Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Studdy.... 1st Review
Studdy.... 1st Review
Uploaded by
Dinesh KrishnanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Studdy.... 1st Review
Studdy.... 1st Review
Uploaded by
Dinesh KrishnanCopyright:
Available Formats
A telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals.
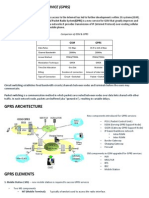
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information Network planning and design is an iterative process, encompassing topological design, networksynthesis, and network-realization, and is aimed at ensuring that a new network or service meets the needs of the subscriber and operator. There are two types of radio networks currently in use around the world: the one-to-many broadcast type commonly used for public information and mass media entertainment; and the two-way type used more commonly for public safety and public services such as police, fire, taxicabs, and delivery services. In mobile or wireless communication, the air interface is the radio-based communication link between the mobile station and the active base station The mobile station (MS)[1] [2]comprises all user equipment and software needed for communication with a mobile network. 2g and 3g 1.GSM uses TDMA technology with narrowband 200Khz. To make a call, each user must occupy a frequency. This is reason of interference as well as limited frequency resource during frequeny planning when expanded coverage. 2. 3G (WCDMA) use CDMA technology with broadband 5Mhz, the same frequency carrier, time and division following code. Hence, the speed is increased as well as intererence of frequency do not happen.
Gsm: Gsm for second generation (2G) digital cellular networks, a replacement for first generation(1G) analog cellular networks, the GSM standard originally described a digital, Modulation in gsm: The modulation used in GSM is Gaussian minimum-shift keying (GMSK), a kind of continuous-phase frequency shift keying. In GMSK, the signal to be modulated onto the carrier is first smoothed with a Gaussian low-pass filter prior to being fed to a frequency modulator, which greatly reduces the interference Packet data transmission speeds were later increased via EDGE(Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) planning GSM networks operating in the 900 MHz or 1800 MHz bands.
Gaussian minimum-shift keying
In digital communication, Gaussian minimum shift keying or GMSK is a continuous-phase frequency-shift keying modulation scheme. It is similar to standard minimum-shift keying (MSK); however the digital data stream is first shaped with a Gaussian filter before being applied to a frequency modulator.
a Gaussian filter is a filter whose impulse response is a Gaussian function.
Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN)
The Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) is a main component of the GPRS network. The GGSN is responsible for the interworking between the GPRS network and external packet switched networks, like the Internet and X.25 networks.
Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN)
A Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) is responsible for the delivery of data packets from and to the mobile stations within its geographical service area. Its tasks include packet routing and transfer, mobility management (attach/detach and location management), logical link management, and authentication and charging functions. The location register of the SGSN stores location information (e.g., current cell, current VLR) and user profiles (e.g., IMSI, address(es) used in the packet data network) of all GPRS users registered with this SGSN.
You might also like
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationFrom EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- MECH 370 Exp#2Document9 pagesMECH 370 Exp#2yhdNo ratings yet
- Pdvsa: Engineering Design ManualDocument17 pagesPdvsa: Engineering Design ManualJaviel SánchezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - The Verdict On Groupthink Case StudyDocument2 pagesChapter 9 - The Verdict On Groupthink Case StudyAdelson Arado100% (2)
- Expt: 3G CommunicationDocument10 pagesExpt: 3G CommunicationSachin RuikarNo ratings yet
- Mod1 SlideDocument22 pagesMod1 Slide2020ecpriyanshnigambNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document32 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)divyeshchauhan014No ratings yet
- Introduction To 3G, GSM, GPRS, EDGE NetworkDocument22 pagesIntroduction To 3G, GSM, GPRS, EDGE NetworkRavi YarrabothuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 3G, GSM, GPRS, EDGE NetworkDocument22 pagesIntroduction To 3G, GSM, GPRS, EDGE NetworkBucek BuddyNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Minimise Network Blocking in 4g For Better AccessibilityDocument5 pagesA New Approach To Minimise Network Blocking in 4g For Better AccessibilityericNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document32 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Zatin GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3G & 4G Standards: 1. Explain About Global System For Mobile (GSM)Document8 pages3G & 4G Standards: 1. Explain About Global System For Mobile (GSM)vinod3457No ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Unit-3Document12 pagesMobile Computing Unit-3Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- GPRS - User CountDocument6 pagesGPRS - User CountAlthaf HussainNo ratings yet
- SPEED: Theoretical Maximum Speeds of Up To 171.2 Kilobits Per Second (KBPS)Document32 pagesSPEED: Theoretical Maximum Speeds of Up To 171.2 Kilobits Per Second (KBPS)yuben josephNo ratings yet
- Packet Call Flow UMTSDocument14 pagesPacket Call Flow UMTSTripathy Kumar SarthakNo ratings yet
- Mobile Comm Short NoteDocument8 pagesMobile Comm Short NoteSarthak BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document44 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Mubassir PatelNo ratings yet
- Electronics - Communication Engineering Topic: (Type The Company Address)Document34 pagesElectronics - Communication Engineering Topic: (Type The Company Address)Varun SainiNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation For Integrated High Altitude Platforms-Terrestrial General Packet Radio Service SystemDocument6 pagesPerformance Evaluation For Integrated High Altitude Platforms-Terrestrial General Packet Radio Service SystemHabib MohammedNo ratings yet
- E5-E6 - Text - Chapter 11. CM TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW 4G 5GDocument13 pagesE5-E6 - Text - Chapter 11. CM TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW 4G 5Gsumit15sksNo ratings yet
- Wireless GSM DocumDocument9 pagesWireless GSM DocumDaniel BelachewNo ratings yet
- 3g Core1Document19 pages3g Core1AbhilashNo ratings yet
- GPRS PDFDocument6 pagesGPRS PDFHandy MoseyNo ratings yet
- GPRS PDFDocument7 pagesGPRS PDFHandy MoseyNo ratings yet
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureDocument7 pagesGPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureSrinivas KaratlapelliNo ratings yet
- 3g Core1Document19 pages3g Core1Pramod RaiNo ratings yet
- Soft Handover in UmtsDocument15 pagesSoft Handover in UmtsSaranyaNo ratings yet
- GPRSDocument32 pagesGPRSSHUBHAM RANKAWAT SVNITNo ratings yet
- Traffic Analysis and Design of Wireless IP Networks: (Aisah)Document32 pagesTraffic Analysis and Design of Wireless IP Networks: (Aisah)Basuki Rahmat HakimNo ratings yet
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 2. Migration To Mobile Technologies Upto 5gDocument19 pagesE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 2. Migration To Mobile Technologies Upto 5gAGM CMS&MNo ratings yet
- GprsDocument5 pagesGprsRavi Ranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- MC Question Bank SolvedDocument11 pagesMC Question Bank SolvedSAHIL LADVANo ratings yet
- Wireless Access GprsDocument11 pagesWireless Access GprsSara AbNo ratings yet
- Gprs Architecture: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document6 pagesGprs Architecture: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Vam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- C C Is A: (November 2007)Document6 pagesC C Is A: (November 2007)Parneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Evolution From 3G To 4GDocument44 pagesEvolution From 3G To 4GKhalid ParkarNo ratings yet
- CC Unit-5 AnswersDocument15 pagesCC Unit-5 AnswersbonangidilleswararaoNo ratings yet
- GPRSDocument4 pagesGPRSddhakalNo ratings yet
- 3G ArchitectureDocument11 pages3G ArchitecturelqcckagopzkluvrayxNo ratings yet
- NOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Document10 pagesNOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Ramesh MattaparthiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. General Packet Radio ServiceDocument25 pagesLecture 4. General Packet Radio ServiceSuparno BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- UMTS NetworkDocument8 pagesUMTS NetworkAbdullah FuzailNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is ADocument8 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is AAjay AryaNo ratings yet
- Agilent Testing GPRS SignallingDocument24 pagesAgilent Testing GPRS SignallingPrasant KumarNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio ServicesDocument8 pagesGeneral Packet Radio ServicesronyiutNo ratings yet
- Wireless CommunicationDocument16 pagesWireless CommunicationhaiderifulNo ratings yet
- Comparison of W-CDMA and Cdma2000Document12 pagesComparison of W-CDMA and Cdma2000AhmadFirdaus Bin HolidyRasyidNo ratings yet
- GprsDocument24 pagesGprsSalahuddin HusseinNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis For Umts Packet (2010)Document15 pagesPerformance Analysis For Umts Packet (2010)Tamara GoriNo ratings yet
- Π1: Wireless Communication Systems: PrefaceDocument16 pagesΠ1: Wireless Communication Systems: PrefaceHaider Al RikabiNo ratings yet
- SPEED: Theoretical Maximum Speeds of Up To 171.2 Kilobits Per Second (KBPS)Document31 pagesSPEED: Theoretical Maximum Speeds of Up To 171.2 Kilobits Per Second (KBPS)Eng W EaNo ratings yet
- Client-Server Services, Which Enable Access To Data Stored in Databases. The Most Famous Example of ThisDocument26 pagesClient-Server Services, Which Enable Access To Data Stored in Databases. The Most Famous Example of ThisIman AliNo ratings yet
- AGPCS - An Automatic GSM-based Positioning and Communication SystemDocument8 pagesAGPCS - An Automatic GSM-based Positioning and Communication Systemqasim443No ratings yet
- Modeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEFrom EverandModeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTENo ratings yet
- Morse Code Vanity Code: Keyword CipherDocument2 pagesMorse Code Vanity Code: Keyword CipherHestia BreeNo ratings yet
- Fl-Acp0led PDF PDFDocument3 pagesFl-Acp0led PDF PDFAndrea QuinoNo ratings yet
- Solution DEC 19Document8 pagesSolution DEC 19anis izzatiNo ratings yet
- Amot - Safety Shutdown Device - Model 2800DDocument8 pagesAmot - Safety Shutdown Device - Model 2800DSamet KarabayNo ratings yet
- MANUAL - Part 1 PN 101328780Document370 pagesMANUAL - Part 1 PN 101328780AlessonNo ratings yet
- Macdermid Inc - Metex Strip Aid - 6810-00-113-0036Document2 pagesMacdermid Inc - Metex Strip Aid - 6810-00-113-0036Luiz FernandoNo ratings yet
- Diagrams of Motion': Stop-Motion Animation As A Form of Kinetic Sculpture in The Short Films of Jan Švankmajer and The Brothers QuayDocument14 pagesDiagrams of Motion': Stop-Motion Animation As A Form of Kinetic Sculpture in The Short Films of Jan Švankmajer and The Brothers Quayshalbafanm81No ratings yet
- Bus121 Course CompactDocument10 pagesBus121 Course CompactFadele1981No ratings yet
- Corken CompressorI100Document16 pagesCorken CompressorI100adriansya7No ratings yet
- CLP 315Document32 pagesCLP 315theBAUNo ratings yet
- Effect of Servicescape and Customer Experience On Social Location Marketing (Case Study at Caf, in Medan)Document8 pagesEffect of Servicescape and Customer Experience On Social Location Marketing (Case Study at Caf, in Medan)Ahmed DahiNo ratings yet
- WMS Sample ReportDocument3 pagesWMS Sample ReportVAIDEHI AGARWAL0% (1)
- Design of Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument6 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete StructuresRavindra MRNo ratings yet
- Personality DeterminantsDocument13 pagesPersonality DeterminantsPranay KarnikNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Assist SystemDocument2 pagesHydraulic Assist SystemengfaridmalkNo ratings yet
- Weather Elementary Eng FileDocument28 pagesWeather Elementary Eng Fileiryna myskivNo ratings yet
- W Ork Ing Sci Ent Ifica LlyDocument30 pagesW Ork Ing Sci Ent Ifica Llyイクラご飯.No ratings yet
- Poval Technical Data SheetDocument4 pagesPoval Technical Data SheetDgek LondonNo ratings yet
- MAE 3272 - Lecture 5 Notes - Load Cell Desgin, Calibration, and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesMAE 3272 - Lecture 5 Notes - Load Cell Desgin, Calibration, and ApplicationsaoeusnthidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MergedDocument65 pagesChapter 1 MergedAdi SaputraNo ratings yet
- SCMPE Edition Four Additions Part TwoDocument42 pagesSCMPE Edition Four Additions Part TwoGiriNo ratings yet
- Quality Manual HETL FCS 17025 2017Document108 pagesQuality Manual HETL FCS 17025 2017Mohamed azarudeenNo ratings yet
- Earth Pressure TheoryDocument30 pagesEarth Pressure TheoryDhananjay ShahNo ratings yet
- Smart Dustbin Report PaperDocument9 pagesSmart Dustbin Report PaperAbhishek JhaNo ratings yet
- Digital Astrophotography A Guide To Capturing The Cosmos (PDFDrive)Document236 pagesDigital Astrophotography A Guide To Capturing The Cosmos (PDFDrive)Paolo Fasselli100% (1)
- Quantum Field Theory - R. Clarkson, D. McKeonDocument266 pagesQuantum Field Theory - R. Clarkson, D. McKeonKepler4246No ratings yet
- User Capacity in Downlink MISO-NOMA SystemsDocument6 pagesUser Capacity in Downlink MISO-NOMA SystemsUsman AliNo ratings yet