Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Example 20
Example 20
Uploaded by
candemirerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Theory of Structures Problems Solved by DK MamonaiDocument72 pagesTheory of Structures Problems Solved by DK MamonaiDarya Memon94% (103)
- B2B - Seca - grp9 - Maersk Line B2B Social MediaDocument2 pagesB2B - Seca - grp9 - Maersk Line B2B Social MediaDivyany Pandey100% (1)
- Fundamental of MIcroelectronics Bahzad Razavi Chapter 8 Solution ManualDocument73 pagesFundamental of MIcroelectronics Bahzad Razavi Chapter 8 Solution Manualmkmkmkmk2No ratings yet
- Library Hub and School Library Action Plan: Areas Objectives Activities Persons Involved Time Line Expected OutcomeDocument4 pagesLibrary Hub and School Library Action Plan: Areas Objectives Activities Persons Involved Time Line Expected OutcomeKaren dale Doble100% (4)
- Crowd Psychology - WikipediaDocument8 pagesCrowd Psychology - WikipediaD BNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument36 pagesMechanicalAyale MnNo ratings yet
- 6Document15 pages6sanand_1992No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2Karl CastilloNo ratings yet
- Shear Forces - Bending MomentsDocument40 pagesShear Forces - Bending MomentsRicardo Guerrero GarciaNo ratings yet
- Winkler Curved Beam TheoryDocument21 pagesWinkler Curved Beam TheoryMuluken TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Assigment 1Document22 pagesAssigment 1Fakhrul Izzuddin RozaliNo ratings yet
- Lesson No.8.EXERCISES - STATICS OF RIGID BODIES - Resultant of Coplanar Non Concurrent Forces - FEB2024Document2 pagesLesson No.8.EXERCISES - STATICS OF RIGID BODIES - Resultant of Coplanar Non Concurrent Forces - FEB2024Lloyd Christian PorlajeNo ratings yet
- M M T T S N N: Sile U Preseku Pravog ŠtapaDocument3 pagesM M T T S N N: Sile U Preseku Pravog Štapaagf_ssNo ratings yet
- Handout2 Kinematics 1Document11 pagesHandout2 Kinematics 1Gipsa JosephNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solutions EX9.1Document9 pagesExercise Solutions EX9.1api-3741518No ratings yet
- Lecture Reading 9Document5 pagesLecture Reading 9Ysac Rocco SongcoNo ratings yet
- Equations Eg 341Document30 pagesEquations Eg 341lopesisnotdamanNo ratings yet
- EDS PontesDocument10 pagesEDS PontesjosielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4dearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Mecanismos SolucionarioDocument16 pagesMecanismos SolucionarioSebastian L MillanNo ratings yet
- Static of RIGID BODIES PART-2Document30 pagesStatic of RIGID BODIES PART-2Eyaa AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Student Ski Rad 2Document27 pagesStudent Ski Rad 2dino_051No ratings yet
- 15.1 (A) For Example:: Problem SolutionsDocument46 pages15.1 (A) For Example:: Problem SolutionsLuis AntonioNo ratings yet
- M #Elementos R #Reacciones Soporte J #Nodos M 9 R 5 J 5 9+5 3 (5) Estaticamente DeterminadoDocument6 pagesM #Elementos R #Reacciones Soporte J #Nodos M 9 R 5 J 5 9+5 3 (5) Estaticamente DeterminadoNicolas Yesid Martinez NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Rotation About An Arbitrary Axis (Line)Document16 pagesRotation About An Arbitrary Axis (Line)Upender DhullNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (ME101) - Answers To Quiz-IDocument5 pagesEngineering Mechanics (ME101) - Answers To Quiz-IMunindra NaikNo ratings yet
- Electrical Equations SheetDocument2 pagesElectrical Equations SheetyeefonglimNo ratings yet
- Tugas 11: Ktk205 - Mekanika Rekayasa IiDocument9 pagesTugas 11: Ktk205 - Mekanika Rekayasa IiDhea PutriNo ratings yet
- I.H.shames Chapter 2 24.06.10Document6 pagesI.H.shames Chapter 2 24.06.10Prosun BiswasNo ratings yet
- Moments 2Document62 pagesMoments 2CharlesNo ratings yet
- Tehnička Mehanika: 6. Vježbe Ravnoteža Općeg Sustava Sila U Ravnini: - Prosta Greda - IV. ProgramDocument19 pagesTehnička Mehanika: 6. Vježbe Ravnoteža Općeg Sustava Sila U Ravnini: - Prosta Greda - IV. ProgramAna ŠpikoNo ratings yet
- 3Eng. Mechanics_Chapter Two ResultantDocument16 pages3Eng. Mechanics_Chapter Two Resultantm4332060No ratings yet
- AresDocument8 pagesAresAngel Mendez RoaringNo ratings yet
- Solution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Document18 pagesSolution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Gulshan KumarNo ratings yet
- Uticajne Linije Za Staticki Neodredjene NosaceDocument81 pagesUticajne Linije Za Staticki Neodredjene NosaceEniz MamukićNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 SF and BM Full PageDocument77 pagesLecture 4 SF and BM Full Pageapi-368340382100% (1)
- Capitulo 9-10Document12 pagesCapitulo 9-10CESAR ADALBERTO GARNICA ALCIVARNo ratings yet
- Files-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 31Document8 pagesFiles-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 31Eyad Abozyd100% (1)
- 2.001 - Mechanics and Materials I Lecture #6 9/27/2006 Prof. Carol LivermoreDocument11 pages2.001 - Mechanics and Materials I Lecture #6 9/27/2006 Prof. Carol LivermorePrasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch15p PDFDocument11 pagesCh15p PDFLuis AntonioNo ratings yet
- Zadatak 3Document13 pagesZadatak 3Amar HodzicNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Ray TracingDocument5 pagesLecture 9 Ray TracingJorge Parra-MichelNo ratings yet
- Analisa GayaDocument2 pagesAnalisa GayaArais Jr.No ratings yet
- PROBLEM 3.120: SolutionDocument10 pagesPROBLEM 3.120: SolutionPedro Noe CMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09Document6 pagesLecture 09derp2ooNo ratings yet
- ELE 201 Soru Çözümü 4Document39 pagesELE 201 Soru Çözümü 4Kadir ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- K L N P R T: Perhitugan Reaksi PerletakanDocument54 pagesK L N P R T: Perhitugan Reaksi PerletakanNumbskulls RainNo ratings yet
- Viga SimpleDocument3 pagesViga SimpleBrenny LópezNo ratings yet
- Chap54 7Document6 pagesChap54 7balakaleesNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering Related Problem & SolutionDocument75 pagesStructural Engineering Related Problem & SolutionFaruque Abdullah100% (1)
- Winkler Curved Beam TheoryDocument21 pagesWinkler Curved Beam TheoryfddssaaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- TeresaDocument24 pagesTeresaWilnaí Ra-HaraktysNo ratings yet
- SYEA Ventures V7 - EnglishDocument25 pagesSYEA Ventures V7 - Englishbashir019No ratings yet
- Aleo Mok, Classification of Soil ContaminationDocument5 pagesAleo Mok, Classification of Soil ContaminationWE THE GAMERSNo ratings yet
- AMI - Moisture IndicatorsDocument2 pagesAMI - Moisture IndicatorssalamrefighNo ratings yet
- 07we Bond Worked Example Anchored Sheet Pile WallDocument12 pages07we Bond Worked Example Anchored Sheet Pile WallPacoNo ratings yet
- Autism-Mind, Emotion, and The Spectrum of Autism - Dr. Dan SiegelDocument2 pagesAutism-Mind, Emotion, and The Spectrum of Autism - Dr. Dan Siegelcinfer75No ratings yet
- DLL Tle-Ia 6 q3 w3Document4 pagesDLL Tle-Ia 6 q3 w3KM BallaoNo ratings yet
- Rivers and CoastsDocument25 pagesRivers and Coastsapi-235865217100% (2)
- A Glimpse Into The Technology of 21 Century NanotechnologyDocument24 pagesA Glimpse Into The Technology of 21 Century Nanotechnologyapi-19937584100% (1)
- The Atheist's Guide To Reality, by Alex Rosenberg REVIEWDocument1 pageThe Atheist's Guide To Reality, by Alex Rosenberg REVIEWJon StewartNo ratings yet
- Mignolo Interview PluriversityDocument38 pagesMignolo Interview PluriversityJamille Pinheiro DiasNo ratings yet
- Science Project: Green Chemistry: The Future of Sustainable ScienceDocument13 pagesScience Project: Green Chemistry: The Future of Sustainable Sciencethuanv2511No ratings yet
- STEP 7 Lite - Programming With Step 7 LiteDocument470 pagesSTEP 7 Lite - Programming With Step 7 LiteSerdar AksoyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics, 8th Edition Halliday, Resnick, WalkerDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Physics, 8th Edition Halliday, Resnick, Walkerabhishekkumar1996No ratings yet
- How To Crack IIT JEEDocument21 pagesHow To Crack IIT JEEeduflix100% (5)
- Chapter FourDocument75 pagesChapter FourMehretu Abate100% (1)
- Fendt 900 Vario s4 Tractors Wiring Diagram 72614890Document23 pagesFendt 900 Vario s4 Tractors Wiring Diagram 72614890michaelskinner200285gcj100% (139)
- Sponsorship LetterDocument3 pagesSponsorship Letterherb100% (1)
- NSO 2010 Papers With Answers For Class 9Document5 pagesNSO 2010 Papers With Answers For Class 9Karan DoshiNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Phan Bo ChuanDocument2 pagesBai Tap Phan Bo Chuannewsletters GMAILNo ratings yet
- 9608 November 2015 Question Paper 42 PDFDocument16 pages9608 November 2015 Question Paper 42 PDFCrustNo ratings yet
- Rights Reserved. 1Document33 pagesRights Reserved. 1rajuyjNo ratings yet
- Mid Unit Practice Test and ObjectivesDocument2 pagesMid Unit Practice Test and ObjectivesHoàng LongNo ratings yet
- Strategi Public Relations Dalam Mempertahankan Citra Perusahaan PT Sumber Alfaria Trijaya TBK (Alfamart)Document8 pagesStrategi Public Relations Dalam Mempertahankan Citra Perusahaan PT Sumber Alfaria Trijaya TBK (Alfamart)Lelian Tiara Harika PutriNo ratings yet
- December Speaking ClassDocument125 pagesDecember Speaking ClassSu Wai M100% (2)
- Raporti I Forumit Ekonomik Botëror - Liria Ekonomike Dhe Faktorët Që Pengojnë Investimet e HuajaDocument2 pagesRaporti I Forumit Ekonomik Botëror - Liria Ekonomike Dhe Faktorët Që Pengojnë Investimet e HuajaTirana TodayNo ratings yet
- PYRAMIDOLOGYDocument92 pagesPYRAMIDOLOGYverdiblue100% (2)
Example 20
Example 20
Uploaded by
candemirerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Example 20
Example 20
Uploaded by
candemirerCopyright:
Available Formats
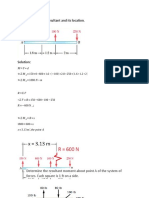
5.
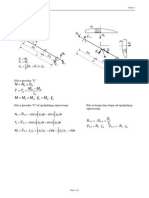
117 The bearings at A, B, and C do not exert couples on the bar and do not exert forces in the direction of the axis of the bar. Determine the reactions at the bearings due to the two forces on the bars.
Look at the free body diagram . Look at the force acting on the body ur u RA = 0 i + RAy + RAz k j ur u RB = RBx i + 0 + RBz k j ur u RC = RCx i + RCy + 0 k j u u r F1 = 200 N i + 0 + 0 k j ur u F = 0 i + 0 + 100 N k j
2
The sum of forces
F F F
x y z
= 0 = R Bx + 200 N + R Cx = 0 = R Ay + R Cy = 0 = R Az + 100 N + R Bz
The components of the moments must be computed individually rBA = 0.15 m i 0.15 m + 0 m k j r = 0 m i + 0.18 m + 0.3 m k j
BC
rBF 1 = 0 m i + 0.18 m + 0 m k j r = 0 m i 0.15 m + 0 m k j
BF 2
The moment created by force at A u u ur ur ur u u M A = rBA RA i j k = 0.15 m 0.15 m 0 m = ( 0.15 m ) RAz i ( 0.15 m ) RAz + ( 0.15 m ) RAy k j 0 RAy RAz The moment generated at C u u u r ur ur u u M C = rBC RC i j k = 0 m 0.18 m 0.3 m = ( 0.3 m ) RCy i + ( 0.3 m ) RCx ( 0.18 m ) RCx k j RCx RCy 0 The moment generated by F1 u ur u u u u u ur u r M F 1 = rBF 1 F1 i j k = 0 m 0.18 m 0 m = 0 i + 0 36 N-m k j 200 N 0 0 The moment generated by F2 u ur u u ur u u ur u M F 2 = rBF 2 F2 i j k = 0 m 0.15 m 0 m = 15 N-m i + 0 + 0 k j 0 0 100 N
Look at the moment about the y axis
(M
uu ur
u u u ur u ur ur u u u u + MC + M F1 + MF 2 A
=0 = ( 0.15 m ) RAz + ( 0.3 m ) RCx RCx = 0.5 RAz
Look at the moment about the x axis
u u u u u ur u ur ur ur u u u u M A + MC + M F1 + MF 2
=0 = ( 0.15 m ) RAz ( 0.3 m ) RCy 15 N-m RCy = 0.5 RAz 50 N
Look at the moment about the z axis
(M
uu ur
u u u ur u ur ur u u u u + MC + M F1 + MF 2 A
=0 = ( 0.15 m ) RAy ( 0.18 m ) RCx 36 N-m RAy = 1.2 RCx + 240 N
From the sum of forces in the y direction
= 0 = R Ay + R Cy R Ay = R Cy
The four equations from moments and the sum of force in y are RCx = 0.5 RAz RAy = RCy RCy = 0.5 RAz 50 N RAy = 1.2 RCx + 240 N Substitute [1] into [4] RAy = 1.2 ( 0.5 RAz ) + 240 N = 0.6 RAz + 240 N Use this equation and equation 3 into equation 2 RCy = 0.5 RAz 50 N RAy = 0.6 RAz + 240 N RAy = RCy 0.6 RAz + 240 N = ( 0.5 RAz 50 N ) 0.1RAz = 190 N RAz = 1900 N RCy = 0.5 ( 1900 N ) 50 N = 900 N RAy = RCy = 900 N RCx = 0.5 ( 1900 N ) = 950 N Look at the sum of forces to find the reactions at B
[ 1] [ 2] [ 3] [ 4]
= 0 = RBx + 200 N + RCx = 750 N
RBx = RCx 200 N = ( 950 N ) 200 N = 0 = RAz + 100 N + RBz = 1800 N
RBz = RAz 100 N = ( 1900 N ) 100 N
You might also like
- Theory of Structures Problems Solved by DK MamonaiDocument72 pagesTheory of Structures Problems Solved by DK MamonaiDarya Memon94% (103)
- B2B - Seca - grp9 - Maersk Line B2B Social MediaDocument2 pagesB2B - Seca - grp9 - Maersk Line B2B Social MediaDivyany Pandey100% (1)
- Fundamental of MIcroelectronics Bahzad Razavi Chapter 8 Solution ManualDocument73 pagesFundamental of MIcroelectronics Bahzad Razavi Chapter 8 Solution Manualmkmkmkmk2No ratings yet
- Library Hub and School Library Action Plan: Areas Objectives Activities Persons Involved Time Line Expected OutcomeDocument4 pagesLibrary Hub and School Library Action Plan: Areas Objectives Activities Persons Involved Time Line Expected OutcomeKaren dale Doble100% (4)
- Crowd Psychology - WikipediaDocument8 pagesCrowd Psychology - WikipediaD BNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument36 pagesMechanicalAyale MnNo ratings yet
- 6Document15 pages6sanand_1992No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2Karl CastilloNo ratings yet
- Shear Forces - Bending MomentsDocument40 pagesShear Forces - Bending MomentsRicardo Guerrero GarciaNo ratings yet
- Winkler Curved Beam TheoryDocument21 pagesWinkler Curved Beam TheoryMuluken TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Assigment 1Document22 pagesAssigment 1Fakhrul Izzuddin RozaliNo ratings yet
- Lesson No.8.EXERCISES - STATICS OF RIGID BODIES - Resultant of Coplanar Non Concurrent Forces - FEB2024Document2 pagesLesson No.8.EXERCISES - STATICS OF RIGID BODIES - Resultant of Coplanar Non Concurrent Forces - FEB2024Lloyd Christian PorlajeNo ratings yet
- M M T T S N N: Sile U Preseku Pravog ŠtapaDocument3 pagesM M T T S N N: Sile U Preseku Pravog Štapaagf_ssNo ratings yet
- Handout2 Kinematics 1Document11 pagesHandout2 Kinematics 1Gipsa JosephNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solutions EX9.1Document9 pagesExercise Solutions EX9.1api-3741518No ratings yet
- Lecture Reading 9Document5 pagesLecture Reading 9Ysac Rocco SongcoNo ratings yet
- Equations Eg 341Document30 pagesEquations Eg 341lopesisnotdamanNo ratings yet
- EDS PontesDocument10 pagesEDS PontesjosielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4dearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Mecanismos SolucionarioDocument16 pagesMecanismos SolucionarioSebastian L MillanNo ratings yet
- Static of RIGID BODIES PART-2Document30 pagesStatic of RIGID BODIES PART-2Eyaa AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Student Ski Rad 2Document27 pagesStudent Ski Rad 2dino_051No ratings yet
- 15.1 (A) For Example:: Problem SolutionsDocument46 pages15.1 (A) For Example:: Problem SolutionsLuis AntonioNo ratings yet
- M #Elementos R #Reacciones Soporte J #Nodos M 9 R 5 J 5 9+5 3 (5) Estaticamente DeterminadoDocument6 pagesM #Elementos R #Reacciones Soporte J #Nodos M 9 R 5 J 5 9+5 3 (5) Estaticamente DeterminadoNicolas Yesid Martinez NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Rotation About An Arbitrary Axis (Line)Document16 pagesRotation About An Arbitrary Axis (Line)Upender DhullNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (ME101) - Answers To Quiz-IDocument5 pagesEngineering Mechanics (ME101) - Answers To Quiz-IMunindra NaikNo ratings yet
- Electrical Equations SheetDocument2 pagesElectrical Equations SheetyeefonglimNo ratings yet
- Tugas 11: Ktk205 - Mekanika Rekayasa IiDocument9 pagesTugas 11: Ktk205 - Mekanika Rekayasa IiDhea PutriNo ratings yet
- I.H.shames Chapter 2 24.06.10Document6 pagesI.H.shames Chapter 2 24.06.10Prosun BiswasNo ratings yet
- Moments 2Document62 pagesMoments 2CharlesNo ratings yet
- Tehnička Mehanika: 6. Vježbe Ravnoteža Općeg Sustava Sila U Ravnini: - Prosta Greda - IV. ProgramDocument19 pagesTehnička Mehanika: 6. Vježbe Ravnoteža Općeg Sustava Sila U Ravnini: - Prosta Greda - IV. ProgramAna ŠpikoNo ratings yet
- 3Eng. Mechanics_Chapter Two ResultantDocument16 pages3Eng. Mechanics_Chapter Two Resultantm4332060No ratings yet
- AresDocument8 pagesAresAngel Mendez RoaringNo ratings yet
- Solution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Document18 pagesSolution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Gulshan KumarNo ratings yet
- Uticajne Linije Za Staticki Neodredjene NosaceDocument81 pagesUticajne Linije Za Staticki Neodredjene NosaceEniz MamukićNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 SF and BM Full PageDocument77 pagesLecture 4 SF and BM Full Pageapi-368340382100% (1)
- Capitulo 9-10Document12 pagesCapitulo 9-10CESAR ADALBERTO GARNICA ALCIVARNo ratings yet
- Files-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 31Document8 pagesFiles-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 31Eyad Abozyd100% (1)
- 2.001 - Mechanics and Materials I Lecture #6 9/27/2006 Prof. Carol LivermoreDocument11 pages2.001 - Mechanics and Materials I Lecture #6 9/27/2006 Prof. Carol LivermorePrasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch15p PDFDocument11 pagesCh15p PDFLuis AntonioNo ratings yet
- Zadatak 3Document13 pagesZadatak 3Amar HodzicNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Ray TracingDocument5 pagesLecture 9 Ray TracingJorge Parra-MichelNo ratings yet
- Analisa GayaDocument2 pagesAnalisa GayaArais Jr.No ratings yet
- PROBLEM 3.120: SolutionDocument10 pagesPROBLEM 3.120: SolutionPedro Noe CMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09Document6 pagesLecture 09derp2ooNo ratings yet
- ELE 201 Soru Çözümü 4Document39 pagesELE 201 Soru Çözümü 4Kadir ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- K L N P R T: Perhitugan Reaksi PerletakanDocument54 pagesK L N P R T: Perhitugan Reaksi PerletakanNumbskulls RainNo ratings yet
- Viga SimpleDocument3 pagesViga SimpleBrenny LópezNo ratings yet
- Chap54 7Document6 pagesChap54 7balakaleesNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering Related Problem & SolutionDocument75 pagesStructural Engineering Related Problem & SolutionFaruque Abdullah100% (1)
- Winkler Curved Beam TheoryDocument21 pagesWinkler Curved Beam TheoryfddssaaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- TeresaDocument24 pagesTeresaWilnaí Ra-HaraktysNo ratings yet
- SYEA Ventures V7 - EnglishDocument25 pagesSYEA Ventures V7 - Englishbashir019No ratings yet
- Aleo Mok, Classification of Soil ContaminationDocument5 pagesAleo Mok, Classification of Soil ContaminationWE THE GAMERSNo ratings yet
- AMI - Moisture IndicatorsDocument2 pagesAMI - Moisture IndicatorssalamrefighNo ratings yet
- 07we Bond Worked Example Anchored Sheet Pile WallDocument12 pages07we Bond Worked Example Anchored Sheet Pile WallPacoNo ratings yet
- Autism-Mind, Emotion, and The Spectrum of Autism - Dr. Dan SiegelDocument2 pagesAutism-Mind, Emotion, and The Spectrum of Autism - Dr. Dan Siegelcinfer75No ratings yet
- DLL Tle-Ia 6 q3 w3Document4 pagesDLL Tle-Ia 6 q3 w3KM BallaoNo ratings yet
- Rivers and CoastsDocument25 pagesRivers and Coastsapi-235865217100% (2)
- A Glimpse Into The Technology of 21 Century NanotechnologyDocument24 pagesA Glimpse Into The Technology of 21 Century Nanotechnologyapi-19937584100% (1)
- The Atheist's Guide To Reality, by Alex Rosenberg REVIEWDocument1 pageThe Atheist's Guide To Reality, by Alex Rosenberg REVIEWJon StewartNo ratings yet
- Mignolo Interview PluriversityDocument38 pagesMignolo Interview PluriversityJamille Pinheiro DiasNo ratings yet
- Science Project: Green Chemistry: The Future of Sustainable ScienceDocument13 pagesScience Project: Green Chemistry: The Future of Sustainable Sciencethuanv2511No ratings yet
- STEP 7 Lite - Programming With Step 7 LiteDocument470 pagesSTEP 7 Lite - Programming With Step 7 LiteSerdar AksoyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics, 8th Edition Halliday, Resnick, WalkerDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Physics, 8th Edition Halliday, Resnick, Walkerabhishekkumar1996No ratings yet
- How To Crack IIT JEEDocument21 pagesHow To Crack IIT JEEeduflix100% (5)
- Chapter FourDocument75 pagesChapter FourMehretu Abate100% (1)
- Fendt 900 Vario s4 Tractors Wiring Diagram 72614890Document23 pagesFendt 900 Vario s4 Tractors Wiring Diagram 72614890michaelskinner200285gcj100% (139)
- Sponsorship LetterDocument3 pagesSponsorship Letterherb100% (1)
- NSO 2010 Papers With Answers For Class 9Document5 pagesNSO 2010 Papers With Answers For Class 9Karan DoshiNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Phan Bo ChuanDocument2 pagesBai Tap Phan Bo Chuannewsletters GMAILNo ratings yet
- 9608 November 2015 Question Paper 42 PDFDocument16 pages9608 November 2015 Question Paper 42 PDFCrustNo ratings yet
- Rights Reserved. 1Document33 pagesRights Reserved. 1rajuyjNo ratings yet
- Mid Unit Practice Test and ObjectivesDocument2 pagesMid Unit Practice Test and ObjectivesHoàng LongNo ratings yet
- Strategi Public Relations Dalam Mempertahankan Citra Perusahaan PT Sumber Alfaria Trijaya TBK (Alfamart)Document8 pagesStrategi Public Relations Dalam Mempertahankan Citra Perusahaan PT Sumber Alfaria Trijaya TBK (Alfamart)Lelian Tiara Harika PutriNo ratings yet
- December Speaking ClassDocument125 pagesDecember Speaking ClassSu Wai M100% (2)
- Raporti I Forumit Ekonomik Botëror - Liria Ekonomike Dhe Faktorët Që Pengojnë Investimet e HuajaDocument2 pagesRaporti I Forumit Ekonomik Botëror - Liria Ekonomike Dhe Faktorët Që Pengojnë Investimet e HuajaTirana TodayNo ratings yet
- PYRAMIDOLOGYDocument92 pagesPYRAMIDOLOGYverdiblue100% (2)