Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2
Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Anem AhiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2
Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Anem AhiaCopyright:
Available Formats
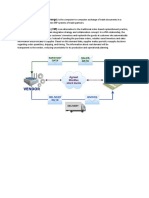
I-GENERAL ENVIRONMENT
influence industries & firm i- DEMOGRAPHIC population size, age structure of customers, geographical distribution, ethnic mix, income distribution iii- POLITICAL taxation laws vi- GLOBAL political event in the country, global markets, emerging countries, different ii- ECONOMIC inflation rate, interest rate, trade deficits, budget deficits, personal savings rates & gross iv -SOCIOCULTURAL - woman in workforce, attitudes about quality of life, concerns about environment, shift in
i- THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS
influenced by 2 factors:
iiBARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
prices & quality means used by suppliers to exert power over firms SUPPLIER IS POWERFUL WHEN: (a)the firms are significant customers, (b)satisfactory substitute products are not available to industry firms, (c)there are few
II-INDUSTRY ENVIRONMENT
influences firm & competitive
(a) RETALIATION FROM CURRENT & EXISTING FIRMS when new entrants are coming into the industry, existing co may give competitive responses to reduce the possibility of new
iii- BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS buyers
vTECHNOLOGICA L products innovations, new communication techniques, application of OBJECTIVE to identify 2 : OPPORTUNITIES conditions that if exploit it helps the co archives its strategic competitiveness THREATS conditions that may hinder a cos effort to achieve strategic competitiveness
(b) BARRIERS OF ENTRY The existing firms should try to develop capabilities so that new firms are barred to enter the industry. Kinds of 7 i- ECONOMIES OF SCALE Economies of scale can be accomplished because a production increases the cost of producing each additional unit falls. Co manufacturing customized products learn how to respond quickly to customers desires rather than developing economies of scale. ii- PRODUCT DIFFRENTIATION Firms product must be unique. Customers who value this kind of product tend to become loyal. However, new entrants may results to offering lower prices to combat these unique product characteristics. iii- CAPITAL REQUIREMENT to successfully enter into a new market in addition to physical facilities. iv- SWITCHING COSTS one-time costs customers incur when they buy from different supplier. When switching cost is high, new entrant would try to either offer low price for its product or offer much-differentiated product to attract customers. v- ACCESS TO DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS a place to distribute the products. New entrants have to persuade distributors to carry their products. vi- COST DISADVANTAGES existing & established competitors have cost adv that new
III-COMPETITOR ANALYSIS focuses
on each co against whom a firm directly competes
-involves gathering data & info that can be useful in understanding its competitors intention & strategic implications. Firms should also gather data & info regarding govt policies. This will give an early warning of threat & opportunities & analyze them on how they will affect the cos strategy.
ii- SLOW INDUSTRY GROWTH when the growth in industry slow, competition becomes intense as firms try to increase their market shares by attracting competitors customers. iii- HIGH FIXED COSTS/HIGH STORAGE COSTS when firm try to increase prod volume, inventories increase/excess inventories exist. To reduce it, firm offer discounts/cut it selling price. iv- LACK OF DIFFERENTIATED/LOW SWITCHING COSTS buyers are loyal to products that suits their needs, so in an industry where differentiated product exist, rivalry is less resulting to lower competition v- HIGH EXIT BARRIERS Co would continue to operate even though at loss. These include economic, strategic, emotional factors that made them remain as is.
want to buy products sold at lower price. When suppliers goods were sold at higher price, buyers would try to reduce their costs by: (a) asking for higher quality products & services (b) greater CUSTOMERS IS POWERFUL WHEN: (a)they purchase large portion of the total output (b)customers purchases significant portion of the sellers product (c)customers can switch to another product at little cost
iv- THREAT OF SUBSTITUTE PRODUCTS
substitute products are goods & services from outside the industry that perform similar
v- INTENSITY OF RIVALRY AMONG COMPETITORS firms actions
always invite competitive responses. Factors that affect the intensity of
These substitute products posses strong threat to the firm when customers: (a)have no switching cost to bear (b)the substitute product is sold at lower price (c)when the quality of the product is better i- MANY EQUALLY BALANCED COMPETITORS- when firms are same size & power, competition is strong. So, intense rivalries exist
IV- EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENTAL ANALYSIS process
gathering more info about the environment to increase the understanding of the general environment
SCANNING MONITORING FORECASTING ASSESSING
EXTERNA L ENVIRON MENT
You might also like
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionFrom EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- San Miguel Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis Threat of New Entrants (LOW)Document4 pagesSan Miguel Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis Threat of New Entrants (LOW)Ashley Gana0% (1)
- Consulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesFrom EverandConsulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesNo ratings yet
- Company ProfileDocument17 pagesCompany ProfileBecca BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Barilla Spa Case FinalDocument6 pagesBarilla Spa Case FinalRohitHarikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Dunkin DonutDocument2 pagesDunkin DonutJofiandy NathanaelNo ratings yet
- Store Layout & DesignDocument60 pagesStore Layout & Designvikash100% (2)
- ENTP CIA 3 - Feasability AnalysisDocument20 pagesENTP CIA 3 - Feasability AnalysisSujith VichuNo ratings yet
- Porters Ch3 SMDocument9 pagesPorters Ch3 SMswetha23venkatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Industry AnalysisDocument6 pagesLecture 3 Industry AnalysiscovenantrjssNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: The External Environment: By: Kristine Mae D. TagaDocument21 pagesChapter Three: The External Environment: By: Kristine Mae D. TagaKristine MaeNo ratings yet
- C6 Environmental ScanningDocument30 pagesC6 Environmental Scanningmyril shyane loocNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument22 pagesBusiness Environmentgetcultured69No ratings yet
- C6 Environmental ScanningDocument32 pagesC6 Environmental ScanningJurie BalandacaNo ratings yet
- Marketing: Business StudiesDocument11 pagesMarketing: Business StudiesKevin KidigaNo ratings yet
- 5 Force ModelDocument14 pages5 Force Modelsrilatha212No ratings yet
- Retail MatrketingDocument26 pagesRetail MatrketingRhythm chordiaNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument7 pagesBusiness EnvironmentokisegereannastaciaNo ratings yet
- Porters Five Force ModelDocument13 pagesPorters Five Force ModelyuvarajNo ratings yet
- Handout 6Document5 pagesHandout 6tracyjoaquintj27No ratings yet
- Case Study: Competitive ForcesDocument3 pagesCase Study: Competitive ForcesArif QureshiNo ratings yet
- Customers: - Suppliers - CompetitorsDocument32 pagesCustomers: - Suppliers - CompetitorsanashussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Business Environment For Competitive StrategyDocument28 pagesChapter 2 The Business Environment For Competitive StrategyRene Dacua PalabricaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document24 pagesModule 2amith.sajja121No ratings yet
- Porter's Five Five Force Analysis (Part-1)Document4 pagesPorter's Five Five Force Analysis (Part-1)Pooja Rani-48No ratings yet
- Economic Analysis Policy - IDocument30 pagesEconomic Analysis Policy - IThaddeus De MenezesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Reviewer: Formula: Price Direct Cost + Overhead + Mark UpDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Reviewer: Formula: Price Direct Cost + Overhead + Mark UpKaira CañaveralNo ratings yet
- PM CT02Document10 pagesPM CT02tahsinahmed9462No ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy + Five Forces ModuleDocument56 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy + Five Forces ModuleWolf's Rain100% (1)
- Opportunities & Threats - Analyzing The External EnvironmentDocument4 pagesOpportunities & Threats - Analyzing The External EnvironmentMaeNo ratings yet
- Extensive Notes On Topic 2 - MarketingDocument12 pagesExtensive Notes On Topic 2 - MarketingjohnNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management NotesDocument46 pagesStrategic Management NotesAccount SpamNo ratings yet
- Fast Moving Consumer Goods Also Known As Consumer-Packaged Goods Is The 4 Largest Sector in Indian Economy. This Industry Deals With Production, Distribution and Marketing ofDocument4 pagesFast Moving Consumer Goods Also Known As Consumer-Packaged Goods Is The 4 Largest Sector in Indian Economy. This Industry Deals With Production, Distribution and Marketing ofKrutarth PatelNo ratings yet
- The General, Industry, and Competitor EnvironmentsDocument6 pagesThe General, Industry, and Competitor EnvironmentsUlfa ZhafirahNo ratings yet
- Opportunity SeekingDocument37 pagesOpportunity SeekingA cNo ratings yet
- Michael Porter Analysis (Five Forces Model)Document18 pagesMichael Porter Analysis (Five Forces Model)popat vishalNo ratings yet
- Category AnalysisDocument42 pagesCategory AnalysisANJALINo ratings yet
- FMCG Industry AnalysisDocument9 pagesFMCG Industry AnalysisStefan G AllicockNo ratings yet
- External Environment Analysis of The FMCG Industry in Sri Lanka post-COVID-19Document23 pagesExternal Environment Analysis of The FMCG Industry in Sri Lanka post-COVID-19dilhaninperera47No ratings yet
- Porter AnalysisDocument35 pagesPorter AnalysisDinesh RaghavendraNo ratings yet
- Courses Arts Business 1478142703 2016 Business Studies NotesDocument10 pagesCourses Arts Business 1478142703 2016 Business Studies Notesneupane.sanjan01No ratings yet
- Ims Management Gaurav NaharDocument1 pageIms Management Gaurav NaharGaurav NaharNo ratings yet
- Michael Porter 5 ForcesDocument52 pagesMichael Porter 5 Forcesvinayakbelwade100% (2)
- Karen Diane Rivera - Course Learning OutcomesDocument17 pagesKaren Diane Rivera - Course Learning OutcomesKaren Diane Chua RiveraNo ratings yet
- B 2 BDocument12 pagesB 2 BlauraNo ratings yet
- THREAT OF ENTRY. New Entrants To An Industry Bring New Capacity and A Desire To Gain Market Share That PutsDocument1 pageTHREAT OF ENTRY. New Entrants To An Industry Bring New Capacity and A Desire To Gain Market Share That PutsLucas Moraes Teixeira SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategyDocument99 pagesMarketing Strategymahtolalan100% (1)
- Competitive Analysis NewDocument17 pagesCompetitive Analysis NewKitea ChhakchhuakNo ratings yet
- SBM TSB GRP 6 - Porters 5 ForceDocument27 pagesSBM TSB GRP 6 - Porters 5 ForceShashank BhootraNo ratings yet
- External Audit NotesDocument3 pagesExternal Audit NotesPatricia May CayagoNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategy MARN04B Final TopicsDocument12 pagesPricing Strategy MARN04B Final TopicsLevNo ratings yet
- Finance and Marketing: Masters Engineering RoutesDocument76 pagesFinance and Marketing: Masters Engineering RoutesHoàngAnhNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1Document3 pagesMarketing 1Vimansa JayakodyNo ratings yet
- B2B MarketingDocument182 pagesB2B MarketingAngela LopezNo ratings yet
- I. Analysis of External Environment II. Competitive IntelligenceDocument28 pagesI. Analysis of External Environment II. Competitive IntelligenceRoberto SanchezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document8 pagesUnit 2Martina PerezNo ratings yet
- 1207 - Chapter 2Document4 pages1207 - Chapter 2Matthew CivelloNo ratings yet
- Industry AnalysisDocument13 pagesIndustry AnalysisKasiira HatimuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Marketing Mix - 4P's Class X 3Document9 pagesChapter 2 Marketing Mix - 4P's Class X 37g7wg65tz4No ratings yet
- EXTERNAL ANALYSIS Opportunities and ThreatsDocument8 pagesEXTERNAL ANALYSIS Opportunities and ThreatsPrincess SagunNo ratings yet
- Marketing ReportingDocument4 pagesMarketing ReportingDumpp Acc.3No ratings yet
- FOW9 - PMK - Note Chapter 11Document4 pagesFOW9 - PMK - Note Chapter 11khanhphamngoc1716No ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurshipJim Jose AngNo ratings yet
- Model Answer: E-Commerce store launch by Unilever in Sri LankaFrom EverandModel Answer: E-Commerce store launch by Unilever in Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- Soal 2Document2 pagesSoal 2putriNo ratings yet
- ICS (Internal Control System) Over PurchasesDocument3 pagesICS (Internal Control System) Over PurchasesAsma AliNo ratings yet
- The Supply Chain of Italian Parmigiano-Reggiano: An Interpretative Analysis of Market DynamicsDocument8 pagesThe Supply Chain of Italian Parmigiano-Reggiano: An Interpretative Analysis of Market DynamicsEd ZNo ratings yet
- Jewellery IndustryDocument73 pagesJewellery IndustrySahil100% (2)
- Nintendo Marketing StrategiesDocument8 pagesNintendo Marketing StrategieshumasNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Skills & Selling SkillsDocument21 pagesNegotiation Skills & Selling SkillsFiroz khanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Assignment 1Document5 pagesStrategic Management Assignment 1Shafiq RehmanNo ratings yet
- Cmi & VmiDocument3 pagesCmi & VmiTruongthe KietNo ratings yet
- Category ManagementDocument3 pagesCategory ManagementAdeval SilvaNo ratings yet
- SC Finance JP Morgan PDFDocument34 pagesSC Finance JP Morgan PDFPrashanth ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- AE 23 Pre-Final ExamDocument4 pagesAE 23 Pre-Final ExamZerJethroNo ratings yet
- 118 Cosmetics Industry Report Final July2017Document31 pages118 Cosmetics Industry Report Final July2017Osman Bin Salam100% (1)
- Kara Wipes Project FinalDocument46 pagesKara Wipes Project FinalSoumik SettNo ratings yet
- 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials HMDM and HLMDocument32 pages2008 DECA Ontario Provincials HMDM and HLMEvan NoorNo ratings yet
- Quotation For Kobelco Sk200-Viii Excavator Spare Parts.: Special PriceDocument1 pageQuotation For Kobelco Sk200-Viii Excavator Spare Parts.: Special PricekumarawassNo ratings yet
- FDNMARK ReviewerDocument3 pagesFDNMARK ReviewerTrish Bernabe100% (1)
- Jim Vanderbleek Resume' Time LineDocument2 pagesJim Vanderbleek Resume' Time LineAllison TurnerNo ratings yet
- Lifebuoy MKT MixDocument10 pagesLifebuoy MKT MixThùyTrangAppleNo ratings yet
- TanishqDocument4 pagesTanishqAkarsh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Cloey Nicholas Maries Piercing Studio Business PlanDocument4 pagesCloey Nicholas Maries Piercing Studio Business Planapi-459491960No ratings yet
- JWB Thesis 05 04 2006Document70 pagesJWB Thesis 05 04 2006Street Vendor ProjectNo ratings yet
- 5Document15 pages5Mohammed LubNo ratings yet
- Case Study On IKEADocument30 pagesCase Study On IKEAPooja Patnaik100% (3)
- 1520954299311Document1 page1520954299311AlokNo ratings yet
- Discount ModelDocument7 pagesDiscount ModelPrateek KonvictedNo ratings yet
- PT Teknocal Energi Bersinar PROFILEDocument3 pagesPT Teknocal Energi Bersinar PROFILEJamal LamajNo ratings yet