Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Krisha Miel DomedeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Krisha Miel DomedeCopyright:
Available Formats
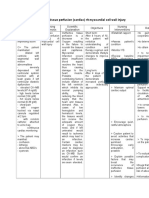
ASSESSMENT
EXPLANATION OF THE PROBLEM The ECG result of the client shows a Sinus Bradycardia in which the impulse originating from the sinoatrial node has a slow rate thus it creates a slower heart rate than normal leading to decreased cardiac output. Decreased cardiac output is evident in the client because she has a slow HR which is 60 bpm, she was easily exhausted from doing normal activities in life. Though the client is acyanotic. She has a pinkish palpebral conjunctiva and a capillary refill of 1- 2 seconds.
GOALS AND OBJECTIVES LTO> After 72 hours of nursing intervention, the client will demonstrate: increased HR from 60 bpm to 80 bpm Regular rhythm of the heart by ECG No more episodes of angina Able to do normal activities without any difficulty STO> After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the client will be demonstrate: Increased HR from 60 bpm to 70 bpm Increased activity tolerance with minimal exhaustion as manifested by slight increase in VS
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
S> Madali ako mapagod. Tapos bumibigat ang dibdib ko di ako makahinga. Minsan sumasakit pa ang dibdib ko. O> with abnormal ECG result revealing Sinus Bradycardia; with HR of 60 bpms regular; increased VS after activity such as going to the CR; with capillary refill of 1-2 seconds;with pinkish palpebral conjunctiva; acyanotic; A > Decreased Cardiac Output related to altered cardiac rhythm
Assess mentation.
Increasing lethargy, confusion, restlessness and / or irritability can be early signs of cerebral hypoxia from decreased cardiac output Increased respiratory rate and use of accessory muscles may be seen in patients with hypoxia
Assess patient respirations by observing respiratory rate and depth and use of accessory muscles
Observe patient for restlessness, agitation, confusion and (late stages) lethargy
Changes in behavior and mental status can be early signs of impaired gas exchange which will result from decreased cardiac output
Assess patient for chest pain or discomfort noting location, severity, duration, quality and radiation
Chest pain is generally indicative of inadequate blood supply to the heart which can result in decreased cardiac output Pallor or cyanosis, cool moist skin and slow capillary refill time may be present from peripheral vasoconstriction and decreased oxygen saturation Weak, thready peripheral pulses may reflect hypotension, vasoconstriction, shunting and venous congestion Heart irritability is common with conduction defects and/or ischemia from a poorly
Observe patient for changes in skin color, moisture, temperature and capillary refill time
Assess peripheral pulses
Monitor patient for changes in heart rate and/or rhythm
perfused heart Monitor hourly urine output Decreased cardiac output results in decreased perfusion to the kidneys and decreased urine output. Urinary output < 30 ml/hr. indicates inadequate renal perfusion Rest and a quiet environment reduces a catecholamineinduced stress response and decreases cardiac workload thus increasing cardiac output Decreases oxygen consumption and risk for decompensation
Promote rest
Keep client on bed or chair in position of comfort. Semifowlers position preferably. Assist when performing self-
To facilitate the self-care and
care activities.
reduce the stress and exhaustion felt by the client when doing so. Patient is often on multiple medications which can be difficult to manage, thus increasing the likelihood that medications can be missed or incorrectly used
Educate patient and caregivers about the importance of taking prescribed medications at prescribed times
You might also like
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis93% (15)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02Document6 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02AgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisDocument142 pagesNCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisEllamae Chua88% (8)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dysrhythmias Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDysrhythmias Cheat SheetKatie Coughlan100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureRalph Dumawaa60% (5)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputChristine MatasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HF FinalDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan HF FinalCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Demonstrator at Faculty of Nursing MTI UniversityDocument14 pagesPrepared By: Demonstrator at Faculty of Nursing MTI UniversityDESALEGN BIRHANUNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument6 pagesCase PresCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputCarmela Balderas Romantco80% (5)
- Subjective: Fully Met If:: Short Term ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSubjective: Fully Met If:: Short Term ObjectiveDan Gerald Alcido SalungaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension NCPDocument4 pagesHypertension NCPChristian Karl B. Llanes0% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac Output RM 7Document9 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output RM 7api-283470660No ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputRae AnnNo ratings yet
- NUR3111 Nursing Care Plan Copy 1Document19 pagesNUR3111 Nursing Care Plan Copy 1liNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument8 pagesMyocardial InfarctionOdai AL KarkiiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesNursing Care PlanChic Dian UsmanNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesCardiomyopathyBianca SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)Document15 pagesDeep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)arcci balinasNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journaling 1Document12 pagesReflective Journaling 1Nosheen ShahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument26 pagesNursing Care PlanPrincessLienMondejarNo ratings yet
- NCP Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 pagesNCP Cardiogenic ShockTrixia Camporedondo100% (1)
- Supplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Document14 pagesSupplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Andrea Love PalomoNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument30 pagesCase StudyprathibaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument6 pagesPulmonary EdemaJelly BeanNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Care PlanDocument6 pagesHeart Failure Care PlanOlivia Winkler StuartNo ratings yet
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 pagesDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNo ratings yet
- Continuation (Altered Tissue Perfusion)Document59 pagesContinuation (Altered Tissue Perfusion)Grace Jane DionaldoNo ratings yet
- .SHOCK, Alice - 1704638750000Document12 pages.SHOCK, Alice - 1704638750000Nakintu AliceNo ratings yet
- Shock CorrectedDocument70 pagesShock CorrectedrajevikramNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Marvick F. Galima RNDocument42 pagesHeart Failure: Marvick F. Galima RNSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- 8.syncope & PresyncopeDocument11 pages8.syncope & PresyncopeIbrahim RamizNo ratings yet
- U World Cardiac FinalDocument15 pagesU World Cardiac FinalAcohCChaoNo ratings yet
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- Elevated Blood PressureDocument3 pagesElevated Blood PressureSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument49 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument7 pagesCardioGerald AndrinNo ratings yet
- Thea Laurene T. Tonelada BSN Iv-C Dysrhythmia: TachydysrhythmiasDocument5 pagesThea Laurene T. Tonelada BSN Iv-C Dysrhythmia: Tachydysrhythmiasscribd_lostandfoundNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: Submitted ToDocument5 pagesCardiogenic Shock: Submitted Toal-obinay shereenNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: Medical Surgical NursingDocument7 pagesCase Analysis: Medical Surgical NursingMaria ThereseNo ratings yet
- Approach To ShockDocument19 pagesApproach To Shocksarath100% (1)
- Case 2 SlosDocument7 pagesCase 2 SlosNamarNo ratings yet
- Handouts in NGCM103 Oxygenation Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesHandouts in NGCM103 Oxygenation Cardiovascular SystemJeenah HannahNo ratings yet
- SVTDocument8 pagesSVTJulieNo ratings yet
- Shock: DR Vishwabharathi TDocument51 pagesShock: DR Vishwabharathi TSumaNo ratings yet
- Shock 19Document7 pagesShock 19Teema UmarNo ratings yet
- NCP HCVD (Final)Document8 pagesNCP HCVD (Final)khrizaleeh100% (1)
- Nursing Study GuideDocument21 pagesNursing Study GuideYanahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disorders HandoutDocument14 pagesCardiac Disorders HandoutRizielle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Types of ArrhythmiaDocument10 pagesTypes of ArrhythmiaRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC FAILURE and Acute MIDocument6 pagesCARDIAC FAILURE and Acute MIDaniel GeduquioNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mitral Valve Regurgitation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMitral Valve Regurgitation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Concussion - PathophyDocument4 pagesCerebral Concussion - PathophyFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter - Meghan L. ShalvoyDocument1 pageCover Letter - Meghan L. ShalvoyMeghan Equality ShalvoyNo ratings yet
- Executive Order No. 030 S. 2022Document1 pageExecutive Order No. 030 S. 2022SAMMY SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Semester I Test: Part 1: Reading (10 Marks)Document3 pagesSemester I Test: Part 1: Reading (10 Marks)monorea mapNo ratings yet
- Parent-Teen Talk Facilitator's Guide - LexcodeDocument135 pagesParent-Teen Talk Facilitator's Guide - LexcodeRochelle AdlaoNo ratings yet
- Workshop Modern OSH Legislation: International Labour Standards On OshDocument24 pagesWorkshop Modern OSH Legislation: International Labour Standards On OshVijayakumarVageesanNo ratings yet
- Total Hip Replacement: Presented By: Atillio Castellani Brendan Cochren Trevor Kelly Shuntaro Maruyama Mustafa SharifDocument30 pagesTotal Hip Replacement: Presented By: Atillio Castellani Brendan Cochren Trevor Kelly Shuntaro Maruyama Mustafa SharifSaurabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ethics of DentistryDocument20 pagesEthics of DentistrytayabakhanNo ratings yet
- What Is IVF and How Does It WorkDocument6 pagesWhat Is IVF and How Does It Workanjali kummariNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ VIP 31 - PHÁT TRIỂN ĐỀ MINH HỌA THAM KHẢO BGD MÔN ANH NĂM 2024 (MC8) - nNowVm4ShZDocument4 pagesĐỀ VIP 31 - PHÁT TRIỂN ĐỀ MINH HỌA THAM KHẢO BGD MÔN ANH NĂM 2024 (MC8) - nNowVm4ShZnhuphuongnacc2No ratings yet
- Scored Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA)Document2 pagesScored Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA)Misbah sabirNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Introduction-to-Midwifery-Obstetrical-NursingDocument43 pagesUnit I - Introduction-to-Midwifery-Obstetrical-NursingN. Siva100% (9)
- Flowchart Covid 19 ResponseDocument2 pagesFlowchart Covid 19 ResponseAlberto SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Amputation: Dr. Abdul Rashad Senior Lecturer DPT, Mphill (Opt), Mppta United College of Physical TherapyDocument31 pagesAmputation: Dr. Abdul Rashad Senior Lecturer DPT, Mphill (Opt), Mppta United College of Physical Therapypasha100% (1)
- Research Proposal Senior People and Digital Technology in Singapore Jose RojasDocument35 pagesResearch Proposal Senior People and Digital Technology in Singapore Jose Rojasjz00hjNo ratings yet
- The 9 Best Benefits of Playing ChessDocument7 pagesThe 9 Best Benefits of Playing Chesssandip nagareNo ratings yet
- On Smartphone Addiction Among AdolescentsDocument14 pagesOn Smartphone Addiction Among AdolescentsBlaizy mol PcNo ratings yet
- MaternalDocument3 pagesMaternalEsvinch EsvinchNo ratings yet
- 8th TNM Clasification - Lung CancerDocument10 pages8th TNM Clasification - Lung CancerEma ȚurcașNo ratings yet
- Tes Potensi Skolastik: Try Out Simulasi Program Persiapan LangsungDocument4 pagesTes Potensi Skolastik: Try Out Simulasi Program Persiapan LangsungRikhwanul LukmanNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 HandoutsDocument18 pagesNCM 107 HandoutsGeneva Amandy Roxas50% (2)
- Lesson Plan in HOPE 1 (Sports)Document2 pagesLesson Plan in HOPE 1 (Sports)Michael Cayacap100% (1)
- Elizabeth Pineda - CrocsDocument37 pagesElizabeth Pineda - Crocsapi-285910404No ratings yet
- Massage and Its EffectsDocument2 pagesMassage and Its EffectsAmimul EhsanNo ratings yet
- Writing Clinical NotesDocument27 pagesWriting Clinical NotesZaid MazinNo ratings yet
- Scope and DelimitationDocument8 pagesScope and DelimitationLiza MarigondonNo ratings yet
- Mammography Sas 10Document11 pagesMammography Sas 10faith mari madrilejosNo ratings yet
- 2.induction of Labour & Prolonged PregnancyDocument20 pages2.induction of Labour & Prolonged PregnancyMiswar Abdul HalimNo ratings yet
- LAS-Cookery 8 Week 6-7Document5 pagesLAS-Cookery 8 Week 6-7jon pantz100% (1)
- Artikel Bahasa Inggris: Vitamin For A Healthy HeartDocument3 pagesArtikel Bahasa Inggris: Vitamin For A Healthy HeartSumayyah FitriNo ratings yet