Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F4 Sci Chap2
F4 Sci Chap2
Uploaded by
Yee YingOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F4 Sci Chap2
F4 Sci Chap2
Uploaded by
Yee YingCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
6 Hormonal Coordination in the body 1) Hormone are chemical substances that secreted by the endocrine glands directly into the bloodstream. 2) Each type of hormone is: - A kind of protein - Released in small quantities - slow to response but responses last longer - Specific to the target organ 3) Endocrine glands coordinate body activities chemically by secreting hormones. Endocrine glands are ductless gland. Why are endocrine glands are also known as ductless gland? Hormones are not secrete through ducts. Instead the hormone are secreted directly into the bloodstream, which distribute them all over the body. 4) One hormone may have several target organs. 5) How hormonal coordination work.
The effect of hormonal imbalance on health. 1) Hormonal imbalance can be the result of too much (excessive) or too little (deficiency) of hormone produced. 2) Table shows examples of the effects of excessive and deficiency in some of this hormone. Hormone Growth hormone Thyroxine Effect of Over secretion - Gigantism (child) - Acromegaly (adult) - Increase in metabolic rate Exophthalmic goiter indicated by protruding eyeballs and swelling of the neck. Under secretion - Dwarfism
Insulin
- Stunted physical and mental development in children (cretinism) - Lack of energy in adults (myxodema) - Simple goiter Abnormally low blood sugar - high blood sugar level in
Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone
level (hypoglycemia) which may lead to shock and coma Early puberty - Early puberty
the blood (hyperglycemia) and urine ( diabetes mellitus) Late puberty - Menstrual disorder - Miscarriage - Late puberty - Low sperm count
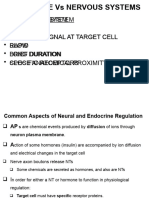
2005 SPM question The overproduction of hormone by the thyroid gland causes a) stunted growth b) exophtalmic goiter c) gigantism d) diabetes Quiz 1) Identify the following hormones: a) Hormone that prepares in the body for emergency b) The hormone that reduce the amount of glucose in the body c) The hormone that controls the metabolic rate of body d) The hormone that controls the formation of male secondary sexual characteristic e) The hormone that controls the menstrual cycle 2) State the function of a hormone produced by a) the thyroid gland b) the ovary c) the pancrease 3) Name the disease caused by a) insufficient insulin b) excessive thyroxine c) insufficient growth hormone 2.7) Coordination between the nervous system and endocrine system 1) Body coordination is controlled and regulated by the nervous system and the endocrine system. Both the systems help us to carry out our daily activities. 2) Comparison between the nervous system and endocrine system. Nervous coodination Differences in term of Electrical impulse Type of impulse Directly by neurons in the Method of transmission nerve fibres Fast Speed of transmission Effectors Parts affected Localised, temporary and Effects reversible Rapid and short-lived Response Similarities of hormonal and nervous system Hormonal substance Chemical substance Carried by the blood circulatory Slow Target organs only Widespread, permanent and irreversible Slow, diffuse and long lasting both are involved in body coordination both involves the passing of information
3) an example of the coordination between the nervous and endocrine system during a time or excitement, fright or stress. Stimulus the source of danger, a loud sound of explosion Receptor Sense organ (ear) Parts of body affected Brain Pupil of eye Heart Lungs Liver Muscle Effect of hormonal system Effect of nervous system Secretion of adrenaline by Secretion of adrenaline by adrenal gland the autonomous nervous system. Blood supply increase Blood supply increase Dilates Dilates Heart rate increase Heart rate increase Bronchioles dilate Bronchioles dilate Glycogen converted to Glycogen convert to glucose glucose Blood supply increase Blood supply increase; muscles contract
Quiz 1) what are the similarities between the hormonal system and the nervous system? 2) Name four ways in which the hormonal system is different from the nervous system
3) Why is coordination between the nervous system and the endocrine system important?
2.8) Effects of drug abuse on body coordination and health 1) Drugs are externally administered chemical substances that affect chemical reactions within the body. 2) Drugs may be beneficial or harmful to the body depending on how it is used. 3) Beneficial drugs are used as medicine to treat diseases. - Antibiotics are used to treat disease caused b y bacteria. Eg: penicillin - Drugs are taken under medical supervision to treat diseases. Eg: steroid - Drugs are also used to relieve pain. Eg: anesthetics and analgesics like aspirin 4) Drugs can be divided into five groups based on their characteristics and effects on body coordination. Types of drugs Examples Effects Stimulants Cocaine, amphetamines Counteract depression,
Depressants Hallucinogens Narcotics Inhalants
Barbiturate, sleeping pills Marijuana Opium, morphine, heroin Glue, paint thinner
prevent fatigue, increase alertness and reduce sleepiness. Cause drowsiness, slow down nerve impulses, reduce stress. Cause the person to experience hallucinations and illusions Relieve pain and induce pain Cause hallucinations and damage to the brain and kidneys
5) Drug abuse is the taking of drugs excessively, not under a doctor prescription. 6) The effects of drug abuse on health: - High blood pressure - Heart problems - Damage to the liver - Weakens the immune system - Cause brain damage and mental problem - Sharing of needle among drugs addicts results in the transmission of AIDS Quiz 1a) What are drugs? b) Name three beneficial drugs. 2a) What is drug abuse? b) What is its effect on nervous system? 3) List five groups of drugs. For each group, name an example.
2.9) The effects of excessive consumption of alcohol on body coordination and health 1) All alcoholic drinks contain ethanol which is a type of alcohol 2) Alcoholic drinks are made from fruits and cereals. Examples of alcoholic drinks Wine and brandy Whisky and beer Toddy Made up of Grapes Barley Coconut
Tapai , tuak, sake, rice wine Cider
Rice Apple
3) Sugar from these fruits and cereal are fermented by yeast to produce ethanol. The fermentation process and the period of fermentation affect their quality. 4) Alcohol is a central nervous system depressant. It generally slows down the brain function. 5) Effects of alcohol on health Brain Liver Stomach Heart Effect of alcohol on - Slows down brain function - Damage to the brain cell - Inflammation of the liver (Hepatitis) - Cirrhosis or hardening of liver - Irritates the stomach lining - Cause bleeding and stomach ulcer - Cause high blood pressure - Stroke
Quiz 1a) Name the type of alcohol found in wine. b) What type of drug is it? 2) What are the effects of excessive alcohol on the a) brain? b) liver? c) stomach 3) List three effects of excessive alcohol consumption.
You might also like
- The DeadDocument837 pagesThe DeadLee Keeron86% (7)
- J. Raymond DePaulo, Leslie Alan Horvitz, Kay Redfield Jamison - Understanding Depression - What We Know and What You Can Do About It (2002) PDFDocument305 pagesJ. Raymond DePaulo, Leslie Alan Horvitz, Kay Redfield Jamison - Understanding Depression - What We Know and What You Can Do About It (2002) PDFBlondYNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 (Endocrine System)Document7 pagesUNIT 6 (Endocrine System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
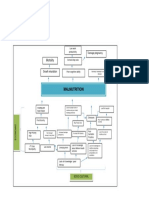
- Problem Tree Analysis MalnutritionDocument1 pageProblem Tree Analysis MalnutritionMho Dsb50% (6)
- CH 45 Guided ReadingDocument7 pagesCH 45 Guided ReadingmharirajNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Dissecting A FrogDocument1 pageBiology 2 Dissecting A Froggbs040479No ratings yet
- Saladin 17.1Document6 pagesSaladin 17.11613405No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument46 pagesEndocrine Systemespinajeff07No ratings yet
- Module 9 The Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesModule 9 The Endocrine SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Assessment of The Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesMODULE 1 Assessment of The Endocrine SystemLorraine GambitoNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology SupplementDocument85 pagesEndocrinology Supplementfreecouch100% (1)
- Endocrine System 13 معدلDocument11 pagesEndocrine System 13 معدلhanaalhadidi567No ratings yet
- ICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)Document14 pagesICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)TAHMEENA ZAFARNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI EndocrineDocument8 pagesChapter VI EndocrineTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Study Guide (1169)Document7 pagesExam 3 Study Guide (1169)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Control and IntegrationDocument40 pagesChemical Control and IntegrationdiyNo ratings yet
- Part 1-MIDTERM - 117 LECDocument7 pagesPart 1-MIDTERM - 117 LECfrechel kimNo ratings yet
- Ch24 ShortAnswer and Essay QuestionsDocument3 pagesCh24 ShortAnswer and Essay Questionsomar86% (7)
- The Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Grade VIII Biology Synopsis Theme 4: Unit 1 Name of The Chapter: Human Body-Endocrine System Date: 20-10-2021 No. of Pages: 6Document6 pagesGrade VIII Biology Synopsis Theme 4: Unit 1 Name of The Chapter: Human Body-Endocrine System Date: 20-10-2021 No. of Pages: 6shashwatthegamerytNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity Endocrinology: Table 1: Different Classes of HormonesDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity Endocrinology: Table 1: Different Classes of HormonesJohn Fritz Gerald BascoNo ratings yet
- 3.5.3 Responses in The Human Endocrine System1Document22 pages3.5.3 Responses in The Human Endocrine System1John Mark JuarezNo ratings yet
- RenalHormoneRegLecture Zeman (Spring2020)Document50 pagesRenalHormoneRegLecture Zeman (Spring2020)Sahil ParikhNo ratings yet
- 14disorders of Endocrine SystemDocument54 pages14disorders of Endocrine SystemAli RazaNo ratings yet
- 1016MSC T1 2023 Module 5 Tutorial WorksheetsDocument21 pages1016MSC T1 2023 Module 5 Tutorial WorksheetsTina HussainiNo ratings yet
- AP100 Final Exam Study GuideDocument27 pagesAP100 Final Exam Study Guidebhilligoss35100% (1)
- Pages 152 Physiological Psychology HormonesDocument7 pagesPages 152 Physiological Psychology HormonesLei CorralesNo ratings yet
- Hormones and It's TypesDocument10 pagesHormones and It's TypesSidraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnshNo ratings yet
- Endocrineppt-160928081943-1 (1) .PDF - 20240424 - 010613 - 0000.pdf - 20240424 - 010745 - 0000Document58 pagesEndocrineppt-160928081943-1 (1) .PDF - 20240424 - 010613 - 0000.pdf - 20240424 - 010745 - 0000sarahfatimakhan04No ratings yet
- 50 Revision Questions B1aDocument50 pages50 Revision Questions B1aLadyJokaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 The Role of Hormones in HumansDocument35 pages3.3 The Role of Hormones in HumansIMELDANo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesClass 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine SystemDXN LUDHIANANo ratings yet
- 3-Coordination in AnimalsDocument23 pages3-Coordination in AnimalsDerrick MNo ratings yet
- 3rd BSC Endocrinology NotesDocument25 pages3rd BSC Endocrinology NotesPratyashaNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problem On EndocrineDocument48 pagesCare of Clients With Problem On EndocrineAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument24 pagesEndocrine Systempromisefo65No ratings yet
- Module 5 PPT Endocrine System and Homeostasis 2022Document41 pagesModule 5 PPT Endocrine System and Homeostasis 2022mazibukonokwanda146No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Nama Kelompok: 1. Diah Ayu Wulandari 2. Febi Tribawanti 3. Ivo Pramaysella 4. Werdini SapitriDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: Nama Kelompok: 1. Diah Ayu Wulandari 2. Febi Tribawanti 3. Ivo Pramaysella 4. Werdini SapitriSabil fananiNo ratings yet
- Hormones CompleteDocument30 pagesHormones CompleteAqsa NoorNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument40 pagesEndocrine SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - Module 1 & 2 - Final TermDocument46 pagesHuman Anatomy - Module 1 & 2 - Final TermwelpNo ratings yet
- Not Testable Subject Matter, Just Know Endocrine System Works With Other SystemsDocument23 pagesNot Testable Subject Matter, Just Know Endocrine System Works With Other Systemsjnoah111No ratings yet
- HAPL4 - HUMAN ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY - MODULE 4 & 5Document47 pagesHAPL4 - HUMAN ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY - MODULE 4 & 5welpNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesEndocrine SystemMerrin EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument16 pagesAdrenal GlandTanya SinghNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Function(s) of Hormones (1) Hypothalamus (2) PituitaryDocument5 pagesEndocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Function(s) of Hormones (1) Hypothalamus (2) PituitaryJohn Ericsson RobariosNo ratings yet
- GroupNo2 Bauyon LabActivityNo12Document6 pagesGroupNo2 Bauyon LabActivityNo12tel krisNo ratings yet
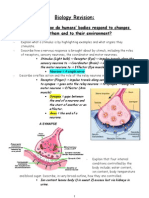
- Biology Revision:: Topic 11.1 - How Do Humans' Bodies Respond To Changes Inside Them and To Their Environment?Document11 pagesBiology Revision:: Topic 11.1 - How Do Humans' Bodies Respond To Changes Inside Them and To Their Environment?lghobrial16No ratings yet
- Hormones in The BodyDocument9 pagesHormones in The BodySherry SinghNo ratings yet
- GenBio EndocrineOutlineDocument12 pagesGenBio EndocrineOutlineJhon AmorNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands: Subject AboutDocument17 pagesAdrenal Glands: Subject AboutHareth mohammad mahmod NawajaNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Biology Unit 1 Summary NotesDocument23 pagesAqa Gcse Biology Unit 1 Summary Notesapi-320022467No ratings yet
- What Does The Endocrine System Do?Document10 pagesWhat Does The Endocrine System Do?hadiqa azizNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands The Producers of Chemical MessengersDocument10 pagesEndocrine Glands The Producers of Chemical Messengersahmed100% (1)
- endocrine فسيولوجياDocument49 pagesendocrine فسيولوجياAUDEH AHMADNo ratings yet
- Last ChapterDocument24 pagesLast ChapterVector AcademyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument13 pagesEndocrine GlandsJoan GalarceNo ratings yet
- BBT221 Lecture 6Document41 pagesBBT221 Lecture 6Al Sabri Bhuiyan 1812098042No ratings yet
- Endocrine System DiseasesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System DiseasesPrincess Xzmae Ramirez100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology - The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology - The Endocrine SystemKraig Andre RellegueNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Fatigue Cure Guide (Beat Chronic fatigue): Restoring your Hormones and Controling Thyroidism: Restoring your Hormones and Controling ThyroidismFrom EverandAdrenal Fatigue Cure Guide (Beat Chronic fatigue): Restoring your Hormones and Controling Thyroidism: Restoring your Hormones and Controling ThyroidismRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Presentation 2013-04-03 DR SURESHDocument15 pagesPresentation 2013-04-03 DR SURESHbilafarNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument113 pagesDrugsCARE CATH LABNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Repair of Large Type III Hiatal Hernia: Objective Followup Reveals High Recurrence RateDocument8 pagesLaparoscopic Repair of Large Type III Hiatal Hernia: Objective Followup Reveals High Recurrence RateAtulOsaveNo ratings yet
- 2025 Osteoarthritis 2013 PDFDocument40 pages2025 Osteoarthritis 2013 PDFwahyu andayaniNo ratings yet
- Tympanostomy Tube Insertion For Otitis Media in Children: A Systematic ReviewDocument28 pagesTympanostomy Tube Insertion For Otitis Media in Children: A Systematic ReviewYostesara Maurena SantosaNo ratings yet
- Frazalni Glagoli Na PrimerimaDocument3 pagesFrazalni Glagoli Na PrimerimaakshalmaNo ratings yet
- Exually Tran Mitted Disease: Rean Jane EscabarteDocument14 pagesExually Tran Mitted Disease: Rean Jane EscabarteRan Jung EscabarteNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument28 pagesGastrointestinal AgentsAbdur RaquibNo ratings yet
- 2001 Pathology MCQDocument8 pages2001 Pathology MCQHAJI RASHIDNo ratings yet
- MSDS For AluminiumDocument6 pagesMSDS For Aluminiumஅரவிந்தன் மகாலிங்கம்No ratings yet
- Colonoscopy ProcedureDocument3 pagesColonoscopy Procedurejmarcos84No ratings yet
- 15 ConclusionDocument2 pages15 ConclusionAnjnaKandariNo ratings yet
- Botany and TaxonomyDocument25 pagesBotany and TaxonomyDennard Dacumos100% (1)
- COURSE TASK 2 - PeraltaDocument2 pagesCOURSE TASK 2 - PeraltaPaola CruzNo ratings yet
- Alexanders Care of The Patient in Surgery Rothrock 16th Edition Test BankDocument9 pagesAlexanders Care of The Patient in Surgery Rothrock 16th Edition Test Bankjoshuabakergpctsonbwj100% (40)
- Diarrhea: Activated Charcoal or AttapulgiteDocument3 pagesDiarrhea: Activated Charcoal or AttapulgiteMabesNo ratings yet
- Scholar Ship Entrance Exam 2016 Sample Paper 8th STDDocument9 pagesScholar Ship Entrance Exam 2016 Sample Paper 8th STDBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Thyroid GlandDocument13 pagesWeek 13 Thyroid GlandAlyhana MedinaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Safety Information 224: No. May 2006Document36 pagesPharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Safety Information 224: No. May 2006osama.khalifaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Exposition TextDocument14 pagesAnalytical Exposition TextRiyan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- System Disorder: PneumothoraxDocument1 pageSystem Disorder: PneumothoraxEli ReyesNo ratings yet
- Module - Wk1 - An Overview of AbPsyDocument11 pagesModule - Wk1 - An Overview of AbPsyaudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- Castor Oil-Olio Di RicinoDocument14 pagesCastor Oil-Olio Di Ricinosabina111No ratings yet
- E - V - Visiting The DoctorDocument3 pagesE - V - Visiting The DoctorLavinio VenturaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument81 pagesUntitledAmbar100% (2)
- Autonomic HyperreflexiaDocument3 pagesAutonomic HyperreflexiaGibe BebitaNo ratings yet
- CPG 2021 Management of Schizophrenia (Second Edition) For ReviewersDocument77 pagesCPG 2021 Management of Schizophrenia (Second Edition) For ReviewersKA KABUANNo ratings yet