Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Enthalpy - Entropy Diagram For Steam (MOLLIER CHART) : Problems On Processes of Vapors
The Enthalpy - Entropy Diagram For Steam (MOLLIER CHART) : Problems On Processes of Vapors
Uploaded by
Enriv YasiladOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Enthalpy - Entropy Diagram For Steam (MOLLIER CHART) : Problems On Processes of Vapors
The Enthalpy - Entropy Diagram For Steam (MOLLIER CHART) : Problems On Processes of Vapors
Uploaded by
Enriv YasiladCopyright:
Available Formats
Problems on Processes of Vapors
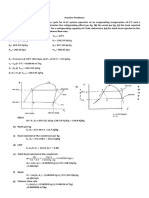
The enthalpy entropy diagram for steam (MOLLIER CHART) To follow the different types of vapor processes, an H-S diagram is drawn complete with pressures and temperatures, showing entropy on the horizontal axis, and enthalpy on the vertical axis.
H-S for isenthalpic process
Problem: A saturated vapor is 5 bar and 150 0C is expanding to 1 bar, S1 = 6.875 KJ/kg-K; S2 = 7.5 KJ/kg-K and h1 = h2 2750 KJ/kg
Problems on Processes of Vapors
H-S diagram for isentropic process
Problem: A superheated steam at 20 bar and 350 0C extracting to 0.1 bar, h1 = 3100 KJ/kg, h2 = 2200 KJ/kg; S1 = S2 6.95 KJ/kg-K
PROPERTY DIAGRAMS AND STEAM TABLES SUMMARY 1. MOLLIER DIAGRAM is an H-S plot 2. MOLLIER DIAGRAM is applicable when the steam quality is greater than 50% and for superheated steam 3. STEAM TABLES can be used to determine the properties of water, through: v = x(vg) + y(vf) x+y=1 y = 1-x v = x(vg) + (1-x)vf v = vg - y(vfg) v = vf + x(vfg) x= x= x=
Problems on Processes of Vapors
PROBLEMS 1. Using Steam Tables: A superheated steam at 48.263 bar and 359.99 0C is expanded at constant entropy to 9.65 bar. Determine the change in enthalpy? ANS. h = - 361.71 kJ/kg
2. Using steam Tables: What is the specific volume, enthalpy of steam having a quality of 90% at 27.579 bar?
SOLVED PROBLEMS 1. Five kg of O2 expands at a constant-pressure of 190 Kpa in a closed system from a temperature of 29 0C to a final state of 205 0C. Determine the work needed expanding the oxygen? Given: O2 (oxygen): m = 5 kg P1 = c = 190 Kpa T1 = 29 0C T2 = 205 0C Required: Work, in KJ Solution: Closed system: Work is work non-flow process, W nf P = constant (Isobaric process) Wnf = P(V2-V1)
= 190(3.610 2.281) = 252.572 KJ
Problems on Processes of Vapors
2. An ideal gas at 30 psig, 70 0F is heated in a closed container to 100 0F. Determine the final absolute temperature inside the container, psi? Given: P1 = 30 psig T1 = 70 0F T2 = 100 0F Required: Solution: Rigid container/closed container, V = constant, (CHARLES LAW) P1/T1 = P2/T2 Absolute Pressure: Pabs = Pg + Patm Pabs = 30 + 14.7 Pabs = 44.7 psi P2 = 47.20 psi P2, in psi
3. A SCUBA tank contains 3 kg of air at 13 0C. The tank is left near at the exhaust line resulting to the tank pressure doubled. What is the new temperature, 0K? Given: m = 3 kg T1 = 13 0C P1 = 1 atm P2 = 2P1 Required: T2, 0K Solution: SCUBA TANK: V = C P1/T1 = P2/T2 1 atm/286 = 2 atm/T2 T2 = 572 0K
10
Problems on Processes of Vapors
4. A rigid vessel contains 2 kg of steam at 6.35 Mpa, 375 0C. Determine its enthalpy in KJ? Given: STEAM: m = 2 kg P1 = 6.35 Mpa T1 = 375 0C Required: Solution: Rigid vessel: Closed system: Using Steam Tables, (Table 3. Vapor) P1 = 6.35 Mpa (Tsat = 279.26 0C) T1 = 375 0C h = 3107.3 KJ/kg h = 6214 KJ h, in KJ
11
You might also like
- Wear CoinsDocument3 pagesWear Coinstbejitual100% (1)
- Steel Staircase DesignDocument6 pagesSteel Staircase Designserafini75% (4)
- Final Round and ClincherDocument8 pagesFinal Round and Clincherponcatoera0% (2)
- MEL1 (3) Fuels& CombustionDocument22 pagesMEL1 (3) Fuels& CombustionEnriv Yasilad86% (7)
- Prelim Quizzes To Midterms Heat TransferDocument11 pagesPrelim Quizzes To Midterms Heat TransferNiño Gerard JabagatNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 Module #2 Ideal and Actual Reheat Rankine CycleDocument25 pagesThermodynamics 2 Module #2 Ideal and Actual Reheat Rankine CycleJohn Rexel CaroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Velocities in MachinesDocument13 pagesLesson 3: Velocities in MachinesMark MarkNo ratings yet
- H. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)Document20 pagesH. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)HectorCabzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Gas Compressors 1Document11 pagesChapter 7 Gas Compressors 1Ervenjee Basco100% (1)
- Edited Thermo Problems 1Document5 pagesEdited Thermo Problems 1Darlene Bacatan AmancioNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument25 pagesThermoJerryco AlviarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Problem SetDocument49 pagesThermodynamics: Problem SetStephanie Palomares LevitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document3 pagesChapter 07Gianne Karl AlmarinesNo ratings yet
- 8 ThingsDocument184 pages8 ThingsLester Garcia33% (3)
- 80 81,84 86,87 88,95 97Document5 pages80 81,84 86,87 88,95 97Ivy Joy Ubina100% (1)
- ASTM C533-17 (Aislamiento Térmico)Document4 pagesASTM C533-17 (Aislamiento Térmico)Àngel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Viscosity by Efflux TimeDocument3 pagesViscosity by Efflux TimeAmit Jharbade67% (3)
- Isobaric ProcessDocument24 pagesIsobaric ProcessWhindy Bagawisan CasugaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 Module #2 Rankine CycleDocument19 pagesThermodynamics 2 Module #2 Rankine CycleJohn Rexel CaroNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Problems:: Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument10 pagesSupplementary Problems:: Mechanical Engineering DepartmentJhun Briones100% (1)
- THERMODYNAMICS - MODULE 2 - Lesson 4 5 - Week 8 11 - As of Nov 4Document42 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS - MODULE 2 - Lesson 4 5 - Week 8 11 - As of Nov 4Kim OpenaNo ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set No 2 ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesSolution To Problem Set No 2 ThermodynamicsMark Augusto V. AgusNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument1 pageProblem SetJohn Lester Ocampo30% (10)
- ThermodynamicsDocument57 pagesThermodynamicsMei Lamfao100% (1)
- MaterialsDocument16 pagesMaterialsyeng botzNo ratings yet
- PUMPS Part 2Document11 pagesPUMPS Part 2Kaiser CarloNo ratings yet
- Concept Question IPEDocument65 pagesConcept Question IPEAnne Gabrielle DavidNo ratings yet
- Algebraic MethodDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Methodstephen james100% (1)
- Energy Concepts For Students FileDocument19 pagesEnergy Concepts For Students Filech0k3 iii100% (1)
- Pipe ProbsDocument6 pagesPipe ProbsTrecia Ann Combalicer HuploNo ratings yet
- Thermo1 (20162)Document37 pagesThermo1 (20162)hillary100% (2)
- Common ConstantsDocument3 pagesCommon Constantskristan7No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Problems BSME 5ADocument30 pagesChapter 5 Problems BSME 5AAldren ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDocument54 pagesThermodynamics 2: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezAlvin RazoNo ratings yet
- Dual Cycles LessonDocument17 pagesDual Cycles LessonMae Anj100% (1)
- BSME ME122 MidtermDocument30 pagesBSME ME122 MidtermAnjo Jose JasarenoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2docx PDF FreeDocument8 pagesThermodynamics 2docx PDF FreeMaria PerezNo ratings yet
- Ompad Ipe 02 Prob.8Document3 pagesOmpad Ipe 02 Prob.8Sam Ompad100% (1)
- ME 2121 Module PDFDocument96 pagesME 2121 Module PDFGreen BrainNo ratings yet
- JayDocument13 pagesJaySam SepiolNo ratings yet
- W/M - °K °K: Both Sides of The PlateDocument4 pagesW/M - °K °K: Both Sides of The Platebryant SiboaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Practice ProblemsDocument9 pagesThermodynamics Practice ProblemsJohnNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Power Plan1Document1 pageDay 2 Power Plan1Dennis AleaNo ratings yet
- The Heat Transfer Across A 5" Wall of Firebrick Is...Document3 pagesThe Heat Transfer Across A 5" Wall of Firebrick Is...MelindaNo ratings yet
- Question: Two Walls of A Storage Plant Composed of Insulating Material (Document3 pagesQuestion: Two Walls of A Storage Plant Composed of Insulating Material (MelindaNo ratings yet
- Module 2.4 Enthalpy and 2ND Corollary of 1ST LawDocument6 pagesModule 2.4 Enthalpy and 2ND Corollary of 1ST LawsubyNo ratings yet
- 2-21 LastDocument22 pages2-21 LastAlexis CarpenaNo ratings yet
- Plain Wall ConductionDocument7 pagesPlain Wall Conductionbryant Siboa0% (1)
- Thermo 2Document26 pagesThermo 2Marcial Jr. Militante100% (1)
- (Solved Problems) : Thermodynamics 01Document6 pages(Solved Problems) : Thermodynamics 01Ben0% (1)
- Ajsute InterferenteDocument5 pagesAjsute InterferenteDavid LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Problem SetsDocument5 pagesRefrigeration Problem SetsNiño Gerard JabagatNo ratings yet
- Processes of Ideal GasesDocument28 pagesProcesses of Ideal GasesVincent LagunillaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Ideal GasDocument11 pagesThermodynamics - Ideal GasMae Belle AngayNo ratings yet
- Psme QuizDocument9 pagesPsme QuizJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Marco LuigiNo ratings yet
- Alcorcon Engineering Review Center: Mathematics - AlgebraDocument4 pagesAlcorcon Engineering Review Center: Mathematics - AlgebraChloe OlazoNo ratings yet
- 20 The Temperature of An Ideal Gas Remains Constant While The Absolute Pressure Changes From 103Document5 pages20 The Temperature of An Ideal Gas Remains Constant While The Absolute Pressure Changes From 103Aproski tadaNo ratings yet
- Donguiz, Shiela MareDocument12 pagesDonguiz, Shiela Mareyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Prelims ThermoDocument96 pagesPrelims ThermoJoshua BarteNo ratings yet
- Week 5 & 6Document10 pagesWeek 5 & 6Mariel MirafloresNo ratings yet
- Inbound 1167419644168481477Document11 pagesInbound 1167419644168481477Clint Ford PacaldoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic AnsweranssDocument11 pagesHydraulic AnsweranssJanelle D. Puti-an0% (1)
- Example 4Document41 pagesExample 4Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument4 pagesThermowong zhi chengNo ratings yet
- Terminal Report ShredderDocument25 pagesTerminal Report ShredderEnriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- Mep - Quiz No. 6 - A: Machine DesignDocument4 pagesMep - Quiz No. 6 - A: Machine DesignEnriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- Gant T ChartDocument2 pagesGant T ChartEnriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- Energy Saving Water PumpDocument4 pagesEnergy Saving Water PumpEnriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam (MEP521)Document6 pagesMidterm Exam (MEP521)Enriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering ProblemDocument2 pagesMechanical Engineering ProblemEnriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering ProblemsDocument2 pagesMechanical Engineering ProblemsEnriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Problems-1Document2 pagesMechanical Engineering Problems-1Enriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine ExperimentDocument7 pagesSteam Turbine ExperimentEnriv Yasilad100% (1)
- Hydraulic MachineryDocument2 pagesHydraulic MachineryEnriv YasiladNo ratings yet
- MEL1Document24 pagesMEL1Enriv Yasilad100% (2)
- Standard Tungsten Carbide Cladding Formulas - OilfieldDocument2 pagesStandard Tungsten Carbide Cladding Formulas - OilfieldTamara Maria Ortiz MendezNo ratings yet
- Worked Annotated Sample Problems CreateDocument8 pagesWorked Annotated Sample Problems CreateJohnrenald SuelloNo ratings yet
- Superpro DesignerDocument2 pagesSuperpro DesignerSergio Fernando Mendoza MendozaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of UHPC Reinforced Masonry StructureDocument10 pagesFinite Element Analysis of UHPC Reinforced Masonry StructureTAMANA SHAMSINo ratings yet
- Indian Electricity Act, 1910 (3 Pages)Document3 pagesIndian Electricity Act, 1910 (3 Pages)Kritika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Specific Heat CapacityDocument5 pagesMeasuring Specific Heat CapacityhernanNo ratings yet
- AFTES - Tunnel Support & LiningDocument17 pagesAFTES - Tunnel Support & LiningLeventNo ratings yet
- Lineplus PF 150-P - TDSDocument2 pagesLineplus PF 150-P - TDSSAURAVENDRA TOMARNo ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On The Dynamic Compressive and Tensile Strength of Clay Brick Under High Strain RatesDocument12 pagesExperimental Studies On The Dynamic Compressive and Tensile Strength of Clay Brick Under High Strain RatesalokaNo ratings yet
- Applied Fluid Mechanics: ACU Course Instructor Dr. Ashraf I. SayedDocument21 pagesApplied Fluid Mechanics: ACU Course Instructor Dr. Ashraf I. SayedMahmoud AbdelghfarNo ratings yet
- 4 Optimum Prestress of Tanks With Pinned BaseDocument6 pages4 Optimum Prestress of Tanks With Pinned BaseCarlotaGomesNo ratings yet
- ROB AMBALA FinelDocument121 pagesROB AMBALA FinelEr Navneet JassiNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of New Class Brushless DC Motor FSMDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of New Class Brushless DC Motor FSMKitaba TolesaNo ratings yet
- AHDocument114 pagesAHReyza PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Metallic Material Specification: Title: 2.25 Cr-1 Mo (ASTM A182, Grade F22 Mod), 85 KSI Min Yield Strength - Unified SpecDocument6 pagesMetallic Material Specification: Title: 2.25 Cr-1 Mo (ASTM A182, Grade F22 Mod), 85 KSI Min Yield Strength - Unified SpecReginaldo SantosNo ratings yet
- Lab Report H3Document14 pagesLab Report H3Safin Rafin HaqNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetEdgarNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Fin Efficiency EnhancementDocument4 pagesA Review Paper On Fin Efficiency EnhancementEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Possibilities of LASER Conservation of Metal Objects From Archaeological ContextDocument1 pagePossibilities of LASER Conservation of Metal Objects From Archaeological ContextPenny1314No ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument2 pagesAssignment IShivpreet SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2015 07 23 Homework PhysioEx 5 KeyDocument3 pages2015 07 23 Homework PhysioEx 5 KeyMonica Sario Policina100% (1)
- Lecture 37Document17 pagesLecture 37raynecoeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document8 pagesTutorial 2Ng JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Quality Management CertificateDocument2 pagesLaboratory Quality Management CertificateMuhammad Daud AliNo ratings yet
- T 91 WeldingDocument12 pagesT 91 WeldingMohammad KhaliquzzamaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021979717312122 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0021979717312122 MainSahin CoskunNo ratings yet