Professional Documents
Culture Documents
In For Matics
In For Matics
Uploaded by
Jerry AbleCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- St. Anthony'S College San Jose, Antique: Outcomes-Based Curriculum Pacing GuideDocument14 pagesSt. Anthony'S College San Jose, Antique: Outcomes-Based Curriculum Pacing GuideJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Leadership TheoryDocument31 pagesLeadership TheoryJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Plant VirusDocument195 pagesPlant Virusbrkica2011No ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide To Poultry Layer FarmingDocument19 pagesA Beginners Guide To Poultry Layer Farmingarthur guil-anNo ratings yet
- Safety Guidelines For Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: By: Prof. Marites L. RoblezaDocument32 pagesSafety Guidelines For Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: By: Prof. Marites L. RoblezaJerry Able100% (1)
- DOJ Legal Opinion On CHED Opening of Classes in HEIsDocument3 pagesDOJ Legal Opinion On CHED Opening of Classes in HEIsJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Delivery and Care of The NewbornDocument57 pagesDelivery and Care of The NewbornJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Triage in Emergency Department: Triage Waiting Room Team LeaderDocument27 pagesTriage in Emergency Department: Triage Waiting Room Team LeaderJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- CMO No. 4 S. 2020 Guidelines On The Implementation of Flexible LearningDocument10 pagesCMO No. 4 S. 2020 Guidelines On The Implementation of Flexible LearningRalph Evander IdulNo ratings yet
- Related Literature - New Normal Educatonal SystemDocument20 pagesRelated Literature - New Normal Educatonal SystemJerry AbleNo ratings yet
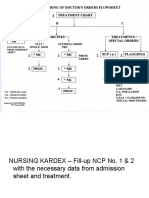
- Transcribing Doctors Order EDITED-2Document21 pagesTranscribing Doctors Order EDITED-2Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent: Lena Haygood (R) RT Radiology Instructor: Arizona Western Community College SourceDocument18 pagesInformed Consent: Lena Haygood (R) RT Radiology Instructor: Arizona Western Community College SourceJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- INFECTION Control and PREVENTION-1Document49 pagesINFECTION Control and PREVENTION-1Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Film ReviewDocument2 pagesFilm ReviewJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Emergency Red Flags: DR - Magdy Khames AlyDocument58 pagesEmergency Red Flags: DR - Magdy Khames AlyJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- DLP Physical Science SeptemberDocument2 pagesDLP Physical Science SeptemberJerry Able100% (5)
- Po1 Po2 Po3 Po4 Po5 Po6 Po7 Po8 Po9 Po10 Po11 Po12 Po13 Po14Document16 pagesPo1 Po2 Po3 Po4 Po5 Po6 Po7 Po8 Po9 Po10 Po11 Po12 Po13 Po14Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- OB - CPG Health Assessment 2018-2019Document21 pagesOB - CPG Health Assessment 2018-2019Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- DLP Caregiving NC 2 September 24-29Document2 pagesDLP Caregiving NC 2 September 24-29Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony'S College San Jose, Antique: Outcomes-Based Curriculum Pacing GuideDocument15 pagesSt. Anthony'S College San Jose, Antique: Outcomes-Based Curriculum Pacing GuideJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- NCP Marilou.... SanitariumDocument9 pagesNCP Marilou.... SanitariumJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- WASH in Schools in Emergencies Guidebook For Teachers PDFDocument80 pagesWASH in Schools in Emergencies Guidebook For Teachers PDFJerry Able100% (1)
- Business Environment & Business Ideas DLP 3Document24 pagesBusiness Environment & Business Ideas DLP 3Jerry Able100% (2)
- Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocument16 pagesTrigeminal NeuralgiaJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Principles of BioethicsDocument80 pagesPrinciples of BioethicsYashmine Castrence0% (1)
- Sangandiwa PaperDocument52 pagesSangandiwa PaperJoseph RosalNo ratings yet
- Ca3 Therapeutic Modality Grp.3Document15 pagesCa3 Therapeutic Modality Grp.3Valjim PacatangNo ratings yet
- Attending Rounds: Fernando C. FervenzaDocument9 pagesAttending Rounds: Fernando C. FervenzaGita Christy KekenusaNo ratings yet
- 6 Weeks To 6-Pack Abs - Dr. Bradley EvsichDocument33 pages6 Weeks To 6-Pack Abs - Dr. Bradley Evsicharamisbirsan2132No ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Structure & FunctionDocument28 pagesHemoglobin Structure & Functiondeepak3027315No ratings yet
- Estudio SEDCOMDocument11 pagesEstudio SEDCOMElias Vera RojasNo ratings yet
- Lymphadenopathy: Soheir Adam, MD, MSC, MrcpathDocument34 pagesLymphadenopathy: Soheir Adam, MD, MSC, MrcpathWilly OematanNo ratings yet
- OMT Range of MotionDocument1 pageOMT Range of MotionMedShare100% (2)
- Staff Handbook SECTION 8Document27 pagesStaff Handbook SECTION 8Funda HandaNo ratings yet
- Bioterrorism: By: Berlian Isnia FitrasantiDocument35 pagesBioterrorism: By: Berlian Isnia FitrasantiKevin FachriNo ratings yet
- Physician Board Exam Room Assignment (Prelims)Document2 pagesPhysician Board Exam Room Assignment (Prelims)proffsgNo ratings yet
- Otalgia & TinnitusDocument19 pagesOtalgia & Tinnitushonda matizNo ratings yet
- Not For Reproduction: Doctor'S Order/Nurse'S Compliance Sheet (Authenticate All Orders)Document2 pagesNot For Reproduction: Doctor'S Order/Nurse'S Compliance Sheet (Authenticate All Orders)Mcgee OcnicnatNo ratings yet
- Teori Keperawatan: T. Pangandaheng., S.Kep., NS., MSNDocument22 pagesTeori Keperawatan: T. Pangandaheng., S.Kep., NS., MSNTommy PangandahengNo ratings yet
- RippedBody - Nutrition GuideDocument62 pagesRippedBody - Nutrition GuideHan100% (1)
- Cover LetterDocument2 pagesCover LetterXara VillaNo ratings yet
- 46 Dani Preventivne Medicine-Zbornik RezimeaDocument182 pages46 Dani Preventivne Medicine-Zbornik RezimeaМилош МујовићNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Family SurveyDocument3 pagesComprehensive Family SurveyGem HimenaceNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Lymphatic SystemDocument153 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Lymphatic SystemNellie Grace Montes Aba-aNo ratings yet
- I. Choose The Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced Differently From That of The OthersDocument3 pagesI. Choose The Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced Differently From That of The Othershuy phạmNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument33 pagesAcute Myeloid LeukemiardLuis1No ratings yet
- Manual Endoscopios EG290Kp EC380LKpDocument52 pagesManual Endoscopios EG290Kp EC380LKpBenito SoltechmedNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kesehatan Gigi: Emergency Management of Ingestion Bur (Case Study)Document6 pagesJurnal Kesehatan Gigi: Emergency Management of Ingestion Bur (Case Study)Qasrini ZatilNo ratings yet
- Project Greymouth - Arrest SubjectsDocument3 pagesProject Greymouth - Arrest SubjectswindsorstarNo ratings yet
- Spring Life News - 2019 (DIGITAL)Document8 pagesSpring Life News - 2019 (DIGITAL)Jim KerrNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Dan AspirinDocument10 pagesWarfarin Dan Aspirindita novia maharaniNo ratings yet
In For Matics
In For Matics
Uploaded by
Jerry AbleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
In For Matics
In For Matics
Uploaded by
Jerry AbleCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Informatics (IT)
Course Description: This course deals with the use of information technology system and data standards based on nursing informatics principles/theories. It further deals with the utilization of clinical information systems in the management and decision-making of patient care. A laboratory session shall be provided for practice application. Course Objectives: At the end of the course and given relevant actual or simulated situations/conditions, the student will be able to: 1. Apply concepts, theories and principles of informatics in nursing and health care; 2. Discuss issues and trends in informatics relevant to nursing and health. Placement: Second Year, Summer Course Credit: 2 Units Lecture; 1 Unit Laboratory Contact Hours per Semester: 36 Lecture hours; 54 Laboratory hours
Textbook: Essentials of Nursing Informatics, International Edition, 4th Ed. by Virginia K. Saba and Kathleen A. McCormick Lecturers: CYGNETTE S. LUMBO, RN, MN (BSN 2A)
RUBY A. LECCIO, RN, MN (BSN 2B)
COURSE OUTLINE A. Computers and nursing 1. Computers and nursing a. Overview 2. Historical perspectives of nursing and the computer a. Six Time periods b. 4 major nursing areas c. Standards initiatives d. Significant landmark events 3. Electronic health record from a historical perspective a. The Davies Program B. Computer system 1. Computer hardware a. Definition b. Fundamentals - CPU - Memory: ROM, RAM - Input and Output Devices - Storage Media: Hard Drive, Diskette Drive, CD-ROM, USB Disk, Others - Bits and Bytes - Computer Speed c. Descriptive terms used in Computing d. History of Computers e. Types of Computers f. Common Hardware Peripherals - Keyboard - Monitor - Mouse and Trackball - Floppy Disks/ Diskettes and CD-ROMs - Touch pad and Mouse Button - Light Pen/ Touch Screen - Optical Character Recognition - Magnetic Ink character recognition - Voice synthesizer - Imaging - Digital Versatile Disk (DVD) - Printers - Modems g. Basics of Computer Network Hardware 2. Computer software and systems a. Definition b. Brief History of computer programming and software
c. Types of software d. Common software useful to nurses e. Computer programming f. Systems Theory; System Elements and Classifications g. Computer Systems h. Information Systems i. Hospital Information systems j. Network Systems 3. Open source and free software a. Introduction to OSS/FS b. OSS/FS Theory c. OSS Definition d. Open Source Licensing e. OSS/FS Applications f. OSS/FS Healthcare Applications - openEHR, FreeMed, OpenEMR, CARE2X, EU- Funded Projects g. Advocate organizations and resources of OSS/FS 4. Data processing a. Definition - Data, databases, information, Information systems b. Types of data c. Database Management Systems d. Fields, Records and Files e. Types of Files f. Database Models g. Conceptual Models h. Database Life Cycle i. Detailed Systems Design j. Data Warehouse - Development, purposes, functions, quality k. Data to Knowledge (D2K) l. The Nursing Context - The Nelson Data to Wisdom Continuum 5. The Internet: A Nursing Resource a. The history of the internet b. The internet technology - The Domain Name System (DNS) - Top-Level Domains (TLDs) - Scope and coverage - The internet Use- Then and Now c. E-mail - The anatomy of an E-mail Address - Using the E-mail : Emoticons, abbreviations, organizing received files, file attachments, etiquette, cautions and suggestions - Mailing list : List fundamentals, finding a list, etiquette
d. The World Wide Web (WWW) - Origins, functions, value e. The Internet as an Information source - Searching the web - Cookies - Evaluating Information from the web f. Getting on the information superhighway - Finding and evaluating an ISP - Creating a web page - Home page design - Links, Forms and maintenance g. Patient/ Consumer Use of the internet 6. PDA and wireless devices a. Continuum of Information technology for Personal Computing - Desktop Computer vs. Smartphone Physical Characteristics - Notebook/ laptop vs. tablet vs. PDA Physical Characteristics - Mobile Devices - Wireless Devices b. PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) - Usability - Functions and their applications to clinical practice c. Add-on Software for PDA 7. Incorporating evidence: Use of Computer-Based Clinical Decision Support System for health professionals a. DSS/ CDSS - Definition, expanded use, history b. Types and characteristics of DSS c. Key CDSS functions, d. Examples of CDSS Applications e. CDSS impact on Clinicians and Clinical decisions - Evidence-based practice, barriers to its use, evaluation f. Knowledge and Cognitive process g. Ethical and Legal responsibility of user h. Implications for future uses of CDSS in Nursing C. Issues in informatics 1. Nursing informatics and healthcare policy as a specialty - Differentiated and interdisciplinary practice - Patient Safety and Nursing Informatics - Nursing informatics initiatives and nursing informatics - National agenda and advocacy to nursing informatics 2. The role of technology in the medication-use process - Computerized prescriber Order Entry (CPOE) - Bar Code-Enabled Point-of-care technology - Automated Dispensing Cabinets - Smart infusion Pump Delivery Systems - Implementation of technology
3. Healthcare data standards - Message Format Data Standards - Terminologies - Data content standards - The standards development process - Framework for strategic action - The business value of data standards 4. Electronic health record systems: U.S. federal initiatives and public/private Partnerships 5. Dependable systems for quality care - Guidelines for dependable systems 6. Nursing minimum data set systems - Clinical nursing visibility from national to international contexts - NMDS (Concept Nursing Minimum Data Set) - NMDS Relationship to International Nursing Minimum Data Set (iNMDS) D. Informatics theory 1. Theories, models and frameworks a. Foundational Documents Guide Nursing Informatics practice b. Informatics and healthcare Informatics c. Nursing informatics as a specialty d. Models for nursing informatics e. Data, information and knowledge f. Registered nurses as Knowledge Workers g. Competencies h. Electronic Health Record i. Terminologies - NANDA-I - NIC - NOC - CCC - Omaha System - PNDS - SNOMED CT - ABC codes - PCDS - LOINC - ICNP - NMMDS j. Organizations as Resources - AMIA, HIMSS, National League for Nursing, Society for Health Systems, ACM, ARMA international, American Society for Information Science and technology
2. Advanced terminology systems a. Background and definitions b. Components of advanced terminology systems c. Advantages of advanced terminology systems d. Advanced terminological approaches in nursing, summary and implications 3. Implementing and upgrading clinical information systems a. Clinical Information System - Planning phase - The key role of the Nurse Administrator - System Analysis Phase - System Design Phase - Testing Phase - Document system - Training phase - Implementation Phase - Evaluation phase b. Upgrading clinical information systems, workstations, system issues and future trends E. Practice application 1. Practice applications a. History and evolution b. Standards for practice - Problem solving as an organizing framework c. Information technology and the actual work of nurses - Nursing documentation, care planning, decision-making, outcomes management, discharge planning, healthcare collaboration 2. Critical care applications a. IT capabilities and applications in critical care settings b. Device Connectivity Infrastructure - Physiologic monitoring systems - Hemodynamic monitors - Arrhythmia monitors - Critical Care Information Systems - Coordination and Scheduling of Patient care activities 3. Community health applications a. Community health Nursing System Development b. Home health c. Public health challenges d. Data sets e. Vocabulary Languages - Clinical care Classification System f. Omaha System g. Community health Intensity Rating Scale
h. Community health Systems i. Home Health Information Systems j. Telemedicine, Community Health telemedicine Systems k. Community health Network Systems l. Home High-tech Monitoring Systems m. Educational Technology systems 4. Ambulatory care systems a. Applications necessary in the Ambulatory environment - Financial, administrative and clinical benefits; regulatory Requirements b. The Role of the nurse using informatics concepts in the ambulatory arena 5. Internet tools for advanced nursing practice a. Basic and advanced internet search methods b. Internet- available clinical practice tools 6. Informatics solutions for emergency preparedness and response 7. Vendor applications a. Current trends toward prime vendors, EHRs and systems integration b. Historical perspective c. New technologies and current situation - Care flow diagram d. Key clinical system nursing and multidisciplinary care components - Patient access, admission assessments, diagnosis, - Nursing and multidisciplinary orders and plans of care - Integrated plans of care, Kardex, Workplans - Clinical documentation and discharge summaries e. Standard Terminology provided with clinical applications F. Consumers use of informatics 1. Consumer and patient use of computers for health a. Consumer use of computers for health - Information seeking - Communication and support - Personal health records 2. Decision support for consumers - Disease management 3. Issues in consumer computing for health - Variability in quality of information available to consumers - Lack of security in internet-based transactions - Uneven Accessibility across age, ethnic and socioeconomic Groups - Educational and cultural barriers - Physical and cognitive disabilities - Impact on relationship with health care providers 4. The Nurse Informaticians role in consumer and patient computing - Areas of nursing expertise that can be applied to consumer/
patient computing G. International perspectives 1. Nursing informatics in Canada 2. Nursing informatics in Europe 3. Pacific Rim 4. Nursing informatics in Asia 5. Nursing informatics in South America H. The future of informatics 1. Future directions a. The New Twenty-first century scenario b. Trends toward 2030 - Demography, growth in chronic diseases, emerging infectious disease threats - Changes in health-seeking behavior on the internet - Security and biodefense - Genetic revolution - Nanotechnology - Nursing and the core competencies for the future c. Ethical, Social and Legal Issues ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________
Prepared by: CYGNETTE S. LUMBO, RN, MN Lecturer, Nursing Informatics
///032711
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- St. Anthony'S College San Jose, Antique: Outcomes-Based Curriculum Pacing GuideDocument14 pagesSt. Anthony'S College San Jose, Antique: Outcomes-Based Curriculum Pacing GuideJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Leadership TheoryDocument31 pagesLeadership TheoryJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Plant VirusDocument195 pagesPlant Virusbrkica2011No ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide To Poultry Layer FarmingDocument19 pagesA Beginners Guide To Poultry Layer Farmingarthur guil-anNo ratings yet
- Safety Guidelines For Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: By: Prof. Marites L. RoblezaDocument32 pagesSafety Guidelines For Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: By: Prof. Marites L. RoblezaJerry Able100% (1)
- DOJ Legal Opinion On CHED Opening of Classes in HEIsDocument3 pagesDOJ Legal Opinion On CHED Opening of Classes in HEIsJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Delivery and Care of The NewbornDocument57 pagesDelivery and Care of The NewbornJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Triage in Emergency Department: Triage Waiting Room Team LeaderDocument27 pagesTriage in Emergency Department: Triage Waiting Room Team LeaderJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- CMO No. 4 S. 2020 Guidelines On The Implementation of Flexible LearningDocument10 pagesCMO No. 4 S. 2020 Guidelines On The Implementation of Flexible LearningRalph Evander IdulNo ratings yet
- Related Literature - New Normal Educatonal SystemDocument20 pagesRelated Literature - New Normal Educatonal SystemJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Transcribing Doctors Order EDITED-2Document21 pagesTranscribing Doctors Order EDITED-2Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent: Lena Haygood (R) RT Radiology Instructor: Arizona Western Community College SourceDocument18 pagesInformed Consent: Lena Haygood (R) RT Radiology Instructor: Arizona Western Community College SourceJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- INFECTION Control and PREVENTION-1Document49 pagesINFECTION Control and PREVENTION-1Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Film ReviewDocument2 pagesFilm ReviewJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Emergency Red Flags: DR - Magdy Khames AlyDocument58 pagesEmergency Red Flags: DR - Magdy Khames AlyJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- DLP Physical Science SeptemberDocument2 pagesDLP Physical Science SeptemberJerry Able100% (5)
- Po1 Po2 Po3 Po4 Po5 Po6 Po7 Po8 Po9 Po10 Po11 Po12 Po13 Po14Document16 pagesPo1 Po2 Po3 Po4 Po5 Po6 Po7 Po8 Po9 Po10 Po11 Po12 Po13 Po14Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- OB - CPG Health Assessment 2018-2019Document21 pagesOB - CPG Health Assessment 2018-2019Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- DLP Caregiving NC 2 September 24-29Document2 pagesDLP Caregiving NC 2 September 24-29Jerry AbleNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony'S College San Jose, Antique: Outcomes-Based Curriculum Pacing GuideDocument15 pagesSt. Anthony'S College San Jose, Antique: Outcomes-Based Curriculum Pacing GuideJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- NCP Marilou.... SanitariumDocument9 pagesNCP Marilou.... SanitariumJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- WASH in Schools in Emergencies Guidebook For Teachers PDFDocument80 pagesWASH in Schools in Emergencies Guidebook For Teachers PDFJerry Able100% (1)
- Business Environment & Business Ideas DLP 3Document24 pagesBusiness Environment & Business Ideas DLP 3Jerry Able100% (2)
- Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocument16 pagesTrigeminal NeuralgiaJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Principles of BioethicsDocument80 pagesPrinciples of BioethicsYashmine Castrence0% (1)
- Sangandiwa PaperDocument52 pagesSangandiwa PaperJoseph RosalNo ratings yet
- Ca3 Therapeutic Modality Grp.3Document15 pagesCa3 Therapeutic Modality Grp.3Valjim PacatangNo ratings yet
- Attending Rounds: Fernando C. FervenzaDocument9 pagesAttending Rounds: Fernando C. FervenzaGita Christy KekenusaNo ratings yet
- 6 Weeks To 6-Pack Abs - Dr. Bradley EvsichDocument33 pages6 Weeks To 6-Pack Abs - Dr. Bradley Evsicharamisbirsan2132No ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Structure & FunctionDocument28 pagesHemoglobin Structure & Functiondeepak3027315No ratings yet
- Estudio SEDCOMDocument11 pagesEstudio SEDCOMElias Vera RojasNo ratings yet
- Lymphadenopathy: Soheir Adam, MD, MSC, MrcpathDocument34 pagesLymphadenopathy: Soheir Adam, MD, MSC, MrcpathWilly OematanNo ratings yet
- OMT Range of MotionDocument1 pageOMT Range of MotionMedShare100% (2)
- Staff Handbook SECTION 8Document27 pagesStaff Handbook SECTION 8Funda HandaNo ratings yet
- Bioterrorism: By: Berlian Isnia FitrasantiDocument35 pagesBioterrorism: By: Berlian Isnia FitrasantiKevin FachriNo ratings yet
- Physician Board Exam Room Assignment (Prelims)Document2 pagesPhysician Board Exam Room Assignment (Prelims)proffsgNo ratings yet
- Otalgia & TinnitusDocument19 pagesOtalgia & Tinnitushonda matizNo ratings yet
- Not For Reproduction: Doctor'S Order/Nurse'S Compliance Sheet (Authenticate All Orders)Document2 pagesNot For Reproduction: Doctor'S Order/Nurse'S Compliance Sheet (Authenticate All Orders)Mcgee OcnicnatNo ratings yet
- Teori Keperawatan: T. Pangandaheng., S.Kep., NS., MSNDocument22 pagesTeori Keperawatan: T. Pangandaheng., S.Kep., NS., MSNTommy PangandahengNo ratings yet
- RippedBody - Nutrition GuideDocument62 pagesRippedBody - Nutrition GuideHan100% (1)
- Cover LetterDocument2 pagesCover LetterXara VillaNo ratings yet
- 46 Dani Preventivne Medicine-Zbornik RezimeaDocument182 pages46 Dani Preventivne Medicine-Zbornik RezimeaМилош МујовићNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Family SurveyDocument3 pagesComprehensive Family SurveyGem HimenaceNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Lymphatic SystemDocument153 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Lymphatic SystemNellie Grace Montes Aba-aNo ratings yet
- I. Choose The Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced Differently From That of The OthersDocument3 pagesI. Choose The Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced Differently From That of The Othershuy phạmNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument33 pagesAcute Myeloid LeukemiardLuis1No ratings yet
- Manual Endoscopios EG290Kp EC380LKpDocument52 pagesManual Endoscopios EG290Kp EC380LKpBenito SoltechmedNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kesehatan Gigi: Emergency Management of Ingestion Bur (Case Study)Document6 pagesJurnal Kesehatan Gigi: Emergency Management of Ingestion Bur (Case Study)Qasrini ZatilNo ratings yet
- Project Greymouth - Arrest SubjectsDocument3 pagesProject Greymouth - Arrest SubjectswindsorstarNo ratings yet
- Spring Life News - 2019 (DIGITAL)Document8 pagesSpring Life News - 2019 (DIGITAL)Jim KerrNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Dan AspirinDocument10 pagesWarfarin Dan Aspirindita novia maharaniNo ratings yet