Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Sugar Levels Are Regulated by Negative Feedback in Order To Keep The Body in Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Levels Are Regulated by Negative Feedback in Order To Keep The Body in Homeostasis
Uploaded by
Shemeka LaroseCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Load Cell Simulator v2Document1 pageLoad Cell Simulator v2Ivica LukicNo ratings yet
- Mineral Water Plant ProjectDocument14 pagesMineral Water Plant ProjectSourav OjhaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document21 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol50% (4)
- Metro Line 7A & 9 (CSIA To Mira-Bhayandar)Document483 pagesMetro Line 7A & 9 (CSIA To Mira-Bhayandar)Faihzan F Ahmad Shaikh100% (1)
- IPS120-10 Superconducting Magnet Power Supplies ManualDocument86 pagesIPS120-10 Superconducting Magnet Power Supplies ManualoybpviskNo ratings yet
- Pacreas and Gonads - TILLESDocument7 pagesPacreas and Gonads - TILLESAna Marie D. BorjaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiologykrizzia raymundoNo ratings yet
- Pancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDocument8 pagesPancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsansahNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Question Experiment 5Document6 pagesPost Lab Question Experiment 5Skefadiuto100% (3)
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyKyla CalzadoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy PancreasDocument6 pagesAnaphy PancreasAELYN SEVILLANo ratings yet
- Glucose ResearchDocument3 pagesGlucose Researchapi-321551246No ratings yet
- Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDocument4 pagesCells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsSophia OcayNo ratings yet
- Feedback Loops: Glucose and Glucagon: Name: - Ishaan SinghDocument3 pagesFeedback Loops: Glucose and Glucagon: Name: - Ishaan SinghIshaan SinghNo ratings yet
- Blood Sugar Reg-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesBlood Sugar Reg-WPS Officetanjidul islamNo ratings yet
- Glucose Homestasis and Diabetes PresentationDocument23 pagesGlucose Homestasis and Diabetes Presentationapi-320112884No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemKelly Camero ÜNo ratings yet
- Feedback Loops - Glucose and GlucagonDocument3 pagesFeedback Loops - Glucose and GlucagonAnisa Karim IsraelNo ratings yet
- محاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFDocument124 pagesمحاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- 4M TheoryDocument10 pages4M TheoryGwenn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Overview and Function of PanecreaseDocument3 pagesOverview and Function of PanecreaseBuddhika NawagamuwaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJeffrey Calicdan BucalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DMDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DMJisel-Apple Bulan100% (3)
- The Discussion of The Pathophysiology Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesThe Discussion of The Pathophysiology Diabetes MellitusMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- The Discussion of The Pathophysiology Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesThe Discussion of The Pathophysiology Diabetes MellitusMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitusmar_ouqNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gestational DMDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gestational DMAnonymous GtR96jCNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The PancreasDocument4 pagesPhysiology of The PancreasClayton VerBerkmösNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood Glucose Level Lecture 9 10Document34 pagesRegulation of Blood Glucose Level Lecture 9 10Hawaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitus: Fatima Abdulwahid Ghadeer AlarayedhDocument22 pagesInsulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitus: Fatima Abdulwahid Ghadeer Alarayedhghadeer1No ratings yet
- Explain The Mechanism Involved During OGTTDocument2 pagesExplain The Mechanism Involved During OGTTLumaho Greg Mikael DulawanNo ratings yet
- Mammalian HormonesDocument6 pagesMammalian Hormonest0000123No ratings yet
- How Diabetes Works: Click HereDocument13 pagesHow Diabetes Works: Click HereVishal Kumar ShawNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Bartolata, Greyna Mercado RegeanDocument21 pagesSubmitted By: Bartolata, Greyna Mercado RegeanRegean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanisms 2Document14 pagesFeedback Mechanisms 2Jade Mark PantuaNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes MellitusDocument22 pagesInsulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitusghadeer1No ratings yet
- "Regulation of Blood Glucose": Submitted By: Bemisal Ayaz Roll #. 1 1 DPT 2 Proff EveningDocument5 pages"Regulation of Blood Glucose": Submitted By: Bemisal Ayaz Roll #. 1 1 DPT 2 Proff Eveningaza bellaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Endocrine System: HypothalamusDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Endocrine System: HypothalamusPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Secretion of PancreasDocument17 pagesHormonal Secretion of PancreasNazia WasimNo ratings yet
- Part 6 PancreasDocument3 pagesPart 6 PancreasDesadaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pancreas & Fuel Homeostasis: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesEndocrine Pancreas & Fuel Homeostasis: Learning ObjectivesEmmanuel NhandaraNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Suggested Text: How Our Bodies Turn Food Into EnergyDocument26 pages1.6 Suggested Text: How Our Bodies Turn Food Into EnergyRamsses ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Homeostatis Principles and Regulation of Glucose in BloodDocument13 pagesHomeostatis Principles and Regulation of Glucose in Bloodk75544863No ratings yet
- Digestion of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesDigestion of CarbohydratesVarsha SadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 GlycemiaDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Glycemiakillua zoldyckNo ratings yet
- GLUCOSE_HOMEOSTASIS[1]Document13 pagesGLUCOSE_HOMEOSTASIS[1]shreyamahajan010No ratings yet
- TM 13 - Hormon Sistem MetabolismDocument46 pagesTM 13 - Hormon Sistem MetabolismBudidiv SantosoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument150 pagesDiabetes MellitusIan Mizzel A. Dulfina100% (1)
- FSG Pracrical Quiz NotesDocument3 pagesFSG Pracrical Quiz Notesprimsharon123No ratings yet
- Glucose regulation-RSKDocument4 pagesGlucose regulation-RSKdevilalshingh9525No ratings yet
- Wallah THAK GI ME?Document5 pagesWallah THAK GI ME?Usman EngNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Assignment GLUCAGONE by IQRA ARIFDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Assignment GLUCAGONE by IQRA ARIFIqra BaigNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesDiabetes MellitusWeeaboo Franz VlogsNo ratings yet
- Pancreas 2021Document32 pagesPancreas 2021Dr. AliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Homeostasis: and Controlling Blood Glucose LevelsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Homeostasis: and Controlling Blood Glucose LevelsazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Polyuria Polydipsia PolyphagiaDocument1 pagePolyuria Polydipsia PolyphagiaAnna Lyse MosesNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis of The BodyDocument60 pagesHomeostasis of The BodyKusuma PujariNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 1. Normal Physiology/anatomyDocument13 pagesDiabetes 1. Normal Physiology/anatomyJed AbadNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 1. Normal Physiology/anatomyDocument13 pagesDiabetes 1. Normal Physiology/anatomyJed AbadNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates HandoutDocument15 pagesCarbohydrates HandoutnullNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio ScriptDocument5 pagesPathophysio ScriptJelly beansNo ratings yet
- Biology 10Document2 pagesBiology 10teslaboy301No ratings yet
- Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesFrom EverandHealthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesNo ratings yet
- Bloom BoxDocument23 pagesBloom BoxRaghu BharathulaNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Sutan Iqbal Siregar: Electical EngineeringDocument9 pagesMuhammad Sutan Iqbal Siregar: Electical EngineeringStanindo ArthalanggengNo ratings yet
- 2301A Electric Governor ControlDocument15 pages2301A Electric Governor ControlAnonymous V9fdC6100% (1)
- Fly Ash in India: From Waste Pollutant To Ecofriendly ResourcesDocument11 pagesFly Ash in India: From Waste Pollutant To Ecofriendly ResourcesNovitaWahyuniDlyNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifireDocument9 pagesFull Wave Rectifireالزهور لخدمات الانترنيت100% (1)
- Ac/Dc Machinery Chapter Compilation: John Alfred A. Ceniza BSME-5Document42 pagesAc/Dc Machinery Chapter Compilation: John Alfred A. Ceniza BSME-5John A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- JLH 1985 HeadphoneDocument5 pagesJLH 1985 HeadphoneDave LeeNo ratings yet
- Inspection Gaz. NotificationDocument21 pagesInspection Gaz. NotificationKatuNo ratings yet
- NTPCDocument4 pagesNTPCSriram VenkatachariNo ratings yet
- Principles of SolidificationDocument74 pagesPrinciples of SolidificationAnand ShivannaNo ratings yet
- Number 19, 1997 Middle East Well Evaluation ReviewDocument9 pagesNumber 19, 1997 Middle East Well Evaluation ReviewKarim IsmailNo ratings yet
- 1588244806UPHTE-601 Unit3.7 JU - Hysteresis CurveDocument2 pages1588244806UPHTE-601 Unit3.7 JU - Hysteresis CurveMihir RanaNo ratings yet
- Courtney Love Science 101 Electricity and HeatDocument41 pagesCourtney Love Science 101 Electricity and HeatCourtney Love Arriedo OridoNo ratings yet
- Harshitha Energy Systems: MR K A Anand Kumar Garu KakinadaDocument3 pagesHarshitha Energy Systems: MR K A Anand Kumar Garu KakinadaLizzi JNo ratings yet
- Kobelco Hydraulic Crawler Crane Sl4500r Spec BookDocument6 pagesKobelco Hydraulic Crawler Crane Sl4500r Spec Bookina100% (43)
- Datasheet-TB6560 3axis Stepper Motor Driver: Sunwind Electronics Company LTDDocument6 pagesDatasheet-TB6560 3axis Stepper Motor Driver: Sunwind Electronics Company LTDAdelNo ratings yet
- 1973 Oil Crisis: BackgroundDocument28 pages1973 Oil Crisis: BackgroundRoberto Ortega MicalizziNo ratings yet
- Curvade SecadoDocument3 pagesCurvade SecadoBen LimNo ratings yet
- RMIT University Vietnam Busm 4692 - Mibr: Subject CodeDocument12 pagesRMIT University Vietnam Busm 4692 - Mibr: Subject CodePhạmVũĐứcAnhNo ratings yet
- Creative Approaches To Develop Pupils' High Order Thinking SkillsDocument7 pagesCreative Approaches To Develop Pupils' High Order Thinking SkillsRatno Tri LaksonoNo ratings yet
- PECATDocument23 pagesPECATichal_zaidanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 7th Edition BrownDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry 7th Edition Browna157293279No ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual 1400 HP DEMUsDocument556 pagesMaintenance Manual 1400 HP DEMUsKaushal Shrivastava100% (1)
- The Science of NASCARDocument2 pagesThe Science of NASCARBurhanMalikNo ratings yet
- Essco Product CatalogueDocument23 pagesEssco Product CatalogueMohammedAasimUmairNo ratings yet
Blood Sugar Levels Are Regulated by Negative Feedback in Order To Keep The Body in Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Levels Are Regulated by Negative Feedback in Order To Keep The Body in Homeostasis
Uploaded by
Shemeka LaroseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Sugar Levels Are Regulated by Negative Feedback in Order To Keep The Body in Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Levels Are Regulated by Negative Feedback in Order To Keep The Body in Homeostasis
Uploaded by
Shemeka LaroseCopyright:
Available Formats
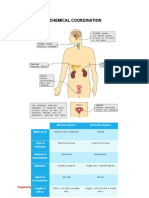
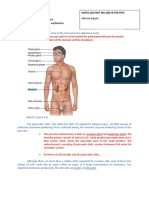
Blood sugar levels are regulated by negative feedback in order to keep the body in homeostasis.
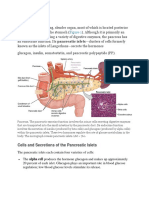
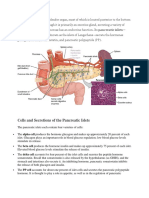
The levels of glucose in the blood are monitored by the cells in the pancreas's Islets of Langerhans. If the blood glucose level falls to dangerous levels (as in very heavy exercise or lack of food for extended periods), the Alpha cells of the pancreas release glucagon, a hormone whose effects on liver cells act to increase blood glucose levels. They convert glycogen into glucose (this process is called glycogenolysis). The glucose is released into the bloodstream, increasing blood sugar levels.\
Role of Insulin: When we take food and glucose is made from the food metabolism, this glucose is than transported to our body cells by blood to be used as energy source. In this phase we need a hormone named Insulin which assists the glucose in the blood to enter in the cells. When blood glucose levels rise, cells named beta cells in pancreas release insulin. Pancreas is an organ located behind our stomach. Without the presence of insulin our body cells cannot take up the glucose from the blood leading to glucose crisis in the body cells for performing activities. If we insulin deficit, the process of glucose metabolism begins working improperly. Instead of being transported into body cells, glucose starts building up in the bloodstream. This situation may occur in two conditions. 1) When body cells become resistant to the action of insulin. Exactly why the cells become resistant to insulin's effects is still not clearly known. 2) If there is deficit in glucose production in the body by the glucose producing cells in pancreas. These two situations can lead towards the disease condition called diabetes mellitus. Role of Glucagon When there is accesses glucose in our body, this glucose is stored for future use by out body as fat cells. If in any case there is any shortage of glucose in our body and there is no supply available than body goes for the alternative way to fulfill the deficit. When blood glucose levels fall, cells named alpha cells in pancreas release glucagon. When blood glucose is high, no glucagon is secreted from the alpha cells. Glucagon has the greatest effect on the liver although it affects many different cells in the body. When glucose levels are low our liver releases the stored glucose into the bloodstream to keep blood glucose level within a normal range and Glucagon's main function is to cause the liver to release stored glucose from its cells into the blood.
You might also like
- Load Cell Simulator v2Document1 pageLoad Cell Simulator v2Ivica LukicNo ratings yet
- Mineral Water Plant ProjectDocument14 pagesMineral Water Plant ProjectSourav OjhaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document21 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol50% (4)
- Metro Line 7A & 9 (CSIA To Mira-Bhayandar)Document483 pagesMetro Line 7A & 9 (CSIA To Mira-Bhayandar)Faihzan F Ahmad Shaikh100% (1)
- IPS120-10 Superconducting Magnet Power Supplies ManualDocument86 pagesIPS120-10 Superconducting Magnet Power Supplies ManualoybpviskNo ratings yet
- Pacreas and Gonads - TILLESDocument7 pagesPacreas and Gonads - TILLESAna Marie D. BorjaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiologykrizzia raymundoNo ratings yet
- Pancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDocument8 pagesPancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsansahNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Question Experiment 5Document6 pagesPost Lab Question Experiment 5Skefadiuto100% (3)
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyKyla CalzadoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy PancreasDocument6 pagesAnaphy PancreasAELYN SEVILLANo ratings yet
- Glucose ResearchDocument3 pagesGlucose Researchapi-321551246No ratings yet
- Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDocument4 pagesCells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsSophia OcayNo ratings yet
- Feedback Loops: Glucose and Glucagon: Name: - Ishaan SinghDocument3 pagesFeedback Loops: Glucose and Glucagon: Name: - Ishaan SinghIshaan SinghNo ratings yet
- Blood Sugar Reg-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesBlood Sugar Reg-WPS Officetanjidul islamNo ratings yet
- Glucose Homestasis and Diabetes PresentationDocument23 pagesGlucose Homestasis and Diabetes Presentationapi-320112884No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemKelly Camero ÜNo ratings yet
- Feedback Loops - Glucose and GlucagonDocument3 pagesFeedback Loops - Glucose and GlucagonAnisa Karim IsraelNo ratings yet
- محاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFDocument124 pagesمحاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- 4M TheoryDocument10 pages4M TheoryGwenn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Overview and Function of PanecreaseDocument3 pagesOverview and Function of PanecreaseBuddhika NawagamuwaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJeffrey Calicdan BucalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DMDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DMJisel-Apple Bulan100% (3)
- The Discussion of The Pathophysiology Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesThe Discussion of The Pathophysiology Diabetes MellitusMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- The Discussion of The Pathophysiology Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesThe Discussion of The Pathophysiology Diabetes MellitusMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitusmar_ouqNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gestational DMDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gestational DMAnonymous GtR96jCNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The PancreasDocument4 pagesPhysiology of The PancreasClayton VerBerkmösNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood Glucose Level Lecture 9 10Document34 pagesRegulation of Blood Glucose Level Lecture 9 10Hawaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitus: Fatima Abdulwahid Ghadeer AlarayedhDocument22 pagesInsulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitus: Fatima Abdulwahid Ghadeer Alarayedhghadeer1No ratings yet
- Explain The Mechanism Involved During OGTTDocument2 pagesExplain The Mechanism Involved During OGTTLumaho Greg Mikael DulawanNo ratings yet
- Mammalian HormonesDocument6 pagesMammalian Hormonest0000123No ratings yet
- How Diabetes Works: Click HereDocument13 pagesHow Diabetes Works: Click HereVishal Kumar ShawNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Bartolata, Greyna Mercado RegeanDocument21 pagesSubmitted By: Bartolata, Greyna Mercado RegeanRegean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanisms 2Document14 pagesFeedback Mechanisms 2Jade Mark PantuaNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes MellitusDocument22 pagesInsulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitusghadeer1No ratings yet
- "Regulation of Blood Glucose": Submitted By: Bemisal Ayaz Roll #. 1 1 DPT 2 Proff EveningDocument5 pages"Regulation of Blood Glucose": Submitted By: Bemisal Ayaz Roll #. 1 1 DPT 2 Proff Eveningaza bellaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Endocrine System: HypothalamusDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Endocrine System: HypothalamusPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Secretion of PancreasDocument17 pagesHormonal Secretion of PancreasNazia WasimNo ratings yet
- Part 6 PancreasDocument3 pagesPart 6 PancreasDesadaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pancreas & Fuel Homeostasis: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesEndocrine Pancreas & Fuel Homeostasis: Learning ObjectivesEmmanuel NhandaraNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Suggested Text: How Our Bodies Turn Food Into EnergyDocument26 pages1.6 Suggested Text: How Our Bodies Turn Food Into EnergyRamsses ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Homeostatis Principles and Regulation of Glucose in BloodDocument13 pagesHomeostatis Principles and Regulation of Glucose in Bloodk75544863No ratings yet
- Digestion of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesDigestion of CarbohydratesVarsha SadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 GlycemiaDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Glycemiakillua zoldyckNo ratings yet
- GLUCOSE_HOMEOSTASIS[1]Document13 pagesGLUCOSE_HOMEOSTASIS[1]shreyamahajan010No ratings yet
- TM 13 - Hormon Sistem MetabolismDocument46 pagesTM 13 - Hormon Sistem MetabolismBudidiv SantosoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument150 pagesDiabetes MellitusIan Mizzel A. Dulfina100% (1)
- FSG Pracrical Quiz NotesDocument3 pagesFSG Pracrical Quiz Notesprimsharon123No ratings yet
- Glucose regulation-RSKDocument4 pagesGlucose regulation-RSKdevilalshingh9525No ratings yet
- Wallah THAK GI ME?Document5 pagesWallah THAK GI ME?Usman EngNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Assignment GLUCAGONE by IQRA ARIFDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Assignment GLUCAGONE by IQRA ARIFIqra BaigNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesDiabetes MellitusWeeaboo Franz VlogsNo ratings yet
- Pancreas 2021Document32 pagesPancreas 2021Dr. AliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Homeostasis: and Controlling Blood Glucose LevelsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Homeostasis: and Controlling Blood Glucose LevelsazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Polyuria Polydipsia PolyphagiaDocument1 pagePolyuria Polydipsia PolyphagiaAnna Lyse MosesNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis of The BodyDocument60 pagesHomeostasis of The BodyKusuma PujariNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 1. Normal Physiology/anatomyDocument13 pagesDiabetes 1. Normal Physiology/anatomyJed AbadNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 1. Normal Physiology/anatomyDocument13 pagesDiabetes 1. Normal Physiology/anatomyJed AbadNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates HandoutDocument15 pagesCarbohydrates HandoutnullNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio ScriptDocument5 pagesPathophysio ScriptJelly beansNo ratings yet
- Biology 10Document2 pagesBiology 10teslaboy301No ratings yet
- Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesFrom EverandHealthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesNo ratings yet
- Bloom BoxDocument23 pagesBloom BoxRaghu BharathulaNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Sutan Iqbal Siregar: Electical EngineeringDocument9 pagesMuhammad Sutan Iqbal Siregar: Electical EngineeringStanindo ArthalanggengNo ratings yet
- 2301A Electric Governor ControlDocument15 pages2301A Electric Governor ControlAnonymous V9fdC6100% (1)
- Fly Ash in India: From Waste Pollutant To Ecofriendly ResourcesDocument11 pagesFly Ash in India: From Waste Pollutant To Ecofriendly ResourcesNovitaWahyuniDlyNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifireDocument9 pagesFull Wave Rectifireالزهور لخدمات الانترنيت100% (1)
- Ac/Dc Machinery Chapter Compilation: John Alfred A. Ceniza BSME-5Document42 pagesAc/Dc Machinery Chapter Compilation: John Alfred A. Ceniza BSME-5John A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- JLH 1985 HeadphoneDocument5 pagesJLH 1985 HeadphoneDave LeeNo ratings yet
- Inspection Gaz. NotificationDocument21 pagesInspection Gaz. NotificationKatuNo ratings yet
- NTPCDocument4 pagesNTPCSriram VenkatachariNo ratings yet
- Principles of SolidificationDocument74 pagesPrinciples of SolidificationAnand ShivannaNo ratings yet
- Number 19, 1997 Middle East Well Evaluation ReviewDocument9 pagesNumber 19, 1997 Middle East Well Evaluation ReviewKarim IsmailNo ratings yet
- 1588244806UPHTE-601 Unit3.7 JU - Hysteresis CurveDocument2 pages1588244806UPHTE-601 Unit3.7 JU - Hysteresis CurveMihir RanaNo ratings yet
- Courtney Love Science 101 Electricity and HeatDocument41 pagesCourtney Love Science 101 Electricity and HeatCourtney Love Arriedo OridoNo ratings yet
- Harshitha Energy Systems: MR K A Anand Kumar Garu KakinadaDocument3 pagesHarshitha Energy Systems: MR K A Anand Kumar Garu KakinadaLizzi JNo ratings yet
- Kobelco Hydraulic Crawler Crane Sl4500r Spec BookDocument6 pagesKobelco Hydraulic Crawler Crane Sl4500r Spec Bookina100% (43)
- Datasheet-TB6560 3axis Stepper Motor Driver: Sunwind Electronics Company LTDDocument6 pagesDatasheet-TB6560 3axis Stepper Motor Driver: Sunwind Electronics Company LTDAdelNo ratings yet
- 1973 Oil Crisis: BackgroundDocument28 pages1973 Oil Crisis: BackgroundRoberto Ortega MicalizziNo ratings yet
- Curvade SecadoDocument3 pagesCurvade SecadoBen LimNo ratings yet
- RMIT University Vietnam Busm 4692 - Mibr: Subject CodeDocument12 pagesRMIT University Vietnam Busm 4692 - Mibr: Subject CodePhạmVũĐứcAnhNo ratings yet
- Creative Approaches To Develop Pupils' High Order Thinking SkillsDocument7 pagesCreative Approaches To Develop Pupils' High Order Thinking SkillsRatno Tri LaksonoNo ratings yet
- PECATDocument23 pagesPECATichal_zaidanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 7th Edition BrownDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry 7th Edition Browna157293279No ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual 1400 HP DEMUsDocument556 pagesMaintenance Manual 1400 HP DEMUsKaushal Shrivastava100% (1)
- The Science of NASCARDocument2 pagesThe Science of NASCARBurhanMalikNo ratings yet
- Essco Product CatalogueDocument23 pagesEssco Product CatalogueMohammedAasimUmairNo ratings yet








































![GLUCOSE_HOMEOSTASIS[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/747352994/149x198/94f3bf247e/1719941429?v=1)