Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecosystem, GPP, NPP: Energy Flow Through Ecosystems
Ecosystem, GPP, NPP: Energy Flow Through Ecosystems
Uploaded by
alwfanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ecosystem, GPP, NPP: Energy Flow Through Ecosystems
Ecosystem, GPP, NPP: Energy Flow Through Ecosystems
Uploaded by
alwfanCopyright:
Available Formats
Ecosystem, GPP, NPP
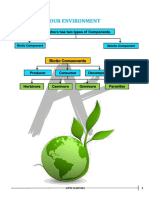
Energy Flow through Ecosystems Class Notes Producer: autotroph, self sufficient/feeding Organic: contain carbon (except for CO2) Autotroph: organisms that can synthesise the organic materials needed from inorganic sources. Includes all green plants. Heterotroph: Organisms that take in 'ready made' organic materials made by other organisms. Food chain: a pathway of energy from one organism to another. Producer (1 trophic level) Primary consumer (2
nd st
trophic level)
rd
Secondary consumer (3 trophic level) Tertiary consumer (4 trophic level) Quaternary consumer (5 trophic level) Chemosynthetic autotrophy: they use chemical energy to produce the organic molecules that they need. Usually live deep in the oceans. Primary productivity: the rate at which energy is incorporated into organic molecules in an organism. Biosphere: the inhabited areas of the planet. Habitat: area which an organism lives, with distinct conditions. Population: the number of individuals of a species living in an area at a given time. Community: the various populations sharing a habitat/ecosystem makes up the community (includes plants). Niche: the conceptual position a species has in the habitat. If more then one species tries to occupy this niche, they will compete. How efficiently is is energy conserved?
th th
The productivity/biodiversity of an ecosystem will depend on how much energy is caught by the producers and passed onto the subsequent trophic levels. Energy entering a trophic level must equal the amount used or lost by that trophic level. Energy loss between trophic levels explains why food chains and food webs rarely have more then 4/5 trophic levels. 40% of energy from sun can be used by plants, energy transfer decreases as you move up the trophic levels. Plants are inefficient at absorbing light. Less then 5% of total light energy is captured by plants out of 1x10^6 kJm^-2y. The plant is green as it as the plant reflects green light. The plant mainly absorbs red and blue wavelengths of light. Limiting factors: Temperature Light intensity CO2 concentration When a process is affected by more then one limiting factor its rate is determined by the factor that is furthest away from the optimum level. Gross Primary Productivity: This is what a plant gets. The total rate at which energy is converted into organic molecules by an ecosystem. Net Primary Productivity: The rate at which energy is incorporated to new plant biomass from organic materials. NPP = GPP - Respiration. Ecosystems are areas that are self sustaining. Due to niches, competition between species should not occur. Interspecific: between species. Intraspecific: within a species. Biotic: Living factors. Abiotic: Non living factors.
Biotic factors are density dependent, the effects are relative to the size of the area available. Anthropogenic factors: human factors such as building.
You might also like
- Ess Revision NotesDocument36 pagesEss Revision NotesVishnu Sharma100% (8)
- IB ESS: Topic 2 - EcosystemsDocument5 pagesIB ESS: Topic 2 - EcosystemsIssabella Ver100% (1)
- Video Recap of Food Webs Energy Pyramids and Intro To Biodiversity by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Food Webs Energy Pyramids and Intro To Biodiversity by Amoeba Sistersapi-29768151050% (2)
- What Is Ecology PDFDocument113 pagesWhat Is Ecology PDFDarshan MarjadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReviewDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Reviewjessica_3256No ratings yet
- Dynamics of EcosystemDocument36 pagesDynamics of EcosystemPORAKH MONE GOHAINNo ratings yet
- Energy Pyramid Definition: Trophic LevelDocument3 pagesEnergy Pyramid Definition: Trophic LevelGlorylourd Joana FulloNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Ecology, Greenhouse Gases, Global Warming & PollutionDocument41 pagesUnit 4 Ecology, Greenhouse Gases, Global Warming & Pollutionbody fayezNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow Through Ecosystems: Group 4Document42 pagesEnergy Flow Through Ecosystems: Group 4Febe AnneNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document8 pagesTopic 4Alianna GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems: Reading: Freeman Chapter 54Document51 pagesEcosystems: Reading: Freeman Chapter 54hhvuong5859No ratings yet
- ProductivityDocument15 pagesProductivityapi-253170211No ratings yet
- 1.2 The Biosphere and Energy QuestionsDocument8 pages1.2 The Biosphere and Energy QuestionsHaresh SenthilkumaranNo ratings yet
- Focus On Essay - Ecology PDFDocument7 pagesFocus On Essay - Ecology PDFLim Yu En100% (1)
- Ecosystem NotesDocument7 pagesEcosystem Notesraushankumar05072No ratings yet
- Ecosystem SelfnotesDocument10 pagesEcosystem SelfnotesPranav Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Class 12 BiologyDocument11 pagesEcosystem Class 12 BiologykusumabshuklaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Energy and Ecosystems: SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 7: Energy and Ecosystems: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Env-2203Document29 pagesEnv-2203shapritom0No ratings yet
- Intro To EcologyDocument44 pagesIntro To EcologyJinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Energy Dynamics Notes (04:25)Document3 pagesEnergy Dynamics Notes (04:25)Diana SanchezNo ratings yet
- Ecology: Biology Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument26 pagesEcology: Biology Notes GCE Study Buddyzm_khalidNo ratings yet
- Energy Fixation Student Copy 2024Document23 pagesEnergy Fixation Student Copy 2024Marvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Our Environment 3Document11 pagesOur Environment 3Vishal DeyNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument8 pagesEcosystembn65dgcqdfNo ratings yet
- Our Environment-YTDocument59 pagesOur Environment-YTMeenal Sinha0% (2)
- EcologyDocument36 pagesEcologynanaNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument32 pagesEcologyMaryam SabirNo ratings yet
- Ecology - Organisms &the EnvironmentDocument111 pagesEcology - Organisms &the EnvironmentAli MirzaNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Q4Document17 pagesScience Notes Q4Nyx hshshshNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Energy FlowDocument4 pagesEcosystem and Energy FlowRohini SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Communities and EcosystemsDocument27 pages4.1 Communities and EcosystemsMihika ShethNo ratings yet
- FM4 Bio NotesDocument37 pagesFM4 Bio Notesmsimbarashe681No ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document10 pagesChapter 14a34146525No ratings yet
- Split 20231113 1916Document9 pagesSplit 20231113 1916ashadbolajiNo ratings yet
- The Living EnvironmentDocument6 pagesThe Living EnvironmentMuhammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- Bio 4.2Document5 pagesBio 4.2pjhaveNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument38 pagesECOSYSTEMbluedB27No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Lesson 1Document24 pagesBioenergetics Lesson 1azwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and Energy FlowDocument78 pagesEcosystems and Energy Flowabhinavgupta2010No ratings yet
- Ecosystem: Conversion ofDocument11 pagesEcosystem: Conversion ofMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Our Environment (Prashant Kirad)Document49 pagesOur Environment (Prashant Kirad)sumitverma78929.svNo ratings yet
- Our EnvironmentDocument11 pagesOur EnvironmentHVBCBMNZNo ratings yet
- Transcript-Energy Flow in An Ecosystem.Document6 pagesTranscript-Energy Flow in An Ecosystem.Suraj O V 1820368No ratings yet
- Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The EnvironmentDocument6 pagesEnergy Flow, Ecosystems and The EnvironmentChowdr XPNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 5 Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The Environment - Edexcel IAL Biology A-LevelDocument6 pagesDefinitions - Topic 5 Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The Environment - Edexcel IAL Biology A-LeveldewjadymNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument39 pagesUntitledKapoor LakshNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 and 3 - ESSDocument22 pagesTopic 2 and 3 - ESSCarmen Saez HerreroNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Energy Transfer Between Trophic LevelsDocument9 pages5.2 Energy Transfer Between Trophic Levelsapril ma heyresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Our Environment (1) CLASS 10Document9 pagesChapter 15 Our Environment (1) CLASS 10shallowNo ratings yet
- BSIT-2B (Task #5, PEE)Document2 pagesBSIT-2B (Task #5, PEE)Kris Areane RebanalNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem ProductivityDocument2 pagesEcosystem ProductivityvijendNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument8 pagesEssayShontel ArcherNo ratings yet
- Energy & Nutrients Flows Within EcosystemsDocument14 pagesEnergy & Nutrients Flows Within Ecosystems4L Anisha SieudassNo ratings yet
- Coping With Environmental Variation: EnergyDocument4 pagesCoping With Environmental Variation: EnergyKim CaelianNo ratings yet
- The Science of EcologyDocument2 pagesThe Science of EcologybluepixarlampNo ratings yet
- Our EnvironmentDocument9 pagesOur EnvironmenthafsaNo ratings yet
- AQA (B) A2 Module 5: EnvironmentDocument24 pagesAQA (B) A2 Module 5: EnvironmentAthul TomyNo ratings yet
- HG Biology NotesDocument19 pagesHG Biology Notesbatman2468No ratings yet
- Contact IsolationDocument2 pagesContact IsolationIsworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- 120108004Document3 pages120108004abhiroopNo ratings yet
- Demography Final Handout CorrectedDocument20 pagesDemography Final Handout Correctedmadanlal sainiNo ratings yet
- Fertility and Its MeasurementDocument124 pagesFertility and Its MeasurementmercythruxtNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Introduction To HydrologyDocument12 pagesLecture 1: Introduction To HydrologyKristine CervanciaNo ratings yet
- Ecological Footprint BasicsDocument15 pagesEcological Footprint BasicsAbigailNo ratings yet
- Narrative On Tree Planting ProjectDocument4 pagesNarrative On Tree Planting ProjectDhenniz FlorezNo ratings yet
- 05.1 - Web STR - Client Letter - Business - To - Client-MgtDocument2 pages05.1 - Web STR - Client Letter - Business - To - Client-MgtFranky KenNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument8 pagesSustainable DevelopmentShubham BankaNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing 116 final exam 19/12/2019 دونج تايحت عم 116 نيلوهجملا MCQDocument6 pagesCommunity Health Nursing 116 final exam 19/12/2019 دونج تايحت عم 116 نيلوهجملا MCQA.A M.A.RNo ratings yet
- Urbanisation and Urban Growth in MalaysiaDocument23 pagesUrbanisation and Urban Growth in Malaysiasue rozlan100% (1)
- Test (S.P.M.)Document160 pagesTest (S.P.M.)nayan159No ratings yet
- Sustainable TourismDocument2 pagesSustainable TourismMystique TiaraNo ratings yet
- Infant and Child Mortality: Mothers and Infants, As Well As The Effectiveness ofDocument3 pagesInfant and Child Mortality: Mothers and Infants, As Well As The Effectiveness ofhendraNo ratings yet
- CHN Part 2 - Vital StatisticsDocument2 pagesCHN Part 2 - Vital StatisticsMichelle Gambol100% (1)
- Energy, Ecology, Environment, Lecture1-2-3Document20 pagesEnergy, Ecology, Environment, Lecture1-2-3Vibhanshu LodhiNo ratings yet
- DafpusDocument2 pagesDafpusIrma DewayantiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 Biodiversity & Healthy SocietyDocument37 pagesCHAPTER 9 Biodiversity & Healthy SocietyJevelyn Mendoza Farro100% (1)
- DR Otieno Dorcas BerylDocument17 pagesDR Otieno Dorcas BerylQlance DeqqoNo ratings yet
- GE6351-Environmental Science and Engineering PDFDocument6 pagesGE6351-Environmental Science and Engineering PDFVisalakshi ChockalingamNo ratings yet
- ILO 8019 Environmental ManagementDocument2 pagesILO 8019 Environmental ManagementErvin DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Notice: Endangered and Threatened Species: Incidental Take Permits— Missisquoi National Wildlife Refuge, VT Comprehensive Conservation PlanDocument2 pagesNotice: Endangered and Threatened Species: Incidental Take Permits— Missisquoi National Wildlife Refuge, VT Comprehensive Conservation PlanJustia.comNo ratings yet
- NSTP Module 5 Environmental Awareness and ProtectionDocument6 pagesNSTP Module 5 Environmental Awareness and ProtectionFatima DajoyagNo ratings yet
- Online ENVR 1401-Ecological Footprint NEW 2017-Text Only-JcDocument6 pagesOnline ENVR 1401-Ecological Footprint NEW 2017-Text Only-JcsameerNo ratings yet
- HiMCM Problem and Solution 2012 American - ElkDocument17 pagesHiMCM Problem and Solution 2012 American - ElkAnonymous j6r5KRtrH2No ratings yet
- Environmental Terms - QuizletDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Terms - QuizletMildred ClarkeNo ratings yet
- BIOLS 340: General Ecology: Chapter 1: Introduction To EcologyDocument11 pagesBIOLS 340: General Ecology: Chapter 1: Introduction To EcologyZainab MukhtarNo ratings yet
- NMIMS Business and Natural EnvironmentDocument27 pagesNMIMS Business and Natural EnvironmentUtkarsh ZopeNo ratings yet
- Essay SustainabilityDocument7 pagesEssay SustainabilitykiriyasovayuliyaNo ratings yet