Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answers To Final Exam Sem 1 2007/08: V1 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6
Answers To Final Exam Sem 1 2007/08: V1 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6
Uploaded by
voon sia yuenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lecture21 Multistage AmplifiersDocument10 pagesLecture21 Multistage AmplifierscitraumariNo ratings yet
- 10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument69 pages10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualVinita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DC Analysis of A NPN BJT Using Voltage Divider BiasDocument5 pagesDC Analysis of A NPN BJT Using Voltage Divider Biasnirmal_inboxNo ratings yet
- KIA6283 CoreanDocument7 pagesKIA6283 CoreanCris VMNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FDocument44 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Transito RampDocument30 pagesTransito RampMarium AliNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Power Amp PDFDocument41 pagesCh7 Power Amp PDFy shuangNo ratings yet
- S.A. Gate Question 28Document9 pagesS.A. Gate Question 28premalathaNo ratings yet
- 06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALDocument70 pages06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALSan AngadiNo ratings yet
- L-407 Lab ManualDocument48 pagesL-407 Lab ManualAnu George100% (1)
- 06ESL37 - Analog Electronics LabDocument70 pages06ESL37 - Analog Electronics LabqwertyjklfghNo ratings yet
- Calculation For The Value of Stabilizing Resistor REF SettingDocument17 pagesCalculation For The Value of Stabilizing Resistor REF Setting1453hNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument6 pagesPower SupplyGianne ObusanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report-3 - ACDocument21 pagesLab Report-3 - ACAkif ZamanNo ratings yet
- MC34063A, MC33063A, NCV33063A 1.5 A, Step Up/Down/ Inverting Switching RegulatorsDocument14 pagesMC34063A, MC33063A, NCV33063A 1.5 A, Step Up/Down/ Inverting Switching RegulatorsVũ TưởngNo ratings yet
- Analog MeterDocument31 pagesAnalog MeterAnooshe Asadian100% (1)
- Pertemuan6 Diode AplcDocument46 pagesPertemuan6 Diode AplcmbloexNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2014-15 CP0267 08-Jan-2015 RM01 Aec2 PDFDocument7 pagesWINSEM2014-15 CP0267 08-Jan-2015 RM01 Aec2 PDFKunal KaushikNo ratings yet
- Solutions Exam 2001Document17 pagesSolutions Exam 2001bmmostefaNo ratings yet
- Calculation For The Value of Stabilizing Resistor REF SettingDocument18 pagesCalculation For The Value of Stabilizing Resistor REF SettingVishwanath TodurkarNo ratings yet
- 7+Diode+Circuits RectifiersDocument31 pages7+Diode+Circuits RectifiersRyan Anthony AndalNo ratings yet
- Simulation LabDocument17 pagesSimulation LabARVINDNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost Regulator PresentationDocument6 pagesBuck Boost Regulator PresentationBoutros MongareNo ratings yet
- 20IM10045 - Sahil Agrawal - Exp 4Document13 pages20IM10045 - Sahil Agrawal - Exp 4Sahil AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics 2Document66 pagesBasic Electronics 2Sandhya DeviNo ratings yet
- Low Power Quad Operational Amplifier: Description Pin ConfigurationDocument8 pagesLow Power Quad Operational Amplifier: Description Pin ConfigurationPaulbert ThomasNo ratings yet
- 3 AC AmplificationDocument58 pages3 AC AmplificationAnthony BeltranNo ratings yet
- MC1594 DataSheetDocument16 pagesMC1594 DataSheetKWojtekNo ratings yet
- R-L & R-C CircuitsDocument41 pagesR-L & R-C CircuitsAlamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DiodeDocument15 pagesTutorial DiodeAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument37 pagesRectifierMahendra Mandalapu MNo ratings yet
- Common Collector (Emitter Follower) AmplifierDocument24 pagesCommon Collector (Emitter Follower) AmplifierBaljeet Singh SinwarNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier LAbDocument17 pagesOperational Amplifier LAbAhmad DboukNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Power Amps6 v2Document73 pagesCh7 Power Amps6 v2sadyehclenNo ratings yet
- Pre - Lab: Half-Wave Rectifier, and The Constant Voltage Drop (0.7V) Diode Model CalculationsDocument7 pagesPre - Lab: Half-Wave Rectifier, and The Constant Voltage Drop (0.7V) Diode Model Calculationsfaraherh amberNo ratings yet
- The Common-Emitter Amplifier: Basic CircuitDocument5 pagesThe Common-Emitter Amplifier: Basic CircuitNicolas Mora RestrepoNo ratings yet
- EEE 241 EEE 241 Analog Electronics 1 Tutorial Tutorial DR Norlaili Mohd NohDocument42 pagesEEE 241 EEE 241 Analog Electronics 1 Tutorial Tutorial DR Norlaili Mohd NohMd Anwar HossainNo ratings yet
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument25 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsHariPonnanaNo ratings yet
- 9019Document17 pages9019Dan Esenther100% (1)
- 2N3904 MMBT3904: NPN General Purpose AmplifierDocument7 pages2N3904 MMBT3904: NPN General Purpose AmplifierhuvillamilNo ratings yet
- XR 2206 V 1Document16 pagesXR 2206 V 1Leon F AceroNo ratings yet
- Integrator DiffentiatorDocument7 pagesIntegrator Diffentiatorআব্দুল্লাহ আল ইমরানNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems On Transistor Audio Power AmplifiersDocument10 pagesSolved Problems On Transistor Audio Power Amplifiersgowri thumburNo ratings yet
- ECE 402 - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design CAIMDocument109 pagesECE 402 - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design CAIMMark Niño MagdayoNo ratings yet
- Tipuri de TranzistoriDocument39 pagesTipuri de Tranzistorisokyb2004No ratings yet
- BEE2123 TUT4 - Bridge AnswerDocument9 pagesBEE2123 TUT4 - Bridge AnswerWatashiNoNo ratings yet
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNo ratings yet
- Volt RegDocument59 pagesVolt RegAyesha AmbaniNo ratings yet
- EIEN307 ch2Document54 pagesEIEN307 ch2Munkhsukh100% (1)
- Mit Aec Labmanula 10esl37Document45 pagesMit Aec Labmanula 10esl37anon_70724250No ratings yet
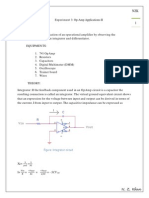
- Experiment 1: Aim of The ExperimentDocument9 pagesExperiment 1: Aim of The ExperimentAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 ReportDocument13 pagesAssignment 01 ReportSalaudeen IlyasNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Elo S5Document12 pagesMarking Scheme Elo S5ves vegasNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 2.5G 850nm 550m SFP TransceiverDocument6 pages2.5G 850nm 550m SFP TransceiverGLsun MallNo ratings yet
- NP2035 Anschutz 3578 E 032 A4 PDFDocument119 pagesNP2035 Anschutz 3578 E 032 A4 PDFmrservice7782No ratings yet
- PXR Spare PartDocument40 pagesPXR Spare PartThành Hậu ĐặngNo ratings yet
- RTD1509-004 - GXR-SD - Installation Guide2580 - UnlockedDocument51 pagesRTD1509-004 - GXR-SD - Installation Guide2580 - UnlockedMarcus RiveraNo ratings yet
- Ic JW1779Document10 pagesIc JW1779ZaegorNo ratings yet
- ADU4516R0: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesADU4516R0: Antenna SpecificationsMaria MartinsNo ratings yet
- POLIM-K enDocument5 pagesPOLIM-K enDejanTomasevicNo ratings yet
- Gruas DemacDocument28 pagesGruas DemacJesus Perez0% (1)
- Rotoverter Manual 10121Document6 pagesRotoverter Manual 10121pfalencarNo ratings yet
- Dis ProtecDocument2 pagesDis Protecm khNo ratings yet
- 15-8 Feeder Cable - 500 009 03Document2 pages15-8 Feeder Cable - 500 009 03Brian A. MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Dali Oberon: ManualDocument35 pagesDali Oberon: ManualEric SNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, PuneDocument8 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, PunemorerheaNo ratings yet
- CCTV Paper 1Document2 pagesCCTV Paper 1Bilal Ahmed JanNo ratings yet
- MR22 Beee Manual 10-09-2022 FinalDocument131 pagesMR22 Beee Manual 10-09-2022 FinalSrinivasBattuNo ratings yet
- Laser Sensor 2Document46 pagesLaser Sensor 2A.Subin DasNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Instrumentation EngineeringDocument7 pagesElectronics and Instrumentation EngineeringME SAVRNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering I CDocument4 pagesReverse Engineering I COskar RossignolNo ratings yet
- Lightining ArrestarDocument18 pagesLightining ArrestarRohan MittalNo ratings yet
- 3 A Low Drop Positive Voltage Regulator: Adjustable and FixedDocument27 pages3 A Low Drop Positive Voltage Regulator: Adjustable and FixedTT DVNo ratings yet
- 3g Radio Parameter Huawei Ver 1 0Document74 pages3g Radio Parameter Huawei Ver 1 0Abdilla RaisNo ratings yet
- 2090-Series Power and Feedback Cables: Installation InstructionsDocument12 pages2090-Series Power and Feedback Cables: Installation InstructionsMisael PiñaNo ratings yet
- GTP For 250kva Star-2Document6 pagesGTP For 250kva Star-2Geetha BNo ratings yet
- Meccalte Decs150 Manual enDocument228 pagesMeccalte Decs150 Manual enengkos koswaraNo ratings yet
- IoT Based Home Security and Automation System: A ReviewDocument20 pagesIoT Based Home Security and Automation System: A ReviewInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- By Bob Eckweiler, AF6C: Heathkit of The Month: #30Document7 pagesBy Bob Eckweiler, AF6C: Heathkit of The Month: #30Rafael Suarez0% (1)
- Electrical Training Presentation 260912 Issue 1 PDFDocument251 pagesElectrical Training Presentation 260912 Issue 1 PDFdaniel100% (7)
- DC MachinesDocument54 pagesDC MachinesPrashant ChinamalliNo ratings yet
- Etcs Level 1 Trackside Equipment: Engineering Specification SignalsDocument9 pagesEtcs Level 1 Trackside Equipment: Engineering Specification SignalsjmmfonsecaNo ratings yet
- LG Reciprocating Catalog para Frezzer y Dispensadores de AguaDocument41 pagesLG Reciprocating Catalog para Frezzer y Dispensadores de AguaRelavson Refacciones100% (2)
Answers To Final Exam Sem 1 2007/08: V1 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6
Answers To Final Exam Sem 1 2007/08: V1 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6
Uploaded by
voon sia yuenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers To Final Exam Sem 1 2007/08: V1 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6
Answers To Final Exam Sem 1 2007/08: V1 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6
Uploaded by
voon sia yuenCopyright:
Available Formats
ANSWERS TO FINAL EXAM SEM 1 2007/08
SECTION A (TRUE/FALSE) 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. T 6. T 7. T 8. F 9. T 10. F
SECTION B (OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS) 1. C 2. A 3. C 4. D 5. C f := 150 kHz L := 1 C
2
R := 100 L = 45.032 mH
C := 25 pF
:= 2 f
V1
12V
V1 := 12 V
R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6
R1 := 150 k R2 := R1 R3 := R1
Ammeter
00.000 + A
R4 := 2 R1 R5 := 2 R1 R6 := 2 R1
R123 :=
1 1 R1 + 1 R2 + 1 R3
R123 = 50 k
R456 :=
1 1 R4 + 1 R5 + 1 R6
R456 = 100 k
R T :=
R123 R456 R123 + R456
R T = 33.333 k
V1 IT := RT I456 :=
IT = 0.36 mA
Current reads by the ammeter :
R123 R123 + R456 IT
I456 = 0.12 mA
I1 :=
R2 + R3 R1 + R2 + R3 + R4 + R5 +
I R T
I123 :=
R456 R123 + R456 IT
I123 = 0.24 mA
I1 = 0.103 mA -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Given PDmax := 1 W PDmax IC IC := 125 mA
VCE :=
VCE = 8 V
SECTION C (SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS) Question 1 Varactor diode - also known as variable-capacitance diode because the junction capacitance varies with the amount of reverse-bias voltage. A varactor diode operates in reverse-bias such that the depletion region widens by the increase of the reverse-bias.
Ripple voltage - The variation in the capacitor voltage due to the charging and discharging. Smaller ripple is obtained when large capacitor is used and larger ripple when smaller capacitor is used.
Question 2 V1 := 30 V
R1
R1 := 220
VZ := 5.1 V
IZK := 1 mA
IZM := 100 mA ZZ := 0
V1
D1
Rx
Since ZZ is zero current in R1 is given as V1 VZ IR1 := IR1 = 113.182 mA R1
R x( min) is determined by setting minimum current through the diode, i.e IZK and maximum current in the load resistor, ILmax := IR1 IZK R xmin := VZ ILmax R xmin = 45.462
R x( max) is determined by setting maximum current through the diode, i.e IZM and minimum current in the load resistor, ILmin := IR1 IZM R xmax := VZ ILmin R xmax = 386.897
Question 3
Question 4 Data for the circuit VBB := 10 V R B := 47 k DC := 150 VBE := 0.7 V VCC VCEsat RC VBB VBE RB VCC := 15 V R C := 640 VCEsat := 0.3 V
Saturation collector current :
ICsat :=
ICsat = 22.969 mA
Base current :
IB := IC := DC IB
IB = 0.198 mA IC = 29.681 mA VCE = 3.996 V
Collector current :
Collector-Emitter voltage : IC < ICsat = 0
VCE := VCC IC RC
1=true therefore Linear or active region 0=false, therefore Saturates
If Rc is changed to 240 Ohm, the transistor will be in linear or active region
Question 5 VCC := 15 V VBE := 0.7 V VCEsat := 0.3 V DC := 100 R 1 := 22 k R 2 := 4.7 k R C := 2.2 k R E := 1 k
DC RE = 100 k DC RE 10 R2 = 1 R INbase := DC RE 0= so loaded vdivider 1= so unloaded vdivider VCC VCEsat RC + RE
ICsat :=
ICsat = 4.594 mA
a.
For the unloaded voltage divider bias :
VB :=
R2 VCCVB = 2.64 V R1 + R2
VE = 1.94 V IC = 1.94 mA VC = 10.731 V VCE = 8.791 V IE = 1.94 mA
VE := VB VBE VE IE := RE IC := IE
VC := VCC IC RC VCE := VC VE
b.
C1 and C2 as blocking capacitors
R4 = 300 k
You might also like
- Lecture21 Multistage AmplifiersDocument10 pagesLecture21 Multistage AmplifierscitraumariNo ratings yet
- 10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument69 pages10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualVinita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DC Analysis of A NPN BJT Using Voltage Divider BiasDocument5 pagesDC Analysis of A NPN BJT Using Voltage Divider Biasnirmal_inboxNo ratings yet
- KIA6283 CoreanDocument7 pagesKIA6283 CoreanCris VMNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FDocument44 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Transito RampDocument30 pagesTransito RampMarium AliNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Power Amp PDFDocument41 pagesCh7 Power Amp PDFy shuangNo ratings yet
- S.A. Gate Question 28Document9 pagesS.A. Gate Question 28premalathaNo ratings yet
- 06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALDocument70 pages06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALSan AngadiNo ratings yet
- L-407 Lab ManualDocument48 pagesL-407 Lab ManualAnu George100% (1)
- 06ESL37 - Analog Electronics LabDocument70 pages06ESL37 - Analog Electronics LabqwertyjklfghNo ratings yet
- Calculation For The Value of Stabilizing Resistor REF SettingDocument17 pagesCalculation For The Value of Stabilizing Resistor REF Setting1453hNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument6 pagesPower SupplyGianne ObusanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report-3 - ACDocument21 pagesLab Report-3 - ACAkif ZamanNo ratings yet
- MC34063A, MC33063A, NCV33063A 1.5 A, Step Up/Down/ Inverting Switching RegulatorsDocument14 pagesMC34063A, MC33063A, NCV33063A 1.5 A, Step Up/Down/ Inverting Switching RegulatorsVũ TưởngNo ratings yet
- Analog MeterDocument31 pagesAnalog MeterAnooshe Asadian100% (1)
- Pertemuan6 Diode AplcDocument46 pagesPertemuan6 Diode AplcmbloexNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2014-15 CP0267 08-Jan-2015 RM01 Aec2 PDFDocument7 pagesWINSEM2014-15 CP0267 08-Jan-2015 RM01 Aec2 PDFKunal KaushikNo ratings yet
- Solutions Exam 2001Document17 pagesSolutions Exam 2001bmmostefaNo ratings yet
- Calculation For The Value of Stabilizing Resistor REF SettingDocument18 pagesCalculation For The Value of Stabilizing Resistor REF SettingVishwanath TodurkarNo ratings yet
- 7+Diode+Circuits RectifiersDocument31 pages7+Diode+Circuits RectifiersRyan Anthony AndalNo ratings yet
- Simulation LabDocument17 pagesSimulation LabARVINDNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost Regulator PresentationDocument6 pagesBuck Boost Regulator PresentationBoutros MongareNo ratings yet
- 20IM10045 - Sahil Agrawal - Exp 4Document13 pages20IM10045 - Sahil Agrawal - Exp 4Sahil AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics 2Document66 pagesBasic Electronics 2Sandhya DeviNo ratings yet
- Low Power Quad Operational Amplifier: Description Pin ConfigurationDocument8 pagesLow Power Quad Operational Amplifier: Description Pin ConfigurationPaulbert ThomasNo ratings yet
- 3 AC AmplificationDocument58 pages3 AC AmplificationAnthony BeltranNo ratings yet
- MC1594 DataSheetDocument16 pagesMC1594 DataSheetKWojtekNo ratings yet
- R-L & R-C CircuitsDocument41 pagesR-L & R-C CircuitsAlamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DiodeDocument15 pagesTutorial DiodeAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument37 pagesRectifierMahendra Mandalapu MNo ratings yet
- Common Collector (Emitter Follower) AmplifierDocument24 pagesCommon Collector (Emitter Follower) AmplifierBaljeet Singh SinwarNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier LAbDocument17 pagesOperational Amplifier LAbAhmad DboukNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Power Amps6 v2Document73 pagesCh7 Power Amps6 v2sadyehclenNo ratings yet
- Pre - Lab: Half-Wave Rectifier, and The Constant Voltage Drop (0.7V) Diode Model CalculationsDocument7 pagesPre - Lab: Half-Wave Rectifier, and The Constant Voltage Drop (0.7V) Diode Model Calculationsfaraherh amberNo ratings yet
- The Common-Emitter Amplifier: Basic CircuitDocument5 pagesThe Common-Emitter Amplifier: Basic CircuitNicolas Mora RestrepoNo ratings yet
- EEE 241 EEE 241 Analog Electronics 1 Tutorial Tutorial DR Norlaili Mohd NohDocument42 pagesEEE 241 EEE 241 Analog Electronics 1 Tutorial Tutorial DR Norlaili Mohd NohMd Anwar HossainNo ratings yet
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument25 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsHariPonnanaNo ratings yet
- 9019Document17 pages9019Dan Esenther100% (1)
- 2N3904 MMBT3904: NPN General Purpose AmplifierDocument7 pages2N3904 MMBT3904: NPN General Purpose AmplifierhuvillamilNo ratings yet
- XR 2206 V 1Document16 pagesXR 2206 V 1Leon F AceroNo ratings yet
- Integrator DiffentiatorDocument7 pagesIntegrator Diffentiatorআব্দুল্লাহ আল ইমরানNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems On Transistor Audio Power AmplifiersDocument10 pagesSolved Problems On Transistor Audio Power Amplifiersgowri thumburNo ratings yet
- ECE 402 - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design CAIMDocument109 pagesECE 402 - Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design CAIMMark Niño MagdayoNo ratings yet
- Tipuri de TranzistoriDocument39 pagesTipuri de Tranzistorisokyb2004No ratings yet
- BEE2123 TUT4 - Bridge AnswerDocument9 pagesBEE2123 TUT4 - Bridge AnswerWatashiNoNo ratings yet
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNo ratings yet
- Volt RegDocument59 pagesVolt RegAyesha AmbaniNo ratings yet
- EIEN307 ch2Document54 pagesEIEN307 ch2Munkhsukh100% (1)
- Mit Aec Labmanula 10esl37Document45 pagesMit Aec Labmanula 10esl37anon_70724250No ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Aim of The ExperimentDocument9 pagesExperiment 1: Aim of The ExperimentAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 ReportDocument13 pagesAssignment 01 ReportSalaudeen IlyasNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Elo S5Document12 pagesMarking Scheme Elo S5ves vegasNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 2.5G 850nm 550m SFP TransceiverDocument6 pages2.5G 850nm 550m SFP TransceiverGLsun MallNo ratings yet
- NP2035 Anschutz 3578 E 032 A4 PDFDocument119 pagesNP2035 Anschutz 3578 E 032 A4 PDFmrservice7782No ratings yet
- PXR Spare PartDocument40 pagesPXR Spare PartThành Hậu ĐặngNo ratings yet
- RTD1509-004 - GXR-SD - Installation Guide2580 - UnlockedDocument51 pagesRTD1509-004 - GXR-SD - Installation Guide2580 - UnlockedMarcus RiveraNo ratings yet
- Ic JW1779Document10 pagesIc JW1779ZaegorNo ratings yet
- ADU4516R0: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesADU4516R0: Antenna SpecificationsMaria MartinsNo ratings yet
- POLIM-K enDocument5 pagesPOLIM-K enDejanTomasevicNo ratings yet
- Gruas DemacDocument28 pagesGruas DemacJesus Perez0% (1)
- Rotoverter Manual 10121Document6 pagesRotoverter Manual 10121pfalencarNo ratings yet
- Dis ProtecDocument2 pagesDis Protecm khNo ratings yet
- 15-8 Feeder Cable - 500 009 03Document2 pages15-8 Feeder Cable - 500 009 03Brian A. MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Dali Oberon: ManualDocument35 pagesDali Oberon: ManualEric SNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, PuneDocument8 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, PunemorerheaNo ratings yet
- CCTV Paper 1Document2 pagesCCTV Paper 1Bilal Ahmed JanNo ratings yet
- MR22 Beee Manual 10-09-2022 FinalDocument131 pagesMR22 Beee Manual 10-09-2022 FinalSrinivasBattuNo ratings yet
- Laser Sensor 2Document46 pagesLaser Sensor 2A.Subin DasNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Instrumentation EngineeringDocument7 pagesElectronics and Instrumentation EngineeringME SAVRNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering I CDocument4 pagesReverse Engineering I COskar RossignolNo ratings yet
- Lightining ArrestarDocument18 pagesLightining ArrestarRohan MittalNo ratings yet
- 3 A Low Drop Positive Voltage Regulator: Adjustable and FixedDocument27 pages3 A Low Drop Positive Voltage Regulator: Adjustable and FixedTT DVNo ratings yet
- 3g Radio Parameter Huawei Ver 1 0Document74 pages3g Radio Parameter Huawei Ver 1 0Abdilla RaisNo ratings yet
- 2090-Series Power and Feedback Cables: Installation InstructionsDocument12 pages2090-Series Power and Feedback Cables: Installation InstructionsMisael PiñaNo ratings yet
- GTP For 250kva Star-2Document6 pagesGTP For 250kva Star-2Geetha BNo ratings yet
- Meccalte Decs150 Manual enDocument228 pagesMeccalte Decs150 Manual enengkos koswaraNo ratings yet
- IoT Based Home Security and Automation System: A ReviewDocument20 pagesIoT Based Home Security and Automation System: A ReviewInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- By Bob Eckweiler, AF6C: Heathkit of The Month: #30Document7 pagesBy Bob Eckweiler, AF6C: Heathkit of The Month: #30Rafael Suarez0% (1)
- Electrical Training Presentation 260912 Issue 1 PDFDocument251 pagesElectrical Training Presentation 260912 Issue 1 PDFdaniel100% (7)
- DC MachinesDocument54 pagesDC MachinesPrashant ChinamalliNo ratings yet
- Etcs Level 1 Trackside Equipment: Engineering Specification SignalsDocument9 pagesEtcs Level 1 Trackside Equipment: Engineering Specification SignalsjmmfonsecaNo ratings yet
- LG Reciprocating Catalog para Frezzer y Dispensadores de AguaDocument41 pagesLG Reciprocating Catalog para Frezzer y Dispensadores de AguaRelavson Refacciones100% (2)