Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is A Zener Diode
What Is A Zener Diode
Uploaded by
Surendra PeddireddyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is A Zener Diode
What Is A Zener Diode
Uploaded by
Surendra PeddireddyCopyright:
Available Formats
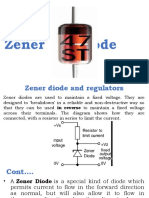
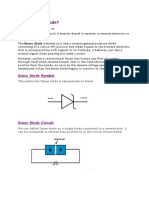
What is a Zener Diode
A Zener Diode is a special kind of diode which permits current to flow in the forward direction as normal, but will also allow it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value the breakdown voltage known as the Zener voltage.
The Zener voltage of a standard diode is high, but if a reverse current above that value is allowed to pass through it, the diode is permanently damaged. Zener diodes are designed so that their zener voltage is much lower - for example just 2.4 Volts. When a reverse current above the Zener voltage passes through a Zener diode, there is a controlled breakdown which does not damage the diode. The voltage drop across the Zener diode is equal to the Zener voltage of that diode no matter how high the reverse bias voltage is above the Zener voltage.
The illustration above shows this phenomenon in a Current vs. Voltage graph. With a zener diode connected in the forward direction, it behaves exactly the same as a standard diode - i.e. a small voltage drop of 0.3 to 0.7V with current flowing through pretty much unrestricted. In the reverse direction however there is a very small leakage current between 0V and the Zener voltage - i.e. just a tiny amount of current is able to flow. Then, when the voltage reaches the breakdown voltage (Vz), suddenly current can flow freely through it.
Uses of Zener Diodes
Since the voltage dropped across a Zener Diode is a known and fixed value, Zener diodes are typically used to regulate the voltage in electric circuits. Using a resistor to ensure that the current passing through the Zener diode is at least 5mA (0.005 Amps), the circuit designer knows that the voltage drop across the diode is exactly equal to the Zener voltage of the diode. NEW Click here to visit Zener-Diode.co.uk for a site dedicated to zener diodes, their characteristics, usage, and other information.
Zener Diode Voltage Regulator Circuit
A zener diode can be used to make a simple voltage regulation circuit as pictured above. The output voltage is fixed at the zener voltage of the zener diode used and so can be used to power devices requiring a fixed voltage. Click here to find out more about the Zener Diode Voltage Regulator and how you go about selecting the resistor and zener diode. NEW The above mentioned article on zener diode voltage regulators has now been updated and a handy calculator has been added to help you select the correct resistor and zener diode values and power ratings.
Zener Diodes in Series With Loads
If you have a regulated fixed voltage - say 12 Volts from a desktop PC power supply, and you want to power something requiring a lower voltage, it is possible to simply place a zener diode in series with the load device. You would choose a diode with a zener voltage equal to the supply voltage minus the voltage drop across the load.
For example, if you have a 1 Watt 6 Volt lightbulb to power from a 12 Watt regulated power supply, a 6.2V zener diode could be placed in series with the bulb giving the bulb 5.8V, or you could overpower the bulb a little using a 5.6V zener diode and dropping 6.4V across the bulb. Heat would be generated in
the zener diode so it is essential to calculate the power lost in it so a suitably rated diode could be chosen. Using a 5.6V zener diode, and knowing the bulb draws a current of around one-sixth of an Amp, we can calculate the power loss in the diode (with Ohm's Law) to be just under 1 Watt. Therefore a standard 1.3 Watt zener diode should be up to the job.
Circuits with Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are key components in the circuits presented in the following articles: Make a Simple Battery Status Monitor, LM741 Voltage Indicator, and High Capacity Alternative to 9V Battery.
You might also like
- Cathodic Disbondment Mul Tiple Channel Testing Unit MODEL #CD-16Document10 pagesCathodic Disbondment Mul Tiple Channel Testing Unit MODEL #CD-16Masood AlamNo ratings yet
- Tle Reviewer For Let RevieweesDocument222 pagesTle Reviewer For Let RevieweesRaymond Wagas Gamboa100% (1)
- 108 PDFDocument28 pages108 PDFcoulibalyoumarNo ratings yet
- A Zener Diode by Muhammad Arif RattarDocument2 pagesA Zener Diode by Muhammad Arif RattarMuhammad Arif RattarNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator TutorialDocument12 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator TutorialAyanda MhlangaNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument8 pagesZener Diodekumar_9583No ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial PDFDocument11 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial PDFGunda TejaNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeMD. Abdullah Al NomanNo ratings yet
- A Zener Diode, Also Known As A Breakdown Diode, Is A Heavily Doped Semiconductor Device That Is Designed To Operate in The Reverse DirectionDocument7 pagesA Zener Diode, Also Known As A Breakdown Diode, Is A Heavily Doped Semiconductor Device That Is Designed To Operate in The Reverse DirectionJhan Ray Gomez BarrilNo ratings yet
- Electronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeDocument10 pagesElectronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage RegulatorDocument2 pagesZener Diode As Voltage RegulatorRATONNo ratings yet
- ZenerDocument5 pagesZeneraravindh rhssNo ratings yet
- U-1 (Boe 8-18)Document11 pagesU-1 (Boe 8-18)Tisha SetiaNo ratings yet
- The Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesThe Zener DiodeKeshav JhaNo ratings yet
- University Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation TechnologyDocument6 pagesUniversity Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technologyvishnu ramaNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument11 pagesZener DiodeFitzpatrick CunananNo ratings yet
- The Zener DiodeDocument8 pagesThe Zener DiodemaanibrahimNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode TheoryDocument7 pagesZener Diode TheoryCarlos IbaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode ExplanationDocument6 pagesZener Diode ExplanationShubham SwamiNo ratings yet
- Zener DRDocument4 pagesZener DRArchana SadanandanNo ratings yet
- ZenerDocument14 pagesZeneraravindh rhssNo ratings yet
- The Zener DiodeDocument7 pagesThe Zener Diodecelo81No ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode?Document4 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode?Riaz IsraniNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument3 pagesZener Diodekanak-825262No ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument36 pagesZener DiodeSurajguptarocks100% (1)
- Zener Diode Applications 1. Zener Diode As A VoltageDocument3 pagesZener Diode Applications 1. Zener Diode As A VoltageSaravananNo ratings yet
- Be Unit-IiDocument12 pagesBe Unit-Iihenryhorrid384No ratings yet
- Zenner DiodeDocument23 pagesZenner DiodeKrishanu NaskarNo ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode - Its Principle Working and Example UsageDocument21 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode - Its Principle Working and Example UsageferdinandNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument14 pagesZener DiodePrasanth. SNo ratings yet
- The Zener Diode orDocument1 pageThe Zener Diode orLupu DanielNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode - WikipediaDocument29 pagesZener Diode - WikipediaLupu DanielNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diode in Reverse Bias Condition: Basic Types of DiodesDocument7 pagesSemiconductor Diode in Reverse Bias Condition: Basic Types of DiodesrahulNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial 4Document5 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial 4Srimonta RoyNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument7 pagesZener DiodeMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Basic Operation and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesZener Diode Basic Operation and ApplicationsEvelyn P. GalanoNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument14 pagesZener DiodeTanya SoodNo ratings yet
- Zener 2Document7 pagesZener 2Mouaz MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Basic Analog Electrnics PPT IN PDFDocument67 pagesBasic Analog Electrnics PPT IN PDFMusa KunrooNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALANo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document81 pagesUnit 1Eswar suryaNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument3 pagesZener DiodeInnocentOvickNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument7 pagesZener DiodeLuiza Raluca100% (1)
- Dioda ZenerDocument2 pagesDioda ZenerGeorge TimpauNo ratings yet
- Edu Expansion Presentation (Circuits)Document16 pagesEdu Expansion Presentation (Circuits)nandinigupta613No ratings yet
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALANo ratings yet
- Application of Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesApplication of Zener DiodeARVIND SINGH RAWAT100% (1)
- BEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 6Document31 pagesBEEE UNIT IV - Lecture 6Girish Shankar MishraNo ratings yet
- Exp2 ZenerDocument6 pagesExp2 ZenerEdward Sevilla Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As A WaveshaperDocument15 pagesZener Diode As A WaveshaperpriyaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesZener Diode: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaApri ZaldyNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeNeal John VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode ProjectDocument16 pagesZener Diode ProjectJsmBhanot83% (6)
- Be Q3 Led ZenerDocument31 pagesBe Q3 Led ZenerLouis Miguel LauritoNo ratings yet
- ECE 027 - Zener DiodeDocument63 pagesECE 027 - Zener DiodeMiyuki NakiriNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode: As Voltage RegulatorDocument39 pagesZener Diode: As Voltage RegulatorRey Francis FamulaganNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesZener Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitNo ratings yet
- 02 Zenerdiodes PPT PRPDocument29 pages02 Zenerdiodes PPT PRPVarsha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument6 pagesZener DiodeKumar shantanu BasakNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument13 pagesZener DiodePhenoमिनल IdiotsNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode & ApplicationsDocument13 pagesZener Diode & Applicationssrakhisharma41No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Laws and Equations: Andrew Mchutchon Michaelmas 2013Document13 pagesElectromagnetism Laws and Equations: Andrew Mchutchon Michaelmas 2013Burhan AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: EGCI 232 Engineering ElectronicsDocument26 pagesLab Manual: EGCI 232 Engineering ElectronicsgapswitNo ratings yet
- VersaJet ManualDocument36 pagesVersaJet ManualJOSE LUIS HERNANDEZ CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Kirloskar: Diesel Generating SetsDocument4 pagesKirloskar: Diesel Generating Setsالطاهر الفاتح حامدNo ratings yet
- ASTM-Designation G109 99aDocument5 pagesASTM-Designation G109 99aJorge LeconaNo ratings yet
- Newage Sx440 Avr, Replacement: Same Fit Form and Function As The Original Newage SX440Document4 pagesNewage Sx440 Avr, Replacement: Same Fit Form and Function As The Original Newage SX440marcosluna68No ratings yet
- 639Document412 pages639ccbulgariaNo ratings yet
- Phy3303 2Document11 pagesPhy3303 2Lai Yeek Hrve100% (1)
- Maintenance of Electrical Switch GearDocument190 pagesMaintenance of Electrical Switch Gearmustaqu100% (3)
- Calculation Method of Corona Loss of-AAAAAAAADocument4 pagesCalculation Method of Corona Loss of-AAAAAAAAWaleed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- r7210102 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument1 pager7210102 Electrical and Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- CableDocument13 pagesCablejugnudubeyNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricalsDocument123 pagesBasic Electricalskarunarathnej7970No ratings yet
- Engines Teaching ManualDocument177 pagesEngines Teaching ManualSteve FoleyNo ratings yet
- Measurement Noise and Signal ProcessingDocument6 pagesMeasurement Noise and Signal Processingname lastNo ratings yet
- S2 Science SSS - 16 Electrical SystemsDocument6 pagesS2 Science SSS - 16 Electrical SystemsSHANNON TAN S2-02No ratings yet
- Tech 2Document6 pagesTech 2Karlo Sam DiegoNo ratings yet
- DTQ 2133SSFNDocument35 pagesDTQ 2133SSFNjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Term 3 2019 Physical Sciences Resource Pack PDFDocument146 pagesGR 12 Term 3 2019 Physical Sciences Resource Pack PDFKevin SmithNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics - AC - DC PDFDocument20 pagesBasic Electronics - AC - DC PDFRowena ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Test Procedures For HV Transition Joints: For Rated Voltages 30kV (Um 36kV) Up To 500kV (Um 550kV)Document4 pagesTest Procedures For HV Transition Joints: For Rated Voltages 30kV (Um 36kV) Up To 500kV (Um 550kV)Morty_scribdNo ratings yet
- Disney Research Paper Generators FinalDocument8 pagesDisney Research Paper Generators Finaljanaaidaas1996No ratings yet
- Define The FFDocument2 pagesDefine The FFTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Final Step-B BookletDocument72 pagesFinal Step-B BookletHalfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- Single Switched Capacitor Battery BalancingDocument25 pagesSingle Switched Capacitor Battery BalancingJordan LimNo ratings yet
- Generator MQ DCA150Document96 pagesGenerator MQ DCA150josmaisea33No ratings yet
- Studyguide Advanced ElectronicsDocument27 pagesStudyguide Advanced ElectronicsApollos JehuNo ratings yet