Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Sole Trading Firm Is The Oldest and The Simplest Form of Business Organisation
The Sole Trading Firm Is The Oldest and The Simplest Form of Business Organisation
Uploaded by
Pankaj MehtaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Sole Trading Firm Is The Oldest and The Simplest Form of Business Organisation
The Sole Trading Firm Is The Oldest and The Simplest Form of Business Organisation
Uploaded by
Pankaj MehtaCopyright:
Available Formats
; (1) Simplicity:
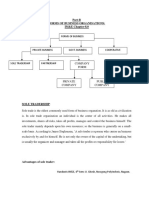
The sole trading firm is the oldest and the simplest form of business organisation.
(2) No legal formalities: No legal formalities are required for the formation and closing of a sole trading firm. (3) Single ownership business: It is a one man show. It is owned and managed by a single person. The total required capital is invested by sole person. (4) Self employment: The sole trader puts his own labour in conducting his business. If necessity arises, he may employ a few paid assistants or use the service of the members of his family. (5) No sharing of profits and risks: The sole trader enjoys all the profits of the enterprise and similarly bears all the losses or risks involved in the business. (6) Exclusive managerial rights: The sole trader possesses the sole authority and right to manage the business. (7) Ere from Government regulations: The sole trading concern is not required to undergo any special legislation of legal formalities. (8) Unlimited liability: The liability of a sole trader is unlimited. Hence, for business debts, not only his business assets but also his private assets become liable. (9) Generally local business: The activities of a sole trader are generally confined to a certain locality. (10) Legal status: The legal status of a sole trader and that of the concern is the same. Hence, a sole trading concern solely depends upon the life of the sole trader.
(1) Easy of Establish : Sole trading concern can be established very quickly and easily. Anybody who wants to start a business can do so, whenever, he likes. In Nepal, only nominal
legal formality of registration is necessary. (2) Easy to Dissolve : Dissolution of sole trading concern equally simple. There are no legal formalities in this regard. Proprietor can dissolve business whenever he likes to do so. (3) Effective Control : In this form of business organization proprietor is responsible for all types of activities. He controls all functions and takes decisions at appropriate time. So, the business is controlled in an effective way. He controls all functions and takes decisions at appropriate time. So, the business is controlled in an effective way. (4) Direct Motivation : The direct relationship between effort and reward serves as a powerful incentive to the proprietor to manage the concern efficiently. The proprietor being entitled to the entire profits of the concern tries to maximize profits by utilizing his talents and activities in the best possible way. (5) Personal Supervision : The proprietor is able to supervise every work of the business himself. This helps to build up a close and cordial relationship with the employees. He can take personal interest in his customers and he can meet their individual and typical needs easily and adequately. It ensures effectively and economy in the operation. (6) Benefit of Unlimited Liability : The proprietor can obtain loan on his personal credit. The liability being unlimited, the creditors feel secure in extending credit. (7) Prompt Decision : The owner has full control over his business. So he is able to take decision promptly without consulting anybody. If more than one person is involved in decision making then delay is bound to occur. (8) Secrecy : The proprietor can maintain business secrets. There is no legal regulation regarding the disclosure of business information. So he can maintain secrecy from his competitors. Secrecy is very vital for business success. (9) Flexible : Sole trader enjoys the maximum flexibility in his business. If any change in business is required, he does no have to consult any one and can make the change without delay. No legal formalities are required for making changes in operations. This gives flexibility to this type of business.
(10) Social Importance : From social viewpoint sole trading concern is important because: (a) It is a means for earning livelihood independently. (b) It avoids concentrating wealth in few hands. (c) It brings competition among sole proprietors, so they provide goods in cheaper rates to the society. (d) Qualities like self-reliance, self-confidence, tact and initiative are developed in this organization. The disadvantage of sole trading concern are as follows : (1) Limited Capital : The capital of one proprietor is usually small. It is limited to his personal savings andborrowing on personal security. Hence, he cannot undertake further expansion and development lack of excess capital and fails to enjoy the internal and externaleconomics of scale. (2) Limited Management Ability : In the present competitive world complexities of managerial jobs are increasing everyday. One man cannot be expert in each and every function of the business. For lack of resources he may not be able to use the services of experts. So limited managerial ability will hinder the growth of the firm. (3) Unlimited Liability : The unlimited liability of sole proprietorship is a greatdisadvantage. A loss in business may deprive the proprietor of his assets too. So big business firms requiring more economic risk are not established under this organization. (4) Uncertain Life : The success of this type of business depends on thepersonal capacity of proprietor. In case of his death business may be discontinued. The successors may not have the same degree of self-reliance and ability. Thus, there is no continuous existence of the firm. (5) Dull and Monotonous Work : The proprietor has the sole right on profit of the business. So he tries to work more to earn more profit. Consequently the work becomes dull and monotonous. His health is badly affected and he is deprived of pleasant social relations and cordial family life. (6) No Large Economics and Specialization : A small scale business cannoteconomies in purchases, production and marketing. Similarly the benefit of specialization of service of experts cannot be obtained. (7) Loss in Absence : A sole trading has to suffer from the long illness of the proprietor. In his absence business comes to a standstill. This can lead to heavy losses. Employees may not be efficient or they may not take sincere interest.
(8) Possibility of Wrong Decision : In sole trading a businessman alone makes all the decisions. Hence, decisions may not be always right and wise. When a considerable number of people are involved in decision making process a wise and mature decision is possible.
Advantages of Partnership:
i. Easy formation: The formation of partnership is very easy. Simply an agreement among the partners in oral or written words can bring a partnership into existence. It includes very less legal formalities and expenses. ii. Large resources: A partnership is in a position to accumulate large resources as more than one contributes capital. The added financial strength of the partners can be utilised to increase the scale of operation of the business. New partners can be admitted to meet the additional requirement of fund. iii. Diverse skills and expertise: Partnership provides a scope for association of persons with diverse skills and expertise. Partners having expertise and skills in different functional areas of business can manage the business efficiently. iv. Flexibility of operations: Like that of sole proprietorship the partnership can bring changes in its operation easily and quickly looking at the changing circumstances. Such changes cannot be implemented in a company with ease because of the restrictions imposed. v. Sharing of risk: The losses of the firm and other associated risk in business are shared by the partners. Hence, the share of risk of each partner is less in comparison to sole proprietorship. vi. Benefits of unlimited liability: Since the liability of the partners is unlimited it acts as great check against speculative activities and partners shall not be careless in managing the business. Further, the firm enjoys good credit standing and easily obtain loans because the creditors can realise their loan amount from the private property of the partners. vii. Promptness in decision making:
Since the partners meet quite frequently, they can arrive at decisions promptly. Thus, business opportunities requiring quick decision shall not be lost. viii. Close supervision: Partners take active part in the management of the business. The close supervision of partners eliminates wastage and leads to greater efficiency. ix. Reduced management cost: Since different functional areas are managed by the partners themselves, the huge managerial expenses can be saved to a great extent. x. Secrecy: There is no statutory obligation on the part of partnership to publish the accounts of the firm. Hence, the business secrecy can be maintained to a certain extent. xi. Protection of minority interest: Every partner has a right to participate in the management. All important decisions are taken unanimously by the partners. There is no scope to disregard the interest of a minority group of partners. xii. Relationship between effort and reward: There is a direct relationship between effort put by partners and reward. If the business is managed efficiently, the reward shall b< in the form of more profit, better customer satisfaction and good image of the business.
Disadvantages of Partnership:
Eventhough, partnership form of business is comparatively better than sole proprietorship form of business, still it is not the only best option available to an entrepreneur. The following are some of the important shortcomings of partnership form of organisation which must b carefully studies before finalization of this form of business. i. Limited capital: There is a limit to the maximum number of partners in a partnership Therefore, the capital that can be raised from the partners is limited. Large-scale business requires huge capital and partnership is not the proper form to meet the requirement. ii. Unlimited liability:
Like that of the sole proprietorship, unlimited liability is a important drawback of partnership. The risk of loss of private property of the partnership influences the partners to avoid further risk and play safe. iii. Instability: There is instability in existence because a successful firm can be dissolve on the death, insolvency or lunacy of a partner. The difference of opinion may also bring about closure of the business. The sudden closure of a successful business is a great social loss. iv. Risk of implied authority: A partner acts as an agent of the firm and his acts bind the firm and other partners. A dishonest or incompetent partner may lead the firm in difficulties because the other partners shall have to pay for the dishonesty or inefficiency < a partner. v. Lack of harmony: Difference of opinion is the natural consequence in partnership. The conflicts and lack of harmony among the partners may not be beneficial for the business and sometimes even that lead to dissolution of the firm. vi. Non-transferability of interest: No partner can transfer his interest in a firm to third party without the consent of the other partners. Thus, a partner does not enjoy the freedom of converting his interest in the firm into cash. vii. Lack of public confidence: There is no legal binding on the firm to publish accounts. The public may suspect that the firm is earning huge profit at the cost of the consumers. Thus, the firm lacks confidence of the public. viii. Cautious approach: The very approach of unlimited liability make the partners over cautious. This restrict the partners in taking up any risky ventures and thus misses ma business opportunities.
You might also like
- Pure Nudism GalleryDocument2 pagesPure Nudism GalleryHenry Benjamin0% (4)
- Cultural Genocide Yossef Ben JochannanDocument198 pagesCultural Genocide Yossef Ben JochannanDeyonne Chante Howard100% (31)
- How To Hack Facebook Account Through Keylodger - 1Document3 pagesHow To Hack Facebook Account Through Keylodger - 1Joshua JosephNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Steps Involved in Establishing BusinessDocument17 pagesUnit 3 - Steps Involved in Establishing BusinessMR PRONo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Legal Issues For EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Legal Issues For EntrepreneurshipKariuki CharlesNo ratings yet
- BM Notes - Part IIDocument7 pagesBM Notes - Part IIsherlschris43No ratings yet
- Unit V Notes (Part I)Document15 pagesUnit V Notes (Part I)21EBKCS074PARULNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3Document22 pagesUnit - 3naveennanni988No ratings yet
- Unit Ii Forms of Business OrgDocument40 pagesUnit Ii Forms of Business OrgKainos GreyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02, BusinessDocument20 pagesChapter 02, BusinessAnna ShanonNo ratings yet
- Sole Proprietorship Offers The Following ProsDocument13 pagesSole Proprietorship Offers The Following ProsMubeen JavedNo ratings yet
- 3.sole Proprietorship& PartnershipDocument10 pages3.sole Proprietorship& PartnershipAnonymous 8Pyd22rExNo ratings yet
- Plane Text Business OMDocument187 pagesPlane Text Business OMnerkar_scribdNo ratings yet
- BFN 111 - Week 3Document60 pagesBFN 111 - Week 3Gift AnosiNo ratings yet
- Fbo Module 1Document12 pagesFbo Module 1nishutha3340No ratings yet
- 4 Form of OrganisationDocument35 pages4 Form of OrganisationSeiya KapahiNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OrganisationDocument28 pagesForms of Business OrganisationPembaLama100% (1)
- Forms of Business: Sole Proprietorship and PartnershipDocument17 pagesForms of Business: Sole Proprietorship and PartnershipTavleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Itb Chap 3Document17 pagesItb Chap 3Qaiser MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Sole Proprietorship: Ownership PatternsDocument7 pagesSole Proprietorship: Ownership PatternsDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mefa 4th UnitDocument21 pagesMefa 4th UnitNaga Lakshmi0% (1)
- Week 8Document25 pagesWeek 8aminajubril8No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BST NotesDocument20 pagesChapter 2 BST Notesrudraksh singhalNo ratings yet
- MEFA UNIT-III (II PArt)Document17 pagesMEFA UNIT-III (II PArt)mba departmentNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight Legal Forms of Business OrganizationDocument12 pagesChapter Eight Legal Forms of Business OrganizationYonatan MazengiaNo ratings yet
- Module One Essentials of Business Ownership Page One To 27Document55 pagesModule One Essentials of Business Ownership Page One To 27Solomon ThomasNo ratings yet
- Sole Proprietorrship ND CompanyDocument4 pagesSole Proprietorrship ND Companykhushityagi1338No ratings yet
- Edp Cia 1Document9 pagesEdp Cia 1alinNo ratings yet
- Forms of BusinessDocument10 pagesForms of BusinessInarjit RayNo ratings yet
- Business UnitsDocument17 pagesBusiness UnitsAtabongakeng DerickNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Notes F2Document188 pagesBusiness Studies Notes F2Joe KamashNo ratings yet
- Question # 1 (A) Critically Examine The Difference Between Various Forms of Organization Exists in PakistanDocument14 pagesQuestion # 1 (A) Critically Examine The Difference Between Various Forms of Organization Exists in Pakistanayub_balticNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BST NotesDocument20 pagesChapter 2 BST Notesrudraksh singhalNo ratings yet
- Finance and Budgetting DestinyDocument9 pagesFinance and Budgetting DestinyEdeh chikamma DestinyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Legal Forms of Business OrganizationDocument12 pagesChapter Six Legal Forms of Business Organizationdaniel jemiamNo ratings yet
- ENTREP Chapter 5Document8 pagesENTREP Chapter 5TrevoreNo ratings yet
- The Forms of Business OrganisationDocument30 pagesThe Forms of Business OrganisationMet MalayoNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS STUDIES FORM TWO NOTES BY MRDocument83 pagesBUSINESS STUDIES FORM TWO NOTES BY MRPatroba WamalwaNo ratings yet
- Business Structure and Organization: MeaningDocument17 pagesBusiness Structure and Organization: MeaningNavaneethakrishnan RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- CH 02 - Business, Trade - Commecer AkDocument17 pagesCH 02 - Business, Trade - Commecer AkArundhoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Befa Unit-1Document35 pagesBefa Unit-1Phanith SaiNo ratings yet
- Corporate Law AnswerDocument22 pagesCorporate Law AnswerAmir KhanNo ratings yet
- A Business Formation Deals With The Formalization And: Actual Implementation of Business Ideas Into PracticeDocument38 pagesA Business Formation Deals With The Formalization And: Actual Implementation of Business Ideas Into PracticeobishutolaniNo ratings yet
- Business Economics Unit - 1Document19 pagesBusiness Economics Unit - 1Naresh GuduruNo ratings yet
- Business o UnitsDocument93 pagesBusiness o Unitseunice musembiNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 07 - BusinessDocument17 pagesLecture # 07 - BusinessRamjan Ali SiamNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics & Financial AnalysisDocument79 pagesManagerial Economics & Financial Analysis18-592 Yaseen ArsalaanNo ratings yet
- Business Ownership - Bo Unit 2Document5 pagesBusiness Ownership - Bo Unit 2DIPANSHU PRASADNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Commerce NotesDocument48 pages1st Year Commerce NotesDivya Chowdary AdusumilliNo ratings yet
- MEFA Unit 5Document22 pagesMEFA Unit 5Anusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Financial Management: (A) To Ensure Availability of Sufficient Funds at Reasonable Cost (Liquidity)Document10 pagesMeaning of Financial Management: (A) To Ensure Availability of Sufficient Funds at Reasonable Cost (Liquidity)Rana AhmedNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS NOTES (July Monthly Test)Document18 pagesBUSINESS NOTES (July Monthly Test)siddhieieichawrijalNo ratings yet
- Contingency PlanDocument5 pagesContingency PlanShikha AhlawatNo ratings yet
- CH 02 - Business, Trade - Commecer AkDocument13 pagesCH 02 - Business, Trade - Commecer AkArundhoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Mefa - Mech III - Civil - II - Unit-5Document10 pagesMefa - Mech III - Civil - II - Unit-5wasimrahmanwapsNo ratings yet
- Proprietorship, Partnership, and Corporation-And Each Comes WithDocument21 pagesProprietorship, Partnership, and Corporation-And Each Comes WithsamreenNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Business Structures and Legal OwnershipDocument35 pagesCH 3 Business Structures and Legal OwnershipMihretab Bizuayehu (Mera)No ratings yet
- ch3 EntreDocument60 pagesch3 EntreeyoyoNo ratings yet
- YayaDocument36 pagesYayami920865No ratings yet
- Unit IV - MEFA-1Document27 pagesUnit IV - MEFA-1Shaik ZubayrNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO BusinessDocument16 pagesINTRODUCTION TO BusinessGovindNo ratings yet
- Economics Module 02Document7 pagesEconomics Module 02Sanchari SenNo ratings yet
- LLC: A Complete Guide To Limited Liability Companies And Setting Up Your Own LLCFrom EverandLLC: A Complete Guide To Limited Liability Companies And Setting Up Your Own LLCNo ratings yet
- Sense of Urgency Book Review by TMYDocument17 pagesSense of Urgency Book Review by TMYtajuddinmy100% (2)
- Vocabulary For Text Analysis and Text ProductionDocument2 pagesVocabulary For Text Analysis and Text ProductionchloNo ratings yet
- A-Morally-Defensible Noddings PDFDocument8 pagesA-Morally-Defensible Noddings PDFHazel QuinanteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Emergencies TranscriptDocument7 pagesChemical Emergencies TranscriptLhara Vhaneza CuetoNo ratings yet
- ENG-101 Presentation On The Short Story "The Gift of Magi"Document15 pagesENG-101 Presentation On The Short Story "The Gift of Magi"নরকেররাজপুত্র100% (1)
- DIAC Engineering Practice References - 2017 Mar 28Document5 pagesDIAC Engineering Practice References - 2017 Mar 28Sen HuNo ratings yet
- When Does An Ombudsman Decision Become Final and eDocument4 pagesWhen Does An Ombudsman Decision Become Final and eFender BoyangNo ratings yet
- 2024-03-17Document7 pages2024-03-17MoisésJosyNo ratings yet
- Leslie Turner CH 14Document34 pagesLeslie Turner CH 14AYI FADILLAHNo ratings yet
- The Information Approach To Decision UsefulnessDocument26 pagesThe Information Approach To Decision UsefulnessDiny Fariha ZakhirNo ratings yet
- 08 LeaseVenue PDFDocument12 pages08 LeaseVenue PDFLab LeeNo ratings yet
- The Capital Budgeting Decisions of Small BusinessesDocument19 pagesThe Capital Budgeting Decisions of Small BusinessesPrateek Tripathi100% (1)
- Harikumar Mohanachandran: Accounts 84455.11Document3 pagesHarikumar Mohanachandran: Accounts 84455.11Devil ArtistNo ratings yet
- Procedure Ship Security Officer Training Module WorkbookDocument19 pagesProcedure Ship Security Officer Training Module WorkbookBao TranNo ratings yet
- National GoalsDocument19 pagesNational GoalsdarsaimarasheedNo ratings yet
- People v. Goce, G.R. No. 113161, August 29, 1995Document1 pagePeople v. Goce, G.R. No. 113161, August 29, 1995Mae Clare Bendo100% (4)
- TemplatesDocument3 pagesTemplatesJAYDIPVDNo ratings yet
- Exercitii EnglezaDocument3 pagesExercitii EnglezaGhergheluca BiancaNo ratings yet
- AQWFDocument2 pagesAQWFAlex Jr ValtierraNo ratings yet
- Spread of Unethical Behavior in Organizations A Dynamic Social Network Perspective - AspDocument23 pagesSpread of Unethical Behavior in Organizations A Dynamic Social Network Perspective - AspHidayatul FitriahNo ratings yet
- Hospital Planing and OrganizationDocument15 pagesHospital Planing and OrganizationUdaya SreeNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning - FinalDocument36 pagesAggregate Planning - FinalShailu Sharma100% (1)
- Cojuanco Vs SandiganbayanDocument2 pagesCojuanco Vs SandiganbayanEANo ratings yet
- Pre - Cast Concrete-Designer Perspective Including Customisation of Design by Shri Alok BhowmickDocument28 pagesPre - Cast Concrete-Designer Perspective Including Customisation of Design by Shri Alok BhowmickSreekanth SattirajuNo ratings yet
- Ecocert' (Amm: OF AuxiliariesDocument2 pagesEcocert' (Amm: OF AuxiliariesMadhavKumar ThangavelNo ratings yet
- Cockney Literature ArticolosantipoloDocument39 pagesCockney Literature ArticolosantipolomozaroliveiraNo ratings yet
- Right To EducationDocument11 pagesRight To EducationPrateek KulhariNo ratings yet