Professional Documents
Culture Documents
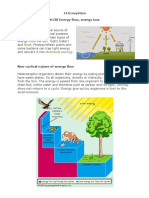
Biology: Food Webs
Biology: Food Webs
Uploaded by
Thalia SandersOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology: Food Webs
Biology: Food Webs
Uploaded by
Thalia SandersCopyright:
Available Formats
COOPERATIVE ACTIVITY 1-1: FOOD CHAINS
(comprehension) Construct a food chain by filling in the blanks below. Use the names of specific organisms (not just "bird" or "plant").
___corn________ producer
____worm_______ primary consumer
____robin__ secondary consumer
__snake_______ tertiary consumer
_bacteria, fungi, mold, etc.____ example of a decomposer or detritus feeder
From the organisms listed in your food chain:
1.
Which are herbivores? __worm______________________
2.
Which are carnivores? ___robin and snake_________
3.
Which perform photosynthesis? __corn____________________
4.
How many different types of consumers are present? _4 (including decomposers______________
5.
Which organism is at the beginning of the food chain? _corn_________________
6.
If the secondary consumers in your food chain died, what would happen to their remains? What would happen to the minerals contained in their bodies? Be specific. Remains would be decomposed and nutrients returned to the soil as the waste produced by decomposers.
7.
On your food chain, circle any organism that could be food for decomposers.
All organisms should be circled.
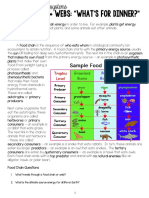
COOPERATIVE ACTIVITY 1-2: FOOD WEBS
(comprehension) Examine the food web in Figure 1-2 and answer the following questions:
1.
Name one organism that functions as both a primary and secondary consumer? _snails____
2.
Name one organism that functions as both a secondary and tertiary consumers? _crayfish__
3.
If a largemouth bass dies of natural causes, draw an arrow indicating the direction of energy transfer and label the arrow with the letter E (for energy). The arrow should show energy transfer to the decomposers in the web, since the bass died of natural causes.
4.
Draw a box around any organisms responsible for nutrient recycling. The box should be drawn around the decomposer bacteria and scavengers (shown at the bottom of the web.)
5.
How many different types of producers support this web? _3______
6.
If all the great blue herons were removed from the ecosystem, the _crayfish_ population would increase the most. This would, in turn, cause a decrease in the _snail______________ population.
7.
Would the situation described in question #6 cause a large change in the population sizes of the trout and bluegill sunfish? Explain your answer.
If the snail population decreases, this would reduce predation on the copepods. This would provide more copepod food for the trout and bluegill sunfish, facilitating their population increase in turn.
COOPERATIVE ACTIVITY 1-3: LONG VS. SHORT FOOD CHAINS
(comprehension) In reference to Figure 1-4, answer the following question: In an overpopulated country, would it be beneficial to make a shift from eating beef to eating food crops such as wheat or rice? Explain your answer.
More people can be supported by eating grain than meat. The addition of cattle into a food chain will mean that less biomass, less food, and therefore, less energy will be available to the next trophic level. It isnt a coincidence that short food chains, consisting of only two trophic levels (such as rice, corn, potatoes people) support the greatest of the worlds population.
COOPERATIVE ACTIVITY 1-4: TROPHIC PYRAMIDS
(comprehension) 1. Arrange the following into their appropriate levels on a trophic pyramid: herring (a small fish), phytoplankton, rockfish (also named striped bass - a large fish), shrimp, and humans. phytoplankton shrimp herring rockfish humans*
2.
What happens to the energy available as you move through the levels of your pyramid? decreases
3.
Draw an asterisk (*) next to the level of the pyramid that would show the greatest amount of toxic accumulation.
(See asterisk in question 1.)
4. Give three examples of substances that might bioaccumulate in the ecosystem represented by the trophic pyramid you drew. Pesticides, PCBs, radioactive isotopes, heavy metals (lead, mercury, copper, cadmium) 5. Suppose the producer level of your pyramid contains 1,000,000 kcal of energy. How much of this energy will be available to feed your secondary consumers?
10,000 kcal
You might also like
- Part 1: The Producers: ChallengeDocument2 pagesPart 1: The Producers: ChallengeJj GrandeNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Ecology Revision SolutionsDocument10 pagesYear 9 Ecology Revision SolutionsHagen SeahNo ratings yet
- Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Pyramid WorksheetDocument10 pagesFood Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Pyramid WorksheetCici LanNo ratings yet
- FIONA ZHENG - Ecology Lab - Predator Prey InteractionsDocument6 pagesFIONA ZHENG - Ecology Lab - Predator Prey InteractionsFiona ZhengNo ratings yet
- Apes Food For ThoughtDocument5 pagesApes Food For Thoughtapi-235617848No ratings yet
- Name: - Year 9 Biology - Ecosystems Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesName: - Year 9 Biology - Ecosystems Practice QuestionsMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Learning Area: Interdependence Among Living Organisms and The Environment Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesChapter Four: Learning Area: Interdependence Among Living Organisms and The Environment Learning ObjectivesRoslaini ZaliNo ratings yet
- 4thGRADE 8 MODULE WEEK 5 6Document3 pages4thGRADE 8 MODULE WEEK 5 6JERIZZA MAGNE PARAFINANo ratings yet
- Foodweb Remote Ready ProtocolDocument10 pagesFoodweb Remote Ready ProtocolEthicalRobin455No ratings yet
- Ms Staar Review Reportingcategory 4Document57 pagesMs Staar Review Reportingcategory 4api-234480965100% (1)
- Food Chain: Who Can Tell Me What A Food Chain Is?Document39 pagesFood Chain: Who Can Tell Me What A Food Chain Is?Ja Na100% (1)
- Checkpoint Food Chains & Webs RSDDocument12 pagesCheckpoint Food Chains & Webs RSDrobd999100% (2)
- Lesson 1 Feeding-RelationshipsDocument16 pagesLesson 1 Feeding-RelationshipsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 1st Q Worksheet 5 Food ChainDocument8 pages1st Q Worksheet 5 Food ChainCornelio T. BavieraNo ratings yet
- Food Web ProtocolDocument9 pagesFood Web ProtocolELOISA N. CASANENo ratings yet
- Year 9 Ecology RevisionDocument10 pagesYear 9 Ecology RevisionHagen SeahNo ratings yet
- 7th Science Calamity 2Document12 pages7th Science Calamity 2yasser yousriNo ratings yet
- Ecology Review KeyDocument5 pagesEcology Review KeyYonasNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Ecology Standard BioDocument103 pagesUnit 10 Ecology Standard BiosabriNo ratings yet
- 09-New Leaf Litter LabDocument5 pages09-New Leaf Litter Labproshni0714No ratings yet
- Ecology and Environment RevisionDocument46 pagesEcology and Environment RevisionlucieNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument28 pagesEcologyJorifNo ratings yet
- April TakehomeDocument4 pagesApril TakehomeDelstien BendiolaNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebDocument4 pagesActivity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Sim Write UpsDocument7 pagesSim Write UpsWilfredo AlipioNo ratings yet
- Food Chain Mini Labs: Define The FollowingDocument3 pagesFood Chain Mini Labs: Define The FollowingReuben AkinsNo ratings yet
- Biology II (Energy and Nutrient Transfer)Document5 pagesBiology II (Energy and Nutrient Transfer)farihatgNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (1) : Food WebDocument9 pagesWorksheet (1) : Food WebVithra MuniVasaNo ratings yet
- CK-12 Biology Chapter 11 WorksheetsDocument23 pagesCK-12 Biology Chapter 11 WorksheetsmaleskunNo ratings yet
- Science8WS Q4 Week5Document8 pagesScience8WS Q4 Week5Desiree Tuares LotasNo ratings yet
- Sesi Intervensi - Soalan (English)Document11 pagesSesi Intervensi - Soalan (English)noldNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet 7 - EcosystemDocument4 pagesPractice Sheet 7 - Ecosystemlalit.chanchlaniNo ratings yet
- Ecology Assignment - AnswersDocument8 pagesEcology Assignment - AnswersRevantVarmaNo ratings yet
- My EcologyDocument30 pagesMy EcologyAnonymous R7NoMuy8No ratings yet
- Ejara - Bfn2e - M1 Activity No.4Document4 pagesEjara - Bfn2e - M1 Activity No.4JAMAICA EJARANo ratings yet
- Our Environment A Our ConcernDocument9 pagesOur Environment A Our ConcernIpshita PathakNo ratings yet
- 1st Q Food ChainDocument6 pages1st Q Food Chainmaricelbaldeviso443No ratings yet
- Grade 6 CT2Document6 pagesGrade 6 CT2shamshadNo ratings yet
- 38 Year 9 Biology Easter Term Note1702724755Document33 pages38 Year 9 Biology Easter Term Note1702724755MochiMocha PlaysNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem PowerpointDocument42 pagesEcosystem PowerpointAllen DagsilNo ratings yet
- Set 1 - CompiledDocument34 pagesSet 1 - Compiledethan.nk7No ratings yet
- Practice 13 3 4Document5 pagesPractice 13 3 4api-235225555No ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1api-236686558No ratings yet
- Unit4 Module 2 Interactions Mms123Document54 pagesUnit4 Module 2 Interactions Mms123Lebiram Mabz91% (11)
- DPP - Our Environment (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesDPP - Our Environment (Prashant Kirad)aahanraj7964No ratings yet
- Lab #5 - Predator-Prey RelationsDocument6 pagesLab #5 - Predator-Prey RelationsEnoc SuazoNo ratings yet
- Pond Water WebsDocument18 pagesPond Water WebsJohn Matthew LagunaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Worksheet KeyDocument5 pages3.3 Worksheet KeyCicy IrnaNo ratings yet
- Multi - Section Test 2Document7 pagesMulti - Section Test 2api-314229616No ratings yet
- Ecosystem PowerpointDocument42 pagesEcosystem Powerpointjeanette Prades100% (1)
- Text Test Bank 11Document11 pagesText Test Bank 11n1n2n3nNo ratings yet
- ds70 Intro To EcologyDocument8 pagesds70 Intro To Ecologyapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Food Chains + Webs: "What'S For Dinner?"Document11 pagesFood Chains + Webs: "What'S For Dinner?"ronaldo100% (1)
- Sample Paper For Class 10Document1 pageSample Paper For Class 10Aishvarya SacchinNo ratings yet
- 8be Ecological RelationshipsDocument17 pages8be Ecological Relationshipsph55krrgpnNo ratings yet
- AP Environmental Science Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date ReviewFrom EverandAP Environmental Science Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date ReviewNo ratings yet
- Jackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonDocument42 pagesJackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonThalia SandersNo ratings yet
- Coolidge v. New Hampshire - 403 U.S. 443 (1971)Document49 pagesCoolidge v. New Hampshire - 403 U.S. 443 (1971)Thalia SandersNo ratings yet
- Washington Post EXPRESS - 12032010Document40 pagesWashington Post EXPRESS - 12032010Thalia SandersNo ratings yet
- W.O.W. Evite 5x7 v4 FINALDocument1 pageW.O.W. Evite 5x7 v4 FINALThalia SandersNo ratings yet
- Daily Kos - Hey America! Can You Please Stop Killing Our (Usually) Innocent Black Male Children NowDocument88 pagesDaily Kos - Hey America! Can You Please Stop Killing Our (Usually) Innocent Black Male Children NowThalia SandersNo ratings yet
- 684-Article Text-1340-1-10-20130211 PDFDocument9 pages684-Article Text-1340-1-10-20130211 PDFYafet AnaktototyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Problems, Their Causes, and SustainabilityDocument29 pagesEnvironmental Problems, Their Causes, and SustainabilityKresna SophianaNo ratings yet
- IDEAS MAGAZINE Edition 2 PDFDocument353 pagesIDEAS MAGAZINE Edition 2 PDFGuzman JulioNo ratings yet
- Pillars of Sustainable DevelopmentDocument31 pagesPillars of Sustainable DevelopmentKareen Joy ManglicmotNo ratings yet
- Piperno (2015) Amazonia and The Anthropocene - What Was The Spatial Extent and Intensity of Human Landscape Modification in The Amazon Basin at The End of PrehistoryDocument10 pagesPiperno (2015) Amazonia and The Anthropocene - What Was The Spatial Extent and Intensity of Human Landscape Modification in The Amazon Basin at The End of PrehistoryGustavo LagaresNo ratings yet
- St. Paul School: I. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle The Letter of The Right Answer in The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesSt. Paul School: I. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle The Letter of The Right Answer in The Following QuestionsAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Macrognathus Aral (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) in WestDocument10 pagesMacrognathus Aral (Bloch and Schneider, 1801) in WestJASH MATHEWNo ratings yet
- Wild Karnataka-"Documentary": Name:-Hafsa ShaikhDocument5 pagesWild Karnataka-"Documentary": Name:-Hafsa ShaikhhafsaNo ratings yet
- Routine Maintenance Dredging For Navigation: Fisheries and Oceans Canada Pacific Region Operational StatementDocument4 pagesRoutine Maintenance Dredging For Navigation: Fisheries and Oceans Canada Pacific Region Operational Statementekia_myNo ratings yet
- Unit Three Red Tide and Harmful Algal BloomsDocument10 pagesUnit Three Red Tide and Harmful Algal BloomsJohnry Guzon ColmenaresNo ratings yet
- BP em CyanideDocument157 pagesBP em Cyanidebalu56100% (1)
- Qualidade Do ArDocument11 pagesQualidade Do ArFabricio DavidNo ratings yet
- Radical American EnvironmentalismDocument13 pagesRadical American EnvironmentalismdcaguenasNo ratings yet
- Konza CityDocument3 pagesKonza CityCollins KipngetichNo ratings yet
- Fevo 10 828503 1Document10 pagesFevo 10 828503 1keilazache2780No ratings yet
- Tree PlantationDocument3 pagesTree PlantationBhavaniPrasadNo ratings yet
- Evs Unit-3 Short NotesDocument14 pagesEvs Unit-3 Short NotesMohammed SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Paper2 PadmajaDocument8 pagesPaper2 PadmajapratignaNo ratings yet
- Murray River Fact SheetDocument2 pagesMurray River Fact SheetPaul TrainorNo ratings yet
- Babi RusaDocument7 pagesBabi RusaRizka Rinintia SariNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Deforestation Free MeatDocument36 pagesSolutions For Deforestation Free MeatStill RageNo ratings yet
- 2002 - Toskeshi - Schmid - Niche Division and Abundance An EvolutionaryDocument12 pages2002 - Toskeshi - Schmid - Niche Division and Abundance An EvolutionaryElaine Cristina Cambui BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Intro Ecology NotesDocument6 pagesIntro Ecology Notesapi-233187566No ratings yet
- PDFsam MergeDocument240 pagesPDFsam MergeKrishna MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Area DevelopmentDocument66 pagesIntegrated Area DevelopmentLogicwengNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Evaluation of Ecotourism Carrying Capacity For Sustainable Development of Karkheh Protected Area, IranDocument14 pagesConceptual Framework For Evaluation of Ecotourism Carrying Capacity For Sustainable Development of Karkheh Protected Area, Iranita faristaNo ratings yet
- 108 Biological Oceanographic ProcessesDocument9 pages108 Biological Oceanographic ProcessesRobyNo ratings yet
- Báo cáo ĐTM dự án đường cao tốc Bến Lức - Long ThànhDocument449 pagesBáo cáo ĐTM dự án đường cao tốc Bến Lức - Long ThànhPham LoanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Answers To End of Chapter 5 QuestionsDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Answers To End of Chapter 5 QuestionsLiezl Odeña CulanibangNo ratings yet
- Managing Manure: The Role of Riparian BuffersDocument5 pagesManaging Manure: The Role of Riparian BuffersGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupNo ratings yet