes Peptide hormones and their functions in regulatory processes Local mediators, cytokines. Thyroid hormones and their functions in regulatory processes. Molecular basis of the humoral immune response. Molecular basis of the cellular immune response Lipid-soluble vitamins Water-soluble vitamins Structure, constituents and properties of cell membranes Membrane transport Compartmentation of biochemical processes at the cellular level
IV. BASIC CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Membrane receptors and their ligands, G-proteins Types of second messengers and their role in signal transduction Signal transduction cascades of cytokines and growth factors Activation of phospholipases and lipid derivates as signaling molecules NO signalling. Overview of signalling pathways Intracellular receptors and their ligands, HSP, interactions of intracellular receptors with DNA 7. 8. 9. Relationships between signal transduction pathways Structure and function of DNA Structure and function of RNA
10. Organization of prokaryotic, eukaryotic and mitochondrial genome 11. Replication of eukaryotic DNA, DNA replication apparatus and its regulation 12. DNA repair 13. Transcription of eukaryotic DNA 14. mRNA - structure, synthesis, posttranscriptional modifications 15. Metabolism of RNA and RNA interference 16. Regulation of gene expression at the level of transcription 17. Genetic code and its properties 18. Eukaryotic, prokaryotic and mitochondrial translation and their regulation
19. Posttranslational modification of proteins, protein transport and targeting, modification and sorting of proteins in Golgi apparatus, biosynthesis of glycoprotein 20. Restriction enzymes and their usage, DNA modification and construction of recombinant DNA molecules, DNA cloning 21. DNA diagnostics, techniques (RFLP, hybridization) 22. Methods of cell fractionation, electrophoretic analysis of nucleic acids and proteins , 23. Polymerase chain reaction, PCR applications in clinical diagnostics, RT-PCR and application of this technique, DNA sequencing 24. Types of human gene mutations, hereditary and somatic mutations, polymorphisms, minisatellite and microsatellite markers and their analysis 25. Retroviruses and pararetroviruses, structure and replication 26. DNA and RNA viruses, replication 27. The role of protooncogenes and tumour suppressor genes 28. Cell cycle, the role of cyclin and cdk complexes 29. Regulation of cell cycle, the role of tumour suppressor genes 30. Ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of proteins 31. Biochemistry of apoptosis 32. Epigenetics, DNA methylation, histone modifications, epigenetic effects in humans
You might also like
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Essentials of Human Anatomy Physiology 12th Global Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Essentials of Human Anatomy Physiology 12th Global Edition PDF Scribdcandace.greco749100% (45)
- Semmelweis Uni Entrance Exam List QuestionDocument6 pagesSemmelweis Uni Entrance Exam List QuestionNgô Minh KhuêNo ratings yet
- Foods To Fight Cancer - What To Eat PDFDocument242 pagesFoods To Fight Cancer - What To Eat PDFdokundot86% (7)
- Nurs3021h Summer 2022 Midterm Evaluation WeigaDocument15 pagesNurs3021h Summer 2022 Midterm Evaluation Weigaapi-547521437No ratings yet
- Seeing The UnseenDocument8 pagesSeeing The UnseenCale HollowayNo ratings yet
- Mbbs BiochemistryDocument12 pagesMbbs BiochemistryKumar KPNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry For Medical Laboratory Science Course Outline 2018Document4 pagesBiochemistry For Medical Laboratory Science Course Outline 2018Vincent Cuyuca100% (1)
- National Asthma - Bronchiolitis - COPD GuidelinesDocument84 pagesNational Asthma - Bronchiolitis - COPD GuidelinesFaisol Kabir86% (7)
- Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry: Exam Questions 2016/2017Document4 pagesMedical Chemistry and Biochemistry: Exam Questions 2016/2017NASIRNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument4 pagesBiochemistryPriya DhanaNo ratings yet
- SU Admission Topics Medical Biology Medical ChemistryDocument3 pagesSU Admission Topics Medical Biology Medical Chemistryahooraakhlaghi01No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY Syllais Ds 1yearDocument3 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY Syllais Ds 1yearPRIYANSHU KAUSHALNo ratings yet
- GPAT Biotechemistry SyllabusDocument2 pagesGPAT Biotechemistry Syllabuskumar HarshNo ratings yet
- mod 3 вопр.q enDocument2 pagesmod 3 вопр.q enSujeewa GunasingheNo ratings yet
- Principles of BiochemistryDocument2 pagesPrinciples of BiochemistryDavid WebNo ratings yet
- Latest Syallabus Outline of 1st Year Biochemistry KEMU 18-1-2017Document5 pagesLatest Syallabus Outline of 1st Year Biochemistry KEMU 18-1-2017gameaus00No ratings yet
- BSC Lectures Schedule 2022 and 2023 SessionDocument14 pagesBSC Lectures Schedule 2022 and 2023 SessionchimebukaanyanwuNo ratings yet
- MedicalBiology Topics 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesMedicalBiology Topics 2020 PDFJINGYE NINo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Carbohydrates and Lipids 30hoursDocument20 pagesUnit - I: Carbohydrates and Lipids 30hoursAbhishek VermaNo ratings yet
- Life SciencesDocument1 pageLife Sciencesrag.1607No ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument1 pageBiochemistryBhavesh JainNo ratings yet
- PUMS Topics For Test Interview 2015-16Document7 pagesPUMS Topics For Test Interview 2015-16Andre ChouNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Syllabus For M.B.B.S. Paper-I (Biochemistry)Document4 pagesBiochemistry Syllabus For M.B.B.S. Paper-I (Biochemistry)nivethaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document11 pagesPaper 1Bharath RajNo ratings yet
- RCET2023-24 62 BiotechnologyDocument7 pagesRCET2023-24 62 Biotechnologysattyadev95No ratings yet
- Latest Syllabus Outline 2nd Year of Biochemistry 02-06-2022Document5 pagesLatest Syllabus Outline 2nd Year of Biochemistry 02-06-2022NM ITCNo ratings yet
- Topics 2023Document3 pagesTopics 2023Achraf RbNo ratings yet
- Booster BiochemistryDocument1 pageBooster BiochemistryAli AlqumaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry scqp05 PDFDocument5 pagesBiochemistry scqp05 PDFnobithasujuka341No ratings yet
- BSC Lectures Schedule 2023Document13 pagesBSC Lectures Schedule 2023chimebukaanyanwuNo ratings yet
- Second Sem SyllabusDocument17 pagesSecond Sem SyllabusbharathNo ratings yet
- Essay Titles + MarkschemesDocument49 pagesEssay Titles + MarkschemesSairah RazakNo ratings yet
- VPB - 112 General Veterinary BiochemistryDocument1 pageVPB - 112 General Veterinary BiochemistryransinghNo ratings yet
- M.sc. Biochemistry SyllabusDocument22 pagesM.sc. Biochemistry SyllabusMohannad WalyNo ratings yet
- P.G. Curriculum MD Biochemistry Index: 1. GoalDocument16 pagesP.G. Curriculum MD Biochemistry Index: 1. GoalHari PrasathNo ratings yet
- M Sc. BiochemistryDocument2 pagesM Sc. BiochemistryFalaque UmarNo ratings yet
- Biochem Exam Topics Dent 2022Document4 pagesBiochem Exam Topics Dent 2022znycdr5kc8No ratings yet
- Syllabus Zoology 2nd FINALDocument11 pagesSyllabus Zoology 2nd FINALmahendrasri306No ratings yet
- Syllabus - MBBSDocument20 pagesSyllabus - MBBSsidsrivNo ratings yet
- Biochem QbankDocument16 pagesBiochem Qbank786waqar786No ratings yet
- Agsc 1142 Agricultural Biochemistry PalabanaDocument3 pagesAgsc 1142 Agricultural Biochemistry PalabanaSALATIEL PHIRI RLNo ratings yet
- GATE 2012 Life ScienceDocument3 pagesGATE 2012 Life ScienceMohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Questions For Correcting Un Satisfactory Grades For Written Control Works (2023-24)Document2 pagesBiochemistry - Questions For Correcting Un Satisfactory Grades For Written Control Works (2023-24)submen81No ratings yet
- SyllabusANSI (ST)Document22 pagesSyllabusANSI (ST)amit kumarNo ratings yet
- DSC - 2014 Sa Physical Sciences Syllabus: Oòßæ Ýlæ Ê ŠL º$ Ýlðéæý Yìlòü ºæšDocument1 pageDSC - 2014 Sa Physical Sciences Syllabus: Oòßæ Ýlæ Ê ŠL º$ Ýlðéæý Yìlòü ºæšsarma410437No ratings yet
- Biochemistry SyllabusDocument2 pagesBiochemistry SyllabusKamlesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Biochemistry (SCQP05)Document5 pagesSyllabus For Biochemistry (SCQP05)Ibrahim SabraNo ratings yet
- Probable Questions I MBBS .Document14 pagesProbable Questions I MBBS .rishitgwsNo ratings yet
- XL-P: Chemistry (Compulsory For All XL Candidates)Document4 pagesXL-P: Chemistry (Compulsory For All XL Candidates)Anonymous QyfBOfGqiHNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Paper 1Document15 pagesImportant Questions Paper 1piyush Kumar 57No ratings yet
- Biochemistry SyllabusDocument1 pageBiochemistry Syllabusdaltonjohn11111No ratings yet
- Bioche, m1 ShortDocument3 pagesBioche, m1 ShortPravesh RajNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For The Post ofDocument4 pagesSyllabus For The Post ofBhavsar NilayNo ratings yet
- The Topics For Lectures ProjectsDocument1 pageThe Topics For Lectures Projectssubmen81No ratings yet
- Syllabus JKPSC Dental SurgeonsDocument14 pagesSyllabus JKPSC Dental SurgeonsAshyana SaeedNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Paper-I - Syllabus & Model QuestionsDocument18 pagesBiochemistry - Paper-I - Syllabus & Model Questionssantoshmuralijoka1316No ratings yet
- GATE 2021 Syllabus For Life Sciences XLDocument10 pagesGATE 2021 Syllabus For Life Sciences XLHarsh DwivediNo ratings yet
- Gset Syyllb p2Document11 pagesGset Syyllb p2taksh valaNo ratings yet
- Topic Allocation 2022 - 2023Document6 pagesTopic Allocation 2022 - 2023Isaac OnigbindeNo ratings yet
- Bas 121 Biochemistry 2 - 0 - 2 3 TheoryDocument1 pageBas 121 Biochemistry 2 - 0 - 2 3 Theoryjyotiraditya palNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document11 pagesPaper 2Bharath RajNo ratings yet
- REPORTING BiochemistryDocument6 pagesREPORTING Biochemistryclent girayNo ratings yet
- Entrance Test Syllabus For Ph.D. (Sci.) All Branches (Admission 2022-2023)Document9 pagesEntrance Test Syllabus For Ph.D. (Sci.) All Branches (Admission 2022-2023)Kmborse Indian21No ratings yet
- Polymers for Biomedicine: Synthesis, Characterization, and ApplicationsFrom EverandPolymers for Biomedicine: Synthesis, Characterization, and ApplicationsCarmen ScholzNo ratings yet
- Protein Carbonylation: Principles, Analysis, and Biological ImplicationsFrom EverandProtein Carbonylation: Principles, Analysis, and Biological ImplicationsJoaquim RosNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Old Question PaperDocument10 pagesBiotechnology Old Question PaperHarshitNo ratings yet
- The Hemodialysis Prescription Past, Present, And.18Document4 pagesThe Hemodialysis Prescription Past, Present, And.18Tim Engineer HD RSUD Dr. SoetomoNo ratings yet
- NCP Karl Jacon M. FerolinoDocument4 pagesNCP Karl Jacon M. FerolinoWhyng CabugayanNo ratings yet
- Indoor Air Quality in Healthcare FacilitiesDocument145 pagesIndoor Air Quality in Healthcare FacilitiesjadewestNo ratings yet
- RGKSU 1st Proff 10 YearsDocument115 pagesRGKSU 1st Proff 10 YearsAranya BhandaryNo ratings yet
- Arunachal Front 15 Mar 2021Document8 pagesArunachal Front 15 Mar 2021John DiniNo ratings yet
- E645 FullDocument11 pagesE645 FullCarlos SanchezNo ratings yet
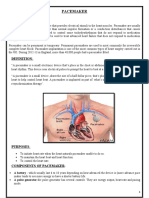
- PACEMAKERDocument5 pagesPACEMAKERPoonam ThakurNo ratings yet
- 2016 ATC Index With DDDDocument317 pages2016 ATC Index With DDDSi CentilNo ratings yet
- Chest Physiotherapy in PediatricDocument10 pagesChest Physiotherapy in Pediatricbuku fisioNo ratings yet
- NeutrophiliaDocument10 pagesNeutrophiliamaria martinezNo ratings yet
- CYSTISERCOSISDocument15 pagesCYSTISERCOSIShelda dwianaNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter 1Document7 pagesFull Chapter 1Afif AzharNo ratings yet
- School of Anaesthesia, 37 Military Hospital BSC Anasthesia (Regular) L 400 Specialized Anaesthesa Ii DATE: 08/0/2021 INDEX NO: SOAR/3719073Document2 pagesSchool of Anaesthesia, 37 Military Hospital BSC Anasthesia (Regular) L 400 Specialized Anaesthesa Ii DATE: 08/0/2021 INDEX NO: SOAR/3719073George Junior AdomakoNo ratings yet
- Ingles 10, Duque MarthaDocument5 pagesIngles 10, Duque MarthaMaicol Stiven RaveNo ratings yet
- Classification of DrugsDocument15 pagesClassification of DrugsAwani ONo ratings yet
- General Anesthesia: Intravenous Induction Agents - UpToDateDocument47 pagesGeneral Anesthesia: Intravenous Induction Agents - UpToDateAhmet PinarbasiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Feasibility Study: Dairy Farm (10 Cows) EnvironmentallyDocument28 pagesPre-Feasibility Study: Dairy Farm (10 Cows) EnvironmentallyShani Ch100% (1)
- Homosexuality: A History (From Ancient Greece To Gay Liberation) Vern L. BulloughDocument209 pagesHomosexuality: A History (From Ancient Greece To Gay Liberation) Vern L. Bulloughhugoprais100% (1)
- SGH Cervical Screening Colposcopy PathwaysDocument13 pagesSGH Cervical Screening Colposcopy PathwaysAbraham ChiuNo ratings yet
- FontAid ReviewDocument849 pagesFontAid ReviewArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- Airway Management (Kuliah Panum)Document43 pagesAirway Management (Kuliah Panum)yudhaNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 08 HSG ANH 9Document16 pagesĐỀ SỐ 08 HSG ANH 9hallo minNo ratings yet
- Evaluascdc Hiv MethodDocument11 pagesEvaluascdc Hiv MethodmasaruddinNo ratings yet
- Science Alzheimer PDFDocument7 pagesScience Alzheimer PDFSinn VolleNo ratings yet