Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data
Data
Uploaded by
Anindita GhoseOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Data
Data
Uploaded by
Anindita GhoseCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation of Data Raw datas are usually presented in either of the two forms i.e. graphical or tabular.
The representation of raw data in a table is known as tabular presentation. Tabular forms are used in collecting and organizing raw data during an experiment and also for representing the final data that can be used for further use. Tabular presentation of data allows researcher to organize the datas for further analysis, allows large amounts of raw data for sorting and reorganizing the datas in an appropriate format. Moreover, it also allows the researcher to identify only the most important or relevant data. The raw data may be presented in a more attractive way that can be very appealing to the eye with the help of some graphical aids, i.e. pictures and graphs. Such presentation of datas carries a lot of power to convey message.
RAW DATA
SORTING OF RAW DATA
TABULAR REPRESENTATION
GRAPHICAL REPRSENTATION
Tabular Representation The representation of raw data in a table is known as tabular presentation. A table is a symmetric arrangement of statistical datas in rows and columns. Rows are horizontal in nature whereas columns are vertical. The tabular representation can be simple, double or complex in nature which has been discussed below: Simple tabulation or one way tabulation: When data tabulation is on one characteristic then it is said to be simple tabulation or one way tabulation. For example: Tabulation of data on people of India classified by one characteristic like language.
Double tabulation: When data is tabulated according to two characteristics at a time it is called double tabulation or two-way tabulation. For example: Tabulation of data on people of India classified by two characteristics like language and religion. Complex tabulation: When data is tabulated according to multiple characteristic at a time it is said to be complex tabulation. For example: Tabulation of data on people in India classified by characteristics like religion, language, geographical origin, literacy, health etc.
Graphical Representation The raw data or statistical data may be presented in a more attractive way that can be very appealing to the eye with the help of some graphical aids, i.e. pictures and graphs. Such presentation of datas carries a lot of power to convey message. One can think that if the datas can be represented in a tabular form then what is the need of representing it in a pictorial form? The need for graphical presentation of data is due to the following reasons: It makes the comparisons between the datas easy. It presents the characteristics of the datas in a simplified way. This method enhances our understanding. This method also enables the researcher to understand the patterns of population growth, distribution and the density, sex ratio, agesex composition, occupational structure, etc. It creates a long lasting impression on mind of the researcher.
There are many ways of representing the datas graphically which has been discussed below: Bar graphs Histograms Frequency polygons Ogive Line graphs Pie charts Pictographs
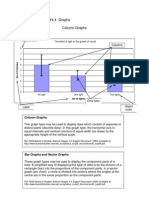
Bar Graphs: A bar graph is a graphical representation of the frequency distributions of the ungrouped datas. In bar diagram, the bars can be plotted either vertically or horizontally. A bar chart is very useful to determine whether the datas are continuous or discontinuous.
Steps for Construction of Bar Graphs 1) First of all say two axes X and Y are drawn on the graph paper. 2) Along the horizontal axis i.e. X axis, the values of the variables are taken and along the vertical axis i.e. Y axis, the frequencies are taken. 3) Along the X axis, the equal width of bars is chosen and the uniform gap between the bars is taken. 4) A suitable scale to determine the heights of the bars is chosen. The scale is chosen according to the space available in the graph paper. 5) The heights of the bars are calculated according to the scale chosen and the bars are then drawn. 6) The axes are marked with proper labeling.
Advantages of Bar Graphs It can easily compare among various sets of data. It helps in easy understanding of the data. It is easy to prepare.
Disadvantages of Bar Graphs It can be used to classify only the discrete datas. This method can be used to emphasize certain effects only.
BAR GRAPH
Histograms: It is a graphical representation of the continuous frequency distribution i.e. grouped frequency distributions. It is a graph which includes vertical rectangles with no space between them. The class-intervals are taken along the horizontal axis (X) and the respective class frequencies are taken on the vertical axis (Y). For each class, a rectangle is drawn with base as width of the class and height as the class frequency. The area of the rectangles must always be proportional to the frequencies of the respective classes.
Steps for Construction of Histograms 1) First of all two axes say X and Y are drawn on the graph paper. 2) Along the horizontal axis i.e. X axis, classes of equal width are taken such as 0-5, 5-10, 10-15,.. 3) A suitable scale on the vertical axis is chosen to represent the frequencies. 4) Then the rectangle histograms are drawn.
Advantages This method is used for the estimation of the density of data. It helps in easy understanding of the data. This method can be compared with the normal distribution curve.
Disadvantages It can be used to classify only the continuous data. This method is difficult to compare two data sets. It cannot read exact values because data is grouped into categories.
HISTOGRAMS
Frequency Polygons: A frequency polygon is the jointed mid-points of the tops of the adjoining rectangles in a histogram. It gives the idea about the shape of the data distribution. The extreme points of a frequency polygon are always joined on the x-axis.
Steps for Construction of Frequency Polygons 1) First of all two axes say X and Y are drawn on the graph paper. 2) Along the horizontal axis i.e. X axis, classes of equal width are taken such as 0-5, 5-10, 10-15,.. 3) A suitable scale on the vertical axis is chosen to represent the frequencies. 4) Then the rectangle histograms are drawn. 5) In the rectangular bars of the histograms, mid-points are taken. All the mid-points are then joined by a line. Now, the graph so obtained is called frequency polygon.
Advantages It is appealing to the eye.
Disadvantages It can be used to classify only the continuous data. As the extremes points of frequency polygon touches x-axis hence it implies that there is no data at all which can be impractical.
FREQUENCY POLYGONS
Ogives: When a researcher wants to express a set of data through a single line, ogive is used. It is basically a cumulative line graph. This method is used by the researcher to display the total frequencies at any given point of time. The word ogive is used in architecture to describe curves or curved shapes. Ogives are of two types: less than ogive and more than ogive.
Steps for Construction of Ogives 1) First of all two axes say X and Y are drawn on the graph paper. 2) Then the cumulative frequencies are calculated. Less than cumulative frequency will give less than ogive whereas more than cumulative frequency will give more than ogive. 3) Class limits are converted into class boundaries. 4) Cumulative frequencies are plotted against the class boundaries, and all the points so obtained are joined. The line so obtained is called ogive.
Advantages This method is used to determine the values of median, quartiles, deciles, percentiles and many more. It can be used to compare more than one distribution. It is useful to determine the number of items above or below a particular value. It can be easily understood due to its widespread use in business and the media. It provides a visual check of the accuracy of the calculations.
Disadvantages It is somewhat complicated to prepare. It can be easily manipulated to yield false results. It reveals little information about central tendency, dispersion, skewness, and kurtosis. This method often requires additional written or verbal explanation. It fails to reveal key assumptions, norms, causes and/or effects.
LESS THAN OGIVE
Line Graphs: A line graph is a type of graph which provides informations by connecting series of data points through a straight line segment. It is also known as line chart. It is a version of scatter diagram. It is one of the most common techniques and is used in many fields. It is often used to visualize a trend in data sets over a specific interval of time.
Steps for Construction of Line Graphs The equation of a straight line is in the form of Y = MX + C By manipulating the value of X, the value of Y can be obtained. The researcher can manipulate any value of his or her choice to obtain a straight line which will be feasible to solve any problem.
Advantages It can compare multiple continuous data sets easily. Interim data can be easily identified from the line graph.
Disadvantages It can be used to classify only the continuous data.
For Example: Y = 3X + 4 Y X 4 0 Y 7 1 10 2 13 3
Y = 3X + 4
Pie Charts: It is a spherical chart in which the sphere is divided into certain parts. Each part visually represents a particular item in a data set. The amount of each part in the pie chart is exactly equal to match the amount of the item as a percentage or fraction of the total data set.
Steps for Construction of Pie Charts 1) The angle of each part of the sphere is calculated using the formula: Angle of a certain portion/part = Corresponding frequency of the data set X 100 Total frequency 2) A circle is drawn using compass. 3) A protractor is used to measure the angle for each portion/part in the circle. 4) Finally the circle graph is labeled and all its parts are shaded differently.
Advantages It is visually appealing to the eye. It shows percent of total for each category.
Disadvantages From a pie chart no exact numerical data can be predicted.
If each part in the pie chart has not been specified then it is completely unknown to any individual that what actually it is representing. It can be used only for discrete datas. It can be best implemented for 3 to 7 categories.
PIE CHART
Pictographs: It is a process through which meaning is conveyed about the physical resemblance of an item. It uses pictures or symbols to represent a given amount of data. It is basically a way of showing data using images.
Steps to Create a Pictograph 1) The datas are entered into an excel sheet and then they are selected. The field headings and titles are also included. 2) On the insert tab in the charts group, a chart is selected. A chart with elements that can support a picture is chosen. 3) In the chart, the first element which the researcher wants to add a picture is selected, and then double-click is done on the element. The picture will be inserted in all the elements that are selected, so it is better to make sure that the selection border is around only the first element. 4) In chart tools, the format tab is clicked and then, in the current selection group, format selection is selected. 5) In the format data point dialog box, in the left navigation pane, fill is clicked. 6) In the right pane, picture or texture fill is clicked. 7) Under insert from, browse for a picture file or clip art image or the contents of the clipboard are inserted.
8) Now it is selected by the researcher to stretch or stack the image. 9) The above steps are repeated for each of the other elements.
Advantages It is very easy to use and read. They seemed to be very funny to use. As a result of this property pictographs can be used to teach children easily. They show trends in data clearly.
Disadvantages A pictograph can be difficult to make. Sometimes it might be difficult to find a symbol or picture to represent a data.
Moreover, pictographs can be used for the analytical explanation of certain geometry like hyperbola, parabola, ellipse and circle. The details of these geometries has been discussed in detail belowHyperbola: It is a smooth curve that lies in a plane. It has got a characteristic equation. The equation of the hyperbola is written as:
You might also like
- Ielts Writing Task I TipsDocument8 pagesIelts Writing Task I TipsMădălina AnaMaria ȚurcanNo ratings yet
- UPSC CSAT IntroDocument15 pagesUPSC CSAT IntroKarthik Saraswathi MalmaruganNo ratings yet
- Assessment - FNSINC602Document25 pagesAssessment - FNSINC602Sabah Khan Raja100% (1)
- Bio StatisticsDocument7 pagesBio StatisticsBaloch Mubin tvNo ratings yet
- Data RepresentationDocument66 pagesData RepresentationMarydelle SubitoNo ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument6 pagesGraphical PresentationAtiqah RazifNo ratings yet
- Research Unit 5 BbaDocument17 pagesResearch Unit 5 Bbayash soniNo ratings yet
- 05 Handout 1Document13 pages05 Handout 1raulNo ratings yet
- Foundation Notes 2013Document25 pagesFoundation Notes 2013Anonymous wXV066fANo ratings yet
- Makerere University: College of Education and External Studies. School of EducationDocument4 pagesMakerere University: College of Education and External Studies. School of EducationKevin SkillzNo ratings yet
- Data Visualization & Data Exploration - Unit IIDocument26 pagesData Visualization & Data Exploration - Unit IIpurusingh23No ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument4 pagesGraphical PresentationSejal PargalNo ratings yet
- Graphical RepresentationDocument34 pagesGraphical RepresentationYukti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chap 7-1Document4 pagesChap 7-1Milkias MuseNo ratings yet
- Presenting and Describing DataDocument7 pagesPresenting and Describing DataQuenne Nova DiwataNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Summarizing Data - Charts and TablesDocument33 pagesUnit 2 - Summarizing Data - Charts and Tablesjemima100% (1)
- Data InterpretationDocument23 pagesData InterpretationArif IqbalNo ratings yet
- How Do You Make A HistogramDocument4 pagesHow Do You Make A Histogramapi-162641823No ratings yet
- MatematikDocument26 pagesMatematikMuhd Hilmi AkhirNo ratings yet
- AIML Practice Questions IA-1 AnsDocument7 pagesAIML Practice Questions IA-1 Ansstudyacc.tcNo ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument6 pagesGraphical PresentationHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation and Narrative WritingDocument42 pagesData Presentation and Narrative WritingBushra SyedNo ratings yet
- Please Download and Read The PDF Below.: 2. Explain The Various Data Presentation Techniques!Document3 pagesPlease Download and Read The PDF Below.: 2. Explain The Various Data Presentation Techniques!MASELIA ADINDA PUTRINo ratings yet
- Module in Statistic Data RepresentationDocument12 pagesModule in Statistic Data RepresentationCarmela UrsuaNo ratings yet
- Presenting Data - GraphsDocument6 pagesPresenting Data - GraphsPrue McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Statistics Mpc006Document30 pagesStatistics Mpc006shaila colacoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Diagrams and GraphsDocument5 pagesMathematics Diagrams and GraphsRaja kamal ChNo ratings yet
- Statistics Essays 1. Classification & TabulationDocument20 pagesStatistics Essays 1. Classification & TabulationShruti S KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Make A HistogramDocument4 pagesHow To Make A Histogramapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Presentation of DataDocument25 pagesPresentation of DataKelliata BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Engdata Module 1Document4 pagesEngdata Module 1Crisalyn BacaniNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation of DataDocument6 pagesGraphical Representation of DataJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument196 pagesStatistics and ProbabilitySiddharth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument253 pagesStatistics and Probabilityanirudhsaxena865No ratings yet
- 5 - Histograms, Frequency Polygons and OglivesDocument26 pages5 - Histograms, Frequency Polygons and OglivesRomell Ambal RamosNo ratings yet
- MAPC006Document12 pagesMAPC0068158Anshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is A HistogramDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Histogramapi-150547803No ratings yet
- 2-3 Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Ogives: Chp.2 Page 1Document2 pages2-3 Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Ogives: Chp.2 Page 1Suniel ChhetriNo ratings yet
- 2 Fields of StatisticsDocument9 pages2 Fields of Statisticsthyrany cattelNo ratings yet
- QT Unit 4 PDFDocument23 pagesQT Unit 4 PDFmojnkuNo ratings yet
- Graphs-Presentation of DataDocument5 pagesGraphs-Presentation of DataUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Data PresentationDocument9 pagesModule 3 Data PresentationHannah BarralNo ratings yet
- Samserali 170529052556Document29 pagesSamserali 170529052556RajeshNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation of Frequency Distribution: Research MethodologyDocument17 pagesGraphical Representation of Frequency Distribution: Research Methodologyvaes2017-19 Vlsi & Embedded systemNo ratings yet
- Statistics (Part 1)Document15 pagesStatistics (Part 1)ABRIANNA HARRISNo ratings yet
- Forms of Presentation of DataDocument29 pagesForms of Presentation of Dataton-ton elcanoNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS STATISTICS - Unit-2Document23 pagesBUSINESS STATISTICS - Unit-2Mandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- KKP mATHDocument6 pagesKKP mATHcegu efaNo ratings yet
- Math 10Document7 pagesMath 10renzlamoste8No ratings yet
- I. About Graphs: What Is A Graph?Document29 pagesI. About Graphs: What Is A Graph?Mae DinDinNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 Presentation of Environmental DataDocument39 pagesLECTURE 4 Presentation of Environmental DataJemdosquadNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 10th EditionDocument38 pagesSolution Manual For Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 10th Editionfootfleececyud5100% (18)
- Solution Manual For Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 10th EditionDocument38 pagesSolution Manual For Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 10th Editiongingivalestrich6ptm100% (25)
- IntroDocument4 pagesIntroJoyce TutopNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Bar PlotDocument24 pagesAssignment-1: Bar PlotANDELA LAHARI 2139465No ratings yet
- Diskusi 7 BING4102Document8 pagesDiskusi 7 BING4102istiqomah100% (1)
- JSMath6 Part2Document64 pagesJSMath6 Part2coffee080403No ratings yet
- Statistics - Docx Unit 1Document9 pagesStatistics - Docx Unit 1Muthukumar V P CS&CANo ratings yet
- Gathering Statistical Data and Organizing Data in A Frequency Distribution Table Grade 7Document2 pagesGathering Statistical Data and Organizing Data in A Frequency Distribution Table Grade 7chariepepitsNo ratings yet
- N Research 06.05.2020 Graphical Representation of DataDocument50 pagesN Research 06.05.2020 Graphical Representation of DataBalasakthiNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Statistical GraphsDocument10 pagesTopic 5 Statistical GraphsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Image Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionFrom EverandImage Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Computer Graphics: Exploring the Visual Realm: Two Dimensional Computer Graphics in Computer VisionFrom EverandTwo Dimensional Computer Graphics: Exploring the Visual Realm: Two Dimensional Computer Graphics in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Diskusi 7 BING4102Document8 pagesDiskusi 7 BING4102istiqomah100% (1)
- IELTS Academic Writing Task 1 KeywordsDocument40 pagesIELTS Academic Writing Task 1 KeywordsANJALI RAJNo ratings yet
- I. About Graphs: What Is A Graph?Document29 pagesI. About Graphs: What Is A Graph?Mae DinDinNo ratings yet
- Statistics 3rd Edition Agresti Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesStatistics 3rd Edition Agresti Solutions ManualMarcusCarlsonerps100% (50)
- Ielts Writing Task 1 Questions by RasulDocument72 pagesIelts Writing Task 1 Questions by RasulHusan SamandarovNo ratings yet
- XII - Revision Sheet - 1 - I.P.Document2 pagesXII - Revision Sheet - 1 - I.P.Nikhil MishraNo ratings yet
- STATS Prep Volume 1Document96 pagesSTATS Prep Volume 1Emad SheikhNo ratings yet
- Meanings of StatisticsDocument28 pagesMeanings of StatisticspapaoniNo ratings yet
- Charts in ExcelDocument12 pagesCharts in Excelpoorna100% (1)
- Conventional Educational MediaDocument36 pagesConventional Educational MediaJason JulladoNo ratings yet
- Barron's Writing For The IELTSDocument6 pagesBarron's Writing For The IELTSNhung LêNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary For The Introduction PartDocument7 pagesVocabulary For The Introduction PartMinh Thư100% (1)
- Chapter-Six: Loan RecoveryDocument15 pagesChapter-Six: Loan RecoveryMithun MohaiminNo ratings yet
- Sample IELTS Speaking TopicsDocument12 pagesSample IELTS Speaking TopicsYulia BarbotkoNo ratings yet
- Chart NotesDocument3 pagesChart NotesRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Vocabulary and TutorialDocument15 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 Pie Chart Vocabulary and TutorialTamunotonye Minaye-IlomboNo ratings yet
- Data Processing and Coding Tabulation and Data PresentationDocument20 pagesData Processing and Coding Tabulation and Data PresentationMohaimen macodNo ratings yet
- Statistics For MGMT I & IIDocument161 pagesStatistics For MGMT I & IIewnetuNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1Document21 pagesWriting Task 1simranjit kaur100% (1)
- Vocabulary To Describe Graphs IntroducinDocument3 pagesVocabulary To Describe Graphs IntroducinCarmen JavierNo ratings yet
- Data Visualization & Data Exploration - Unit IIDocument26 pagesData Visualization & Data Exploration - Unit IIpurusingh23No ratings yet
- Activity For English 10 ModuleDocument4 pagesActivity For English 10 ModuleMarcco Juan MarccoNo ratings yet
- 8614 - Assignment No 1 AIOU Autumn 2022Document10 pages8614 - Assignment No 1 AIOU Autumn 2022سعید اللہNo ratings yet
- 20 Actual Writing Task 1 Questions With Sample AnswersDocument27 pages20 Actual Writing Task 1 Questions With Sample AnswersNa NaNo ratings yet
- Excel ChartsDocument19 pagesExcel ChartsShams ZubairNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W6Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W6WILBERT QUINTUANo ratings yet
- Maths CALA Component CDocument3 pagesMaths CALA Component CChristine Tendai Manyanya100% (2)