Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Further Pure Mathematics FP1 - Mock - Ms
Further Pure Mathematics FP1 - Mock - Ms
Uploaded by
wa030waOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Further Pure Mathematics FP1 - Mock - Ms
Further Pure Mathematics FP1 - Mock - Ms
Uploaded by
wa030waCopyright:
Available Formats
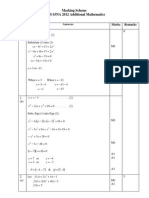
GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP1 mock paper mark scheme 1
Further Pure Mathematics FP1 (6667)
Mock paper mark scheme
Question
number
Scheme Marks
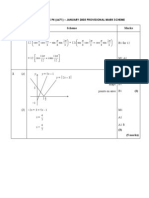
1. (a)
2
1 0
0 1
| |
=
|
\ .
R
B1
(b)
1 0
0 1
| |
=
|
\ .
RS B1 B1
(c) Rotation, 180
about O, or about O
Or enlargement, scale factor 1
B1 B1
(5 marks)
2. Parabola, or y
2
= 4ax seen
a = 3 or a = 3 seen
y
2
= 12x
B1
B1
B1
(3 marks)
3. (a) 1 2 3i 3 1 3i + + + = 1 3 3i +
M1 A1 A1
(3)
(1 3i)(2 3i)
(2 3i)(2 3i)
+ +
+
=
1 3 3 i
7
+
M1 A1 A1
(3)
(6 marks)
4. (a) f(2) = 1, f(3) = 3; and so = 2 +
1
1 3 +
= 2.25
B1 B1;
M1 A1(4)
(b)
2
f ( ) 3 8 5
f (2.5) 3.75
x x x ' = +
' =
f(2.5) = 0.125
M1
A1
B1
(b)
1
.125
2.5
3.75
u = = 2.47
M1 A1 (5)
(9 marks)
GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP1 mock paper mark scheme 2
Question
number
Scheme Marks
5. (a) Determinant 5ab
1
3 2
1
5
b b
a a ab
| |
=
|
\ .
X
B1
M1 A1 (3)
(b)
1
Z= YX
10 5
1
5 0 5
ab ab
ab ab
| |
=
|
\ .
2 1
1 0
| |
=
|
\ .
M1
M1 A1 ft
A1 cao (4)
(7 marks)
6. (a)
3
2 6 r r
M1
2
2
2 ( 1) 6 ( 1)
4 2
n n
n n + + A1
|
( 1) ( 1) 6
2
n
n n n = + +
M1
|
2
( 1) 6
2
n
n n n = + +
( 1)( 3)( 2)
2
n
n n n = + + (*) A1 cos (4)
(b) f(50) f(9) = 3243600 3780 M1
= 3239820 A1 (2)
(6 marks)
7. (a) Solve quadratic to obtain 5 12i z =
M1 A1 A1
(3)
(b)
1 2
13 z z = =
arg
1
z = 1.97 and arg
2
z = 1.97
B1, B1
M1 A1 A1
(5)
GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP1 mock paper mark scheme 3
Question
number
Scheme Marks
(c)
B1 B1 (2)
(d)
24i = 24
M1 A1 (2)
(12 marks)
8. (a)
2
9 c = B1 (1)
(b)
2
9 9 dy
y
x dx x
= = M1
Gradient of curve and of tangent is
2
1
t
A1
Gradient of normal is
1
gradient of tangent
M1
Equation is
2
3
( 3 ) y t x t
t
= giving printed answer
M1 A1 cso
(5)
(c) When t = 2, y = 4x + 1.5 24 M1 A1
9
4 1.5 24 x
x
= + M1
Attempt to solve e.g.
2
4 22.5 9 0 x x = and formula M1 A1;
or factorise x =
8
3
; y = 24 M1 A1 (7)
(13 marks)
GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP1 mock paper mark scheme 4
Question
number
Scheme Marks
9. (a)
1
1, 3 2(1 1) 3 n u = = + = , so result true for n = 1 B1
Assume true for k
Then
1
1
3(3 2(3 1)) 4
k k
k
u
+
= + +
M1
So
1
1
3 2(3 ) 6 4
k k
k
u
+
+
= + +
M1
1
1
3 2(3 ) 2
k k
k
u
+
+
= + =
1
3
+ k
+ 2(3
k
1), so result true for
A1
k+1, so by induction the result is true for all positive integers A1 (5)
(b) (i) A
1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
1 3 3
0 4
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
1 9
0 4
so result true for n = 1 B1
Assume true for k
Then
1
4 0 4 0
9 1
3(4 1) 1
k
k
k
+
| |
| |
=
|
|
|
\ .
\ .
A
B1
=
1
4 0
9.4 3.4 3 1
k
k k
+
| |
|
|
+
\ .
M1
=
1 1
1
4 0 4 0
3.4 (3 1) 3 1 3.4 3 1
k k
k k
+ +
+
| | | |
=
| |
| |
+
\ . \ .
M1 A1
so result true for k + 1 M1
So by induction the result is true for all positive integers A1 (7)
(ii) For n = 1, A
-1
=
|
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
1
4
9
0
4
1
M1
This is the correct inverse of A, so result is valid A1 (2)
(14 marks)
You might also like
- NCSE 2015 Integrated ScienceDocument20 pagesNCSE 2015 Integrated ScienceMath Class90% (10)
- Mark Scheme Paper 2 Oct-Nov 01Document3 pagesMark Scheme Paper 2 Oct-Nov 01Yousef Awamleh50% (6)
- Condon E. Scientific Study of UFO Vol1Document167 pagesCondon E. Scientific Study of UFO Vol1Igor KalytyukNo ratings yet
- Properties and Characteristics of GraphiteDocument39 pagesProperties and Characteristics of GraphitePaden TranNo ratings yet
- January 2006 6663 Core Mathematics C1 Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesJanuary 2006 6663 Core Mathematics C1 Mark SchemeAliKhederNo ratings yet
- 2005 Jan MS PDFDocument4 pages2005 Jan MS PDFeconomides1No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2009: GCE Mathematics (6683/01)Document7 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2009: GCE Mathematics (6683/01)Emi JiHyeon KimNo ratings yet
- FP2 Practice Paper A Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesFP2 Practice Paper A Mark Schemejimbolina92100% (1)
- Seafield 2013 M1 (Q&A)Document8 pagesSeafield 2013 M1 (Q&A)STPMmathsNo ratings yet
- Add11 Pahang P1ansDocument5 pagesAdd11 Pahang P1ansAlexlohmalNo ratings yet
- fp1 Old Ms Jan 2003Document7 pagesfp1 Old Ms Jan 2003Nora BothwelNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Complex Numberp1 - AnswDocument31 pagesQuestion Bank Complex Numberp1 - AnswSivagami SaminathanNo ratings yet
- C4 Mock MSDocument5 pagesC4 Mock MSmahamidahmedNo ratings yet
- UNIT 25 Solving Equations CSEC Revision Test: A A X XDocument2 pagesUNIT 25 Solving Equations CSEC Revision Test: A A X XCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- 3NA SA1 (AM Solution)Document8 pages3NA SA1 (AM Solution)johnlim199No ratings yet
- Gce Mathematics Ms January 2012Document31 pagesGce Mathematics Ms January 2012ElinorRoutleyNo ratings yet
- June 2006 6663 Core Mathematics C1 Mark Scheme: Scheme Marks Number 6 2 3 (+C) M1 A1 2 2 2 A1 +C B1 4Document12 pagesJune 2006 6663 Core Mathematics C1 Mark Scheme: Scheme Marks Number 6 2 3 (+C) M1 A1 2 2 2 A1 +C B1 4alyona1295No ratings yet
- D 16) 1 (1 ) 4) 1 - (Arsinh: January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesD 16) 1 (1 ) 4) 1 - (Arsinh: January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark SchemeykkamNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Mathematics Core Mathematics C3 (6665)Document7 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Mathematics Core Mathematics C3 (6665)Fahema ShafiNo ratings yet
- 3h Nov 08 SolnsDocument15 pages3h Nov 08 SolnsConi ChanNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE Mathematics Further Pure Mathematics (FP1/ 6674)Document11 pagesEdexcel GCE Mathematics Further Pure Mathematics (FP1/ 6674)Mohamed ZayNo ratings yet
- FP2 Practice Paper B Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesFP2 Practice Paper B Mark Schemejimbolina92100% (2)
- Mark Scheme (Results) November 2010: IGCSE Mathematics (4400) Paper 4H Higher TierDocument18 pagesMark Scheme (Results) November 2010: IGCSE Mathematics (4400) Paper 4H Higher TierTrisha HarjaniNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument8 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionSK67% (3)
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: AEA Mathematics (9801)Document8 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: AEA Mathematics (9801)will bellNo ratings yet
- 1306 FP2 June 2013 - Withdrawn Paper Mark SchemeDocument12 pages1306 FP2 June 2013 - Withdrawn Paper Mark SchemenmanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2009: GCE Mathematics (6664/01)Document13 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2009: GCE Mathematics (6664/01)showman007No ratings yet
- C3 Practice Paper A2 Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesC3 Practice Paper A2 Mark Schemebiswas_sanjay727865No ratings yet
- C2 Mock Paper MSDocument5 pagesC2 Mock Paper MSZaviyaniNo ratings yet
- Phs 1ex Eoy 2021 Paper Modified MsDocument4 pagesPhs 1ex Eoy 2021 Paper Modified MsivyNo ratings yet
- Gen Rev MSDocument5 pagesGen Rev MSprofgordito2686No ratings yet
- Skema Mathk1midyearf52007Document13 pagesSkema Mathk1midyearf52007adik5967No ratings yet
- X+ Y) (X+ Y) X Yx+ Xy+ y X+ Y) (X+ Y) (XDocument10 pagesX+ Y) (X+ Y) X Yx+ Xy+ y X+ Y) (X+ Y) (Xapi-108235015No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2010: Core Mathematics C3 (6665)Document12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2010: Core Mathematics C3 (6665)Taqsim RajonNo ratings yet
- Trial SPM MT 2014 Jawapan K2Document12 pagesTrial SPM MT 2014 Jawapan K2Mohd Ellif SarianNo ratings yet
- C2 Practice Paper A1 Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesC2 Practice Paper A1 Mark Schemeshariz500No ratings yet
- C1 2006 May 2006 Mark SchemeDocument17 pagesC1 2006 May 2006 Mark SchemeHashan GodakandaNo ratings yet
- STPM 2014 Maths T Paper 1 Trial Sem 1 SSIJBDocument8 pagesSTPM 2014 Maths T Paper 1 Trial Sem 1 SSIJBKenneth Chan50% (2)
- Further Pure 1 June 2010 MSDocument14 pagesFurther Pure 1 June 2010 MSDaniyal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series - Mark SchemeDocument13 pagesSequences and Series - Mark Schemerussell_mahmood100% (1)
- FP1 January 2003 MSDocument7 pagesFP1 January 2003 MSKaren Chong YapNo ratings yet
- Maximum Mark: 80: University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument8 pagesMaximum Mark: 80: University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelSutoyo SudNo ratings yet
- 7361 GCE O Level Mathematics B MSC 20090220Document22 pages7361 GCE O Level Mathematics B MSC 20090220Shahriar Mullick Swapnil100% (1)
- Mark Scheme Jan 2008Document59 pagesMark Scheme Jan 2008Lee StaplesNo ratings yet
- P5 Jun 02 MSDocument8 pagesP5 Jun 02 MSMichael HartNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Module P4: Marking GuideDocument4 pagesPure Mathematics Module P4: Marking GuideThilina Kalhara PanduwawalaNo ratings yet
- Skema Trial Math k1 N k2 SPM PahangDocument15 pagesSkema Trial Math k1 N k2 SPM PahanglizzielayzieNo ratings yet
- 2013 SMCHMath T1 TrialDocument7 pages2013 SMCHMath T1 TrialchimbiNo ratings yet
- C2 January 2006 Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesC2 January 2006 Mark SchemesheenaNo ratings yet
- 06 Core Mathematics C3 Mock Paper Mark SchemeDocument7 pages06 Core Mathematics C3 Mock Paper Mark SchemeAbhishek DebNo ratings yet
- c4 Jan 2008 MsDocument21 pagesc4 Jan 2008 MsMk D. AssassinoNo ratings yet
- 2016 2 KL SMK Methodist - Maths QADocument12 pages2016 2 KL SMK Methodist - Maths QAlingbooNo ratings yet
- Combined MS - FP1 EdexcelDocument128 pagesCombined MS - FP1 EdexceladamNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Jan 2005Document116 pagesMark Scheme Jan 2005OE94No ratings yet
- C2 Practice Paper A4 Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesC2 Practice Paper A4 Mark Schemeshariz500No ratings yet
- MathDocument7 pagesMathglitteryanonNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) November 2008: IGCSE Mathematics (4400) Paper 4HDocument9 pagesMark Scheme (Results) November 2008: IGCSE Mathematics (4400) Paper 4HJohn HopkinsNo ratings yet
- FP1 2008-01 Jan MSDocument7 pagesFP1 2008-01 Jan MSRuwandi PanagodaNo ratings yet
- Equations: UNIT 24 Solving Quadratic CSEC Revision TestDocument4 pagesEquations: UNIT 24 Solving Quadratic CSEC Revision TestCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Calculus Ibsl MsDocument12 pagesCalculus Ibsl MsfarahNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Rag663 SLR Paper - AmalinaDocument26 pagesRag663 SLR Paper - AmalinaSEVENSEA CLANNo ratings yet
- PHD Offer, Batteries, FranceDocument1 pagePHD Offer, Batteries, FranceSamehHamzawyNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Reservoir Modeling and Simulation Geology Geostatistics and Performance Reduction Sanjay Srinivasan All ChapterDocument54 pagesPetroleum Reservoir Modeling and Simulation Geology Geostatistics and Performance Reduction Sanjay Srinivasan All Chapterleonor.edwards304100% (11)
- IET Generation Trans Dist - 2024 - Tan - Fluid Structure Interaction Simulation and Optical Fibre Stress Analysis ofDocument13 pagesIET Generation Trans Dist - 2024 - Tan - Fluid Structure Interaction Simulation and Optical Fibre Stress Analysis ofsz344015173No ratings yet
- Slope Stability Analysis Analiza Interna Input DataDocument22 pagesSlope Stability Analysis Analiza Interna Input DatananesculNo ratings yet
- Iso 16474-2Document22 pagesIso 16474-2sgqNo ratings yet
- Formal Relational QueryDocument53 pagesFormal Relational QuerySaarthak VadheraNo ratings yet
- Estacion de Control Crouse HindsDocument7 pagesEstacion de Control Crouse HindsCristhJuliangNo ratings yet
- NC590 - Construction Planning L2 QP Supp 2019Document8 pagesNC590 - Construction Planning L2 QP Supp 2019fanafisto04No ratings yet
- CREII-Module-5 - Lecture 22 & 23 PDFDocument16 pagesCREII-Module-5 - Lecture 22 & 23 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- JTCC PsDocument57 pagesJTCC PsTatjana MicevskaNo ratings yet
- 25 Feb Shift 1 JEE Main 2021Document64 pages25 Feb Shift 1 JEE Main 2021Devchand BothraNo ratings yet
- 10 129 139 PDF 13423Document11 pages10 129 139 PDF 13423Sinan YıldızNo ratings yet
- Korean Volume BMS 1002Document9 pagesKorean Volume BMS 1002killeremailNo ratings yet
- Design CaculationsDocument14 pagesDesign Caculationsmkpasha55mpNo ratings yet
- Modern Missile AnalysisDocument37 pagesModern Missile AnalysisamenendezamNo ratings yet
- Effects of Tires and Tire Pressures On Road Pavements: Matti Huhtala,) Ari Pihlajamaki, and Markku PienimakiDocument8 pagesEffects of Tires and Tire Pressures On Road Pavements: Matti Huhtala,) Ari Pihlajamaki, and Markku Pienimakiศิวาเวช อบมาNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer RajputDocument919 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer RajputNS MusicalNo ratings yet
- Wet Gas Sampling in The Upstream Area Rev Brazil - ISO TC193 - SC3 Chairman DocumentDocument13 pagesWet Gas Sampling in The Upstream Area Rev Brazil - ISO TC193 - SC3 Chairman DocumentPhilip A Lawrence C.Eng. F. Inst M.C.No ratings yet
- Cone Penetration of Lubricating Grease: Standard Test Methods ForDocument14 pagesCone Penetration of Lubricating Grease: Standard Test Methods ForRodrigo Briceño IbarraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Composite Material Modeling With SolidWorks Simulation PremiumDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Composite Material Modeling With SolidWorks Simulation Premiumanon_282863388100% (1)
- ASTM D6373 15 Especificacion PGDocument7 pagesASTM D6373 15 Especificacion PGPedro AlvelaisNo ratings yet
- Field Work No. 2 Differential Leveling With and Without Turning PointsDocument23 pagesField Work No. 2 Differential Leveling With and Without Turning PointsJohn Andrae MangloNo ratings yet
- Column-Base Plate Foundation Design Report, How To Design Base Plate Connections, Sample Design Report, ColumnBase Software, PCEESoft Inc.Document5 pagesColumn-Base Plate Foundation Design Report, How To Design Base Plate Connections, Sample Design Report, ColumnBase Software, PCEESoft Inc.ircivilcivilNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric Shoe GeneratorDocument8 pagesPiezoelectric Shoe GeneratorJalla PavanNo ratings yet
- MSDS Tris BufferDocument6 pagesMSDS Tris BuffervombyNo ratings yet
- Ampacimon Presentation STH AmDocument34 pagesAmpacimon Presentation STH AmDouglas RibeiroNo ratings yet