Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Study Guide:: 1 Essay Pig V Shark
Bio Study Guide:: 1 Essay Pig V Shark
Uploaded by
Heidi RechenbergCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Floral Biology Manual PDFDocument262 pagesFloral Biology Manual PDFGANESH Y96% (23)
- PlantsDocument22 pagesPlantsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Amouage Catalog Zahras PerfumesDocument34 pagesAmouage Catalog Zahras PerfumesZahra GajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument80 pagesChapter 23 Plant Reproductionmain.15001068No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument45 pagesChapter 23 Plant ReproductionSara SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument41 pagesSexual Reproductionapi-406307933No ratings yet
- AP Kingdom PlantaeDocument79 pagesAP Kingdom PlantaeDaniel LeeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistDocument59 pagesDr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- Notes - Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesNotes - Flowering PlantsdarkadainNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Plant Reproduction - Sexual ReproductionDocument79 pages3.2 Plant Reproduction - Sexual ReproductionJuanero, Reyean IñigoNo ratings yet
- Tracheophyte NotesDocument11 pagesTracheophyte NotesTracy Lou FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceDocument20 pagesReproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceSharina GeraldNo ratings yet
- LSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument64 pagesLSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsAbraham KangNo ratings yet
- 8 TH PLANTDocument22 pages8 TH PLANTyasukaellahNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Botany - The Study of PlantsDocument26 pagesKingdom Plantae: Botany - The Study of PlantsEric cruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument33 pagesLecture Noteshabib ullahNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSundram DubeyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsJagdeesh Gosine100% (1)
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSDocument76 pagesReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23No ratings yet
- Flowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesDocument76 pagesFlowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesRaja InaNo ratings yet
- Nonvascular Plants and Seedless Vascular PlantsDocument14 pagesNonvascular Plants and Seedless Vascular PlantsGalang AlphaNo ratings yet
- Final Gymnosperm Members Notes by Masters of BotanyDocument8 pagesFinal Gymnosperm Members Notes by Masters of Botanymohantyrajendra1963No ratings yet
- Intro To PlantsDocument33 pagesIntro To PlantsBALQIS NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- Bryophytes and TracheophytesDocument4 pagesBryophytes and TracheophytesNoor NabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Plant AnatomyDocument62 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Plant AnatomyRalph AlbertoNo ratings yet
- 3.2 The PlantsDocument50 pages3.2 The PlantsMohammed Faraaz MustafaNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Organisms and ClassificationDocument25 pagesDiversity of Organisms and Classificationnajaf_shaanNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms NoteDocument61 pagesGymnosperms Notec4655qg67pNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Document12 pages3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- Botn 21n - Prelab - Exercise 10 - Angiosperms (Flowers)Document20 pagesBotn 21n - Prelab - Exercise 10 - Angiosperms (Flowers)Shy ZacharyNo ratings yet
- Is For Master Gardeners: Dan Culbert, Extension Agent III - Environmental HorticultureDocument76 pagesIs For Master Gardeners: Dan Culbert, Extension Agent III - Environmental HorticultureJemuel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Part Two 2021Document6 pagesPlant Diversity Part Two 2021sulimansmart22No ratings yet
- Modern PlantsDocument3 pagesModern PlantshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document79 pagesLecture 4Brian Ngugi KamandeNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument84 pagesAnatomygiaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument17 pagesReproduction in Plantswafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 - Lab Exam 1 - NotesDocument4 pagesBio 101 - Lab Exam 1 - NotesCamille Andrea RositaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Short NotesDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Short NotesSTUDY BEASTNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument120 pagesBiologyMoch. Choirul Anam,S.SiNo ratings yet
- Chap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesChap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsgprasadatvuNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument53 pagesPlant and Animal ReproductionSheryl Osorio100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NewDocument26 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NewFreedom Fighters FanNo ratings yet
- +1 Botany Capsule NotesDocument27 pages+1 Botany Capsule Notesarunankg3No ratings yet
- PteridophyteDocument13 pagesPteridophyteshahilmansuri844No ratings yet
- MF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2Document27 pagesMF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- 普植 第四次期中考 單字Document12 pages普植 第四次期中考 單字sam89911268No ratings yet
- 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocument6 pages1 Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsTumbikani Yamikani E NjovuNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsrichie2885No ratings yet
- Angiosperms: Root System and Shoot SystemDocument4 pagesAngiosperms: Root System and Shoot SystemAiman KaleemNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument49 pagesPlant Reproduction and DevelopmentSK GamingNo ratings yet
- F Kingdom Plantae Part 1Document11 pagesF Kingdom Plantae Part 1JNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowDocument13 pagesKingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Kingdom Plantae EditedDocument6 pagesKingdom Plantae Editedbm-3272No ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Unit 3Document49 pagesKingdom Plantae: Unit 3senjicsNo ratings yet
- Gr11 LS PlantDiversity TheoryDocument9 pagesGr11 LS PlantDiversity TheoryLutendo Assurance MadzivhaaNo ratings yet
- A1.2b Plant Reproduction - 2018Document65 pagesA1.2b Plant Reproduction - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in planTSSDocument56 pagesReproduction in planTSSParis JarrettNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Alevel Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesSexual Reproduction Alevel Flowering Plantsbarasasamuel922No ratings yet
- Life Cycle of An AppleDocument4 pagesLife Cycle of An Applemiru viruNo ratings yet
- Draw. Look and Match. Say.: Reinforcement ? ReinforcementDocument12 pagesDraw. Look and Match. Say.: Reinforcement ? Reinforcementanon_95591020No ratings yet
- Biodiversity (Semester 2 Matriculation)Document32 pagesBiodiversity (Semester 2 Matriculation)Sasikumar Kovalan100% (3)
- Grade 6-Classifying LifeDocument49 pagesGrade 6-Classifying LifenamrataNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Genetic Regulation Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plants PDFDocument17 pagesUnderstanding The Genetic Regulation Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plants PDFfernanda0% (1)
- Alkaloidi Alkaloidi Alkaloidi AlkaloidiDocument35 pagesAlkaloidi Alkaloidi Alkaloidi AlkaloidiElvir MNo ratings yet
- Camille 1 FinalDocument17 pagesCamille 1 FinalJeffersonCaasiNo ratings yet
- Greenleaf Menu PDFDocument5 pagesGreenleaf Menu PDFjeffNo ratings yet
- Beyers Verkerk Mailing en LR PDFDocument2 pagesBeyers Verkerk Mailing en LR PDFJega AlinNo ratings yet
- Nix v. HeddenDocument2 pagesNix v. HeddenhasanfriendshipNo ratings yet
- Cactus Explorer 4 - CompleteDocument76 pagesCactus Explorer 4 - CompleteKaudexKaudex100% (1)
- What Are Angiosperms?Document5 pagesWhat Are Angiosperms?Yolo WoloNo ratings yet
- Grasses CatalogDocument5 pagesGrasses Catalogketelsen100% (2)
- Zahras Perfumes - Swiss ArabianDocument103 pagesZahras Perfumes - Swiss ArabianИринаNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 MCQ - RevisionDocument8 pagesGrade 6 MCQ - RevisionSabina AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda AushadhiDocument6 pagesAyurveda Aushadhiyatish5555No ratings yet
- Test - IPVDocument12 pagesTest - IPVScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Endemic Flora and FaunaDocument22 pagesEndemic Flora and FaunaRalph Andrei Gallardo-Ontoy PamplonaNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument28 pagesBotanyKier PanugaoNo ratings yet
- Embriologija CvjetnicaDocument526 pagesEmbriologija CvjetnicaelviraNo ratings yet
- 8 8 2017 CH 4 AnswersDocument16 pages8 8 2017 CH 4 AnswersNashwa SaadNo ratings yet
- Birbal SahniDocument5 pagesBirbal Sahnidroy21No ratings yet
- International Code of Zoological NomenclatureDocument106 pagesInternational Code of Zoological NomenclatureJonathan P. MillerNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 1115) Germinal Rouhan, Myriam Gaudeul (Auth.), Pascale Besse (Eds.) - Molecular Plant Taxonomy - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2014)Document401 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 1115) Germinal Rouhan, Myriam Gaudeul (Auth.), Pascale Besse (Eds.) - Molecular Plant Taxonomy - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2014)Sergio S. Mejía50% (2)
- Managing Organizational Change A Multiple Perspectives Approach 2nd Edition Palmer Test BankDocument25 pagesManaging Organizational Change A Multiple Perspectives Approach 2nd Edition Palmer Test BankNicholasJohnswjpn100% (56)
- Pbs Kids Writers Contest 2015 Vo Winners ScriptDocument14 pagesPbs Kids Writers Contest 2015 Vo Winners Scriptapi-302258810No ratings yet
- AshitabaDocument6 pagesAshitabaBenjie BugarinNo ratings yet
- Chinese CabbageDocument7 pagesChinese Cabbagesuhaanarora50% (2)
Bio Study Guide:: 1 Essay Pig V Shark
Bio Study Guide:: 1 Essay Pig V Shark
Uploaded by
Heidi RechenbergOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Study Guide:: 1 Essay Pig V Shark
Bio Study Guide:: 1 Essay Pig V Shark
Uploaded by
Heidi RechenbergCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Study Guide:
1 essay pig v shark
Pig
Bone skeleton Small liver(lobes: R/L medial, R/L lateral, caudate lobe) 4 chambered heart Depends on kidney for excreting nitrogenous wastes Thicker skin Diaphragm No egg Nutrition comes from mothers circulation through umbilical cord Many different muscles all over body Penis/vagina
Shark
Cartilage skeleton 1 big liver Larger blood cells to carry oxygen 2 chambered heart Less defined gall bladder Spleen-larger more pronounced Can rely on gills/ skin instead of kidney Baby shark: retained in egg in ovary Nutrition from yolk Ovaries larger Thinner skin Muscle-similar patter Flaciform ligament Pelvic fin, clasper=male Spiracles: dont have to keep moving
6 about hormones but I heard you only need to know 3 cause you do 2 essays per hormone
1 Essay about plants.
Heres the info I used for my book so hopefully it helps a little
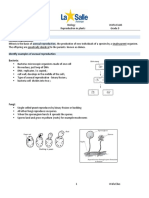
Bryophytes: Nonvascular plants Lowest in plant evolution: no xylem tissue stems or leaves Three main phyla o Bryophyte (mosses) o Marchantiophyta (liverworts) o Anthocerotophyta (hornworts) Attached to ground rock or bark by rhizoids threads Reproduce asexually Absorb mineral nourishment from rainfall running over it Life cycles characterized by alternation of generations: o Sporophyte: diploid with two of each type of chromosome per cell o Gametophyte: haploid with one of each type of chromosome per cell
Pterophytes: Seedless, vascular plants Ferns, horsetails, whisk ferns They are developed: o Branched sporophytes-not dependent of gametophytes o Xylem tissue: transport water o Phloem tissue: distribute sugar o Roots: absorb water and nutrients o Leaves: increase surface area for photosynthesis Reproduction: homosporous o Sporphylls bear sporangia o Each plant has 1 type of sporangium that makes 1 type of spore
Gymnosperms: Vascular plants with naked seeds o Seeds have no coverings o Seeds are on cones Pines cedars spruces firs Do not usually flower/ produce fruit Pine cone= females Microspores cone = males
Reproduction: Heterosporous Microspores and megaspore are produced in cones Haploid develops in the spore wall Pollen cells mature into microspores sperm Megaspores mature into ovuleegg Sperm is transferred by wind/ insects
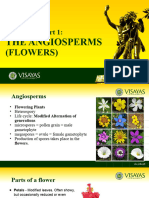
Angiosperms: Vascular, seed, flowering plants o Have coating over seed o Endosperm within seed o Produce fruit Most evolved plant Parts of the flower: o Petal: attracts insect for germination purpose o Stamen: male reproduction o Anther: makes pollen o Ovary: female reproduction o Pistol: tube-pollen travels to the ovary o Stigma: traps pollen at top of pistol o Sepal: protection for the flower bud Pollination by wind, bees, birds, bats
2 types:
1. Monocots: o Seeds in one piece (corn) cotyledon o Flower petals-multiples of 3 o Pollen grain with one opening o Veins-branch up and down parallel o Stem vascular bundles are scattered o Only small branching roots o Corn, blade of grass, tulip, lily 2. Dicots: Seeds easily split (peas) two cotyledon Flower petals multiples 4 or 5 Veins branch from one central midrib (netlike) Stem vascular bundle in a ring Pollen grain with 3 openings Main root (Taproot) with various small roots branching Bean, peanut, snapdragon, citrus
You might also like
- Floral Biology Manual PDFDocument262 pagesFloral Biology Manual PDFGANESH Y96% (23)
- PlantsDocument22 pagesPlantsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Amouage Catalog Zahras PerfumesDocument34 pagesAmouage Catalog Zahras PerfumesZahra GajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument80 pagesChapter 23 Plant Reproductionmain.15001068No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument45 pagesChapter 23 Plant ReproductionSara SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument41 pagesSexual Reproductionapi-406307933No ratings yet
- AP Kingdom PlantaeDocument79 pagesAP Kingdom PlantaeDaniel LeeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistDocument59 pagesDr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- Notes - Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesNotes - Flowering PlantsdarkadainNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Plant Reproduction - Sexual ReproductionDocument79 pages3.2 Plant Reproduction - Sexual ReproductionJuanero, Reyean IñigoNo ratings yet
- Tracheophyte NotesDocument11 pagesTracheophyte NotesTracy Lou FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceDocument20 pagesReproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceSharina GeraldNo ratings yet
- LSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument64 pagesLSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsAbraham KangNo ratings yet
- 8 TH PLANTDocument22 pages8 TH PLANTyasukaellahNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Botany - The Study of PlantsDocument26 pagesKingdom Plantae: Botany - The Study of PlantsEric cruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument33 pagesLecture Noteshabib ullahNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSundram DubeyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsJagdeesh Gosine100% (1)
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSDocument76 pagesReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23No ratings yet
- Flowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesDocument76 pagesFlowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesRaja InaNo ratings yet
- Nonvascular Plants and Seedless Vascular PlantsDocument14 pagesNonvascular Plants and Seedless Vascular PlantsGalang AlphaNo ratings yet
- Final Gymnosperm Members Notes by Masters of BotanyDocument8 pagesFinal Gymnosperm Members Notes by Masters of Botanymohantyrajendra1963No ratings yet
- Intro To PlantsDocument33 pagesIntro To PlantsBALQIS NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- Bryophytes and TracheophytesDocument4 pagesBryophytes and TracheophytesNoor NabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Plant AnatomyDocument62 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Plant AnatomyRalph AlbertoNo ratings yet
- 3.2 The PlantsDocument50 pages3.2 The PlantsMohammed Faraaz MustafaNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Organisms and ClassificationDocument25 pagesDiversity of Organisms and Classificationnajaf_shaanNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms NoteDocument61 pagesGymnosperms Notec4655qg67pNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Document12 pages3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- Botn 21n - Prelab - Exercise 10 - Angiosperms (Flowers)Document20 pagesBotn 21n - Prelab - Exercise 10 - Angiosperms (Flowers)Shy ZacharyNo ratings yet
- Is For Master Gardeners: Dan Culbert, Extension Agent III - Environmental HorticultureDocument76 pagesIs For Master Gardeners: Dan Culbert, Extension Agent III - Environmental HorticultureJemuel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Part Two 2021Document6 pagesPlant Diversity Part Two 2021sulimansmart22No ratings yet
- Modern PlantsDocument3 pagesModern PlantshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document79 pagesLecture 4Brian Ngugi KamandeNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument84 pagesAnatomygiaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument17 pagesReproduction in Plantswafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 - Lab Exam 1 - NotesDocument4 pagesBio 101 - Lab Exam 1 - NotesCamille Andrea RositaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Short NotesDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Short NotesSTUDY BEASTNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument120 pagesBiologyMoch. Choirul Anam,S.SiNo ratings yet
- Chap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesChap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsgprasadatvuNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument53 pagesPlant and Animal ReproductionSheryl Osorio100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NewDocument26 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NewFreedom Fighters FanNo ratings yet
- +1 Botany Capsule NotesDocument27 pages+1 Botany Capsule Notesarunankg3No ratings yet
- PteridophyteDocument13 pagesPteridophyteshahilmansuri844No ratings yet
- MF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2Document27 pagesMF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- 普植 第四次期中考 單字Document12 pages普植 第四次期中考 單字sam89911268No ratings yet
- 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocument6 pages1 Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsTumbikani Yamikani E NjovuNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsrichie2885No ratings yet
- Angiosperms: Root System and Shoot SystemDocument4 pagesAngiosperms: Root System and Shoot SystemAiman KaleemNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument49 pagesPlant Reproduction and DevelopmentSK GamingNo ratings yet
- F Kingdom Plantae Part 1Document11 pagesF Kingdom Plantae Part 1JNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowDocument13 pagesKingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Kingdom Plantae EditedDocument6 pagesKingdom Plantae Editedbm-3272No ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Unit 3Document49 pagesKingdom Plantae: Unit 3senjicsNo ratings yet
- Gr11 LS PlantDiversity TheoryDocument9 pagesGr11 LS PlantDiversity TheoryLutendo Assurance MadzivhaaNo ratings yet
- A1.2b Plant Reproduction - 2018Document65 pagesA1.2b Plant Reproduction - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in planTSSDocument56 pagesReproduction in planTSSParis JarrettNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Alevel Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesSexual Reproduction Alevel Flowering Plantsbarasasamuel922No ratings yet
- Life Cycle of An AppleDocument4 pagesLife Cycle of An Applemiru viruNo ratings yet
- Draw. Look and Match. Say.: Reinforcement ? ReinforcementDocument12 pagesDraw. Look and Match. Say.: Reinforcement ? Reinforcementanon_95591020No ratings yet
- Biodiversity (Semester 2 Matriculation)Document32 pagesBiodiversity (Semester 2 Matriculation)Sasikumar Kovalan100% (3)
- Grade 6-Classifying LifeDocument49 pagesGrade 6-Classifying LifenamrataNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Genetic Regulation Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plants PDFDocument17 pagesUnderstanding The Genetic Regulation Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plants PDFfernanda0% (1)
- Alkaloidi Alkaloidi Alkaloidi AlkaloidiDocument35 pagesAlkaloidi Alkaloidi Alkaloidi AlkaloidiElvir MNo ratings yet
- Camille 1 FinalDocument17 pagesCamille 1 FinalJeffersonCaasiNo ratings yet
- Greenleaf Menu PDFDocument5 pagesGreenleaf Menu PDFjeffNo ratings yet
- Beyers Verkerk Mailing en LR PDFDocument2 pagesBeyers Verkerk Mailing en LR PDFJega AlinNo ratings yet
- Nix v. HeddenDocument2 pagesNix v. HeddenhasanfriendshipNo ratings yet
- Cactus Explorer 4 - CompleteDocument76 pagesCactus Explorer 4 - CompleteKaudexKaudex100% (1)
- What Are Angiosperms?Document5 pagesWhat Are Angiosperms?Yolo WoloNo ratings yet
- Grasses CatalogDocument5 pagesGrasses Catalogketelsen100% (2)
- Zahras Perfumes - Swiss ArabianDocument103 pagesZahras Perfumes - Swiss ArabianИринаNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 MCQ - RevisionDocument8 pagesGrade 6 MCQ - RevisionSabina AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda AushadhiDocument6 pagesAyurveda Aushadhiyatish5555No ratings yet
- Test - IPVDocument12 pagesTest - IPVScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Endemic Flora and FaunaDocument22 pagesEndemic Flora and FaunaRalph Andrei Gallardo-Ontoy PamplonaNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument28 pagesBotanyKier PanugaoNo ratings yet
- Embriologija CvjetnicaDocument526 pagesEmbriologija CvjetnicaelviraNo ratings yet
- 8 8 2017 CH 4 AnswersDocument16 pages8 8 2017 CH 4 AnswersNashwa SaadNo ratings yet
- Birbal SahniDocument5 pagesBirbal Sahnidroy21No ratings yet
- International Code of Zoological NomenclatureDocument106 pagesInternational Code of Zoological NomenclatureJonathan P. MillerNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 1115) Germinal Rouhan, Myriam Gaudeul (Auth.), Pascale Besse (Eds.) - Molecular Plant Taxonomy - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2014)Document401 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 1115) Germinal Rouhan, Myriam Gaudeul (Auth.), Pascale Besse (Eds.) - Molecular Plant Taxonomy - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2014)Sergio S. Mejía50% (2)
- Managing Organizational Change A Multiple Perspectives Approach 2nd Edition Palmer Test BankDocument25 pagesManaging Organizational Change A Multiple Perspectives Approach 2nd Edition Palmer Test BankNicholasJohnswjpn100% (56)
- Pbs Kids Writers Contest 2015 Vo Winners ScriptDocument14 pagesPbs Kids Writers Contest 2015 Vo Winners Scriptapi-302258810No ratings yet
- AshitabaDocument6 pagesAshitabaBenjie BugarinNo ratings yet
- Chinese CabbageDocument7 pagesChinese Cabbagesuhaanarora50% (2)